Introduction
Understanding the Unique Skills and Strengths of Autistic Individuals
Navigating the workplace can be a formidable challenge for autistic individuals, yet their unique qualities, such as exceptional attention to detail, robust problem-solving skills, and unparalleled focus, are assets any employer would value. Despite these strengths, misconceptions about autism persist in professional settings.
This article explores the importance of recognizing and harnessing the abilities of autistic individuals in the workplace, highlighting the need for inclusive hiring practices, job readiness training, ongoing support, and partnerships with community organizations. By embracing neurodiversity and providing the necessary resources, employers can create a work environment that fosters diversity, innovation, and growth.
Understanding the Unique Skills and Strengths of Autistic Individuals
Navigating the workplace can be a formidable challenge for autistic individuals, yet their unique qualities, such as exceptional attention to detail, robust problem-solving skills, and unparalleled focus, are assets any employer would value. Despite these strengths, misconceptions about autism persist in professional settings.
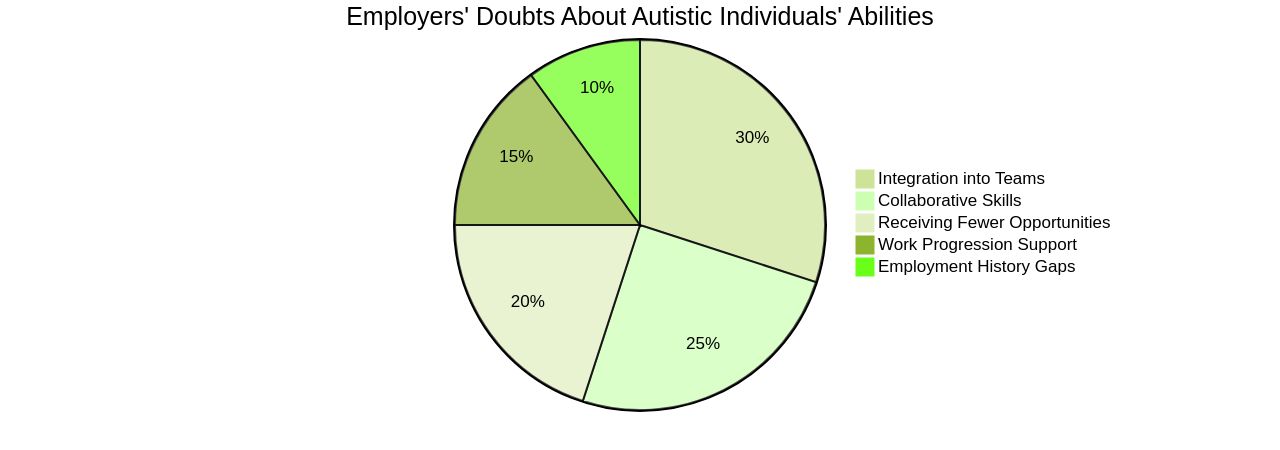
The National Autistic Society's findings are sobering, with 34% of employers doubting an autistic individual's ability to integrate into their teams, and 28% questioning their collaborative skills. These damaging stereotypes hinder autistic people from disclosing their condition, thereby missing out on vital workplace adjustments that could facilitate their success.
To counter these challenges, employers must reconsider job descriptions and work environments, ensuring they are conducive to autistic employees' needs, thus preventing sensory overload from factors like bright lights or excessive noise. Employers are called to action to cultivate an understanding of autism, drawing from the insights of successful initiatives and the guidance of reports like the Buckland Review of Autism Employment.
The Government's Universal Support program and the Neurodiversity Employers Index (NDEI®) are instrumental in this mission, providing tailored support and frameworks for businesses to become inclusive workplaces. These initiatives not only promote awareness and dismantle stigma but also showcase the economic benefits of hiring autistic individuals. Studies reveal that companies employing people with disabilities, including those who are neurodiverse, see higher revenues, net income, and profit margins. In fact, incorporating more individuals with disabilities into the workforce could potentially increase the U.S. GDP by up to $25 billion. The journey to a more inclusive workplace is not just a moral imperative but a strategic business decision that fosters diversity, innovation, and growth.
