Overview
This article shines a light on the diverse experiences and variations within Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), offering examples that resonate with many. It underscores the crucial role of early diagnosis and personalized support, illustrating how tailored interventions can profoundly enhance the quality of life and developmental outcomes for individuals on the spectrum. Through real-life narratives, we see firsthand the transformative impact of understanding and compassion in the journey of those affected by ASD. We invite you to reflect on these stories and consider how such support can make a difference in your own community.
Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted condition that affects individuals in diverse and profound ways. It is crucial to understand its many variations. As awareness of ASD continues to grow, so does the need to explore real-life experiences that illustrate the spectrum's complexity and the unique challenges faced by those on it.
How can recognizing these differences and tailoring support strategies empower individuals with autism to thrive and achieve their full potential? This article delves into the nuances of autism, highlighting personal stories and the importance of early diagnosis. Ultimately, it advocates for a more inclusive and supportive environment for all.
Define Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
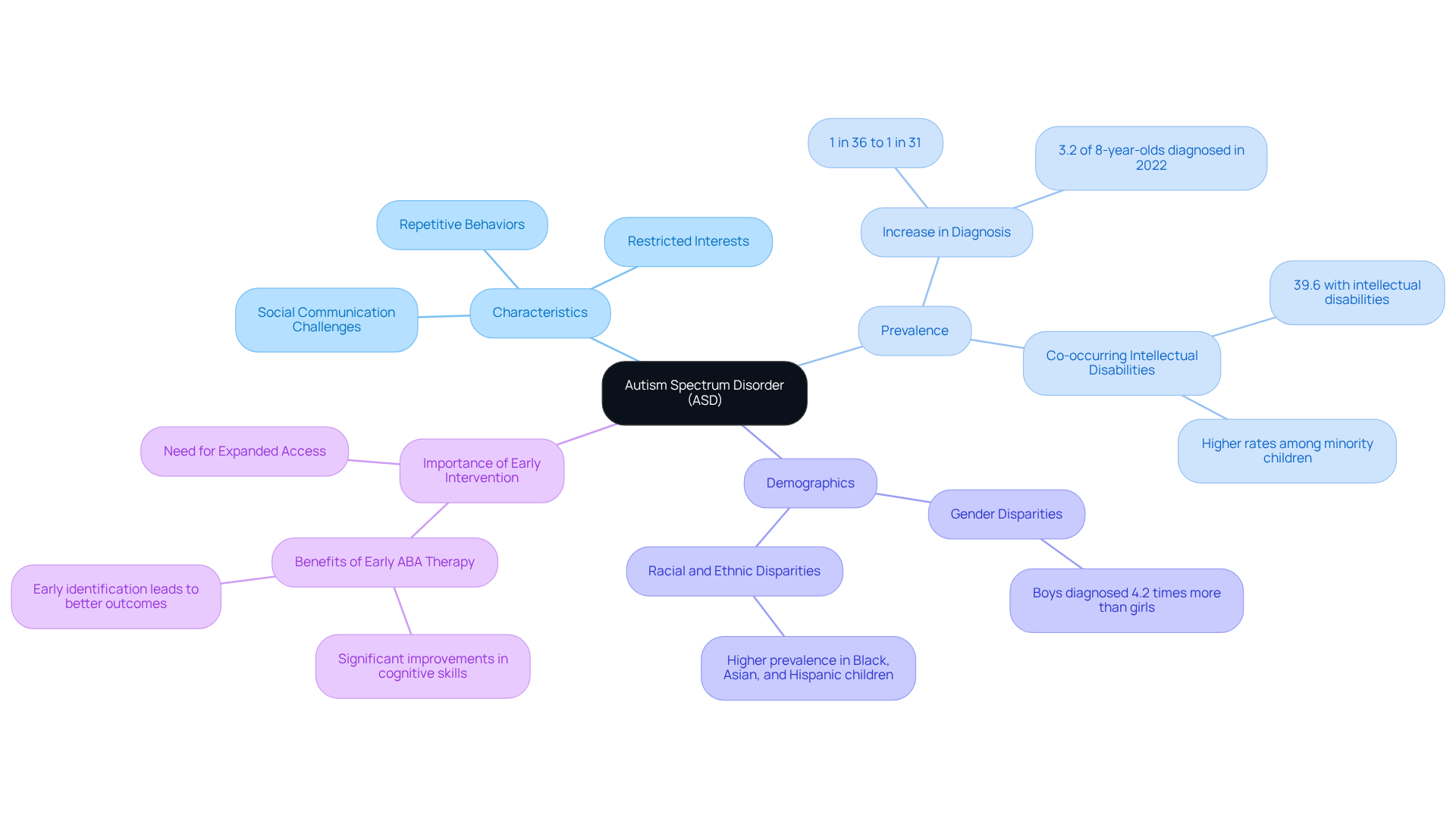
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that brings lasting challenges in social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. The term 'spectrum' highlights the wide range of symptoms and severity levels that individuals with ASD may experience. Often, these symptoms appear in early childhood, typically before the age of 18 months, and can profoundly affect daily life, including communication, social interactions, and behavior management.
