Overview
Teaching autistic children effectively requires a compassionate understanding of their unique characteristics and the use of tailored instructional strategies. Recognizing the social communication challenges they face is crucial, as is employing visual supports that resonate with their learning styles. By fostering individualized instruction, we can collectively enhance the educational experience and writing skills of autistic students.
As parents and educators, we often wonder how to best support these remarkable children. Imagine a classroom where each child's needs are met with empathy and understanding. When we embrace their individuality, we not only help them learn but also empower them to express themselves.
It's important to remember that the journey may have its challenges, but there are numerous resources available to guide us. By sharing our experiences and insights, we can create a supportive community that uplifts both parents and educators alike. Let's continue to learn and grow together, ensuring that every autistic child has the opportunity to thrive.
Introduction
In the world of education, recognizing the unique needs of autistic children is crucial, especially when it comes to nurturing their writing skills. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) brings a diverse array of challenges that can impede communication and self-expression. This makes it vital for parents and educators to create personalized strategies that address these individual needs.
This article explores:
- The fundamental characteristics of autism
- The importance of writing as a means of communication
- The various obstacles autistic students encounter in their writing journeys
By examining effective teaching strategies and the necessity of fostering structured, supportive environments, this piece seeks to empower caregivers and educators with the insights needed to enrich the writing experiences of autistic children, ultimately paving the way for their academic success and personal development.
Understanding Autism: Key Characteristics and Learning Needs
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) encompasses a diverse range of symptoms that significantly impact communication, behavior, and social interaction. Understanding these key traits is essential for parents and educators who are committed to teaching autistic children in nurturing learning environments tailored to their unique needs.
- Social Communication Challenges: Children on the spectrum often face difficulties in interpreting social signals, sustaining conversations, and articulating their emotions. Recent studies reveal that these challenges can lead to feelings of isolation and frustration, highlighting the urgent need for targeted interventions. Notably, findings from the ADDM Network indicate an increased prevalence of ASD compared to previous estimates, reflecting a significant shift in the demographic landscape of youth diagnosed with ASD.
- Repetitive Behaviors: Many individuals with ASD engage in repetitive movements or exhibit a strong preference for routines. These behaviors can offer a sense of comfort and predictability, which is vital for their emotional well-being. Recognizing and embracing these patterns can empower educators to create a more inclusive classroom atmosphere.
- Sensory Sensitivities: Sensory processing challenges are common among individuals on the spectrum, with many experiencing heightened or diminished responses to sensory stimuli such as sounds, lights, and textures. This sensitivity can affect their ability to focus and engage in educational activities, underscoring the necessity for educators to implement sensory-friendly strategies in the classroom.
The emotional challenges faced by families are significant, with approximately 50% of mothers of children with autism showing signs of depression, compared to a rate of 6% to 13.6% for mothers of children without autism. The World Health Organization's commitment to enhancing the management of autism spectrum disorders emphasizes the importance of addressing these issues through collaborative efforts. The resolution adopted in May 2014 underscores the need to improve the quality of life for individuals with autism, aligning with the WHO's Comprehensive Mental Health Action Plan 2013–2030, which aims to bridge gaps in early detection and care.
By fostering an inclusive environment and employing effective teaching strategies, parents and educators can significantly enhance their approach to teaching autistic children, ultimately improving their educational experiences and outcomes.
