Overview
This article serves as a compassionate guide for educators, offering insights on how to effectively teach students with autism by recognizing their unique learning needs and characteristics. It highlights the significance of individualized instruction and structured learning environments, alongside the integration of visual supports and technology. These strategies are designed to cultivate an inclusive atmosphere that not only enhances writing skills but also encourages self-expression. By understanding the challenges faced by these students, educators can foster a nurturing environment that truly supports their growth.
Introduction
In an educational landscape that increasingly values inclusivity, understanding the unique needs of students with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is essential. The journey begins by recognizing the core characteristics of autism and the challenges these students often encounter in communication, behavior, and writing. This article aims to shed light on these challenges and explore effective teaching strategies that can make a significant difference.
Consider the power of visual supports, individualized instruction, and creative writing prompts. These tools not only accommodate but also celebrate the diverse abilities of autistic learners. By embracing tailored approaches and fostering collaborative efforts with parents and support teams, we can transform the educational experience for students with autism.
Imagine a classroom where every student feels empowered to express themselves. Enhancing writing skills and self-expression becomes a shared mission, paving the way for success. Together, we can create an environment that nurtures growth and understanding, ultimately leading to a brighter future for all students.
Understanding Autism: Key Characteristics and Learning Needs
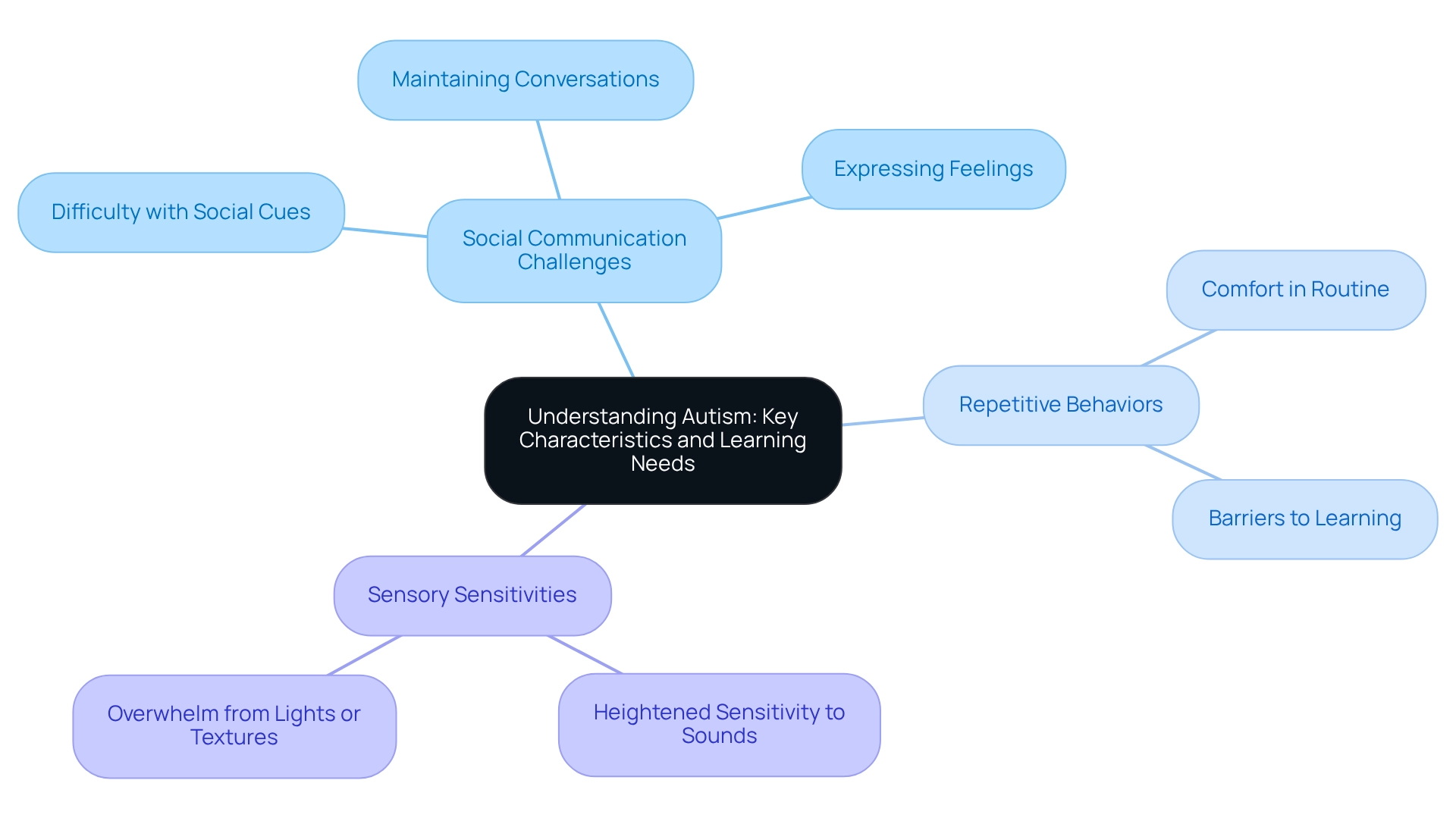
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) encompasses a range of characteristics that can profoundly impact communication, social interaction, and behavior. Understanding these traits is crucial for fostering a supportive environment for students on the spectrum.
