Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can be daunting for any parent. Understanding the early signs and symptoms is essential for ensuring timely support and intervention. From limited eye contact to delayed speech development, recognizing these indicators can be the first step toward securing the resources needed for a child’s growth and well-being.
With statistics revealing significant disparities in diagnosis based on socioeconomic factors, it becomes increasingly important for parents to be informed and proactive. This article delves into the key signs of autism, developmental milestones to watch for, and the essential screening tools available, empowering parents to take charge of their child's developmental journey and advocate for the support they deserve.
Understanding Autism: An Overview of Early Signs
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental disorder that impacts communication, behavior, and social interaction. Timely identification of the condition's indicators is essential for guaranteeing young individuals obtain the assistance required. Common indicators that may signal the presence of autism include:
- Limited Eye Contact: Many children on the spectrum may avoid making eye contact, which can be an early red flag.
- Delayed Speech Development: Observing how to know if your child has autism can be crucial if there is a noticeable delay in speech or a limited vocabulary compared to peers, as these may indicate potential concerns.
- Repetitive behaviors, such as engaging in movements like hand-flapping or rocking, are important indicators to consider when learning how to know if your child has autism.
- A lack of interest in social interactions, including minimal interest in playing with others or participating in shared activities, is one way to know how to know if your child has autism.
Identifying these early signs is crucial, as studies show that the prevalence of ASD is roughly 33.4 per 1,000 youth aged 8 years. Furthermore, the National Survey of Children’s Health highlights a concerning disparity in diagnosis, noting that young individuals from lower-income households are diagnosed at an average age of 4.7 years, compared to 5.2 years for those from higher-income backgrounds. This highlights the urgent need for fair and accessible screening, services, and supports for all youth.
Judith Ursitti, co-founder of the Profound Autism Alliance, emphasizes that acknowledging and researching profound autism will foster inclusivity and better access to essential resources.
