Overview
As parents, observing your child's behavior for common signs of autism can be a heartfelt journey. If you notice anything concerning, it’s essential to consult your pediatrician. They can help you discuss your observations and request a referral for a professional assessment. This article provides a structured approach to navigating this process. It begins with initial screenings, followed by comprehensive evaluations using standardized tools. Understanding the diagnosis report is crucial, as it emphasizes the importance of early detection and intervention. Remember, you are not alone in this journey—support is available, and taking these steps can make a significant difference for your child.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of autism screening can feel overwhelming for parents on their child's developmental journey. With autism spectrum disorder affecting 1 in 31 children in the U.S., recognizing the signs early is not just important—it's essential for timely intervention and support. This article serves as a compassionate guide, outlining the steps parents can take to ensure their child is screened for autism.
From identifying symptoms to understanding the assessment process, we aim to provide clarity and support. What challenges might you face in securing the appropriate evaluation for your child? How can you effectively advocate for their needs? Together, we can explore these questions and empower you to take action.
Identify Signs and Symptoms of Autism
To begin, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the common signs of autism, which can include:
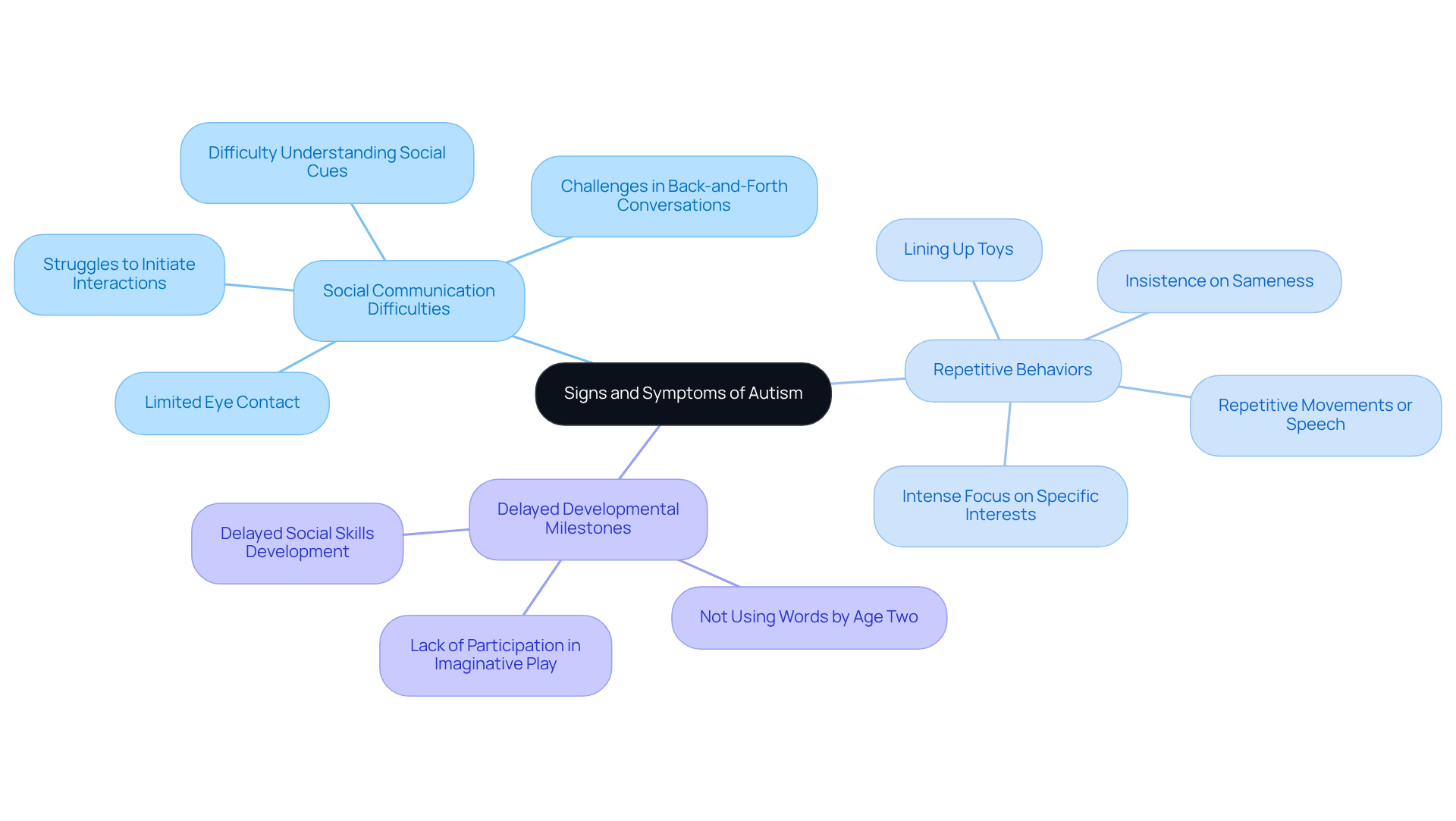
- Social Communication Difficulties: These may manifest as limited eye contact, difficulty understanding social cues, and challenges in engaging in back-and-forth conversations. For instance, a young person might not respond when their name is called or may struggle to initiate interactions with peers, which can hinder their interpersonal development.