Social Communication Challenges often arise, where students may find it difficult to grasp social cues, maintain conversations, or express their thoughts and feelings. Imagine the frustration of a child who wants to connect but struggles to find the right words.
Repetitive Behaviors are also common among many learners. While these behaviors might provide comfort and a sense of routine, they can sometimes create barriers to learning. Consider how a familiar routine can be a source of solace, yet may also limit exploration and growth.
Additionally, Sensory Sensitivities frequently present challenges. Many individuals experience heightened sensitivity to sounds, lights, or textures, which can be overwhelming in a busy classroom setting.
By identifying these characteristics, educators can adapt their teaching approaches. This understanding allows for more effective support for individuals on the spectrum, ensuring that lessons are accessible and engaging. Together, we can create a nurturing learning environment that respects and values the unique experiences of every student.
Identifying Common Writing Challenges for Students with Autism
Learners with developmental disorders often encounter various challenges in composition that can hinder their educational progress and self-expression. These difficulties can be deeply felt and may resonate with many parents and educators. Key challenges include:
- Fine Motor Difficulties: Many students struggle with the physical act of writing, which can lead to poor handwriting and fatigue during writing tasks. Current data reveals that fine motor difficulties are prevalent among children with autism, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to help these students enhance their compositional abilities.
- Organizational Issues: Structuring thoughts coherently can be particularly overwhelming for these students, often resulting in disorganized composition. This lack of organization may stem from challenges in planning and executing written assignments, which are crucial for effective communication.
- Language Processing Delays: Students might find it hard to comprehend prompts or instructions, making it difficult for them to respond appropriately in writing. These delays can significantly affect their ability to convey ideas clearly and effectively.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach. The self-regulated strategy development (SRSD) method has shown promise in enhancing composition abilities among children with developmental disorders, even though some studies suggest a lack of strong associations. Additionally, assistive technologies, such as the First Author® software, can offer valuable support by providing individualized photo images for topic selection and vocabulary assistance through word banks.
This software also includes features for planning, composing, sharing, and publishing written work, making it a comprehensive tool for enhancing language skills. Moreover, data indicate that interrater reliability for evaluating text samples achieved an impressive 90%, underscoring the importance of effective assessment techniques in understanding and improving composition skills in individuals with developmental disorders. Insights from the case study titled "Gender and Age Representation in Writing Studies" suggest that the representation of gender and age in research may influence findings related to written language development in children with ASD, emphasizing the need for further exploration in this area.
As Matthew C. Zajic noted, support from research initiatives is crucial in addressing these composition challenges. Identifying and understanding these obstacles is vital for educators teaching students with autism, enabling them to deliver effective literacy instruction tailored to their unique needs. By implementing effective methods to enhance fine motor skills and organizational abilities, educators can foster a more inclusive and supportive environment for composition.
Creating a Structured Learning Environment for Writing
Creating a structured learning environment that nurtures writing skills is essential for educators. To achieve this, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Establish Clear Routines: For students with autism, consistent daily schedules are vital. They help to reduce anxiety and enhance focus. Implementing predictable routines allows learners to anticipate transitions and daily activities. Many parents have shared that their children often struggle to feel comfortable and included in school, making these routines even more critical.
- Designate Composition Areas: It's crucial to establish specific spaces dedicated to composition activities. These areas should be free from distractions and equipped with all necessary materials, enabling learners to focus entirely on their assignments. A clearly defined space for writing can significantly improve an individual's ability to engage with their tasks. One parent noted that their child made better progress during home-learning due to the absence of classroom distractions, underscoring the effectiveness of distraction-free environments.