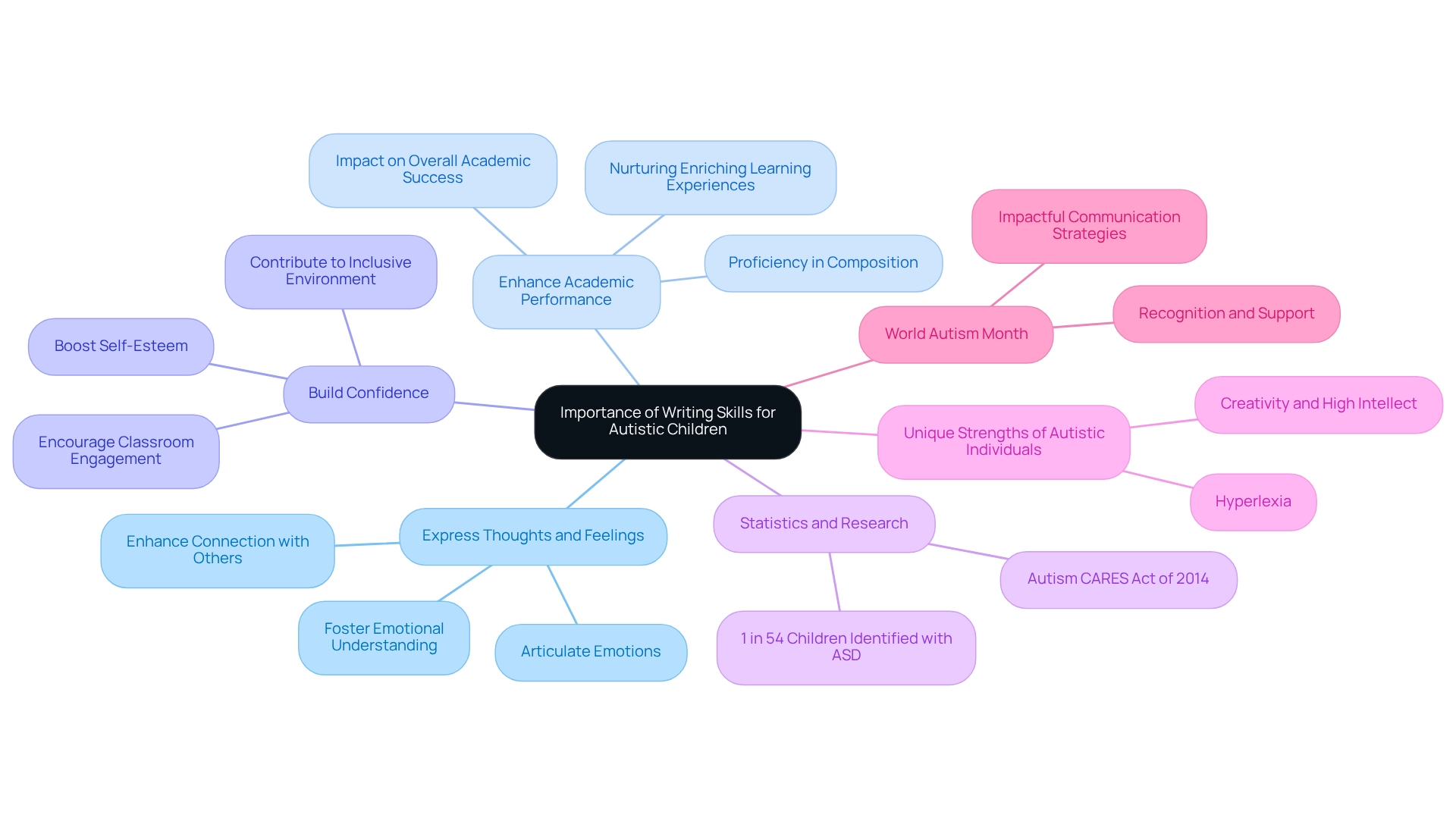
The Importance of Writing Skills for Autistic Children
Writing abilities hold immense importance for autistic individuals, serving as a vital means for communication and self-expression. Effective composition empowers young individuals to:
- Express Thoughts and Feelings: Writing provides a valuable outlet for young people to articulate their thoughts and emotions, especially for those who may find verbal communication challenging. This form of expression fosters greater emotional understanding and connection with others.
- Enhance Academic Performance: Proficiency in composition is closely tied to overall academic success. As a fundamental skill across various subjects, strong writing abilities can significantly impact a student's performance in school, nurturing a more enriching learning experience.
- Build Confidence: Mastering the art of writing can greatly boost self-esteem. When young individuals feel capable of expressing their ideas through writing, they are more inclined to engage in classroom discussions and activities, contributing to a more inclusive educational environment.
Statistics reveal that communication challenges are prevalent among individuals on the spectrum, with many struggling to effectively convey their needs and thoughts. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that approximately 1 in every 54 youths in the U.S. is recognized with autism spectrum disorder, underscoring the importance of tailored interventions to enhance their communication skills. Additionally, the Autism CARES Act of 2014 aims to expand research and improve coordination among NIH components funding ASD research, which is essential for developing effective strategies to bolster communication abilities.
Case studies illustrate that many autistic individuals possess unique strengths, such as creativity and high intellect. By harnessing these strengths through writing, young individuals can explore imaginative avenues that not only enhance their communication skills but also allow them to showcase their talents. For instance, some children may exhibit hyperlexia, enabling them to read beyond their grade level, which can be leveraged to improve their writing abilities.
In 2025, the ongoing recognition of World Autism Month serves as a poignant reminder of the importance of supporting individuals with autism. By focusing on impactful communication strategies, caregivers and educators can learn how to assist autistic children in overcoming their interaction challenges, ultimately leading to greater achievement and autonomy in both their educational and personal lives.
Challenges in Writing for Autistic Students
Autistic students often face significant challenges related to composition, which can deeply affect their academic performance and self-esteem. Understanding these difficulties is essential for fostering a supportive environment. Key challenges include:
- Fine Motor Difficulties: Many children on the autism spectrum struggle with fine motor skills, which can hinder their ability to write legibly and efficiently. Recent studies indicate that these challenges are prevalent, impacting their overall composition performance and leading to frustration during writing tasks.
- Organizational Issues: Students on the spectrum frequently encounter difficulties in organizing their thoughts coherently. This can result in disorganized expression, where ideas are presented in a jumbled manner, making it hard for readers to grasp their intended message. The prevalence of organizational challenges in composition among these students highlights the need for focused interventions. Studies show that individuals with ASD often experience more significant executive dysfunction than their neurotypical peers, further complicating their composition skills. Those with enhanced cognitive flexibility tend to make fewer grammatical errors, underscoring the importance of addressing these executive functioning challenges.
- Anxiety and Frustration: The stress associated with composition tasks can heighten anxiety levels in autistic youth. This increased anxiety can create a cycle of frustration, further obstructing their willingness to engage in writing tasks. It is vital for educators and parents to understand the emotional landscape of these students. Notably, psychiatric conditions are recognized in 70% to 90% of young individuals with ASD, contributing to these emotional difficulties.