- Repetitive Behaviors: Children may engage in repetitive movements or speech, show insistence on sameness, and exhibit intense focus on specific interests. For example, a young person might repeatedly line up toys or fixate on a particular topic, such as trains or dinosaurs.
- Delayed Developmental Milestones: Some children may not meet typical milestones in speech, social skills, or play by the expected ages. Parents might notice that their child isn’t using words by age two or isn’t participating in imaginative play with others.
As a parent, observing your child's behavior in various settings, such as home and social environments, can provide a comprehensive view of their interactions and behaviors. Documenting specific instances can be invaluable when discussing how to get screened for autism with healthcare providers. Pediatricians emphasize that early detection is crucial, and knowing how to get screened for autism can lead to reliable diagnosis by age two, yet the average age for diagnosis in the U.S. is currently five years. Notably, 1 in 31 children in the U.S. is diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), highlighting the prevalence of this condition and the urgent need for early support. Furthermore, boys are 3.4 times more likely than girls to receive a diagnosis related to developmental disorders, an important consideration for parents. Integrating insights from pediatricians can enhance understanding and provide real-world perspectives on recognizing the signs of autism.
Request a Professional Autism Assessment
If you're considering how to get screened for autism for your child, it’s important to approach the assessment process with care and understanding. Here are some steps to guide you:
-
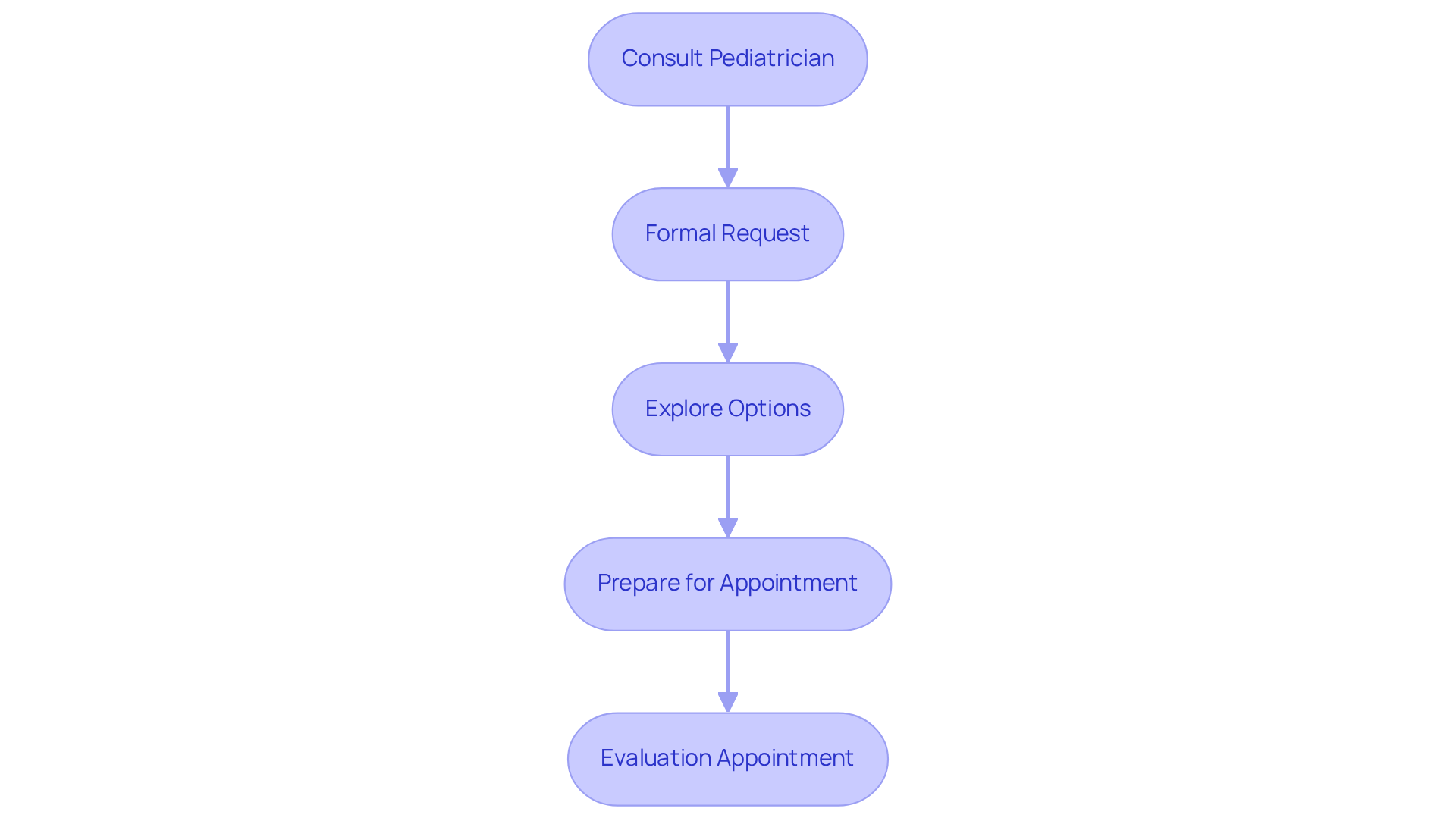
