Introduction
The curtain of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has been drawn back further as scientific scrutiny intensifies, particularly on the genetic stage. In the intricate ballet of neurodevelopment, ASD pirouettes with features such as challenges in social communication and repetitive behaviors.
Clustered amongst our DNA, specific genes stand out, casting longer shadows over the ASD landscape and signaling a hereditary pattern - a whisper of traits passed from one generation to the next. These genetic players take on vital roles, choreographing the synaptic connections and neural signals which form the brain's complex circuitry.
At Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, the dedication to deciphering autism's genetic enigma is embodied in the work of Professor Iossifov. With a tool called Genotypes and Phenotypes in Families (GPF) as his latest brainchild, Iossifov stands at the vanguard, envisioning a future where this tool illuminates dark corners of autism's genetic roots. Although originally focused on disparate fields, Iossifov's journey through biology began elsewhere, yet all paths have led him to the noble endeavor of enhancing life's quality for individuals with autism and their supportive families.
Genetic Factors in Autism Spectrum Disorder
The curtain of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has been drawn back further as scientific scrutiny intensifies, particularly on the genetic stage. In the intricate ballet of neurodevelopment, ASD pirouettes with features such as challenges in social communication and repetitive behaviors.
Clustered amongst our DNA, specific genes stand out, casting longer shadows over the ASD landscape and signaling a hereditary pattern - a whisper of traits passed from one generation to the next. These genetic players take on vital roles, choreographing the synaptic connections and neural signals which form the brain's complex circuitry.
At Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, the dedication to deciphering autism's genetic enigma is embodied in the work of Professor Iossifov. With a tool called Genotypes and Phenotypes in Families (GPF) as his latest brainchild, Iossifov stands at the vanguard, envisioning a future where this tool illuminates dark corners of autism's genetic roots. Although originally focused on disparate fields, Iossifov's journey through biology began elsewhere, yet all paths have led him to the noble endeavor of enhancing life's quality for individuals with autism and their supportive families.
Heritability and Genetic Variations
The involvement of genetic influences in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is profound, with heritability estimates reaching approximately 80%. This significant figure underscores the role that genetics play, but it's crucial to understand that autism's genetic landscape is intricate.
There are numerous genetic variants that may sway the risk of developing ASD, from rare mutations in particular genes to more widespread genetic variations. The complexity increases as these genetic factors do not act in isolation; they interact with one another and with non-genetic influences.
Scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL), like Professor Iossifov, are pioneering tools such as the Genotypes and Phenotypes in Families (GPF) to unravel the genetic web of autism. Through this rigorous scientific quest, the overarching aim remains steadfast: to enhance the lives of those with autism and provide solace to their loved ones. The GPF tool represents hope for unraveling autism's genetic underpinnings, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries that can inform interventions and supports tailored to individuals with ASD.
Environmental Factors and Interactions
While genetic factors play a significant role in autism, it is important to recognize that environmental factors can also contribute to the development of the disorder. Research suggests that there is a complex interplay between genetic and environmental factors in the etiology of autism. Certain environmental factors, such as prenatal exposures to toxins and pollutants, maternal infections during pregnancy, and complications during birth, have been linked to an increased risk of ASD.
Additionally, factors such as parental age, maternal health, and socioeconomic status may also influence the risk of autism. It is worth noting that the interaction between genetic and environmental factors is complex and not fully understood. Ongoing research is focused on identifying specific environmental risk factors and understanding how they interact with genetic vulnerabilities to influence the development of autism.
Epigenetic Influences and Modifiers
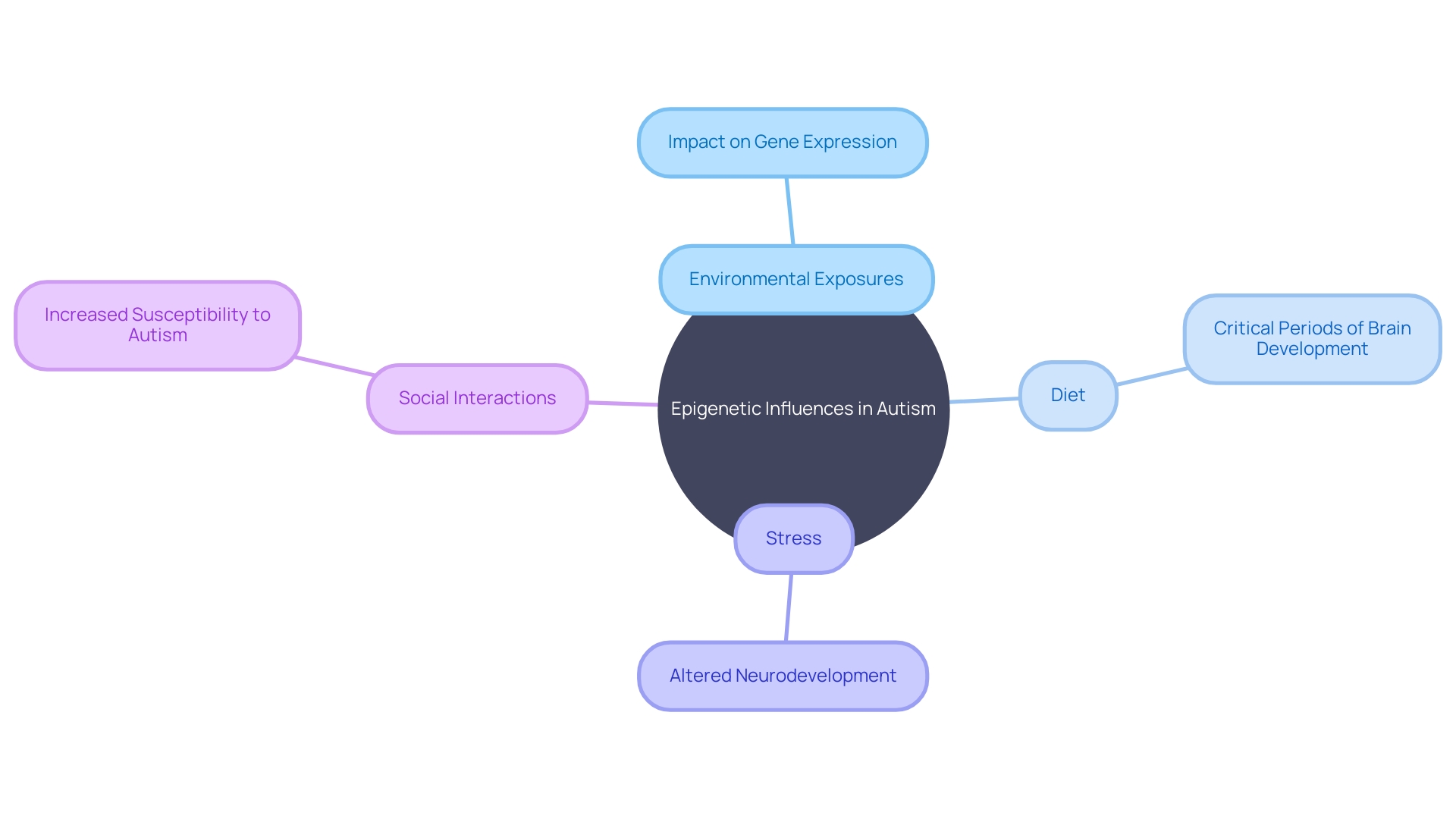
