Introduction
Understanding Asperger's and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Asperger's are both neurodevelopmental disorders that affect individuals throughout their lives. With an estimated one in 45 adults living with ASD, it's crucial to understand the hallmarks and challenges associated with these conditions.
From the role of dopamine and serotonin in development to the link between ASD and anxiety, this article provides valuable insights into ASD and offers strategies for supporting individuals with Asperger's and Autism. Additionally, it explores effective communication and social skill-building techniques and highlights the importance of navigating support services and resources in order to create a more inclusive future for individuals with ASD.
Understanding Asperger's and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Asperger's are both neurodevelopmental disorders. ASD is a broad category that includes many individuals with varying symptoms and characteristics, some of which align with Asperger's.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate that around one in 45 adults, or 5.4 million individuals, live with ASD, including those with high-functioning autism who often receive a diagnosis later in life. The DSM-5, an essential tool for clinicians, provides the criteria for an ASD diagnosis.
These criteria emphasize that the core features of ASD should be present in early childhood. However, sometimes, symptoms do not fully manifest until social demands exceed the individual's capacity to cope.
ASD commonly appears by age 3, but interventions can and should start earlier. Recent research highlights the role of dopamine and serotonin in development and their importance in the construction of neural circuits.
Disrupted dopaminergic signaling has been studied for its potential role in ASD. This research could lead to novel therapeutic targets that could revolutionize autism treatment.
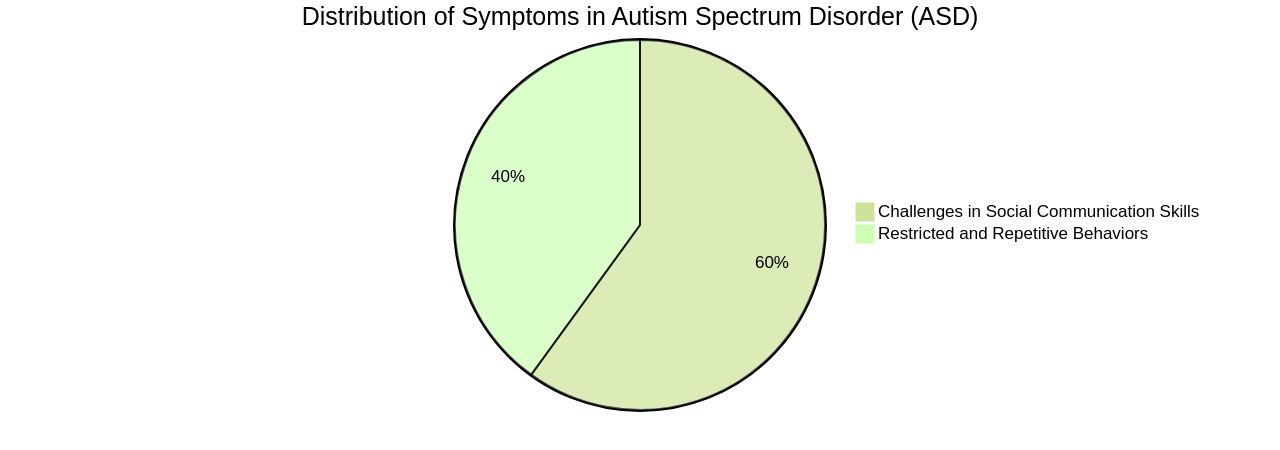
ASD affects individuals differently throughout their lives. It's crucial to understand that the hallmarks of autism, challenges with social communication skills and restricted and repetitive behaviors, are present in adults as well. Major life changes can often result in a shift in these symptoms. Furthermore, the high frequency of anxiety and other psychiatric disorders among individuals with ASD could contribute to their use of alcohol or illegal substances. The need for a strict routine and the tendency toward repetitive behaviors, common traits of autistic individuals, can sometimes lead to behavioral addiction. Understanding ASD is essential, not only for those diagnosed but also for their families, friends, and broader social circles. With awareness and understanding, we can better support individuals with ASD and contribute to a more inclusive future.
