Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects individuals in various ways, impacting communication, social interaction, and behavior patterns. With a rise in its prevalence, it is essential to understand the true nature of autism and debunk misconceptions surrounding its causes.
Additionally, implementing effective management strategies and providing support to individuals with ASD are crucial for their overall well-being. By promoting awareness and acceptance, we can create a more inclusive society that recognizes and embraces the unique strengths and perspectives of those on the autism spectrum.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
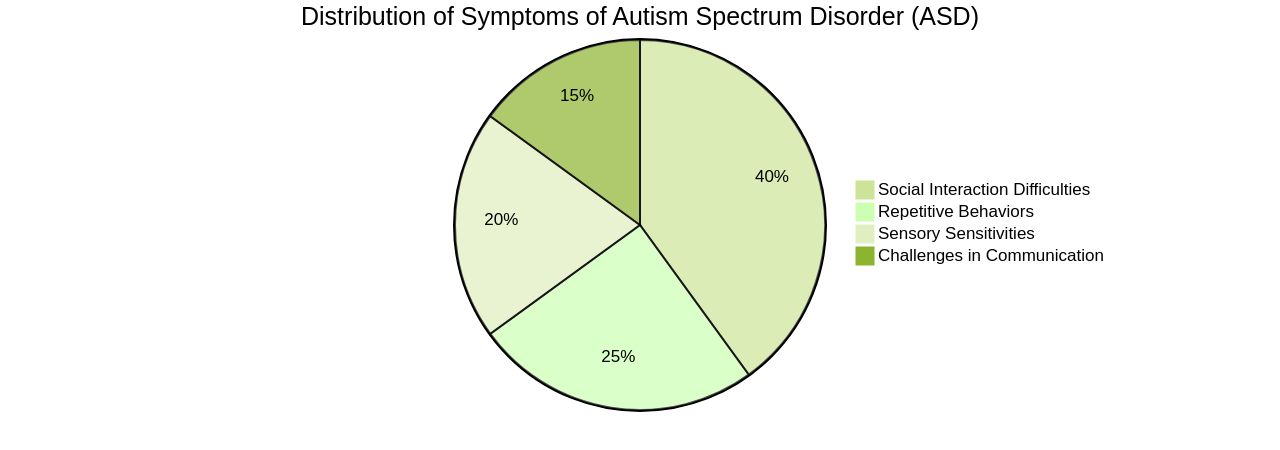
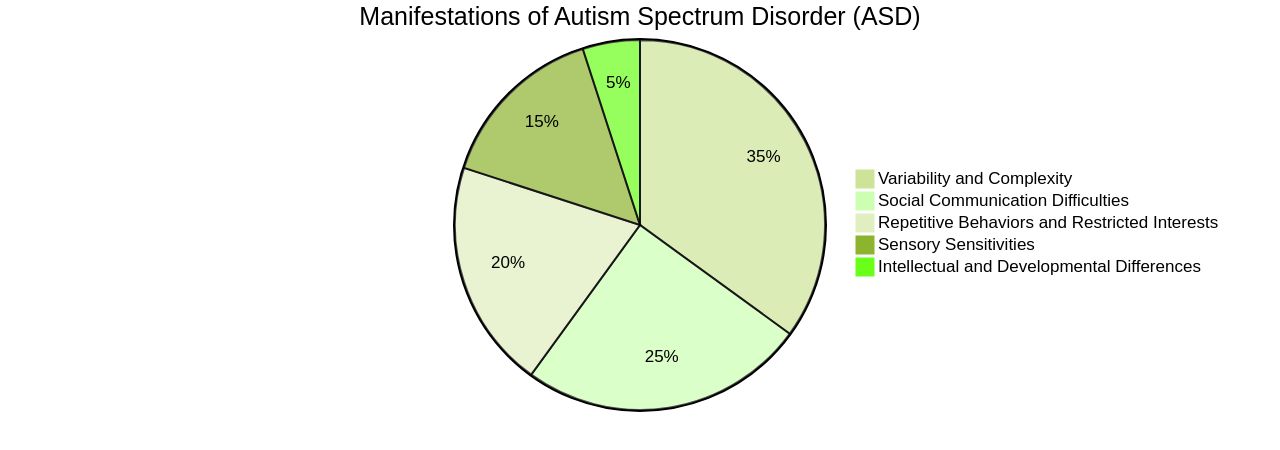
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that manifests itself in various ways, impacting communication, social interaction, and behavior patterns. It is characterized by a spectrum of symptoms, which can range from mild to severe. Core features of ASD, as described in the DSM-5, can include social interaction difficulties, repetitive behaviors, sensory sensitivities, and challenges in both verbal and nonverbal communication.