Recognizing these challenges is the first step toward providing effective support. By implementing tailored strategies and accommodations, educators can empower autistic children to navigate their composition challenges, fostering a more inclusive and supportive learning environment. Additionally, ongoing provider training and quality enhancement efforts are crucial to improving care for youth with ASD, particularly in enhancing their literacy skills in educational settings.
Cheryl M. Scott observes a high prevalence of learning disabilities in composition among youngsters with ASD, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions. Together, we can create a nurturing environment that supports these students in overcoming their challenges.
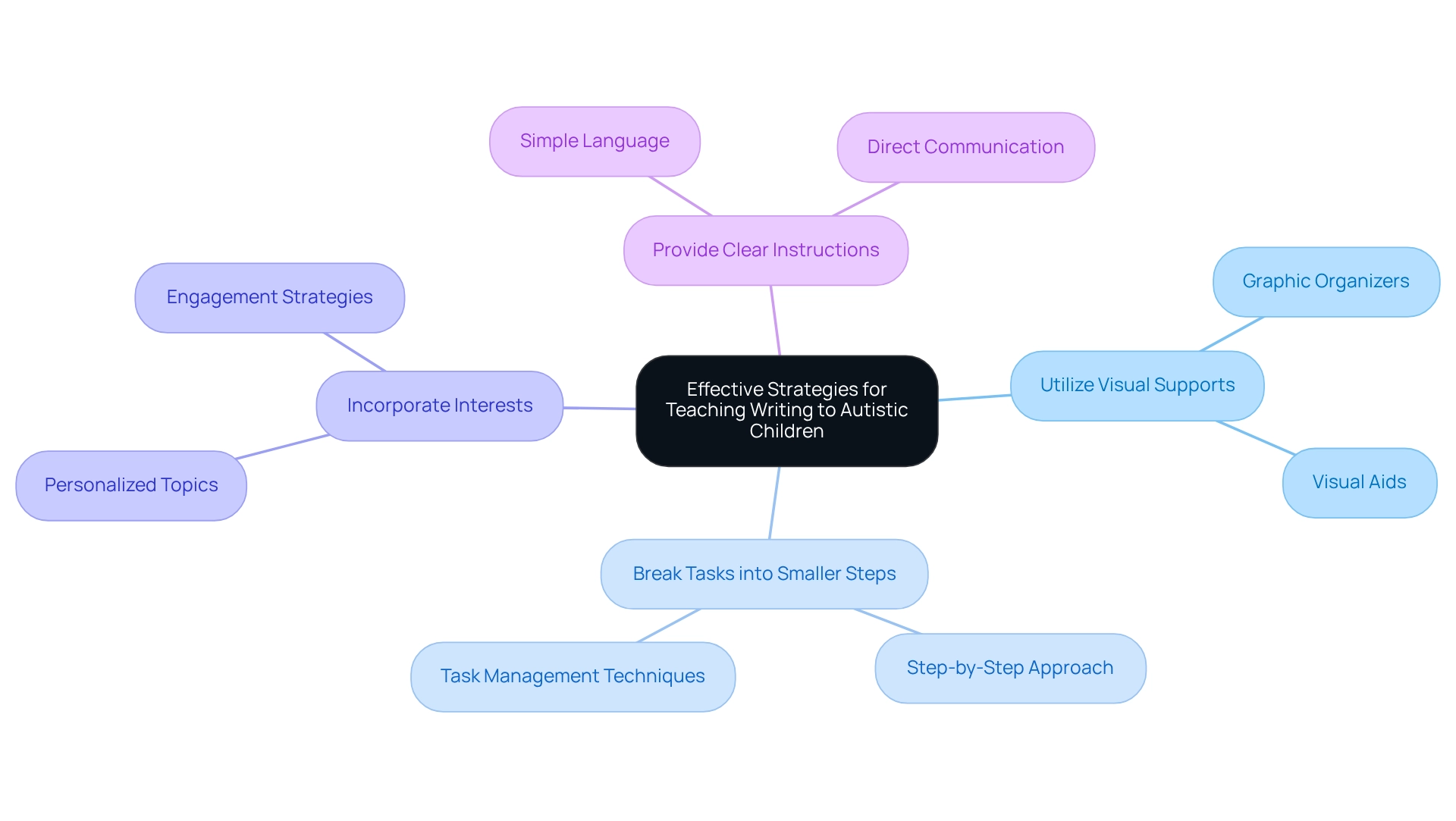
Effective Strategies for Teaching Writing to Autistic Children
To effectively instruct individuals on composition, it is crucial to employ a variety of strategies that address their distinct learning requirements:
- Utilize Visual Supports: Incorporating graphic organizers and visual aids can significantly enhance the composition process. These tools help children structure their thoughts and ideas, making it easier for them to express themselves on paper. Research shows how to teach autistic children that using visual aids can result in enhanced composition abilities, promoting greater independence in their tasks. In fact, 10 articles have addressed content for knowledge development assessable for autistic students in inclusive education, highlighting the effectiveness of such strategies.
- Break Tasks into Smaller Steps: Writing assignments can often feel overwhelming. By dividing tasks into manageable parts, educators can help students maintain focus and reduce anxiety. This step-by-step method enables young learners to gain confidence as they finish each part of their composition.
- Incorporate Interests: Engaging students by utilizing subjects that resonate with their personal interests can make composing more enjoyable and motivating. When children are passionate about what they are creating, they are more likely to invest effort and creativity into their work.