- Use Visual Supports: Incorporating visual schedules and prompts can greatly assist learners in managing the writing process. Visual aids serve as effective resources that guide students, helping them stay focused and understand the steps involved in writing. Research indicates that organized visual tools can enhance concentration and efficiency for students with autism. The transition back to school from home-learning has proven challenging for many children, highlighting the need for supportive approaches that include visual aids.
By embracing these strategies, educators can foster a supportive environment tailored to the unique needs of students with autism, ultimately enhancing their overall learning experience. The importance of organized learning settings is emphasized by case studies showing that learners thrive when provided with clear expectations and supportive resources. As one supporter wisely stated, "If you have this condition, consider it a superpower…you can utilize it for creativity, or do whatever you wish with it."
This perspective can inspire both teachers and caregivers to cultivate a nurturing atmosphere for learners.
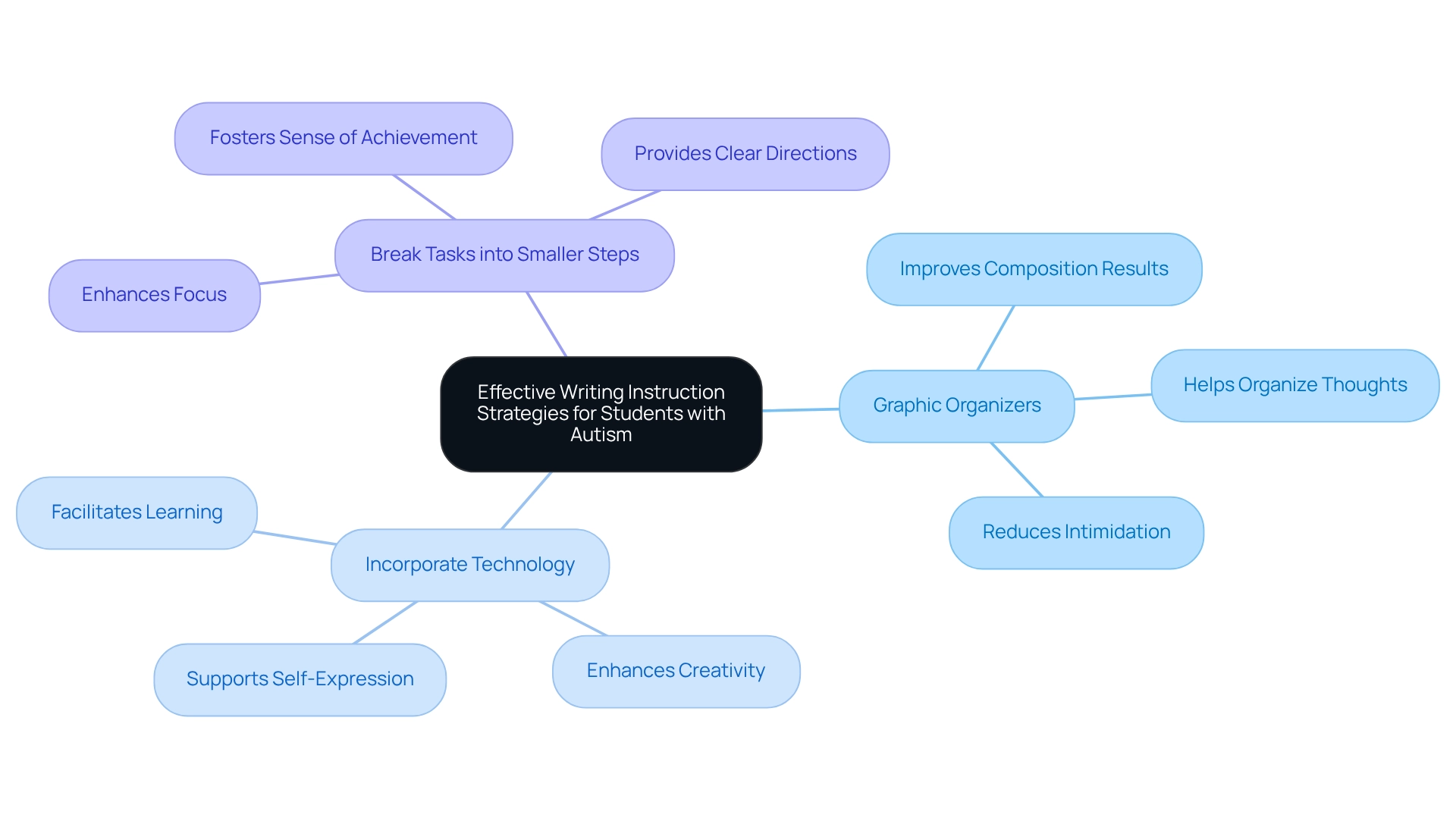
Effective Writing Instruction Strategies for Students with Autism
To enhance writing skills in students with autism, educators can implement several effective strategies that nurture their growth and confidence.