For instance, children with ASD might find it hard to interpret social cues, making it difficult to form friendships. At the same time, they may exhibit intense focus on specific interests, such as mathematics or music, which can coexist with difficulties in executive functioning. Recent studies reveal that nearly two-thirds of youth diagnosed with ASD also encounter significant or borderline intellectual disabilities, with 39.6% having co-occurring intellectual disabilities. Alarmingly, the prevalence of developmental disorders in the U.S. has increased from 1 in 36 young individuals to 1 in 31, underscoring the growing awareness and identification of ASD.
Furthermore, children born in 2018 are more likely to be diagnosed with developmental disorders by age 4 compared to those born in 2014. This highlights the critical importance of early identification and support. It's also essential to recognize that disparities in the prevalence of developmental disorders exist among different racial and ethnic groups, which calls for equitable support systems.
Understanding the characteristics of ASD and the examples of autism is vital for parents and professionals alike. This knowledge lays the groundwork for effective intervention strategies and the development of supportive systems that can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals on the spectrum. As U.S. Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy, Jr. remarked, the developmental disorder epidemic is a pressing public health issue that deserves our immediate attention. Together, we can advocate for awareness, understanding, and the resources necessary to support those affected by ASD.
Explore Variations Within the Autism Spectrum
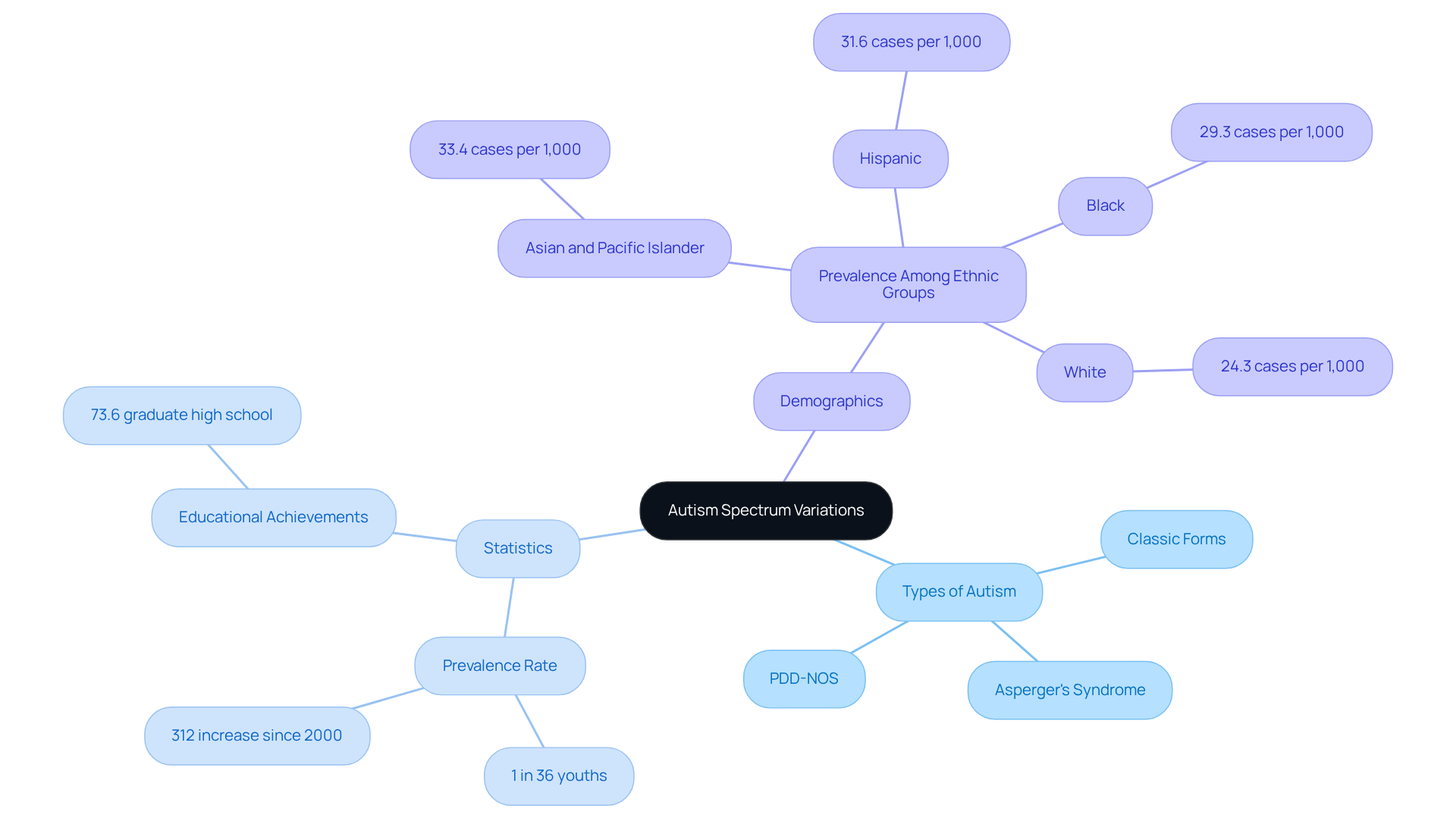
The spectrum of conditions encompasses classic forms, Asperger's syndrome, and pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS). Each individual on this spectrum presents unique combinations of symptoms and challenges, which can vary widely. For example, examples of autism may include individuals who experience significant difficulties with verbal communication, while others might have advanced language skills yet struggle with understanding social cues. Recognizing these variations is vital for developing personalized support strategies that honor each individual's strengths and challenges.
Recent findings indicate that the occurrence of classic developmental disorder is approximately 1 in 36 youths, with the rate of this condition in the US increasing by 312% since 2000. It’s important to note that experts suggest several possible reasons for the higher diagnosis rates of ASD in boys. Additionally, an encouraging statistic reveals that 73.6% of autistic students in the US graduate high school with a diploma, highlighting the educational achievements of individuals on the spectrum.
Currently, the typical age for diagnosis in the U.S. is around 4 years, underscoring the importance of early support. Furthermore, autism is most prevalent among Asian and Pacific Islander children, with a rate of 33.4 cases per 1,000, illustrating the demographic differences within the spectrum. By acknowledging and valuing these distinctions, caregivers and professionals can foster more effective strategies and support systems, ultimately creating a nurturing environment for all individuals on the autism spectrum.