- Provide Clear Instructions: Clarity is crucial when explaining composition tasks. Using simple, direct language helps eliminate confusion and ensures that students understand what is expected of them. Avoiding ambiguity enables a smoother composition process.
These strategies not only enhance the experience for autistic students but also illustrate how to teach autistic children to achieve overall academic success. For example, a case study featuring a student named Caroline illustrated how a collaborative project in a composition course, led by Marc Keith, assisted her in overcoming difficulties with citing and integrating sources. Keith highlighted a cooperative environment where students exchange thoughts and interact with shared materials, which ultimately enhanced Caroline's composition abilities and increased her confidence and pride in her work.
This experience underscores the importance of supportive learning environments. In 2025, the emphasis on creating inclusive learning communities continues to grow, reinforcing the notion that access to quality education is a civil right for all students, including those with disabilities. As Lei et al. noted, several investigations have identified that individuals on the autism spectrum prefer identity-first language, highlighting the importance of respecting personal preferences in educational settings.
By embracing these effective teaching methods, educators can discover how to teach autistic children in a way that cultivates an atmosphere where they flourish and acquire vital communication abilities, in line with ASD Media's goal to create a nurturing community.
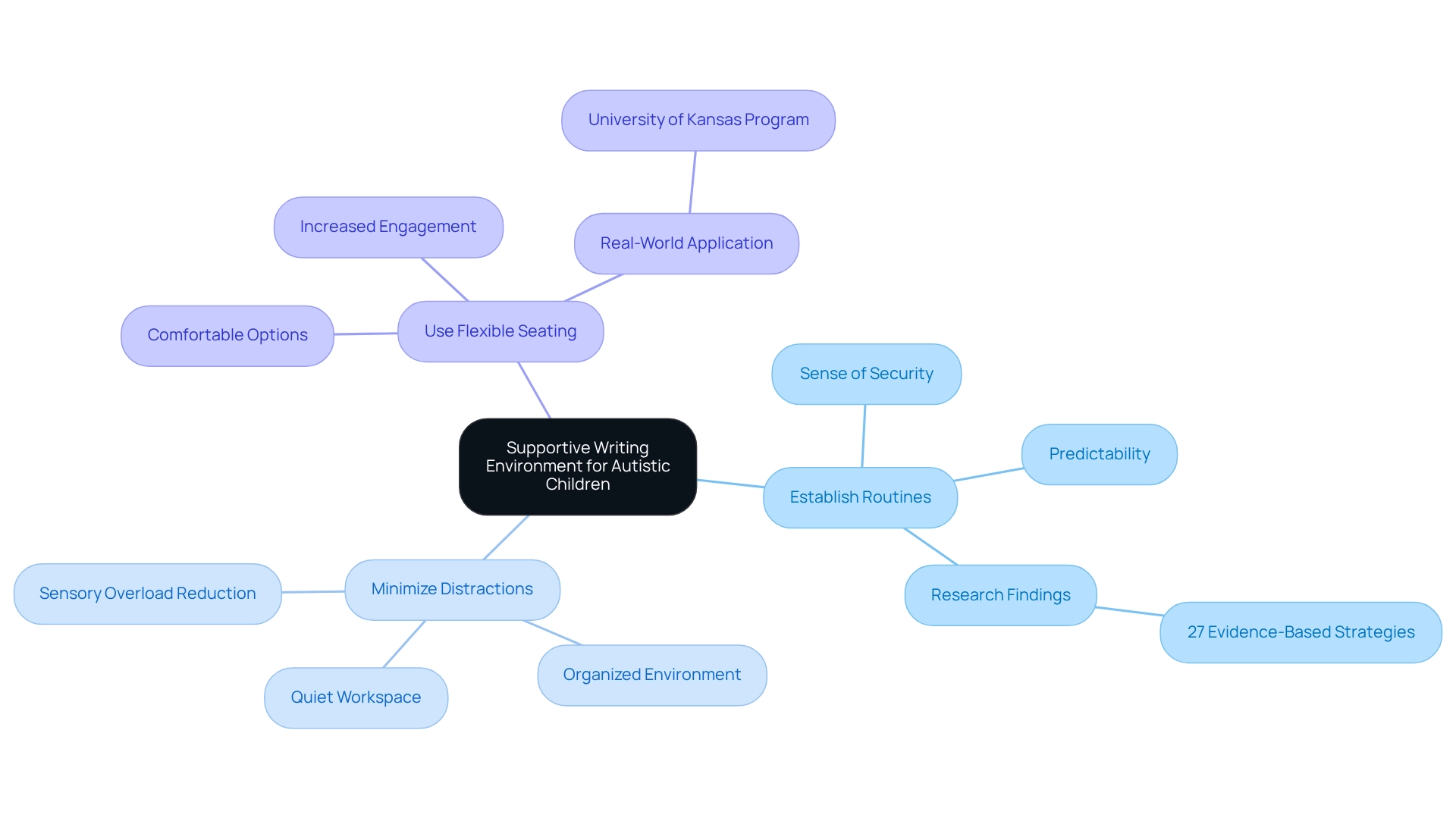
Creating a Structured and Supportive Writing Environment
Creating a nurturing writing environment for autistic children involves several key strategies that can truly make a difference:
- Establish Routines: Consistent routines are crucial as they provide a sense of security and predictability, allowing children to understand what to expect during writing activities. Research shows that structured environments significantly enhance learning outcomes for autistic students, offering valuable insights on how to teach them effectively. The National Professional Development Center on Autism Spectrum Disorder has identified 27 evidence-based strategies for teaching autistic children, highlighting the importance of structured routines in educational settings.