- Utilize Graphic Organizers: Graphic organizers are powerful tools that enable students to visually map out their ideas, simplifying the writing process. By using these tools, educators can help students better understand and organize their thoughts, making writing tasks feel less intimidating. Research from 2025 indicates that graphic organizers significantly improve composition results for students with autism, supported by strong empirical evidence.
- Incorporate Technology: Embracing technology, such as speech-to-text software, can greatly assist individuals who struggle with handwriting. This approach allows them to concentrate on the content of their writing rather than the mechanics, fostering creativity and self-expression. As Tamara Kaldor, Assistant Director of the TEC Center at Erikson Institute, beautifully states, "Using technology to develop inclusive playing and learning experiences supports the social, emotional, and learning needs of ALL children to play, relate, and learn." Current statistics show a growing trend in the use of digital tools within special education, underscoring their vital role in supporting diverse learning needs. Notably, a review of sixty empirical studies on children's technology use emphasizes the need for more observational studies to understand how young children engage with technology effectively.
- Break Tasks into Smaller Steps: Dividing assignments into smaller, manageable sections can help learners avoid feelings of overwhelm. This strategy not only fosters a sense of achievement but also enhances focus and involvement. By providing clear, step-by-step directions, educators can guide students through the writing process more efficiently.
By applying these compassionate approaches, educators can significantly enhance learners' writing skills and boost their overall self-assurance. This is especially important in the context of teaching students with autism, as it fosters a more inclusive and supportive educational atmosphere. Collaborating with organizations like the U.S. Department of Education, UNICEF, and UNESCO emphasizes the importance of a supportive framework to implement these strategies effectively in educational settings.
Individualized Instruction: Tailoring Approaches for Each Student
To provide effective individualized instruction for students with autism, it is essential for educators to embrace several key strategies that can truly make a difference in their students' lives.
- Develop Individualized Education Plans (IEPs): Collaborating closely with special education professionals to create comprehensive IEPs is crucial. These plans should clearly outline specific goals, accommodations, and support services tailored to each student's unique needs. This collaborative approach not only ensures that all stakeholders are aligned in their efforts to support the learner's educational journey but also emphasizes the significance of well-structured IEPs. Public agencies can place individuals with disabilities in private schools to ensure they receive Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE), highlighting the importance of these plans.
- Evaluate Personal Strengths and Weaknesses: Regular evaluations are vital for understanding each learner's progress. By systematically assessing strengths and weaknesses, educators can adapt their teaching techniques and resources to better accommodate the diverse learning styles of their students. Recent data indicates that customized instruction through IEPs leads to notable advancements in academic performance and social abilities. As we approach the 2024-2025 school year, it is essential to ensure that these assessments are effectively utilized to benefit every learner.
- Incorporate Learner Interests: Engaging students by aligning writing prompts and activities with their personal interests can significantly enhance motivation and participation. When learners see relevance in their education, they are more likely to engage deeply with the material, leading to better educational outcomes. As Jeannette G. expressed, "Each one of you are appreciated....You all have made such an amazing difference in Bryton's life in such a short time... We cannot begin to thank you enough... We are excited to watch and see where this journey takes him...With grateful hearts."
By prioritizing these personalized teaching methods, educators can effectively address the varied needs of students with autism, fostering an inclusive and supportive learning environment. However, it is essential to remain vigilant about potential challenges, such as those posed by initiatives like Project 2025, which threaten the rights and protections of individuals with disabilities. This context highlights the critical need for robust IEPs and support services, ensuring that every student has the opportunity to thrive.
Utilizing Visual Supports and Graphic Organizers in Writing
Visual aids and graphic organizers play a vital role in supporting students with autism as they develop their composition skills. Imagine a classroom where every child feels empowered to express their thoughts—this is achievable through effective strategies that cater to their unique needs.
