Introduction
Autism therapies play a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals on the autism spectrum. With a diverse range of symptoms and unique needs, it is important for parents to understand and select appropriate interventions.
This article explores different therapies, including Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), Occupational Therapy (OT), Speech and Language Therapy, and Social Skills Training, highlighting their effectiveness and empowering parents to navigate the options available. By providing guidance and resources, this article aims to support Parent Advocates in ensuring the well-being and development of their children with autism.
Understanding Autism Therapies
Autism therapies are not a one-size-fits-all solution but rather a tailored approach to enhance an individual's quality of life. These therapies are designed to improve communication, foster social engagement, and teach effective behavior management. During World Autism Awareness Month, the spotlight is on the importance of understanding and selecting appropriate interventions.
With 1 in 160 children diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder globally, and an even higher incidence of 1 in 68 in the United States, early intervention is key. Research indicates that beginning therapeutic intervention before age three can significantly impact development, potentially leading to greater independence and higher IQs. The Autism Community in Action (TACA) emphasizes that the information provided about medical research, treatment options, and nutrition is a starting point for parents to explore various therapies.
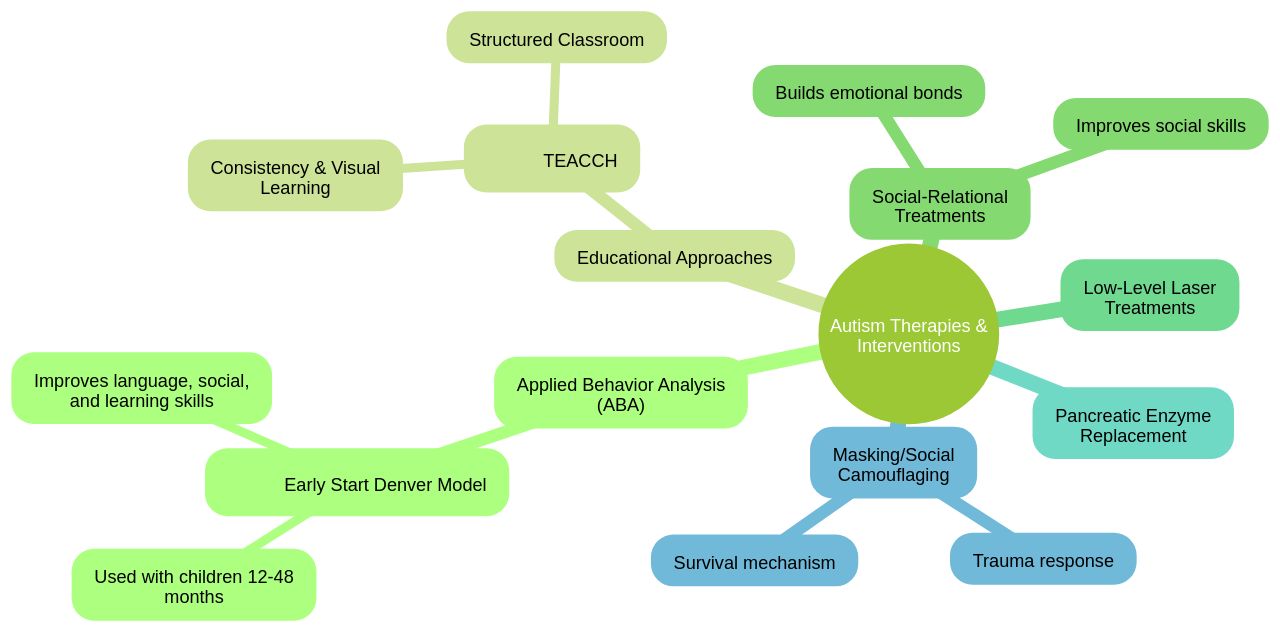
As autism manifests with a diverse range of symptoms, from challenges in social interaction to repetitive behaviors, it is crucial to consider each child's unique needs. The recent advancements in autism therapies, such as the new Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) Practice Guidelines, reflect the evolving understanding of autism. These guidelines aim to ensure high-quality implementation of ABA, which has been lauded for its effectiveness.