Recognizing the Link Between Asperger's and Autism
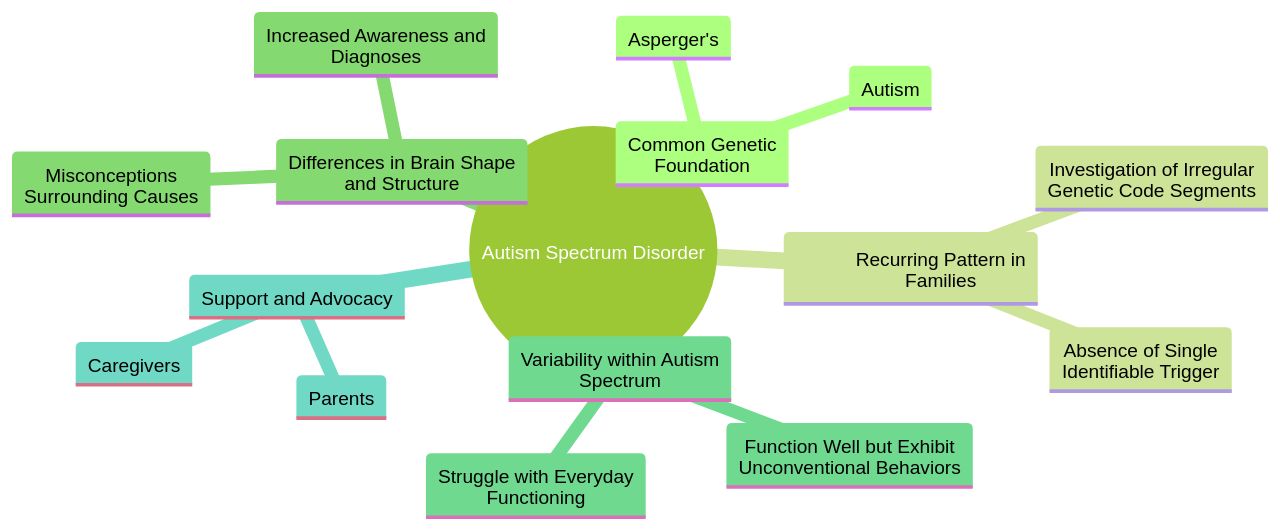
Autism and Asperger's share a common genetic foundation, with Asperger's often interpreted as a less severe manifestation of Autism. This genetic foundation is underscored by the recurring pattern of Autism and related disabilities in many families.
Researchers are actively investigating irregular genetic code segments that individuals with Autism might have inherited. However, there is no single identifiable 'trigger' for Autism, suggesting that a host of unstable genes might unexpectedly affect brain development under certain conditions, leading to Autism.
Differences in brain shape and structure between individuals with Autism and those with neurotypical development have been observed, further supporting the genetic and hereditary theories. Moreover, the rise in Autism diagnoses is linked to increased awareness, especially among adults with high-functioning Autism.
Many of these individuals, often with average or above-average intelligence, were born before high-functioning Autism was recognized in diagnostic literature, and have learned to mask or hide their autistic traits. Contrary to common misconceptions, Autism is not caused by vaccines, parenting styles, or nutrition. It's also important to remember that while Autism is a spectrum disorder, the experiences of individuals within this spectrum can vary significantly. For instance, while some individuals might struggle with everyday functioning, others might be able to function well but choose not to adhere to conventional behaviors. Understanding this spectrum and the unique traits of individuals within it is crucial for parents and caregivers to provide appropriate support and advocacy.
Strategies for Supporting Individuals with Asperger's and Autism
Creating a supportive environment for individuals with Asperger's and Autism is a multifaceted endeavor. It involves recognizing their unique needs and tailoring strategies to address them.
One key aspect is fostering social skills development. This involves identifying and leveraging their innate strengths such as a strong sense of justice, attention to detail, and highly developed interests.
Therapy plays a significant role in this process, helping to enhance communication skills, improve social interactions, manage sensory sensitivities, and cultivate independence. In addition, understanding the phenomenon of 'masking' is paramount.
This is a coping mechanism often adopted by autistic individuals, where they mimic non-autistic behaviors to blend in. Recognizing and addressing this can aid in providing more targeted support.
Early intervention is crucial, but it's equally important to ensure that support continues into adulthood. Research indicates that adults diagnosed with autism are almost three times more likely to experience psychiatric conditions. Therefore, it's necessary to equip them with tools and strategies that promote satisfaction in their daily lives, such as career development activities and self-advocacy training. Lastly, we must remember that language matters - it must be inclusive, respectful, and reflective of the autistic community's priorities. The clinician-caregiver partnership is also crucial in providing successful health care experiences, underscoring the need for caregivers to be viewed as part of the medical team.