Discuss the Importance of Early Diagnosis and Customized Support
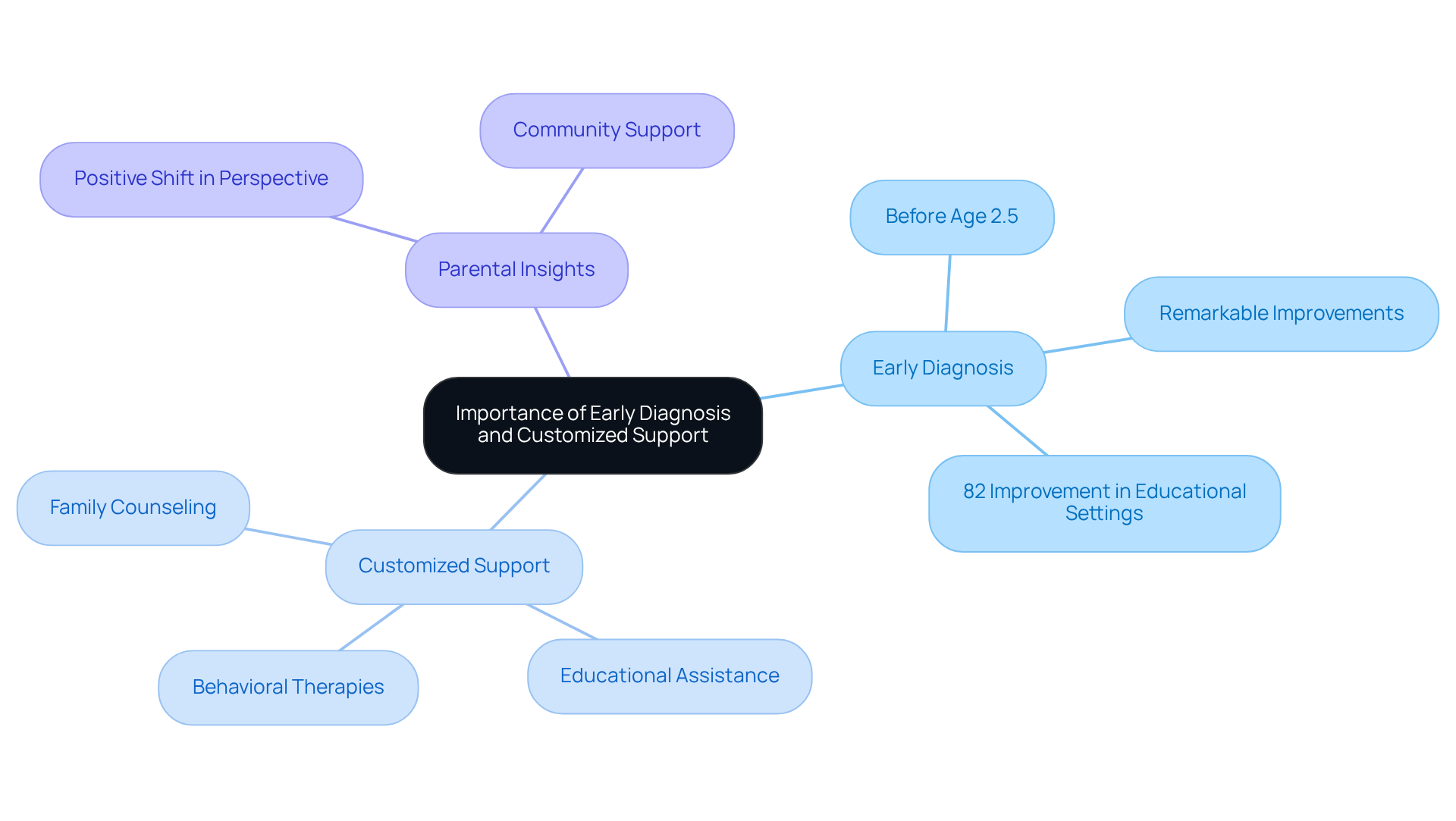
Recognizing Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) early is essential, as it opens the door to timely interventions that can significantly enhance developmental outcomes. Research indicates that children diagnosed before the age of 2.5 years often show remarkable improvements in communication and social skills compared to those diagnosed later. By providing customized support tailored to the unique needs of each child—such as behavioral therapies, educational assistance, and family counseling—families can empower their children to navigate challenges and reach their full potential.
As Temple Grandin wisely notes, "Kids have to be exposed to different things in order to develop." This underscores the importance of varied experiences in nurturing growth. Moreover, studies reveal that taking prompt action can lead to an impressive 82% improvement in educational settings, highlighting the critical nature of addressing developmental disorders from the start. Additionally, 92% of parents of children with autism report that a positive shift in perspective helps them manage challenging days, illustrating the profound benefits of timely support and personalized care.