The DSM-5 emphasizes that these core features should be present from early childhood, although for some, they may not fully manifest until social demands surpass their coping abilities. Misconceptions about autism have clouded its understanding, with unfounded claims attributing it to vaccines, parenting styles, or nutrition. In reality, research indicates a likely genetic basis, with ongoing investigations into specific genes potentially linked to the condition.
Brain scans have revealed differences in the shape and structure of the brain in individuals with autism, further supporting the genetic theory. The occurrence of autism has risen, currently affecting 1 in 36 children, up from 1 in 44 just two years ago. It's essential to note that autism is a complex condition, with no single cause identified to date.
It's also crucial to debunk myths about autism - it's not a mental health disorder, but a neurological one, and it affects individuals differently. This diversity in symptoms and severity is why it's referred to as a spectrum disorder. Understanding autism is an ongoing process, with researchers continually unravelling its complexities and working towards more effective interventions and support services.
Causes of Autism Spectrum Disorder
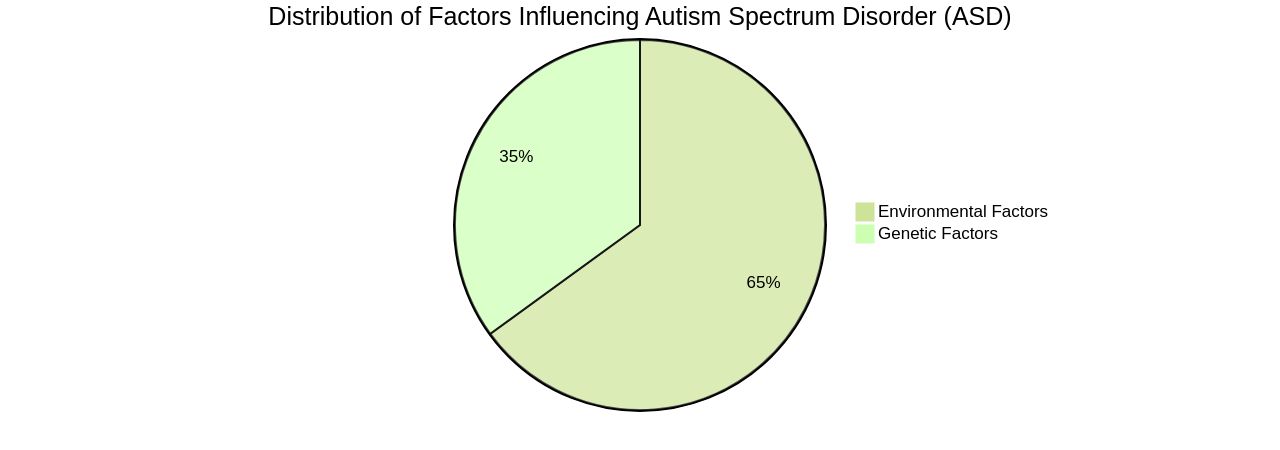
Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) experience a range of symptoms, which are influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. The genetic predisposition to ASD is influenced by a multitude of genes, as observed in Genome-Wide Association studies. These studies demonstrate the polygenic nature of autism, linking it to thousands of genetic variants with small effects on ASD symptoms.
The identification of seven potential risk genes - PLEKHA8, PRR25, FBXL13, VPS54, SLFN5, SNCAIP, and TGM1 - suggests a significant role in the development of ASD symptoms. In addition to environmental factors, the manifestation of ASD symptoms also includes genetic contributions. The risk of ASD symptoms can be amplified by prenatal and perinatal complications, exposure to toxins, and maternal infections during pregnancy.