Building Effective Communication and Social Skills
Navigating the social and communication landscape can prove challenging for individuals with Autism and Asperger's. However, myriad strategies exist to bolster these skills, foster meaningful interactions, and nurture enduring relationships.
Techniques such as the use of visual supports and teaching social cues can significantly enhance the ability of these individuals to form and maintain positive relationships. Recent studies underscore the potential of non-speaking autistic individuals in acquiring literacy.
This understanding shatters the long-held assumption about their inability to comprehend written language, opening new avenues for fostering communication. Technology also provides a promising platform for facilitating social connections.
The advent of computer-mediated communication (CMC) has been particularly beneficial for young adults on the autism spectrum, offering a novel means of expressing their thoughts and feelings. However, it is critical to recognize that the symptoms of autism can vary drastically among individuals.
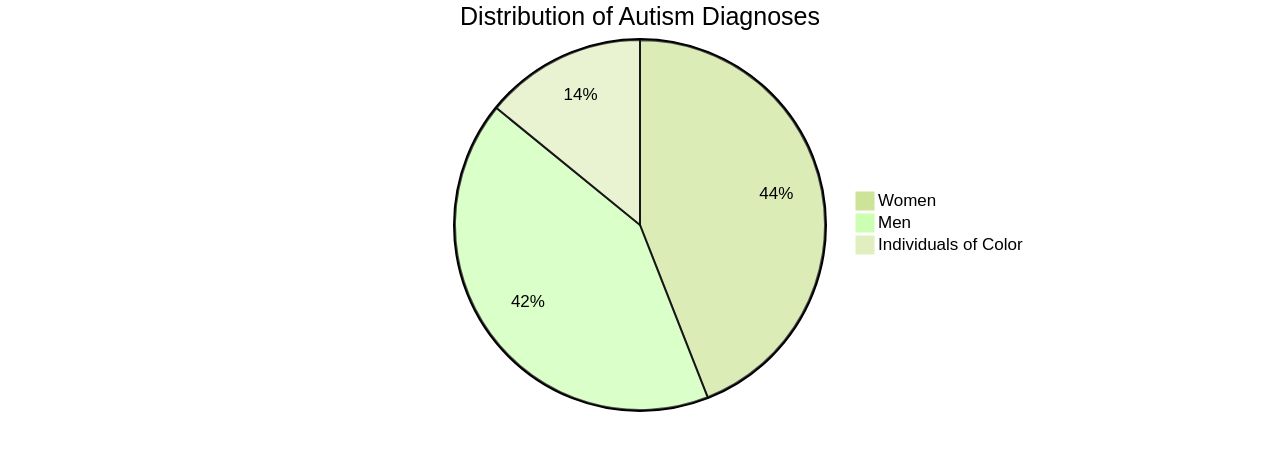
Factors such as age, significant life changes, and co-occurring conditions like anxiety and ADHD can influence the manifestation of autism. The strengths-based approach, which focuses on leveraging the unique abilities of individuals with autism, such as excellent memory, attention to detail, and visual thinking, can significantly enhance their potential. It's important to remember that while autism brings challenges, it also comes with unique strengths that can be harnessed for personal growth and societal contribution. Lastly, acknowledging the high rates of undiagnosed autism, particularly among women and individuals of color, is crucial. Early diagnosis can significantly improve access to services and support, leading to better outcomes.