Graphic Organizers: Consider implementing tools like mind maps or storyboards. These visual aids help students organize their compositions, making the writing process feel less overwhelming. By clarifying their thoughts and structuring concepts visually, learners can navigate their ideas with greater ease.
Visual Prompts: Picture cues and sentence starters can be invaluable in guiding students through their writing tasks. These prompts not only alleviate writer's block but also pave a clear path for self-expression, nurturing creativity and building confidence.
Color-Coding: Encourage students to use color to distinguish different elements of their writing. For example, blue can represent main ideas while green highlights supporting details. This method enhances organization and supports visual learning, making it easier for students to grasp their writing structure.
Recent studies underscore the benefits of incorporating visual aids in writing instruction for students with autism, revealing improvements in writing abilities and increased engagement. It's important to recognize that many youth with autism, particularly those with average-range intelligence, may require academic intervention due to coexisting learning disabilities. By integrating graphic organizers and visual supports, educators can foster a more inclusive and effective learning environment.
Case studies illustrate the positive impact of these strategies. Students who utilized graphic organizers showed remarkable progress in organizing their thoughts and articulating ideas in written tasks. This approach not only enhances composition skills but also bolsters learners' confidence, empowering them to share their thoughts more freely.
Furthermore, the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association highlights the significance of effective communication methods, reinforcing the necessity of visual supports in writing instruction. Understanding the varying graduation rates by disability category further emphasizes the need for tailored educational approaches, spotlighting the critical role of graphic organizers in aiding individuals with developmental disorders.
By embracing these strategies, educators can truly make a difference in the lives of their students, fostering an environment where every learner feels valued and capable.
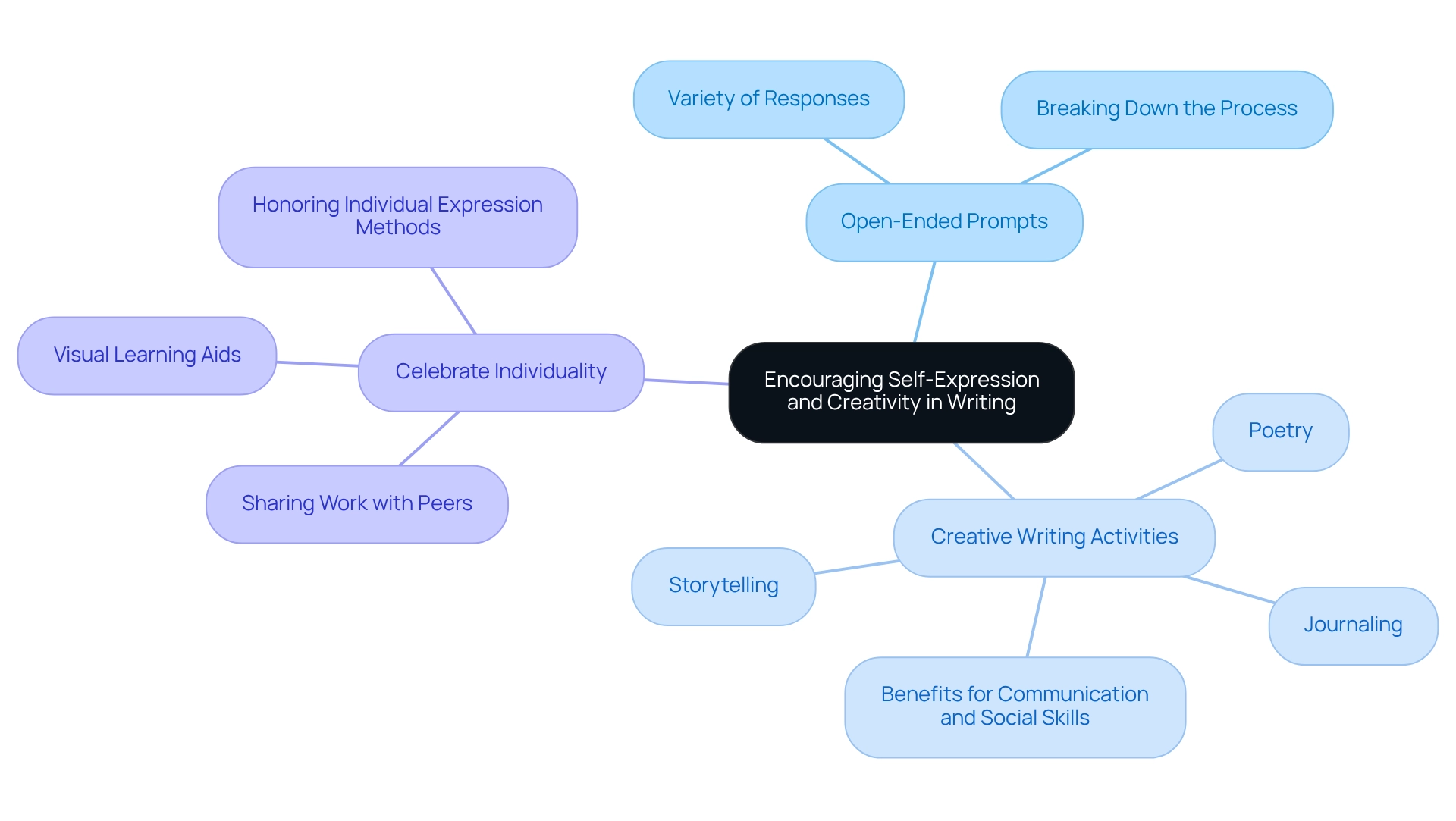
Encouraging Self-Expression and Creativity in Writing
To encourage self-expression and creativity in students with autism, educators can implement several effective strategies that truly resonate with their unique needs:
- Provide Open-Ended Prompts: By utilizing prompts that allow for a variety of responses, educators can encourage students to explore their thoughts and feelings. Research suggests that open-ended prompts greatly boost creativity among individuals, making them particularly beneficial for students with autism. This approach enables learners to express themselves more freely. Additionally, breaking down the composition process into smaller, manageable stages can help minimize feelings of overwhelm, fostering a clearer understanding of each phase.
- Incorporate Creative Writing Activities: Engaging learners in creative writing tasks—such as poetry, storytelling, or journaling—nurtures their creativity and encourages personal expression. A study titled "Opportunities in Creative Arts Therapy for Autism" highlights that such interventions can lead to significant improvements in communication and social skills, reinforcing the value of creative outlets. Cristina Oro-Aparicio notes that the primary challenges in creative arts therapy intervention research relate to the diagnostic variability among participants and the assessment tools used. This underscores the importance of tailored approaches in the classroom, ensuring that each student's unique needs are met.
- Celebrate Individuality: Fostering a classroom culture that appreciates each learner's unique perspective is vital. By encouraging students to share their work with peers, educators can help build confidence and reinforce individuality. Most individuals on the spectrum are visual learners and benefit from visual aids in processing information. Teachers should honor the various methods individuals use to convey their thoughts, which can inspire greater participation in composition.
By creating an environment that prioritizes self-expression, educators teaching students with autism empower individuals to enhance their writing abilities and boost their confidence, ultimately supporting their overall growth. This nurturing approach not only fosters creativity but also cultivates a sense of belonging and acceptance.
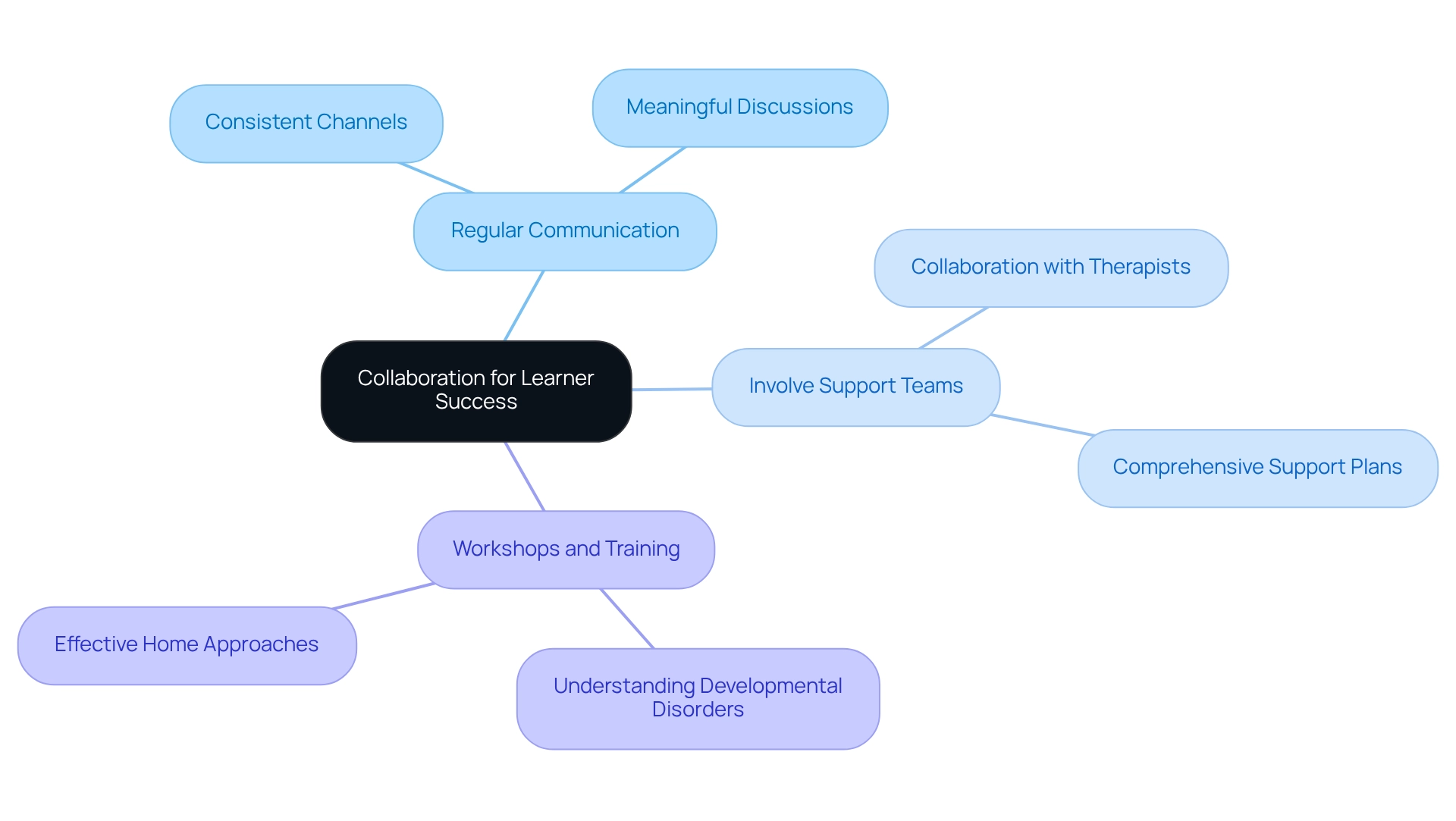
Collaborating with Parents and Support Teams for Success
To foster collaboration among educators and families, it is crucial to establish a supportive environment that enhances learner success.
- Regular Communication: It’s essential to create consistent communication channels with parents. This allows for meaningful discussions about student progress, challenges, and strategies. Imagine how reassuring it is for parents to know they can reach out anytime to discuss their child’s journey.
