Overview
Understanding autism in adults requires a compassionate approach to their unique challenges, including social isolation, communication difficulties, and sensory sensitivities. By implementing supportive strategies—such as clear communication and structured routines—we can make a significant difference. Recognizing these traits and challenges is essential for providing effective support. This understanding can greatly enhance the quality of life and independence for autistic individuals.
As we delve deeper into this topic, consider how these challenges manifest in everyday life. For instance, imagine a social gathering where an autistic adult feels overwhelmed by noise and unfamiliar faces. Such scenarios highlight the importance of tailored strategies that address these specific needs.
We encourage you to explore resources that can offer guidance and support. Sharing experiences and insights can foster a community of understanding and compassion. Together, we can create environments that nurture and empower autistic individuals, helping them thrive in their daily lives.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in adults requires a nuanced understanding of its unique characteristics and the challenges faced by those on the spectrum. Social interaction difficulties and sensory sensitivities are just a few of the varied experiences that autistic adults encounter, significantly influencing their daily lives and mental well-being.
As our society becomes increasingly aware of neurodiversity, fostering empathy and providing effective support tailored to individual needs becomes essential. This article explores the traits of autism in adults, highlights common challenges, and offers practical strategies for enhancing their daily experiences.
Together, we can advocate for a more inclusive environment that recognizes the strengths and potential of autistic individuals.
Understand Autism in Adults
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that profoundly influences how individuals communicate, interact, and perceive the world around them. For many, autism manifests in diverse ways, including challenges in social settings, communication hurdles, and heightened sensory sensitivities. Recognizing these characteristics is vital for fostering empathy and providing effective support. Consider the key traits of autism in adults:
- Social Interaction Difficulties: Many autistic adults find it challenging to understand social cues, which can complicate the process of forming and maintaining relationships.
- Communication Styles: Autistic individuals often prefer direct and literal communication, frequently finding abstract language or sarcasm confusing.
- Sensory Sensitivities: Many individuals with autism experience heightened sensitivity to sensory inputs like noise, light, or touch, leading to discomfort in certain environments.
- Repetitive Behaviors: Engaging in repetitive actions or routines can offer comfort and predictability for those on the autism spectrum.
By acknowledging these traits, caregivers and professionals can gain deeper insights into supporting adults with autism, allowing them to tailor their assistance effectively.
Identify Challenges Faced by Autistic Adults
Autistic individuals encounter a variety of challenges that significantly affect their daily lives and overall well-being. Understanding these issues is crucial for fostering a supportive community. Key challenges include:
- Social Isolation: Many autistic individuals face difficulties with social interactions, often leading to feelings of loneliness and isolation. Initiating or maintaining conversations can be a significant hurdle, making it challenging to build meaningful friendships. Recent studies reveal that over 60% of individuals on the spectrum report experiencing social isolation, and more than 60% of learners express daily stress, highlighting the urgent need for supportive community structures.
- Employment Barriers: In the workplace, autistic adults frequently encounter substantial obstacles such as discrimination, inadequate accommodations, and difficulties in socializing with colleagues. Consequently, their unemployment rates are significantly higher than those of neurotypical peers. Real-life examples show that many individuals on the spectrum face misconceptions about their abilities, which can hinder career advancement and job stability. For instance, case studies indicate that while people with autism often excel in specific tasks, they may struggle with the social interactions crucial for workplace success.
- Mental Health Issues: Anxiety, depression, and other psychological conditions are prevalent among individuals on the spectrum, often exacerbated by social challenges and sensory overload. The interplay of these factors can create a cycle of distress, making it essential to proactively address mental health needs.
- Navigating Daily Life: Routine activities, such as grocery shopping or attending appointments, can become overwhelming for those on the spectrum due to sensory sensitivities and executive functioning challenges. These difficulties can lead to increased stress and anxiety, complicating their ability to engage in everyday tasks.
Recognizing these challenges is vital for providing effective support and fostering an inclusive environment for individuals on the spectrum. Embracing the beauty of neurodiversity encourages a shift in perspective, focusing on the unique abilities and potential within the autism spectrum. As Mary Barbera wisely states, "Embrace the amazing gift of autism," and as Stuart Duncan emphasizes, autism is not a tragedy but a different way of being. This perspective promotes an emphasis on the strengths and potential that individuals on the spectrum possess. Let us work together to create a more inclusive world, where every person is valued for their unique contributions.