- Minimize Distractions: A quiet, organized workspace is vital for reducing sensory overload. By minimizing distractions, young individuals can focus more effectively on their writing assignments. This is especially important for those with autism, who may be sensitive to environmental stimuli. As Rachel Dumont from the Department of Emergency Medicine at Thomas Jefferson University wisely notes, "Structured environments are essential for promoting effective learning experiences for youth with ASD."
- Use Flexible Seating: Providing options for seating arrangements empowers children to choose what makes them most comfortable, whether it’s a traditional desk or a more relaxed setting. This flexibility can lead to increased engagement and participation in composition activities. The University of Kansas offers a top-ranked online Master's program in Special Education, equipping educators with the skills to address the unique challenges faced by students with ASD. Graduates of this program are prepared to implement effective strategies and interventions in their classrooms, demonstrating the real-world application of these concepts.
A nurturing setting not only promotes confidence but also stimulates active participation in tasks, ultimately improving the educational experience for learners with autism. By applying these strategies, educators and parents can learn how to teach autistic children and foster an environment that encourages achievement in composition.
Individualized Instruction: Tailoring Approaches for Each Child
Personalized instruction is essential for effectively teaching autistic children by addressing their unique needs. Understanding how to tailor education to each individual can make a profound difference in their learning experience. Here are some key strategies to consider:
- Assess Individual Strengths and Weaknesses: Regular evaluations of each child's writing abilities are crucial for identifying specific areas for improvement. This evaluation is vital, as recognizing a young person's strengths can guide customized teaching methods that enhance their learning journey. It's important to note that IEPs for students with ASD often face significant litigation regarding educational programs, highlighting the necessity of personalized educational strategies.
- Adapt Teaching Methods: Implementing diverse instructional strategies that align with each child's preferred learning style—be it visual, auditory, or kinesthetic—is essential. Research shows that personalized teaching methods greatly improve engagement and retention. As Fernanda Esqueda Villegas points out, smaller class sizes are beneficial, and teachers emphasize the importance of professional development to effectively support these students.
- Set Personalized Goals: Collaborating with the child to establish achievable objectives not only motivates them but also appropriately challenges them. This customized goal-setting fosters a sense of ownership over their learning journey, promoting growth in their writing abilities.
Integrating these strategies not only enhances writing skills but also demonstrates how to teach autistic children by addressing their broader social needs. A recent study revealed that educators often feel uncertain about incorporating social training within the constraints of the national curriculum. However, they recognize the importance of these skills for effective peer interaction.