Providing Job Readiness Training and Support
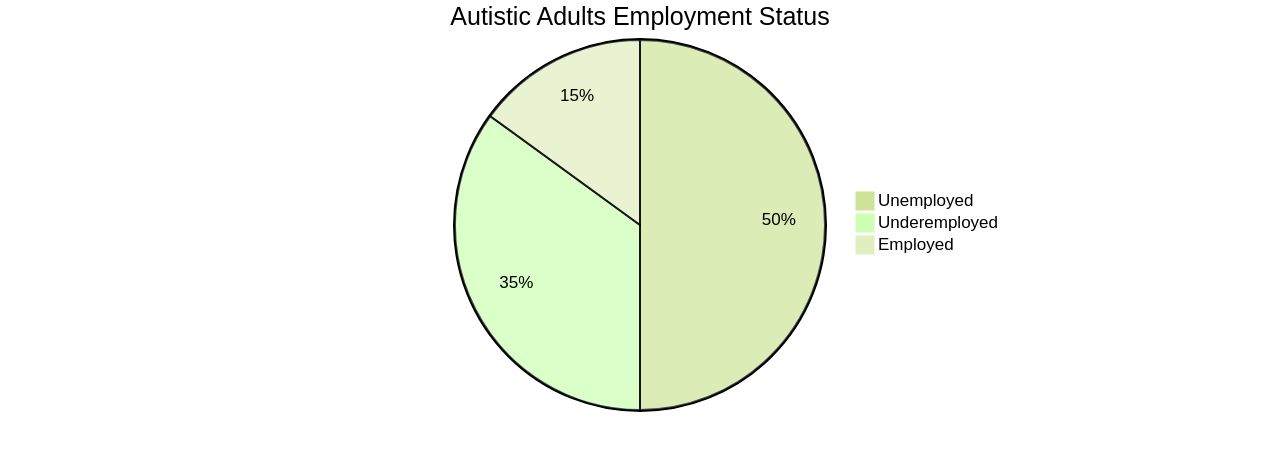
Empowering autistic individuals in their employment journey is about more than just finding a job; it's about nurturing their ability to thrive in the workplace. With 85% of autistic adults facing unemployment or underemployment, targeted job readiness training becomes a crucial stepping stone. This training encompasses essential skills like crafting a professional resume, mastering interview techniques, and understanding the nuances of workplace behavior.
By integrating mock interviews and job shadowing, autistic job seekers can gain valuable experience and build the confidence needed to navigate the employment landscape. These practical exercises allow them to showcase their unique talents and adapt to real-world work scenarios. Furthermore, fostering connections and relationships is vital for their social integration in the workplace.
It's important for employers to recognize the diverse strengths of autistic individuals and create an environment where their skills can be fully utilized and appreciated. By doing so, employers can harness the potential of a neurodiverse workforce and drive meaningful career development for autistic employees. As we strive to bridge the employment gap, it's imperative to celebrate the successes and contributions of autistic professionals across various industries and to disseminate these inspiring stories to promote awareness and reduce stigma.
Creating Inclusive Hiring Practices
In the pursuit of creating workplaces that are truly inclusive, employers must take proactive steps to ensure autistic individuals are not only hired but also supported and given the opportunity to thrive. This means crafting job descriptions that are concise and clear, avoiding lengthy and complex language that may deter autistic applicants.
Employers are called to honor the legal duty set forth by the Equality Act 2010 to provide reasonable adjustments during the recruitment process, such as flexible interviewing techniques that accommodate the unique communication styles of autistic candidates. Businesses like Cafe Track in Northampton exemplify this approach, having successfully guided over 120 autistic individuals into meaningful employment and work placements.
The social enterprise, founded by Thomas Cliffe, operates on the principle that hiring autistic individuals is not just a charitable act but a strategic business decision. By training and supporting other businesses, Cliffe is setting a precedent for how a supportive and inclusive work environment can be beneficial to all.
Moreover, it's important to address the troubling statistic that autistic graduates are twice as likely to be unemployed as their non-disabled counterparts. Employers can counteract this by offering career-progression training tailored to autistic staff, which can help bridge the gap between their potential and actual career trajectories. Ultimately, fostering a workplace that values neurodiversity not only enhances the lives of autistic employees but enriches the entire organization. As Dr. James Cusack of Autistica puts it, embracing different ways of thinking and working is beneficial for everyone. Employers who adopt such inclusive hiring practices are investing in a diverse workforce that is proven to drive innovation and efficiency.
Partnering with Community Organizations
Building inclusive workplaces that embrace the unique talents of autistic individuals is not only a social imperative but also a strategic advantage. By partnering with organizations like NEXT for AUTISM, employers can tap into a wealth of resources and expertise.
These collaborative efforts can help to dismantle barriers to employment and create a more diverse workforce. For example, the Bhatia Foundation’s partnership with NEXT for AUTISM has launched impactful programs that support the transition to adulthood for neurodivergent young adults, indicating a commitment to fostering inclusive environments.