Start by consulting your pediatrician on how to get screened for autism by scheduling an appointment to openly discuss your concerns. Bring along your observations and any documentation of behaviors you've noticed. It’s worth noting that many parents, approximately 30%, seek second opinions for developmental evaluations, highlighting the importance of clear and comprehensive communication.
-
Formal Request: Should your pediatrician agree that an evaluation is necessary, they will typically refer you to a specialist. If they do not see the need, you can still request a referral in writing—be sure to keep a copy for your records. This formal approach can help ensure that your concerns regarding how to get screened for autism are taken seriously and addressed appropriately.
-
Explore Options: Take the time to research nearby experts or facilities that specialize in evaluations for developmental disorders. With the rising prevalence of autism—growing from 1 in 36 in 2020 to 1 in 31 in 2022—understanding how to get screened for autism and finding a qualified professional is crucial. In 2022, the diagnosis rate among children aged 5 to 8 years was 30.3 per 1,000, emphasizing the importance of early evaluation. If you feel your concerns are not being adequately addressed, consider seeking a second opinion.
-
Prepare for the Appointment: Gather any relevant medical history, developmental milestones, and specific behaviors that have raised your concerns to discuss during the evaluation. Experts recommend being as detailed as possible, as this information can significantly influence the evaluation process. Remember, the typical age for diagnosing developmental disorders in the U.S. is around 5 years, so understanding how to get screened for autism and prompt evaluations are essential for successful intervention.