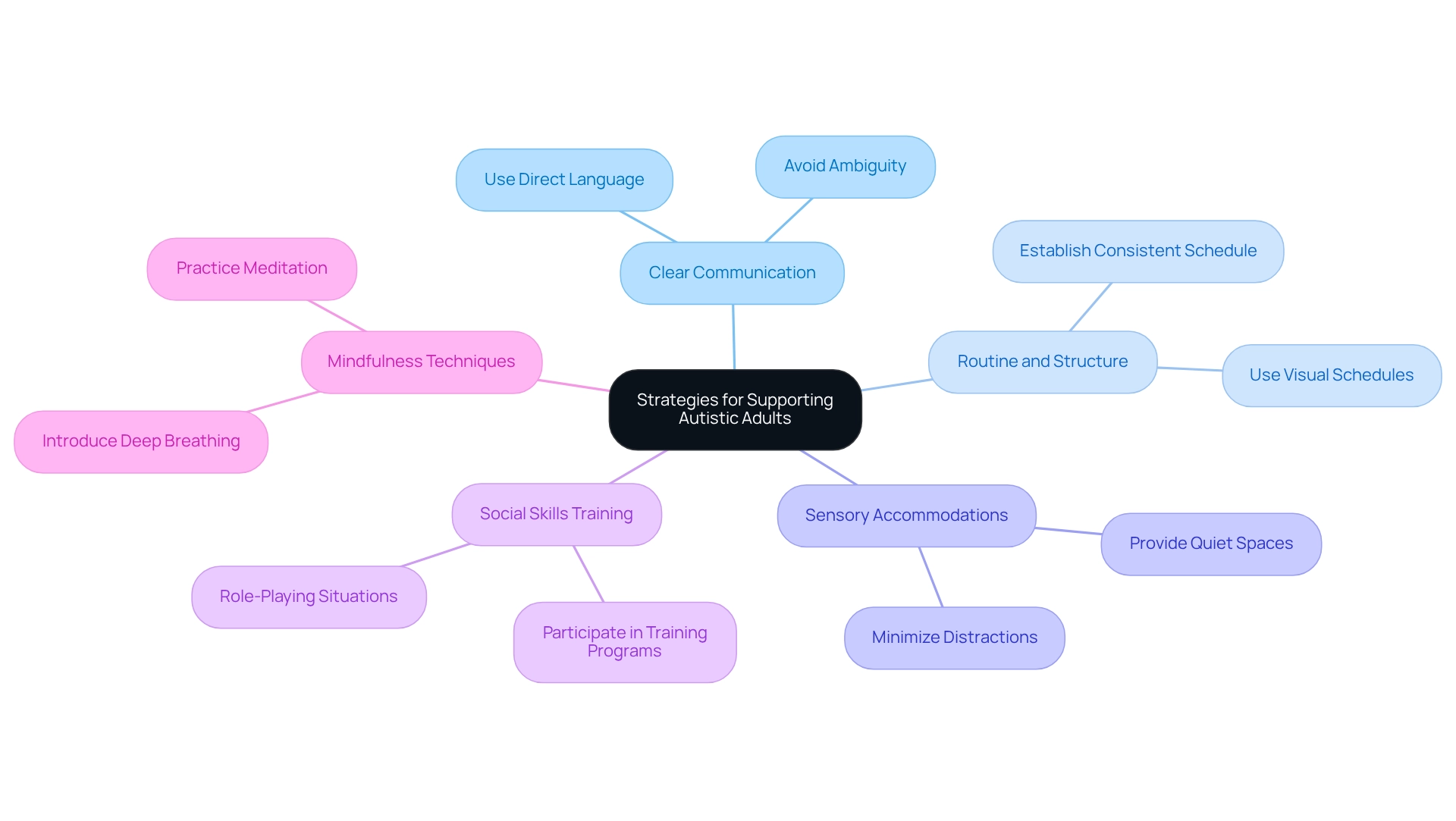
Implement Strategies for Daily Living and Interaction
Supporting autistic adults in their daily lives and interactions is essential. Consider these compassionate strategies:
- Clear Communication: Use direct and straightforward language. Avoid idioms, sarcasm, or ambiguous phrases that may confuse the individual. This clarity fosters understanding and connection.
- Routine and Structure: Establishing a consistent daily schedule can help individuals on the spectrum feel more secure and reduce anxiety. Visual schedules or checklists serve as valuable tools in maintaining this structure.
- Sensory Accommodations: Create a sensory-friendly environment by minimizing distractions, such as loud noises or bright lights. Providing noise-canceling headphones or a quiet space can significantly help manage sensory overload.
- Social Skills Training: Encourage participation in social skills training programs that focus on building communication and interaction skills. Role-playing situations allows individuals on the spectrum to rehearse social exchanges in a supportive setting.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Introduce mindfulness practices, such as deep breathing or meditation, to assist in managing anxiety and enhancing emotional regulation.
