Introduction
In the journey of understanding autism spectrum disorder (ASD), parents often find themselves navigating a landscape filled with myths and misconceptions. The reality is that autism is not a result of parenting choices or isolated environmental factors; it emerges from a complex interplay of genetic and environmental influences. As research continues to unveil the intricacies of autism, it becomes increasingly clear that early diagnosis and intervention can significantly enhance outcomes for children.
This article delves into the multifaceted causes of autism, the importance of recognizing early signs, and the critical role parents play in advocating for their children's needs. By arming themselves with knowledge, parents can foster a supportive environment that empowers their children to thrive, dispelling harmful stereotypes along the way.
Are Individuals Born with Autism? Exploring Genetic and Environmental Influences
Research underscores that the spectrum disorder (ASD) arises from a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Recent studies highlight that specific genetic mutations can increase an individual's risk for developing this condition, while environmental influences—such as prenatal exposure to toxins, maternal infections, and birth complications—significantly contribute to it. Notably, findings from the UK Biobank reveal a substantial dataset, with over 200,080 individuals having their genotyping files analyzed, shedding light on genetic predispositions linked to autism.
Furthermore, emerging research suggests that children with multiple genetic mutations often experience more severe phenotypes, indicating that these gene-disruptive events may co-occur. This aligns with previous studies that have shown a correlation between the number of genetic mutations and the severity of ASD symptoms. As Idan Menashe from the Child Development Center at Soroka University Medical Center articulates, understanding these factors is crucial for caregivers.
This knowledge dispels the myth that people are born with autism due to parenting choices or singular environmental factors. Instead, it empowers parents to comprehend that ASD stems from various influences, prompting them to seek appropriate support and resources for their offspring. Additionally, the historical underrepresentation of female subjects in ASD research has led to a skewed understanding of the disorder, emphasizing the necessity for inclusive studies that examine both sexes together.
In this context, incorporating statistical methods such as those proposed by Benjamini and Hochberg for controlling the false discovery rate can enhance the rigor of research related to developmental disorders. This comprehensive approach is essential for gaining a complete understanding of the condition's causes and manifestations, ultimately aiding informed advocacy for youth with ASD.
Understanding the Risk Factors and Causes of Autism Spectrum Disorder
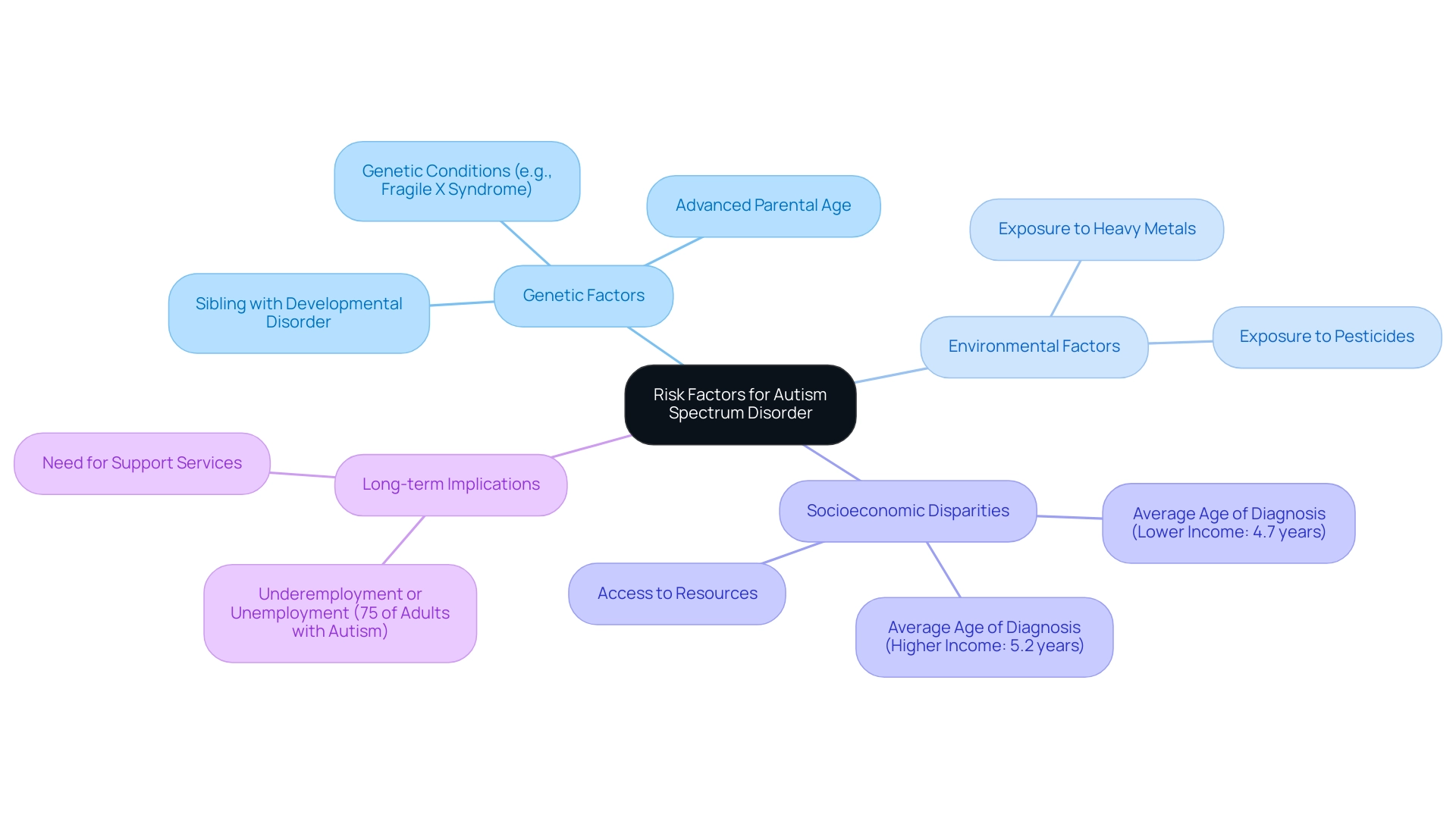
Comprehending the various risk factors for developmental disorders can enable parents to be proactive in their offspring's growth. Research suggests that one major risk factor is having a sibling with a developmental disorder, which significantly raises the chances of a child developing a spectrum disorder. In fact, studies indicate that spectrum disorder has a genetic component, with the risk for siblings of affected individuals significantly heightened.