Moreover, innovative studies, like those examining the impact of low-level laser treatments and pancreatic enzyme replacement supplements, are exploring additional ways to alleviate associated behaviors such as irritability. However, with a myriad of programs available, most designed for preschool-aged children, there remains a gap in empirical studies comparing the effectiveness of these interventions. Parents are encouraged to consult with their child's doctor to navigate these options and identify the best course of action for supporting their child's sensory needs and overall development.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
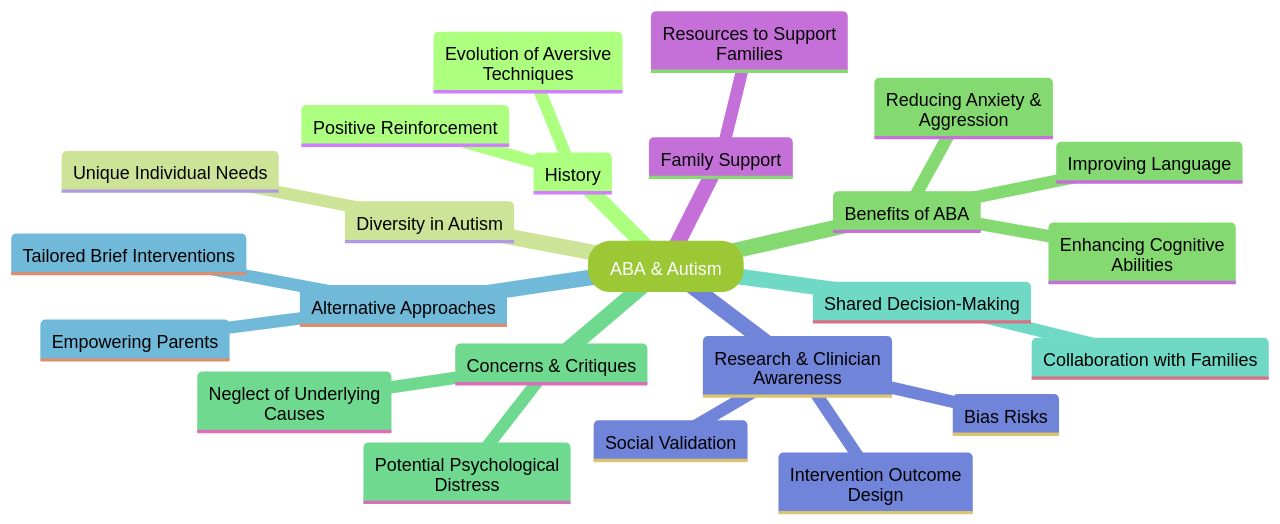
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a therapeutic strategy with a long-standing history in addressing autism, focusing on enhancing positive behaviors and mitigating challenging ones through positive reinforcement. However, it's essential to acknowledge the diversity in autism spectrum disorders and the uniqueness of each individual's needs. The 'one size fits all' concept is obsolete, as various factors influence the effectiveness and reception of ABA.
For instance, intensive recommendations of over 30 hours of therapy per week can pose significant financial burdens, disrupt family dynamics, and encroach on privacy. It's important to maintain a balance that accommodates therapy without overshadowing the child's and family's overall quality of life. Furthermore, the historical context of ABA, which once included aversive techniques, has evolved, yet the critiques remain.
Some argue that ABA can sometimes neglect the underlying causes of behaviors, potentially resulting in psychological distress. The recent emphasis on shared decision-making and collaboration with families in the treatment process is a positive step toward addressing these concerns. Notably, research indicates that tailored, brief interventions can effectively enhance social communication in young children with ASD.
Moreover, empowering parents to deliver interventions has shown promise, although the impact on child outcomes varies. It's clear that while ABA has been beneficial for improving language, cognitive abilities, and reducing anxiety and aggression, the therapeutic landscape is fractured, and the one-dimensional application of ABA is no longer tenable. Clinicians and therapists are encouraged to critically evaluate intervention research, ensuring that they're informed of the potential for both positive outcomes and unintended adverse effects.
Occupational Therapy (OT)
Occupational therapy (OT) is a beacon of hope for individuals with autism, providing a tailored approach to enhance daily living skills. Focused on empowerment, OT hones in on essential life skills—self-care, fine motor abilities, and sensory integration. A recent study at the SAIR rehabilitation center in Rome illustrates the transformative power of OT, where biweekly sessions over three months led to significant progress in children with neurodevelopmental disorders.
Moreover, primary care clinicians trained in autism diagnostics are breaking barriers, ensuring timely intervention—a crucial factor, as highlighted by a Pediatrics journal study, in optimizing outcomes for autistic children. The success of OT is not a standalone story. It echoes in the narratives of autistic individuals thriving in various careers, thanks to initiatives that champion awareness and reduce stigma.
This is backed by a review of 33 studies revealing autistic individuals' desire for career advancement, despite facing multiple barriers. These real-world examples underscore the significance of incorporating OT into daily routines, not just as a therapeutic intervention, but as a stepping stone towards independence and productivity. The testimony of a medical professional working with autistic children reinforces the value of experiences that foster autonomy.
By integrating 'Independence Therapy' and parental education, children, such as an 11-year-old girl with anxiety on the autism spectrum, have achieved remarkable growth. Simple, yet effective strategies like using weighted blankets or sunglasses during medical appointments can substantially alleviate stress for autistic patients, as noted by health experts. These insights pave the way for OT to be a cornerstone in the support system for autism, encouraging a more inclusive and understanding society.
Speech and Language Therapy
Navigating the world of autism can be a profound challenge, especially when it comes to communication. For individuals on the spectrum, speech and language therapy is a vital tool that can significantly enhance their ability to articulate thoughts, comprehend language, and engage in social interactions.
The therapy's goals are ambitious yet attainable: to foster meaningful verbal exchange and to empower nonverbal individuals to express themselves through alternative means, such as writing. Laura Kasbar's experience with her twins, both diagnosed with autism, underscores the immense potential of tailored interventions.