The case study titled "Incorporating the Social Aspect in Teaching" highlighted that, despite their hesitations, teachers acknowledged the necessity of teaching social skills to help students with ASD interact effectively with peers. Furthermore, there is a pressing need for policy transformation to enhance funding and accessibility for educational support for youth with ASD, emphasizing the systemic changes required to ensure inclusivity. By focusing on individualized instruction, educators can create a more inclusive environment that nurtures both academic and social growth.
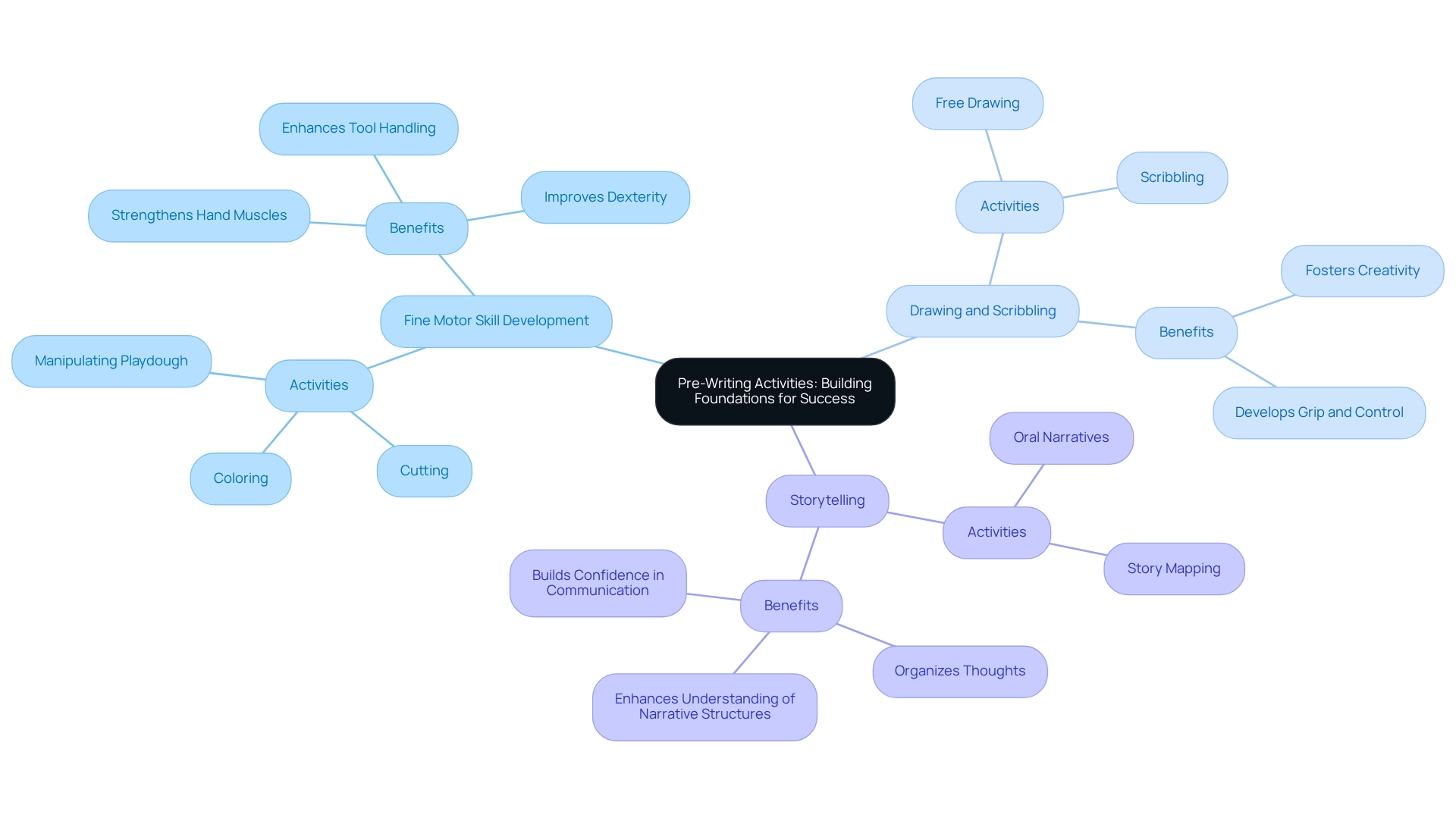
Pre-Writing Activities: Building Foundations for Success
Engaging in pre-writing activities is essential for teaching autistic children and enhancing their readiness to write. Research indicates that effective pre-writing activities can significantly influence success in composition, with 12 studies (26%) highlighting the importance of focus and executive function abilities in this context. Consider these key activities that can nurture writing readiness:
- Fine Motor Skill Development: Activities such as cutting, coloring, and manipulating playdough are vital for strengthening hand muscles and improving dexterity. These skills are crucial for composition, enabling children to handle writing tools effectively. As one instructor noted, 'To better assist the students and truly enable them to develop their composition abilities.'
- Drawing and Scribbling: Encouraging children to express themselves through drawing not only fosters creativity but also aids in developing the motor skills necessary for writing. This form of expression helps children cultivate grip and control, which are essential for future composition tasks.
- Storytelling: Utilizing oral narratives can help young learners organize their thoughts and grasp narrative structures before they begin composing. This approach enhances their understanding of story elements while building confidence in their ability to communicate ideas.
Integrating these vital activities into daily practices equips children for successful writing experiences. Importantly, all intervention studies met at least partial criteria for reliability, reinforcing the effectiveness of these pre-writing activities. Case studies have shown that individuals with autism may face challenges in productivity and grammaticality, yet they often demonstrate strengths in vocabulary and language conventions.
Therefore, educational approaches should include clear lessons on grammar and composition structure, tailored to the unique needs of these children. By focusing on fine motor skill development and engaging in pre-writing exercises, parents and educators can significantly enhance how to teach autistic children regarding readiness for composition and overall communication abilities.
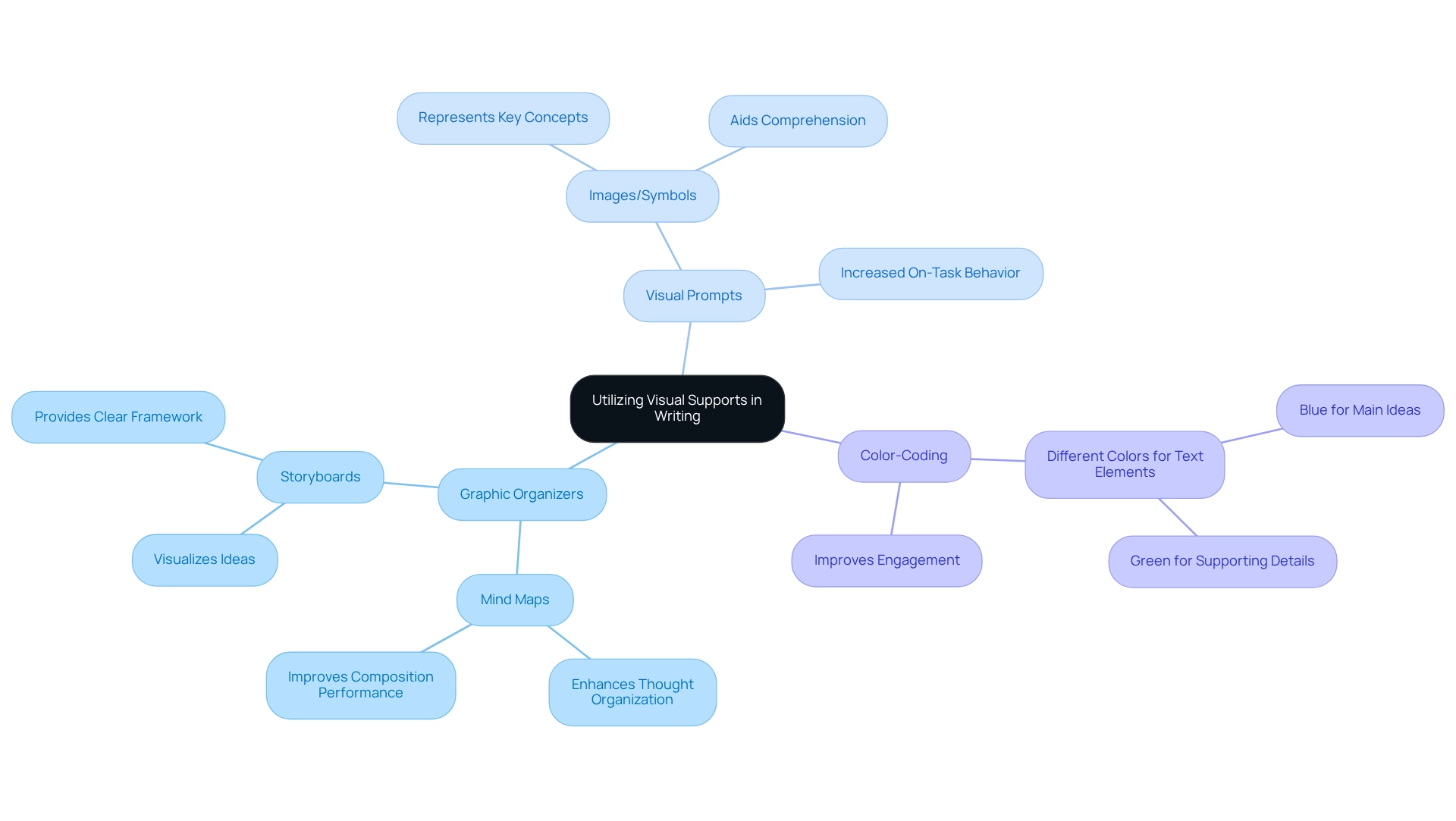
Utilizing Visual Supports and Graphic Organizers in Writing
Visual aids and graphic organizers are vital resources for supporting autistic individuals in their tasks. Here’s how to implement them effectively:
- Graphic Organizers: Consider utilizing tools like mind maps or storyboards to help children organize their thoughts and visualize their ideas. Research shows that these organizers can significantly enhance performance in composition by offering a clear framework for thought organization. Notably, the total points for determining the evidence-based practice (EBP) status of visual schedules was 100, surpassing the threshold of 60, which highlights the effectiveness of visual supports in educational settings.