Furthermore, advanced parental age at conception has been linked to higher rates of the condition, with experts emphasizing the need for awareness surrounding this correlation. Pediatricians have observed that certain genetic conditions, such as fragile X syndrome, also play a critical role in the risk of developmental disorders. Additional environmental factors, including exposure to heavy metals and pesticides during pregnancy, have been linked to a higher risk of developmental disorders, emphasizing the significance of a safe prenatal environment.
It is also crucial to acknowledge differences in diagnosis; the average age of identification for youngsters in lower-income households is 4.7 years, compared to 5.2 years for those in higher-income households. This disparity underscores the need for increased awareness and access to resources across different socioeconomic backgrounds. Moreover, the long-term implications of autism are significant, as roughly 75% of adults diagnosed with autism in the United States experience either underemployment or complete unemployment, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
By being aware of these risk factors, guardians can more effectively oversee their offspring's development, ensuring prompt assessments and access to initial intervention services when needed. This knowledge empowers families to advocate effectively for their kids, fostering an environment of support and understanding.
Developmental Trajectory: When Does Autism Become Apparent?
Autism often becomes apparent in young childhood, with many parents noticing signs by the age of 2 or 3. Common indicators include:
- Delays in speech and social interactions
- Repetitive movements
- Unusual behaviors
It is crucial to recognize that while some individuals may display these signs early, others might not exhibit clear indicators until later, especially as social demands increase with age.
Recent statistics indicate that the prevalence rate of the condition in the United States is about 81 per 10,000 youth, a figure that reflects improved diagnostic criteria and public awareness. Furthermore, it is crucial to take into account the emotional challenges caregivers encounter; a notable 67.1% of mothers indicated experiencing both depression and anxiety symptoms while navigating autism detection and intervention. Fathers also play a critical role, with many placing considerable importance on assistance with their offspring's social development.
Understanding this developmental trajectory enables parents to identify atypical behaviors early, paving the way for timely assessments and interventions. Such proactive measures can lead to significantly enhanced results for individuals with developmental disorders. For instance, a survey indicated that 36.5% of caregivers of autistic individuals utilize ABA therapy, with the majority reporting positive outcomes, including reduced meltdowns and improved communication skills.
Child development specialists stress that identifying these initial signs is crucial, as they frequently relate to significant developmental milestones, which can assist parents in managing the complexities of detection and intervention effectively.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention in Autism
Research continually demonstrates that early diagnosis and intervention are pivotal in achieving favorable long-term outcomes for individuals with autism. Participating in programs that include:
- Behavioral therapy
- Speech therapy
- Social skills training
can profoundly enhance a young person's developmental trajectory and overall quality of life. The Relative Speech and Language Development (RSLD) is calculated using the formula: RSLD = (CA-ESLD)/CA, which underscores the importance of monitoring developmental milestones.