Additionally, a recent case study titled "Emerging Racial and Ethnic Differences in ASD Identification" points to new patterns in how ASD is identified among 8-year-olds, suggesting that targeted strategies are necessary to address the disparities in diagnosis. By remaining alert and knowledgeable about these indicators, parents can understand how to know if your child has autism and take proactive measures to seek support and resources for their offspring, paving the way for a brighter future.
Developmental Milestones: Recognizing Signs of Autism by Age
Monitoring your offspring's developmental milestones is vital for early detection of potential concerns and understanding how to know if your child has autism. Here are some significant age-specific signs to keep in mind:
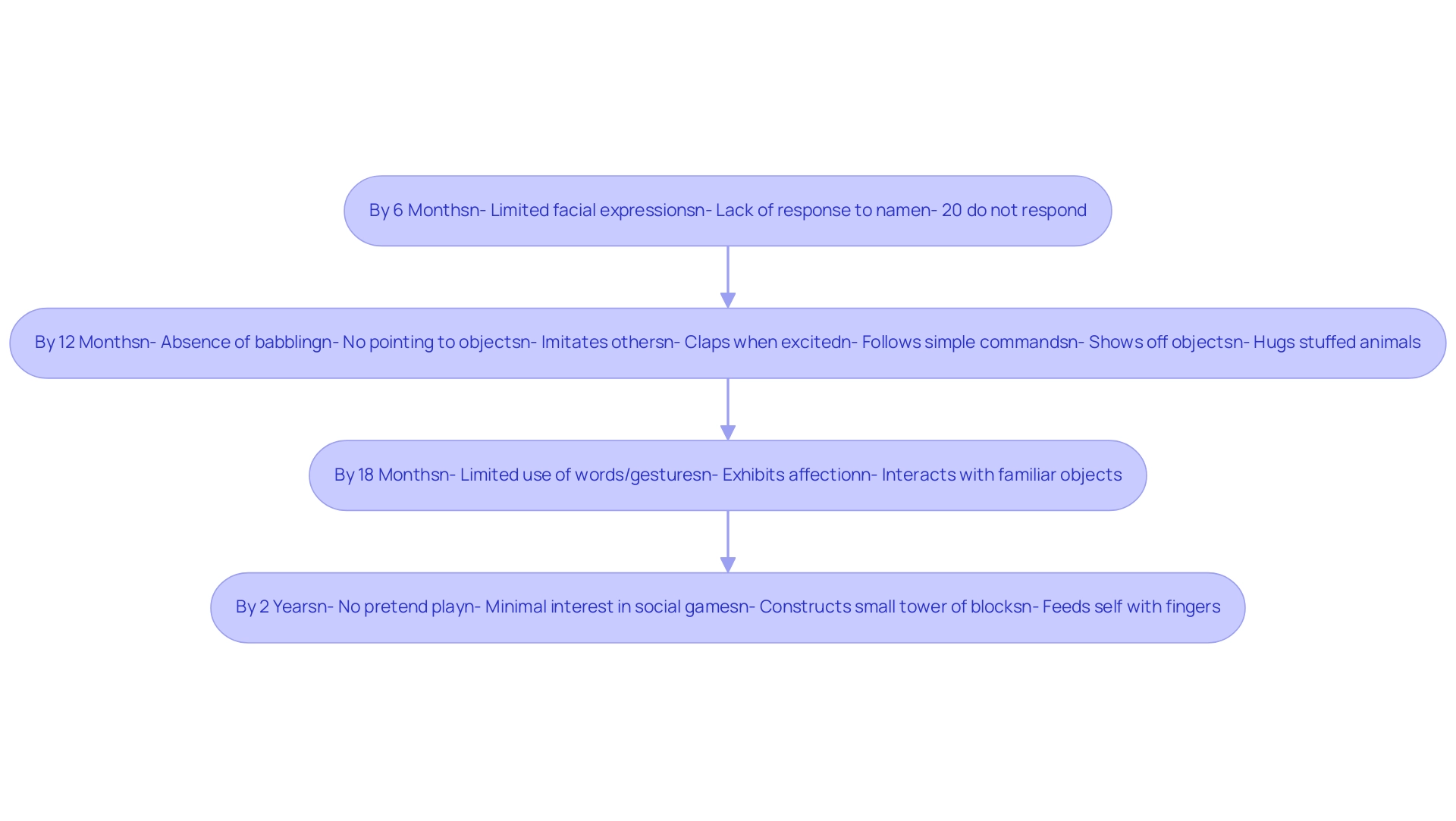
- By 6 Months: Limited facial expressions or a noticeable lack of response when their name is called. Research indicates that approximately 20% of youngsters do not respond to their name by this age, signaling a potential area of concern.
- By 12 Months: The absence of babbling or pointing to objects that catch their interest can be an indicator. At this stage, young ones typically begin to imitate others, clap when excited, and follow simple one-step commands. Additionally, milestones for kids aged 12 to 15 months include showing off objects they enjoy and hugging stuffed animals or toys.
- By 18 Months: A limited use of words or gestures for communication is noteworthy. Young ones should begin to exhibit affection through hugs and kisses, and they frequently interact with familiar objects when identified.
- By 2 Years: If your little one is not participating in pretend play or displays minimal interest in social games, it may be time for further evaluation. At this age, youngsters should be able to construct a small tower of blocks and start to feed themselves with their fingers.
It's important to note that early intervention can significantly impact development and well-being, with the average cost of therapeutic behavioral services being approximately $175.44. Moreover, the average age of diagnosis for youths in lower-income households is 4.7 years, compared to 5.2 years in higher-income households, underscoring the disparities in diagnosis based on socioeconomic status. If you notice any of these signs, consulting with a healthcare professional can help you understand how to know if your child has autism and provide valuable insights for further evaluation.
Early intervention is key, and being proactive can significantly improve outcomes.