Despite initial setbacks, her refusal to accept a future where her son might never speak led to breakthroughs in communication. Similarly, a study by the University of Virginia revealed that non speaking autistic individuals often possess a surprising level of literacy, suggesting that their potential for language acquisition has been gravely underestimated.
This insight opens new avenues for therapy, focusing on literacy as a form of expression for those who do not speak. In practice, speech and language therapy for autism is not just about formal sessions.
It involves integrating social practice into everyday life, such as shopping trips or bank visits, to cultivate social survival skills. This kind of training can lead to social progress and the development of interaction abilities. With a multitude of therapy options available, it's crucial to select those that are effective for each individual, considering their unique needs and strengths. Therapies should aim to enhance communication, social interactions, sensory management, and independence. To make a real difference, it's essential to embrace the strengths of autistic individuals and establish trust. With the right support and a willingness to understand their world, we can unlock the doors to a richer, more communicative life for people with autism.
Social Skills Training
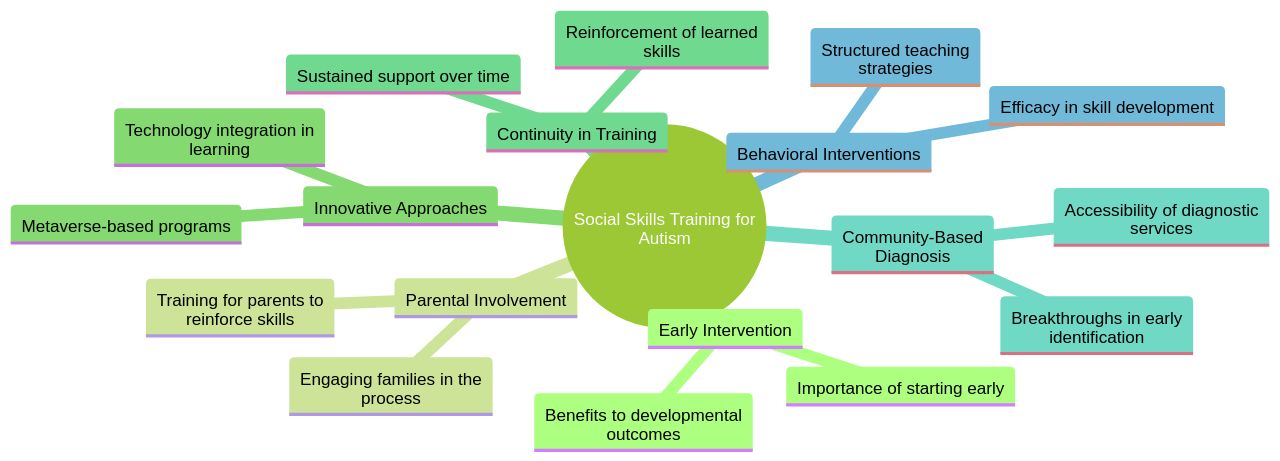
Social skills training is a lifeline for individuals with autism, offering them the tools to navigate social interactions more effectively. Dr. Hannah Schertz emphasizes the critical role of early intervention, particularly the involvement of parents in fostering social communication in toddlers with autism.
By focusing on preverbal social cues, we lay a foundation for future language skills, addressing the core challenges of autism from the onset. Innovative approaches like the metaverse-based social skills program demonstrate the adaptability of these interventions.
Children engaging with this program through platforms like Roblox show promising improvements in social responsiveness, highlighting the potential of technology-assisted learning. The continuity of social skills training is just as significant as its initiation.
Extended school year services prevent the backslide of social abilities during breaks, as evidenced by behavioral challenges observed in students with autism during the COVID-19 pandemic. Moreover, the recent news that trained community-based providers can accurately diagnose autism in most cases is a game-changer, potentially reducing the long wait times for specialist evaluations.
This breakthrough aligns with the need for timely interventions that are known to enhance child and family outcomes. Finally, the efficacy of these interventions is backed by rigorous study designs that mitigate biases and ensure social validation. Behavioral interventions not only improve language and cognitive abilities but also enhance social skills, reduce anxiety, and manage aggression. Furthermore, combining medication with behavioral interventions has proven more effective for reducing aggressive behavior. This comprehensive approach to social skills training is reshaping the landscape of support for individuals with autism, providing them with the resources to thrive in their social environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, autism therapies play a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals on the spectrum. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) focuses on positive reinforcement, but a one-dimensional approach is no longer sufficient. Tailored interventions and empowering parents show promise in enhancing social communication.
Occupational Therapy (OT) promotes independence and inclusivity. Speech and Language Therapy improves communication skills, while Social Skills Training equips individuals for successful social interactions. These therapies provide guidance and resources to support Parent Advocates in ensuring their children's well-being.
By understanding effectiveness and tailoring interventions, parents can empower their children to thrive. In summary, embracing a range of therapies and individual needs allows Parent Advocates to make informed decisions that positively impact their children's lives. Autism therapies offer hope, support, and opportunities for growth, allowing individuals on the spectrum to reach their full potential.