By embracing these strategies, families can create a nurturing environment that fosters growth and development for their children with special needs. We encourage you to share your experiences and insights, as together we can build a supportive community that champions the potential of every child.
Provide Real-Life Examples of Autism Experiences
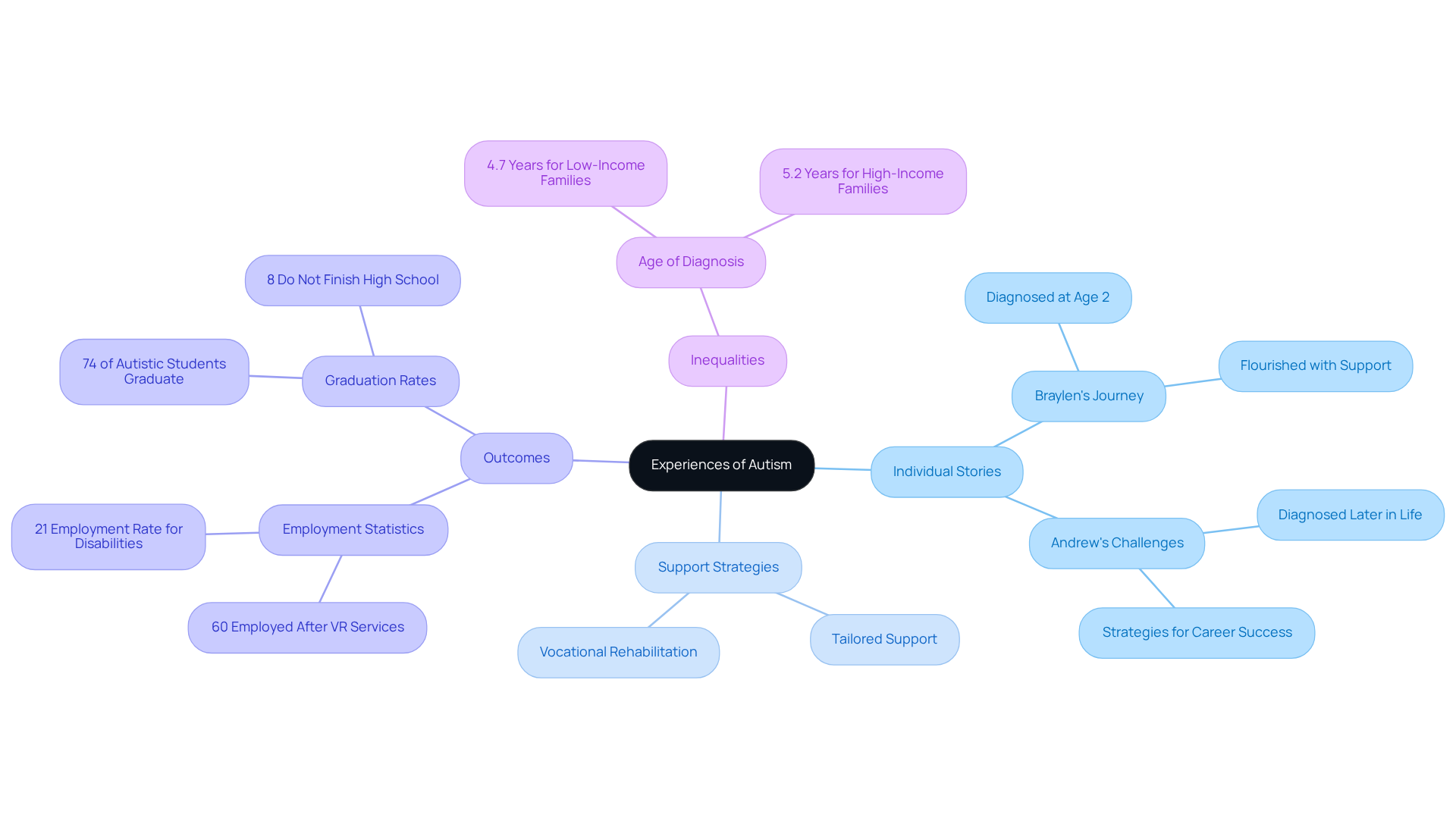
The experiences of individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) serve as valuable examples of autism that are incredibly diverse, reflecting the unique nature of the spectrum. For instance, Braylen, diagnosed at age 2, has flourished through initial support, developing strong social skills and forming meaningful friendships. His journey exemplifies how tailored support can lead to significant improvements in social interactions and overall quality of life, just like the examples of autism. In contrast, Andrew, diagnosed later in life, shares his challenges with social interactions and the strategies he employed to achieve career success. His narrative highlights the significance of understanding the diverse journeys individuals on the spectrum may pursue, which include various examples of autism.