In recent years, there has been increasing interest in the role of epigenetic influences in autism. Epigenetics refers to changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations to the DNA sequence itself but can impact how genes are turned on or off. Epigenetic modifications can be influenced by a variety of factors, including environmental exposures, diet, stress, and social interactions.
Research suggests that epigenetic modifications may play a role in the development of autism by influencing gene expression in critical periods of brain development. These modifications can potentially modify the function of specific genes associated with ASD, leading to altered neurodevelopment and increased susceptibility to the disorder. Understanding the role of epigenetic influences and modifiers in autism could provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying the disorder and help identify new therapeutic targets.
Clinical Implications and Future Research Directions
The exploration of genetic factors in autism is an essential frontier that holds the promise of significantly enhancing our ability to diagnose, treat, and support those on the autism spectrum. Pioneering work in genetics opens doors to invaluable insights for affected families through genetic testing and counseling.
These crucial steps illuminate the potential hereditary aspects of autism and reveal genetic anomalies that could be tailored with specific treatments. Groundbreaking research is continually unfolding, which could lead to highly personalized care strategies.
A key to this progress is the identification of distinct genetic variations linked to ASD. By focusing on the intrinsic biological mechanisms of autism, targeted therapies that go beyond symptom management and address root causes become a real possibility.
As emphasized by Professor Iossifov, a scientist dedicated to the genetic study of autism at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL), the intent behind these scientific endeavors is to forge advancements that tangibly improve the day-to-day lives of those with autism and their loved ones. Harnessing tools like the Genotypes and Phenotypes in Families (GPF), researchers are on a quest to illuminate the disorder’s genetic underpinnings. The relationship between genetic factors and environmental influences in autism is intricate, suggesting that while genetic composition is influential, it also works symbiotically with environmental factors. The ultimate goal remains clear: to enhance the precision of autism diagnoses and the efficaciousness of interventions, while providing a stronghold of support for individuals with autism and their families.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study of genetic factors in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) has revealed crucial insights into the condition. Specific genes and genetic variations have been identified as key players in ASD, pointing to a hereditary pattern.
Researchers, like Professor Iossifov at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, are utilizing innovative tools like Genotypes and Phenotypes in Families (GPF) to better understand autism's genetic complexities. While genetics are influential, it's important to recognize the interplay between genetic and environmental factors in autism.
Prenatal exposures, maternal infections, and birth complications have been linked to a higher risk of ASD. Ongoing research aims to identify specific environmental risk factors and understand their interaction with genetic vulnerabilities.
Epigenetic influences, which involve changes in gene expression without altering DNA, are also being explored in autism research. Factors like environmental exposures, diet, stress, and social interactions can impact critical gene expression during brain development and potentially contribute to ASD.
Studying genetic factors in autism offers promising opportunities for improving diagnosis, treatment, and support for individuals on the autism spectrum. Identifying distinct genetic variations related to ASD enables personalized care strategies and targeted therapies addressing the root causes of the disorder. The dedication of researchers like Professor Iossifov underscores the importance of advancing our understanding of autism's genetic underpinnings. By unraveling this enigma, we can strive for more accurate diagnoses, effective interventions, and robust support systems for individuals with autism and their families. Understanding the complex relationship between genetic factors and environmental influences is key to a brighter future where individuals with autism can thrive. Through ongoing research and scientific endeavors, we can make tangible differences in the lives of those affected by autism, enhancing their well-being and providing the necessary support they deserve.