Furthermore, the investigation is focused on understanding the progression of the disorder by studying the metabolic changes that occur between birth and the presentation of ASD symptoms in later childhood. Autism, which affects 1 in 36 children in the United States, exhibits symptoms related to genetics, physiology, and behavior. However, despite the prevalence, studying the disorder poses a challenge due to its neurological nature, the severity of cases, and the significant role of the extensive microbiome in ASD symptoms.
Additionally, misunderstandings regarding the origins of autism, such as vaccines, parenting style, or nutrition, complicate the comprehension of its true origins and asd symptoms. Access to appropriate expertise is crucial when diagnosing autism, as the disorder's clinical condition, which includes ASD symptoms, is influenced by a complex interplay of genetic and non-genetic factors. Thus, it's vital to continue research and increase understanding of this disorder to support early detection and effective management strategies.
Management Strategies for Autism Spectrum Disorder
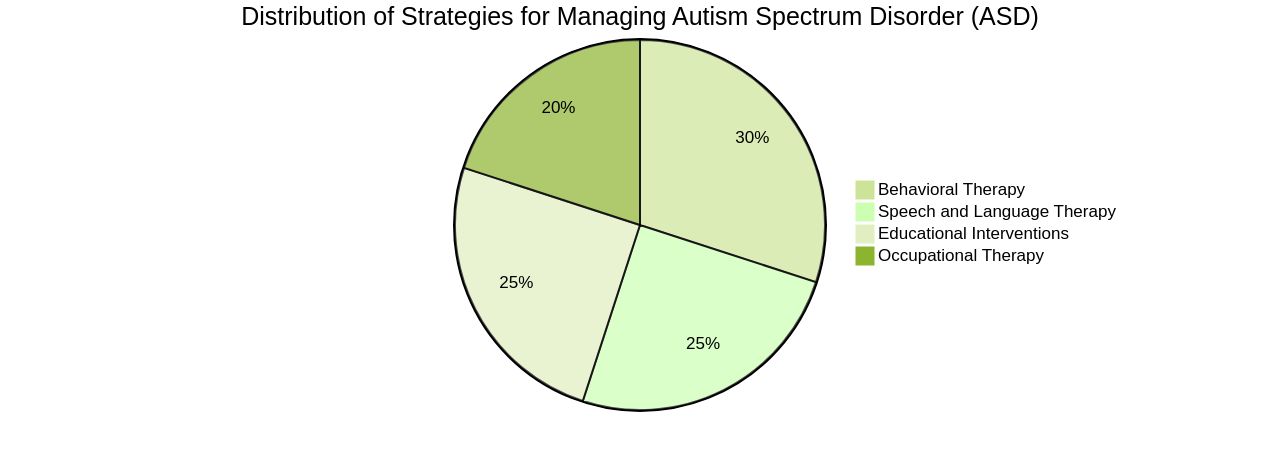
While there isn't a one-size-fits-all cure for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), a wealth of strategies are available to help individuals with ASD lead rewarding lives and maximize their potential. These strategies often involve a multi-faceted approach, incorporating elements of behavioral therapy, speech and language therapy, occupational therapy, and educational interventions.
For instance, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is one such behavioral therapy that has been instrumental in helping individuals with ASD develop adaptive skills, mitigate challenging behaviors, and enhance social interaction. But therapy isn't just about managing challenges.
It's also about identifying and nurturing the unique abilities that are often associated with autism. These can include a strong sense of justice and fairness, the capacity to adhere to principles despite social pressure, an elevated capacity for experiencing emotions such as joy and wonder, meticulous attention to detail and patterns, and a deep expertise in specific subjects.
There's also a pressing need to understand the psychological and societal challenges faced by adults with autism, and those diagnosed as adults. It's crucial that care providers understand their specific needs, rather than automatically referring them to often unattainable specialists.
Many adults with autism report being turned away by practitioners, highlighting the need for increased training and awareness in this area. Initiatives like the Adult Autism Health Resources project launched by Harvard Medical School, made possible by the generous financial backing of the Nancy Lurie Marks Family Foundation (NLMFF), aim to enhance autism care and improve the lives of adults with autism and their families. The project seeks to educate clinicians, caregivers, and self-advocates about effecting meaningful change across healthcare systems. This is a crucial step towards acknowledging the existing population of adults with autism and emphasizing their need for access to quality medical care, much like neurotypical individuals. Understanding autism and its impact is a continuous journey, and it's important to remember that early detection and intervention can make a significant difference. As researchers uncover new detection tools and service models, and as organizations like The Autism Community in Action (TACA) continue to provide invaluable information regarding treatment options and therapies, the future looks promising for individuals with autism to live fulfilling lives.