Studies show that prompt support can save approximately $1.3 million for each individual throughout their life by decreasing the necessity for prolonged special education and intensive care. Furthermore, nearly 60% of people with autism in the U.S. are employed after receiving vocational rehabilitation (VR) services, highlighting the positive outcomes of tailored support. The typical age of diagnosis for children in low-income families is 4.7 years, compared to 5.2 years for those in high-income families, which underscores inequalities in access to timely support.
Additionally, 74% of autistic students in the U.S. graduate with a diploma, compared to 86% of all students, emphasizing the critical role of early intervention in educational success. These narratives provide examples of autism that illustrate the essential role of personalized support in fostering growth and acceptance, demonstrating that every individual's journey is unique and deserving of recognition. We encourage you to share your experiences and thoughts, as together we can continue to advocate for understanding and support for all individuals on the spectrum.
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) invites us to appreciate its complexity and the diverse experiences of those affected. The spectrum includes a wide array of symptoms and challenges, underscoring the necessity for tailored approaches to support. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in enhancing the quality of life for individuals on the spectrum, empowering them to thrive in social, educational, and professional settings.
Key insights from the article highlight the importance of:
- Early recognition
- The variations within the autism spectrum
- The significant impact of customized support
Real-life stories illustrate how individuals like Braylen and Andrew navigate their unique journeys, showcasing the transformative power of timely interventions and personalized care. The statistics presented reinforce the need for equitable access to resources and support, ensuring that every individual with autism can achieve their full potential.
Collectively, these insights urge us to deepen our commitment to understanding and advocating for individuals with ASD. By fostering awareness, sharing experiences, and promoting equitable support systems, we can create a more inclusive environment where all individuals on the spectrum can flourish. The journey toward acceptance and empowerment starts with informed conversations and collaborative efforts to champion the diverse experiences of those living with autism.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by challenges in social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. It encompasses a broad range of symptoms and severity levels.
When do symptoms of ASD typically appear?
Symptoms of ASD often appear in early childhood, usually before the age of 18 months.
How does ASD affect daily life?
ASD can significantly impact daily life, including communication, social interactions, and behavior management, making it difficult for individuals to form friendships and interpret social cues.
What are some common characteristics of children with ASD?
Children with ASD may exhibit intense focus on specific interests, such as mathematics or music, and may experience difficulties in executive functioning.
What is the prevalence of intellectual disabilities among youth with ASD?
Recent studies indicate that nearly two-thirds of youth diagnosed with ASD also face significant or borderline intellectual disabilities, with 39.6% having co-occurring intellectual disabilities.
How has the prevalence of developmental disorders changed in the U.S.?
The prevalence of developmental disorders in the U.S. has increased from 1 in 36 young individuals to 1 in 31, indicating a growing awareness and identification of ASD.
Are there differences in the prevalence of developmental disorders among racial and ethnic groups?
Yes, disparities in the prevalence of developmental disorders exist among different racial and ethnic groups, highlighting the need for equitable support systems.
Why is early identification and support important for ASD?
Early identification and support are crucial as children born in 2018 are more likely to be diagnosed with developmental disorders by age 4 compared to those born in 2014.
What role does understanding ASD play for parents and professionals?
Understanding the characteristics of ASD is vital for parents and professionals as it lays the groundwork for effective intervention strategies and the development of supportive systems to enhance the quality of life for individuals on the spectrum.
What is the public health significance of ASD?
The increasing prevalence of developmental disorders, including ASD, is considered a pressing public health issue that requires immediate attention and advocacy for awareness, understanding, and necessary resources for support.