Screening Tools and Professional Assessments for Autism
Numerous dependable screening instruments and evaluations are crucial for assessing developmental disorders in infants, each fulfilling a distinct role:
- M-CHAT (Modified Checklist for Toddlers): This widely acknowledged screening tool assists in recognizing children at risk for developmental issues, making it a vital initial step in prompt detection. Its effectiveness has been supported by studies, including a systematic review and meta-analysis that followed the PRISMA reporting guideline, indicating substantial reliability in identifying potential developmental concerns. As Dr. Diana L. Robins points out, the M-CHAT has been crucial in early identification efforts, supported by various grants and research initiatives.
- CARS (Childhood Autism Rating Scale): This professional assessment measures the severity of developmental disorder symptoms, providing valuable insights for tailored interventions. Recent findings from a study by Zhang et al. (2022) demonstrate that CARS boasts a sensitivity of 0.688 and a specificity of 0.995, highlighting its robustness in distinguishing autism severity and reinforcing its role in effective screening.
- Consulting with a Pediatrician: Engaging with your pediatrician is vital. They can help address your concerns, guide you through the screening process, and refer you to specialists who can offer further evaluation and support.
Utilizing these tools and seeking professional assessments is a vital step in understanding the unique needs of your young one. As emphasized by experts in the field, early identification and intervention pave the way for better outcomes, ensuring that children receive the support necessary for their development.
Conclusion
Recognizing the early signs of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is paramount for parents striving to secure the best possible future for their children. By staying vigilant and informed about indicators such as:
- Limited eye contact
- Delayed speech
- Lack of interest in social interactions
Parents can take proactive steps towards intervention. Understanding developmental milestones and the specific signs to watch for at various ages further empowers parents to advocate for timely evaluations and support.
The disparities in diagnosis, particularly influenced by socioeconomic factors, highlight the urgent need for equitable access to screening and resources. Utilizing reliable screening tools such as the M-CHAT and engaging with pediatricians can significantly aid in this process. These steps are not merely recommendations; they are essential actions that can lead to meaningful improvements in a child's life.
Ultimately, the journey towards understanding and supporting a child with autism begins with awareness and action. By embracing these insights and advocating for their children's needs, parents can pave the way for a brighter, more inclusive future where every child has the opportunity to thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental disorder that affects communication, behavior, and social interaction.
Why is timely identification of ASD important?
Timely identification of ASD indicators is essential to ensure that young individuals receive the necessary assistance and support.
What are some common indicators that may signal the presence of autism?
Common indicators include limited eye contact, delayed speech development, repetitive behaviors (such as hand-flapping or rocking), and a lack of interest in social interactions.
How can limited eye contact be an early sign of autism?
Many children on the spectrum may avoid making eye contact, which can be an early red flag for autism.
What does delayed speech development indicate in relation to autism?
A noticeable delay in speech or a limited vocabulary compared to peers may indicate potential concerns related to autism.
What types of repetitive behaviors should parents look for?
Parents should look for behaviors such as hand-flapping or rocking, which are important indicators of autism.
How does a lack of interest in social interactions manifest in children with autism?
Children may show minimal interest in playing with others or participating in shared activities, which can signal autism.
What is the prevalence of ASD among youth?
Studies show that the prevalence of ASD is roughly 33.4 per 1,000 youth aged 8 years.
Is there a disparity in the age of diagnosis for ASD based on income?
Yes, young individuals from lower-income households are diagnosed at an average age of 4.7 years, compared to 5.2 years for those from higher-income backgrounds.
What is the significance of acknowledging profound autism?
Acknowledging and researching profound autism can foster inclusivity and improve access to essential resources.
What does the case study 'Emerging Racial and Ethnic Differences in ASD Identification' highlight?
The case study points to new patterns in how ASD is identified among 8-year-olds and suggests that targeted strategies are necessary to address disparities in diagnosis.
How can parents take proactive measures regarding autism?
By remaining alert and knowledgeable about the indicators of autism, parents can seek support and resources for their children, paving the way for a brighter future.