Navigating Support Services and Resources
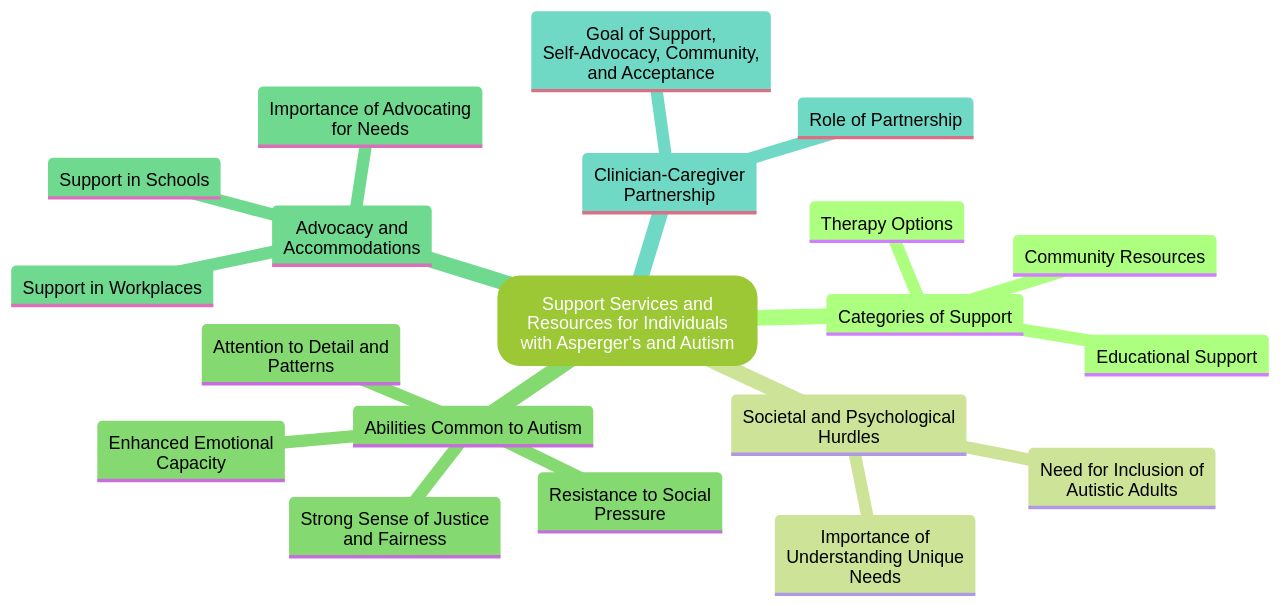
Support services and resources form a vital part of the journey for individuals with Asperger's and Autism, together with their families. This segment will assist parents and caregivers in navigating through available services such as educational support, therapy options, and community resources. The societal and psychological hurdles that autistic individuals face upon reaching adulthood, and those diagnosed in adulthood, are significant.
A comprehensive understanding of the needs of autistic patients is crucial. It is essential to avoid the automatic referral to specialists who are often unavailable. Autistic patients possess unique strengths, and it is necessary to develop skills to establish trust with them.
Autistic adults, much like anyone else, can experience conditions such as anxiety and depression. Their therapeutic needs are not vastly different, yet many report being turned away by practitioners. With willingness, minimal additional training, and a better understanding of the needs of autistic adults, practitioners can effectively include these patients in their caseloads.
It is also crucial to acknowledge and build on the abilities common to autism. These include a strong sense of justice and fairness, the ability to resist social pressure, an enhanced capacity for feeling emotions such as joy and wonder, and a keen attention to detail and patterns. Moreover, advocating for the needs of individuals with Asperger's and Autism is paramount.
Ensuring they receive appropriate support and accommodations in various settings like schools and workplaces is of utmost importance. The clinician-caregiver partnership plays a crucial role in successful health care experiences. With a combination of support, self-advocacy, community, and acceptance, autistic people can thrive.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding Asperger's and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial for creating a more inclusive future for individuals with these conditions. ASD affects individuals throughout their lives, and it's important to recognize the hallmarks of autism and the challenges associated with social communication skills and repetitive behaviors.
Research on the role of dopamine and serotonin in development offers potential therapeutic targets that could revolutionize autism treatment. Additionally, recognizing the link between Asperger's and Autism, as well as understanding the unique traits within the spectrum, helps parents and caregivers provide appropriate support and advocacy.
Strategies for supporting individuals with Asperger's and Autism involve fostering social skills development, addressing coping mechanisms like "masking," and ensuring support continues into adulthood. Effective communication techniques such as visual supports and teaching social cues can enhance relationships, while technology provides opportunities for expression through computer-mediated communication.
Navigating support services and resources is vital for individuals with Asperger's and Autism. It is important to understand their unique needs, advocate for appropriate accommodations in various settings, and build on their strengths such as a strong sense of justice and attention to detail. The clinician-caregiver partnership is crucial in providing successful healthcare experiences. By empowering parent advocates with knowledge, guidance, and resources, we can navigate the challenges associated with Asperger's and Autism Spectrum Disorder. With awareness, understanding, support, self-advocacy, community, and acceptance, individuals with ASD can thrive in a more inclusive society.