- Involve Support Teams: Collaborating with therapists, special education professionals, and other support staff is vital. Together, you can design a comprehensive support plan tailored to each learner’s needs. This teamwork not only strengthens the support network but also reassures families that their child is receiving holistic care.
- Workshops and Training: Offering sessions for parents to understand developmental disorders and effective approaches can empower them. When parents learn how to assist their children at home, it fosters a sense of confidence and capability.
By working together, educators and families can build a nurturing network that significantly improves learner success. Let’s take these steps together to ensure every child thrives.
Key Takeaways and Continuous Improvement in Teaching Practices
Effective instructional methods for teaching students with autism involve a range of approaches customized to address their distinct traits and learning requirements. It's essential to recognize that each autistic student is unique, and understanding their individual needs is crucial. This comprehension empowers educators to tailor their approaches, ensuring that they support each learner's educational journey effectively. As highlighted by Lei et al., many autistic individuals prefer identity-first language, underscoring the importance of respecting individual preferences.
Many individuals with autism face specific composing challenges. By implementing targeted strategies—such as breaking tasks into manageable steps and providing clear examples—educators can significantly enhance their writing skills. Establishing a structured classroom environment also plays a vital role; predictable routines and clear expectations help learners feel secure and prepared to engage in learning.
Visual supports and graphic organizers can greatly improve comprehension and organization. Tools like graphic organizers assist learners in visualizing their thoughts and ideas, making complex information more accessible. Additionally, encouraging self-expression through open-ended prompts and creative activities allows learners to explore their interests and convey their thoughts in a supportive environment.
Collaboration with parents and support teams is another key aspect. Engaging with parents and professionals ensures a consistent approach to education. Regular communication helps align strategies used at school and home, reinforcing learning.