By applying these thoughtful approaches, caregivers and specialists can greatly improve the experience of autism in adults, enhancing their daily lives and promoting greater independence and social involvement. Your support can make a profound difference.
Access Support Systems and Resources
Accessing the right assistance systems and resources is crucial for understanding how to support adults with autism and enhancing their quality of life. It’s essential to explore key avenues that can make a difference:
- Local Autism Organizations: Many communities boast organizations dedicated to supporting autistic individuals and their families. These groups often provide valuable resources, workshops, and networks that foster community engagement and personal growth.
- Online Support Groups: Virtual communities serve as safe spaces for individuals on the spectrum to connect, share experiences, and seek guidance. Organizations like Autism Speaks and the Autistic Self Advocacy Network offer listings of online groups, creating opportunities for peer connections and collective learning.
- Therapeutic Services: Access to mental health professionals who specialize in autism is vital. These therapists can offer tailored support for challenges such as anxiety, depression, and social skills development, specifically addressing the unique hurdles faced by individuals on the spectrum. It’s worth noting that the average cost of therapeutic behavioral services in the U.S. is $175.44, a significant consideration for families seeking these essential services.
- Employment Services: Organizations that focus on employment support can assist individuals on the spectrum with job training, resume building, and interview preparation. Local programs often provide resources that enhance employability and facilitate workplace integration.
- Educational Resources: Numerous online platforms offer courses and materials aimed at enhancing life skills, communication, and social interactions for individuals on the spectrum. These resources empower individuals to navigate daily challenges more effectively.
Utilizing these resources enables individuals on the spectrum and their families to understand how to support adults with autism, fostering a robust support network that encourages growth, independence, and overall well-being. Current initiatives by organizations such as the CDC aim to improve understanding of how to assist adults with autism, ensuring that appropriate services are accessible as they transition into adulthood. As Larkin O’Leary, founder and executive director of Common Ground Society, poignantly states, "That is why we learn from individuals on the spectrum about what those needs might be." With 8% of autistic students not completing high school, the significance of these support systems is profound, as they play a critical role in improving outcomes for autistic individuals.
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder in adults is essential for fostering empathy and creating effective support systems. This article highlights the unique characteristics of autism, such as social interaction difficulties, distinct communication styles, sensory sensitivities, and repetitive behaviors. By recognizing these traits, caregivers and professionals can tailor their support to meet the specific needs of autistic individuals, ultimately enhancing their quality of life.
The challenges faced by autistic adults, including social isolation, employment barriers, mental health issues, and the complexities of daily life, underscore the necessity of advocacy and community support. Addressing these challenges requires a shift in perspective—one that embraces neurodiversity and recognizes the strengths and potential of autistic individuals rather than merely focusing on their difficulties.
Implementing practical strategies for daily living, such as clear communication, structured routines, and sensory accommodations, can significantly enhance the experiences of autistic adults. Additionally, accessing support systems and resources, including local organizations, online communities, and therapeutic services, is vital for promoting independence and well-being.
In conclusion, creating a more inclusive environment for autistic adults is a collective responsibility. By fostering understanding, providing tailored support, and advocating for their needs, society can empower autistic individuals to thrive and contribute their unique perspectives and talents. Embracing neurodiversity not only benefits autistic individuals but also enriches the community as a whole, paving the way for a more empathetic and understanding world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that significantly impacts how individuals communicate, interact, and perceive the world around them.
How does autism manifest in individuals?
Autism manifests in various ways, including challenges in social settings, communication hurdles, and heightened sensory sensitivities.
What are some key traits of autism in adults?
Key traits of autism in adults include social interaction difficulties, distinct communication styles, sensory sensitivities, and repetitive behaviors.
What challenges do autistic adults face in social interactions?
Many autistic adults struggle to understand social cues, which can complicate forming and maintaining relationships.
How do autistic individuals typically communicate?
Autistic individuals often prefer direct and literal communication, finding abstract language or sarcasm confusing.
What are sensory sensitivities in individuals with autism?
Many individuals with autism experience heightened sensitivity to sensory inputs such as noise, light, or touch, which can lead to discomfort in certain environments.
Why do some individuals with autism engage in repetitive behaviors?
Engaging in repetitive actions or routines can provide comfort and predictability for those on the autism spectrum.
How can understanding these traits benefit caregivers and professionals?
By recognizing these traits, caregivers and professionals can gain insights into how to support adults with autism effectively, allowing them to tailor their assistance to meet individual needs.