Supporting Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Supporting individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) necessitates a thorough and personalized approach, recognizing that the impact of autism on people's lives varies significantly. Take the case of identical twins Sam and John Fetters, who despite sharing the same genome, exhibit remarkably different manifestations of ASD. This highlights the complex nature of ASD, emphasizing the need for a supportive environment that fosters understanding and acceptance.
Tangible strategies such as clear communication techniques, visual aids, and sensory accommodations can be instrumental. Yet, it's equally crucial to involve individuals with ASD in decision-making processes, thus promoting their autonomy and allowing them to be active participants in their own lives. This approach aligns with the strengths-based approach theorized by social worker Bertha Reynolds, which focuses on leveraging the inherent strengths of individuals with ASD, such as excellent memory, attention to detail, and honesty.
Moreover, understanding that ASD is not a limiting disorder but a condition that can offer unique perspectives is vital. It's essential to remember that autism could be part of the lives of those around us - our friends, colleagues, or even bosses. With this understanding, we can begin to appreciate the diverse ways in which individuals with ASD experience the world.
Lastly, it's noteworthy that the prevalence of ASD is on the rise. Recent reports from the U.S. Department of Education indicate that nearly 13% of students with disabilities had autism during the 2022-2023 school year. This underlines the critical need for inclusive and supportive environments that are capable of addressing the unique needs of individuals with ASD.
Promoting Awareness and Acceptance
The journey towards a more inclusive society hinges on our collective acceptance and understanding of individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). As we unravel the layers of ASD, we displace stereotypes, advocating for the rights and needs of those within this spectrum.
Sarah Lin's experience as a parent of an autistic child illuminates the universality of parenting, noting that it is a blend of awe, frustration, and boundless love. Her story underscores the need to carve out inclusive spaces for neurodivergent individuals.
The story of Ben Taylor, a racing driver with autism, serves as a beacon of inspiration. Diagnosed with autism and ADHD at 17, he views these as unique strengths that enhance his performance on the track, encouraging others on the autism spectrum to believe in their capabilities.
The Autistic Self Advocacy Network (ASAN) is committed to fostering a world where autistic individuals enjoy equal access, rights, and opportunities. Similarly, the Indian Health Service (IHS) recognizes World Autism Acceptance Day and Month, striving to improve support and education for providers and caregivers of individuals with ASD.
The newly established Champions of Change program by Autism Speaks, and Sesame Workshop's resources for Autism Acceptance Month, further amplify the call for understanding and acceptance. Highlighting the strengths of autistic individuals, the 'auticon' organization emphasizes that 'autism is not a processing error, it’s a different operating system.'
This perspective underscores the importance of appreciating the unique gifts and abilities that autistic individuals bring to our society. Our understanding of autism in adults, particularly undiagnosed ASD, is increasingly vital. Recognizing the signs of autism is the first step towards understanding and acceptance. It is crucial to remember that ASD affects people differently, and individuals may display a variety of symptoms and strengths. Dispelling myths and misconceptions about autism, such as it being a mental health disorder, is equally important. Statistics reveal that many autistic individuals are underemployed and face barriers in career progression. However, with understanding, acceptance, and the right support, we can create a society where individuals with ASD can thrive and contribute meaningfully.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex condition that impacts communication, social interaction, and behavior patterns. It is important to debunk misconceptions and recognize the genetic basis of ASD.
While there is no cure for ASD, management strategies like behavioral therapy can help individuals with ASD lead fulfilling lives. Supporting their unique abilities is crucial.
Supporting individuals with ASD requires personalized approaches like clear communication and involving them in decision-making. Appreciating their diverse perspectives fosters understanding and acceptance.
Promoting awareness and acceptance of individuals with ASD is essential for creating an inclusive society. By dispelling stereotypes and advocating for their rights, we can create spaces where they thrive. In conclusion, by promoting awareness, implementing effective strategies, and fostering acceptance, we can ensure the well-being of individuals with ASD. Together, we can create an inclusive society that embraces their strengths and perspectives.