Continuous improvement in teaching practices is essential for fostering an inclusive educational environment, especially when it comes to teaching students with autism. Recent studies emphasize the effectiveness of art therapy as a means to empower neurodivergent individuals, demonstrating how tailored support can enhance their educational experiences. For instance, a case study titled 'Art Therapy Empowering Neurodivergent Learners' illustrates how integrating practices like kinesthetic learning and sensory-friendly tools can greatly assist these individuals.
Furthermore, Cohen's kappa for consensus among reviewers was calculated at 0.57, indicating a moderate level of agreement on the effectiveness of these teaching methods. By remaining attentive to the changing needs of learners, educators can apply effective approaches for teaching students with autism that promote inclusivity and enhance outcomes. As the landscape of autism education evolves, staying informed about current trends and expert opinions will further improve teaching practices and support the development of all learners. Moreover, qualitative research is crucial for understanding the experiences of students, teachers, and parents regarding inclusive education for autistic students, reinforcing the need for ongoing dialogue and adaptation in teaching methodologies.
Conclusion
Understanding the unique challenges faced by students with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial for fostering an inclusive educational environment that nurtures learning and self-expression. The key characteristics of autism, including social communication challenges and sensory sensitivities, necessitate that educators adapt their teaching methods with care. By acknowledging these traits, educators can implement tailored strategies that specifically address the writing difficulties these students encounter, such as fine motor challenges and organizational issues.
The article emphasizes the significance of structured learning environments. Clear routines and designated writing spaces empower students to focus and thrive. Visual supports, like graphic organizers and color-coded prompts, play an essential role in enhancing comprehension and organization, making the writing process more manageable. Moreover, encouraging self-expression through open-ended prompts and creative activities cultivates a supportive atmosphere that celebrates each student’s individuality.
Collaboration with parents and support teams is vital in reinforcing these strategies, ensuring that students receive consistent support both at school and home. By maintaining regular communication and involving various stakeholders in the educational journey, a comprehensive support plan can be developed for each student, tailored to their unique needs.
As the educational landscape evolves, continuous improvement in teaching practices is necessary to meet the diverse needs of students with autism. By staying informed about effective strategies and nurturing an inclusive environment, educators can empower these students to express themselves confidently and achieve their academic goals. Ultimately, promoting understanding and tailored instruction for students with autism not only enhances their learning experiences but also enriches the entire classroom community, creating a space where every child can flourish.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) encompasses a range of characteristics that can affect communication, social interaction, and behavior.
What are common social communication challenges faced by students with ASD?
Students with ASD may struggle to understand social cues, maintain conversations, and express their thoughts and feelings, which can lead to frustration when trying to connect with others.
What are repetitive behaviors in the context of ASD?
Repetitive behaviors are common among learners with ASD and can provide comfort and routine, but they may also limit exploration and growth in learning.
How do sensory sensitivities affect students with ASD?
Many individuals with ASD experience heightened sensitivity to sounds, lights, or textures, which can be overwhelming, especially in busy classroom environments.
How can educators support students with ASD?
Educators can adapt their teaching approaches by understanding the characteristics of ASD, which allows for more effective support and creates a nurturing learning environment.
What challenges do learners with developmental disorders face in composition?
Key challenges include fine motor difficulties, organizational issues, and language processing delays, which can hinder their educational progress and self-expression.
What is the self-regulated strategy development (SRSD) method?
The self-regulated strategy development (SRSD) method is an approach that has shown promise in improving composition abilities among children with developmental disorders.
How can assistive technologies help students with composition challenges?
Assistive technologies, like the First Author® software, provide individualized support for topic selection, vocabulary assistance, and features for planning and composing written work.
What strategies can educators implement to support writing skills in students with autism?
Educators can establish clear routines, designate distraction-free composition areas, and use visual supports to enhance focus and manage the writing process.
Why are clear routines important for students with autism?
Consistent daily schedules help reduce anxiety and enhance focus, allowing students to anticipate transitions and feel more comfortable in the school environment.
How can visual supports aid students with autism in writing?
Visual schedules and prompts serve as effective resources that guide students through the writing process, improving concentration and efficiency.
What is the overall goal of creating a supportive learning environment for students with ASD?
The goal is to foster an inclusive atmosphere that respects and values the unique experiences of every student, ultimately enhancing their overall learning experience.