Understand the Assessment Process and Tools Used
Navigating how to get screened for autism can feel overwhelming, but understanding the steps involved can provide clarity and reassurance. Here’s how the process typically unfolds:
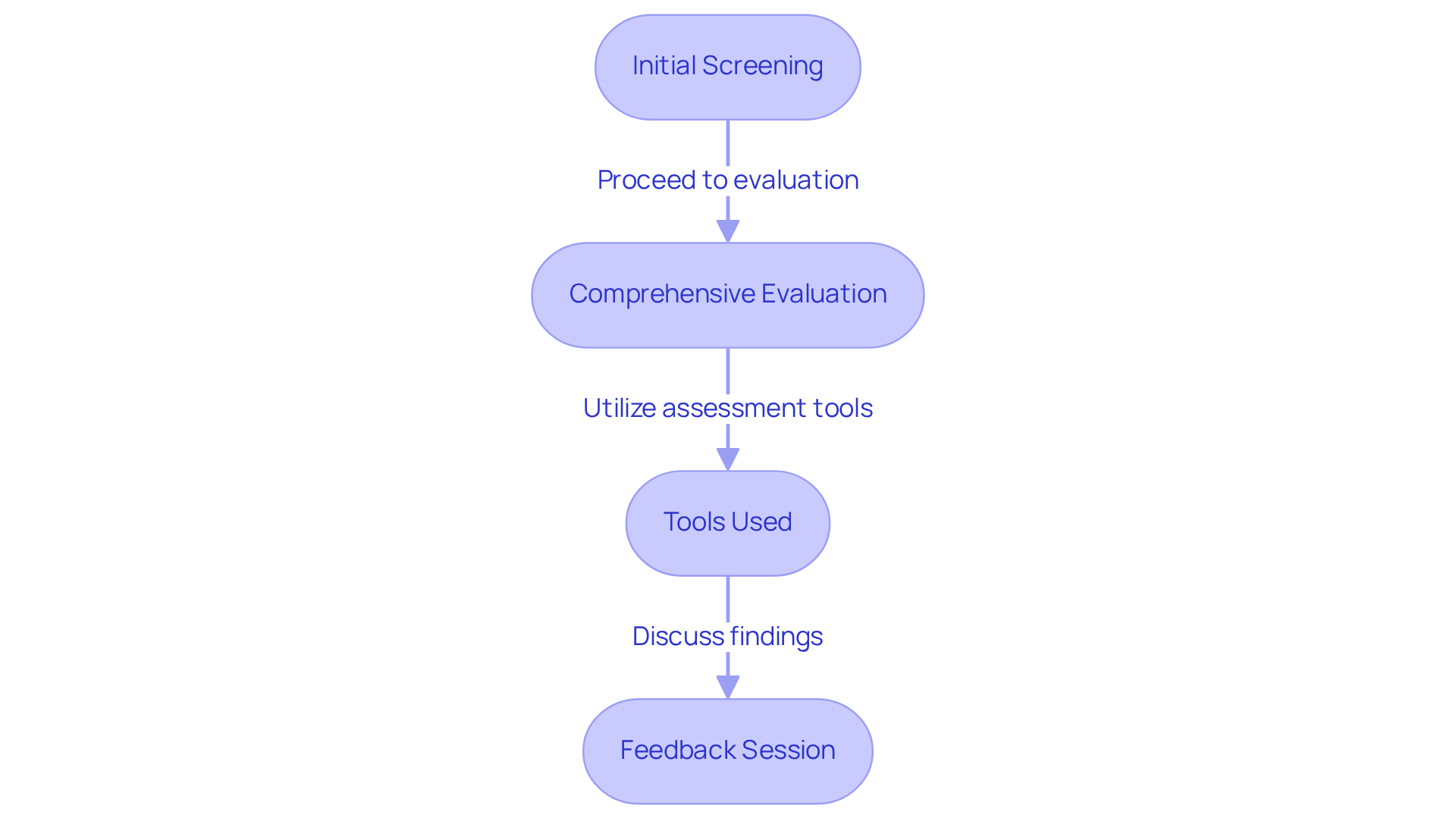
- Initial Screening: The journey often begins with initial screening, where standardized questionnaires like the M-CHAT-R come into play. These tools, completed by parents, offer valuable insights into a child's behavior. With a sensitivity of 91.1% and a specificity of 95.5%, the M-CHAT-R is a reliable first step. When paired with the follow-up (M-CHAT-R/F), its specificity rises to an impressive 99.3%, while sensitivity remains at 85.4%.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: After the initial screening, a caring multidisciplinary team steps in to conduct a comprehensive evaluation. This stage involves interviews, observations, and standardized tests aimed at assessing communication, interpersonal skills, and behavior. Often, the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) is utilized, providing structured interactions that help gauge the individual’s social and communicative abilities.
- Tools Used: Alongside the M-CHAT-R and ADOS, the Autism Diagnostic Interview (ADI) plays a crucial role in this process. Together, these tools equip professionals with a detailed view of the child's developmental history and current functioning, ensuring a holistic understanding of their needs. Notably, the pooled sensitivity of M-CHAT-R/F is 0.83, with a pooled specificity of 0.94, underscoring the effectiveness of these screening tools.