- Visual Prompts: Incorporate images or symbols that represent key concepts or steps in the composition process. This approach not only aids comprehension but also helps maintain focus. Studies have indicated increased on-task behavior when visual supports are used. Additionally, ABA therapy promotes the growth of positive behavioral skills, which can be enhanced through these visual aids.
- Color-Coding: Encourage the use of different colors for various elements of text (e.g., blue for main ideas, green for supporting details). This method improves organization and makes the composition process more engaging.
These strategies can transform the teaching experience for autistic children, making composition more manageable and less intimidating. For instance, a study examining motor skill performance in youths with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) highlighted that visual aids significantly enhanced specific abilities, such as aiming and catching. This aligns with the potential advancements in writing activities. By integrating these tools, educators and parents can foster a more supportive learning environment that empowers autistic children to express their thoughts and ideas effectively.
As L.K., a Data Collection Assistant involved in the research, noted, the use of visual supports is crucial in enhancing educational outcomes for young individuals with ASD.
Encouraging Self-Expression and Creativity in Writing
Promoting self-expression and creativity in composition is essential for understanding how to teach autistic children and improve their engagement. By embracing effective strategies, we can create a nurturing environment that fosters their growth and creativity.
- Utilize Creative Prompts: Open-ended writing prompts can ignite a child's imagination, allowing them to explore their interests freely. For instance, prompts that invite them to describe a favorite place or invent a new character can lead to rich narratives that reflect their unique perspectives.
- Incorporate Art: Integrating art into the composition process can be particularly beneficial. Allowing young learners to depict their narratives or use visual art as a precursor to writing helps them express their thoughts visually, facilitating the transition to written communication.
- Celebrate Unique Voices: Encouraging children to share their personal experiences and viewpoints not only validates their individuality but also nurtures confidence in their composing abilities. This empowering approach allows them to share their unique viewpoints with others, fostering a sense of belonging.
Research indicates that imaginative prompts are crucial in understanding how to teach autistic children, significantly influencing their engagement levels in composition and enhancing their motivation to communicate. A study examining the expository composition abilities of youth aged 8 to 14 years with and without ASD found that tailored strategies can lead to improved outcomes. Furthermore, a case study titled "Hierarchical Regression Analysis of Emotional Expression" emphasized that alexithymic characteristics are important indicators of emotional expression, which is essential for understanding how autistic children interact with composition.
Dominic A. Trevisan highlights that measures of alexithymia can assist in clinical evaluation and inform ideal interventions, underscoring the importance of emotional expression in communication.