The current landscape emphasizes the necessity for guardians to pursue evaluations promptly whenever they suspect any developmental delays or notice atypical behaviors. By acting swiftly, parents not only facilitate essential support for their offspring but also equip themselves with effective strategies to nurture their development. As emphasized by recent discoveries, "These results underscore the significance of timely diagnosis and intervention for youth with autism."
Furthermore, a case study titled "ESLD Testing Results" revealed that assessments conducted at two different testing points showed no significant differences in ESLD scores between younger and older groups, indicating that early intervention strategies can effectively support children across various age ranges. These insights underscore the importance of proactive advocacy by parents.
Debunking Myths: Understanding Autism Beyond Common Misconceptions
Misunderstandings about the condition persist, often leading to harmful stereotypes. A prevalent myth suggests that poor parenting or vaccines are responsible for autism, yet research clearly indicates that people born with autism have a neurodevelopmental disorder stemming from a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. As noted in the National Survey of Children’s Health (2016-2019), "the average age of diagnosis for children in lower-income households is 4.7 years compared to 5.2 years in higher-income households."
This statistic underscores the need for early intervention and awareness across all socioeconomic backgrounds. Additionally, ABA therapy is acknowledged for its effectiveness in facilitating communication for individuals on the spectrum, offering essential assistance for caregivers navigating this journey. Additionally, insights from the case study titled "Sleep Issues in Autism" highlight common challenges faced by individuals on the spectrum, illustrating the real-world impact of misconceptions and the necessity for tailored management strategies.
As parents, it is vital to recognize that this condition, like the fact that are people born with autism, is not a reflection of parenting style or external influences. By educating ourselves and others, we can dismantle these misconceptions, foster acceptance, and advocate effectively for our children's needs. Empowerment through knowledge allows us to confront stigma and promote a clearer understanding of autism's true nature.
Conclusion
Understanding autism spectrum disorder (ASD) requires a comprehensive look at its complex origins, encompassing both genetic and environmental influences. Research reveals that autism is not a result of parenting choices but rather a multifaceted condition shaped by various factors, including genetic predispositions and prenatal environments. By recognizing these influences, parents can dispel harmful myths and better advocate for their children, ensuring they receive the necessary support.
Early diagnosis and intervention play crucial roles in improving outcomes for children with autism. Parents are encouraged to be vigilant in observing early signs and to seek timely evaluations, as proactive measures can lead to significant developmental benefits. Engaging in therapies that enhance communication and social skills can transform a child's trajectory, fostering an environment conducive to growth and understanding.
Moreover, it is essential to confront and debunk the misconceptions surrounding autism. By educating themselves and others, parents can challenge stereotypes and promote a more accurate understanding of the disorder. This empowerment through knowledge not only supports their children but also cultivates acceptance within the broader community.
In conclusion, navigating the journey of autism advocacy is a powerful endeavor. By equipping themselves with accurate information, recognizing early signs, and advocating for timely intervention, parents can create supportive environments that enable their children to thrive. Embracing this knowledge ultimately leads to a brighter future for children with autism, characterized by understanding, acceptance, and opportunity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main factors contributing to Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
ASD arises from a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Specific genetic mutations can increase risk, while environmental influences such as prenatal exposure to toxins, maternal infections, and birth complications also play significant roles.
How do genetic mutations affect the severity of ASD?
Research indicates that children with multiple genetic mutations often experience more severe phenotypes. There is a correlation between the number of genetic mutations and the severity of ASD symptoms.
What misconceptions about autism does recent research address?
Recent findings dispel the myth that autism is solely caused by parenting choices or singular environmental factors. Instead, it emphasizes that ASD results from various influences, empowering parents to seek appropriate support and resources.
Why is there a need for inclusive studies in autism research?
The historical underrepresentation of female subjects in ASD research has led to a skewed understanding of the disorder. Inclusive studies that examine both sexes together are necessary for a comprehensive understanding of ASD.
What statistical methods can enhance autism research?
Incorporating statistical methods, such as those proposed by Benjamini and Hochberg for controlling the false discovery rate, can improve the rigor of research related to developmental disorders.
What are some major risk factors for developmental disorders?
Major risk factors include having a sibling with a developmental disorder, advanced parental age at conception, certain genetic conditions like fragile X syndrome, and exposure to heavy metals and pesticides during pregnancy.
How does socioeconomic status affect the diagnosis of ASD?
There is a disparity in the average age of identification for ASD, with children from lower-income households being identified at an average age of 4.7 years, compared to 5.2 years for those from higher-income households.
What are the long-term implications for adults diagnosed with autism?
Approximately 75% of adults diagnosed with autism in the United States face either underemployment or complete unemployment.
How can awareness of risk factors help parents and guardians?
Understanding risk factors enables guardians to oversee their children's development more effectively, ensuring prompt assessments and access to initial intervention services when needed, ultimately fostering an environment of support and understanding.