- Feedback Session: Once the evaluation is complete, a feedback session is arranged to discuss the findings and outline the next steps. Parents are encouraged to prepare questions, ensuring they fully grasp the implications of the evaluation results and the recommended interventions. The American Academy of Pediatrics emphasizes how to get screened for autism universally at 18 and 24 months, highlighting the critical importance of early identification.
By engaging in this process, you are taking an important step towards understanding and supporting your child's needs. Remember, you are not alone on this journey—reach out for support and resources as needed.
Receive and Interpret the Diagnosis Report
Upon receiving the diagnosis report, it is essential to take the following steps:
-
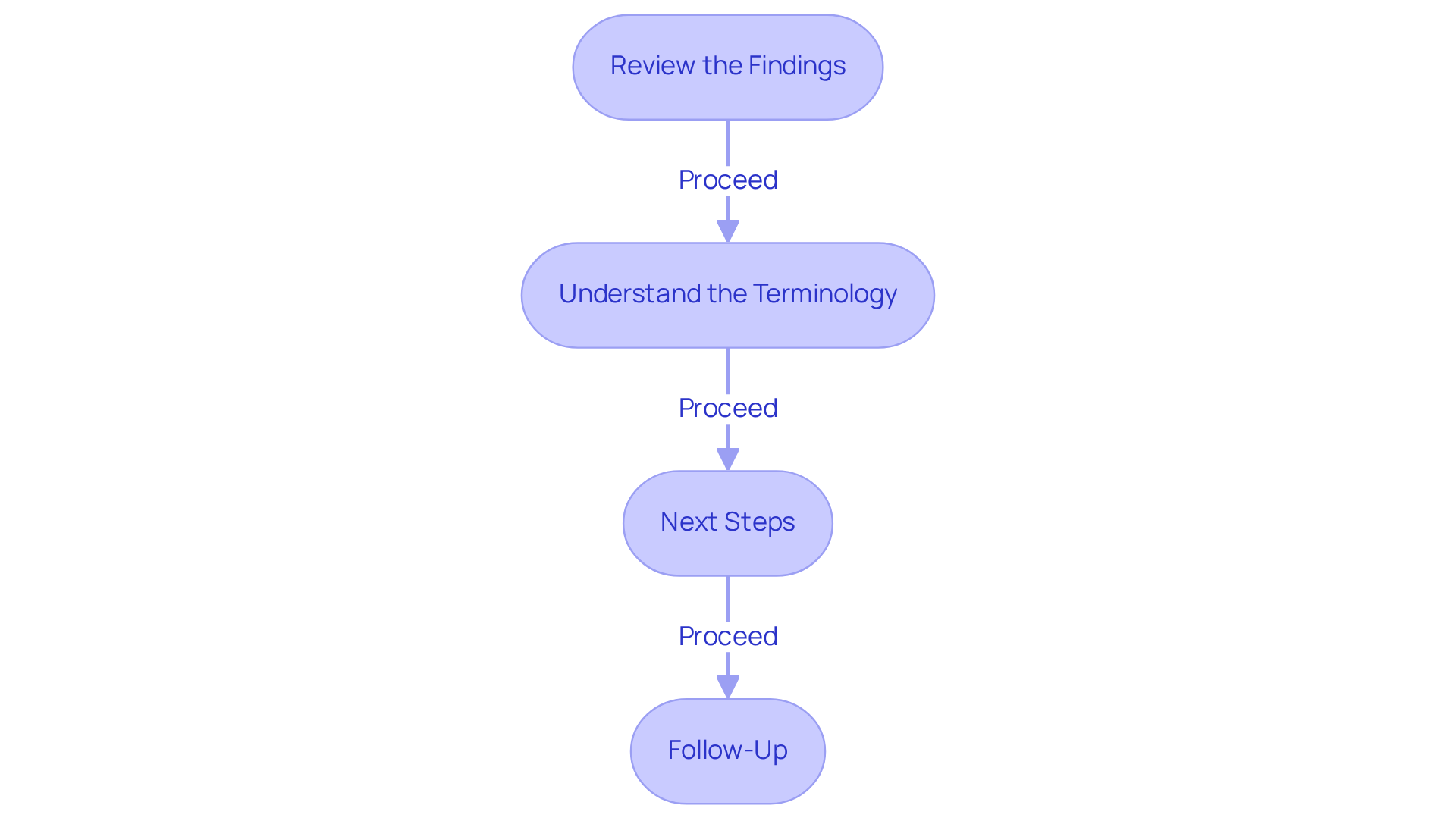
Review the Findings: The report will provide a comprehensive overview of the assessment results, highlighting both strengths and challenges observed during the evaluation. This information is crucial for understanding your child's unique profile. For context, the average age of autism diagnosis in the U.S. is 5 years, and roughly 1 in 36 children are diagnosed with autism, underscoring the importance of prompt comprehension.