By implementing these strategies, parents and educators can learn how to teach autistic children while creating a supportive atmosphere that nurtures creativity and self-expression in composition. This ultimately leads to enhanced skills and emotional expression, enriching their learning journey. This article is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing for unrestricted use and distribution with appropriate credit to the original authors. Additionally, we express gratitude and respect for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples and their culture, recognizing the importance of diverse perspectives in the learning process.

Collaborating with Parents and Support Teams for Effective Instruction
Cooperation between parents, educators, and support teams is essential for effective instruction in composition, especially when teaching autistic children. To enhance this collaboration, consider these key strategies:
- Regular Communication: Establishing open lines of communication between parents and teachers is vital. This connection allows for the sharing of insights and strategies that have proven effective both at home and in the classroom. Regular updates help ensure that everyone is aligned in their approach to supporting the student's writing development. It's important to recognize that behaviors in individuals with autism, such as refusing requests or exhibiting aggression, may be linked to their communication needs, underscoring the significance of this dialogue.
- Team Meetings: Organizing regular meetings with all stakeholders—including parents, teachers, and support staff—facilitates discussions about the student's progress. These gatherings provide a valuable opportunity to evaluate the effectiveness of existing strategies and make necessary modifications to enhance the child's composition abilities. Future research suggests that prolonging study periods can better aid student composition growth, emphasizing the ongoing need for effective methods in composition teaching.
- Shared Resources: Providing parents with access to resources and tools for home use strengthens the composition skills taught in school. This not only empowers parents but also creates a consistent learning environment that bridges home and school. The case study titled 'Advocacy for Inclusive Education as a Civil Rights' highlights the legal and ethical implications of inclusive education, reinforcing the argument for collaboration in instructional practices.
A collaborative approach ensures that young learners receive cohesive support across different settings, which is crucial when considering how to teach autistic children. This ultimately enhances their writing abilities and overall educational experience. By fostering strong partnerships, parents and educators can work together to create an inclusive environment that celebrates the unique strengths of every individual. As John Elder Robison noted, technologies may help erase disabilities that might otherwise be visible and humiliating, further emphasizing the importance of supportive environments for autistic children.
Additionally, the statistic indicating an interrater reliability of 78% for the total number of unique words serves as a quantitative measure of writing development, supporting the discussion on writing instruction.
Conclusion
Creating effective writing experiences for autistic children requires a deep understanding of their unique needs and challenges. It is essential to recognize the fundamental characteristics of autism—such as social communication difficulties, sensory sensitivities, and repetitive behaviors—as these factors significantly influence writing skills. By employing tailored strategies, educators and parents can cultivate environments that promote communication and self-expression, ultimately enhancing academic performance and personal development.
The writing challenges faced by autistic students can vary widely, from fine motor difficulties to organizational issues. These challenges necessitate individualized instruction and structured support. Implementing effective teaching strategies—such as utilizing visual supports, breaking tasks into manageable steps, and incorporating personal interests—can lead to substantial improvements in writing engagement and success. Furthermore, engaging in pre-writing activities and fostering collaborative efforts between parents and educators can solidify the foundation for effective writing instruction.
Ultimately, our goal is to empower autistic children to express themselves confidently through writing. By nurturing creativity, providing clear instructions, and celebrating their unique voices, educators and parents can assist these children in navigating their communication challenges. This holistic approach enriches their educational experiences and paves the way for greater independence and self-advocacy in both their personal and academic lives. A commitment to understanding and addressing the needs of autistic learners is essential in creating a more inclusive and supportive educational landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a condition that encompasses a diverse range of symptoms affecting communication, behavior, and social interaction.
What are the main social communication challenges faced by children with ASD?
Children with ASD often struggle with interpreting social signals, sustaining conversations, and expressing their emotions, which can lead to feelings of isolation and frustration.
How prevalent is ASD among youth?
Recent findings from the ADDM Network indicate an increased prevalence of ASD compared to previous estimates, reflecting a significant shift in the demographic landscape of youth diagnosed with ASD.
What types of repetitive behaviors are common in individuals with ASD?
Many individuals with ASD engage in repetitive movements or have a strong preference for routines, which can provide comfort and predictability.
What are sensory sensitivities in individuals with ASD?
Sensory sensitivities refer to challenges in processing sensory stimuli, leading to heightened or diminished responses to sounds, lights, and textures, which can affect focus and engagement in educational activities.
What emotional challenges do families of children with autism face?
Approximately 50% of mothers of children with autism show signs of depression, compared to 6% to 13.6% for mothers of children without autism.
What initiatives are in place to improve the management of autism spectrum disorders?
The World Health Organization emphasizes collaborative efforts to enhance the management of ASD, aligning with their Comprehensive Mental Health Action Plan 2013–2030.
How can writing abilities benefit autistic individuals?
Writing helps autistic individuals express thoughts and feelings, enhance academic performance, and build confidence, serving as a vital means for communication and self-expression.
What challenges do autistic students face in composition?
Key challenges include fine motor difficulties, organizational issues, and heightened anxiety and frustration associated with writing tasks.
How can educators support autistic children in overcoming composition challenges?
By implementing tailored strategies and accommodations, educators can empower autistic children to navigate their writing challenges, fostering a more inclusive and supportive learning environment.