-
Understand the Terminology: Familiarize yourself with any technical terms used in the report. Common terms may include 'autism spectrum disorder (ASD)', 'intervention', and 'behavioral therapy'. If any points are unclear, do not hesitate to reach out to the evaluating professional for clarification. Understanding the language of the report is vital for effective communication and planning.
-
Next Steps: The report should include specific recommendations for interventions, therapies, or support services customized to your child's needs. Engage in a discussion with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that addresses these recommendations and aligns with your family's goals. Experts like Dr. Kuhlthau emphasize the importance of a tailored approach to intervention.
-
Follow-Up: Schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your child's progress and make necessary adjustments to interventions. Additionally, consider joining support groups or utilizing available resources to gain further guidance and foster a sense of community. Real-life examples show that connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide invaluable support as you navigate this journey.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of autism and understanding how to navigate the screening process is crucial for parents seeking support for their children. By identifying symptoms early and seeking professional assessments, parents can pave the way for timely interventions that significantly enhance their child's development and quality of life. While the journey may seem daunting, taking informed steps can empower parents to advocate effectively for their child's needs.
Throughout this article, we shared key insights, including:
- The importance of observing behavioral signs
- Consulting with healthcare professionals
- Understanding the assessment tools used in diagnosing autism
Early detection is vital, with the average diagnosis age being five years, despite the ability to identify signs as early as two. We guided parents through the process of requesting assessments, preparing for evaluations, and interpreting diagnosis reports, all while highlighting the significance of communication and support.
Ultimately, we encourage parents to take proactive steps in understanding autism screening and assessment processes. By staying informed and engaged, they can foster a supportive environment that promotes their child's growth and development. Connecting with professionals, utilizing available resources, and seeking community support can make a meaningful difference in navigating this journey. The path may be challenging, but the commitment to understanding and addressing autism can lead to positive outcomes for children and families alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common signs of autism?
Common signs of autism include social communication difficulties, repetitive behaviors, and delayed developmental milestones.
How do social communication difficulties manifest in children with autism?
Social communication difficulties may manifest as limited eye contact, challenges in understanding social cues, and difficulties engaging in back-and-forth conversations. For example, a child might not respond when their name is called or struggle to initiate interactions with peers.
What are examples of repetitive behaviors in children with autism?
Examples of repetitive behaviors include engaging in repetitive movements or speech, showing insistence on sameness, and exhibiting intense focus on specific interests, such as lining up toys or fixating on topics like trains or dinosaurs.
What does it mean if a child has delayed developmental milestones?
Delayed developmental milestones mean that a child may not meet typical expectations in areas like speech, social skills, or play by the expected ages. For example, a child might not use words by age two or may not participate in imaginative play with others.
Why is early detection of autism important?
Early detection is crucial because it can lead to a reliable diagnosis by age two, while the average age for diagnosis in the U.S. is currently five years. Early support can significantly benefit children with autism.
What is the prevalence of autism in the U.S.?
In the U.S., 1 in 31 children is diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), highlighting the condition's prevalence and the need for early support.
Are there differences in autism diagnosis rates between boys and girls?
Yes, boys are 3.4 times more likely than girls to receive a diagnosis related to developmental disorders, which is an important consideration for parents.
How can parents prepare for discussions about autism screening with healthcare providers?
Parents can observe their child's behavior in various settings and document specific instances, which can be invaluable when discussing how to get screened for autism with healthcare providers.