Such initiatives align with the Government’s Universal Support program, which aims to provide personalized employment support and align with the national campaign to raise awareness about the benefits of hiring autistic individuals. The Government’s review, as part of its mission to make the UK the most accessible place in the world, reinforces the importance of businesses and government working together to support autistic employment.
With the Buckland Review of Autism Employment available online, and the Disability Action Plan in place, the UK is taking significant steps towards inclusion. Employers are encouraged to showcase their success in employing autistic professionals, as they do with gender and race/ethnicity diversity data.
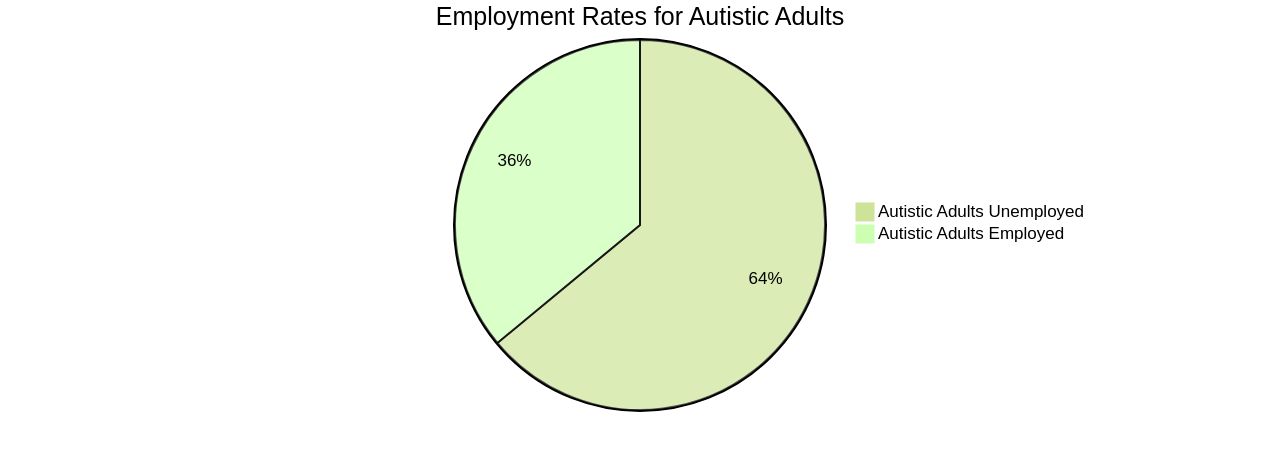
By doing so, they contribute to a national campaign that builds a narrative of success and highlights the support systems that enable such achievements. The statistics are clear: autistic adults face the lowest employment rates among people with disabilities at 58 percent. This not only affects their financial stability but also their access to vital benefits like healthcare. Furthermore, the delay in receiving diagnosis and services, which can span up to four years, exacerbates these challenges. The report underlines that marginalized groups often face even longer waits, highlighting the urgent need for inclusive employment strategies. It's time to recognize autistic individuals as key contributors to our society, deserving of equal opportunities and the right to thrive in the workplace.
Providing Ongoing Support and Accommodations
Supporting autistic employees within the workforce goes beyond the hiring process; it requires a continued commitment to understanding their unique needs and providing necessary accommodations. Tailoring individualized support plans and facilitating mentoring relationships can significantly enhance their work experience.
Additionally, the integration of assistive technologies can play a pivotal role in enabling their success. Regular communication is fundamental to preemptively address potential challenges, ensuring a supportive work environment.
The National Autistic Society's research reveals the prevalence of misconceptions among employers, with 34% doubting an autistic individual's ability to integrate into their teams. These damaging stereotypes contribute to underemployment and hinder career progression for many autistic individuals.
Employers are encouraged to re-evaluate their workplace culture and practices, such as simplifying job descriptions and providing clearer pathways for career development, to better support their autistic staff. As highlighted by recent reviews and studies, a significant portion of the autistic population remains unemployed or underemployed despite their desire for career advancement. Employers can contribute to changing this narrative by fostering an inclusive environment that acknowledges the strengths of autistic employees, such as their ability to hyperfocus, while also offering flexibility and understanding in areas where they may face challenges, like sensory sensitivities or social communication. The shift towards a more inclusive workforce not only benefits autistic individuals but also enhances business performance, as demonstrated by studies showing that companies with diverse employment practices outperform their peers financially.
Conclusion
In conclusion, employers must recognize and harness the unique skills of autistic individuals in the workplace. By creating inclusive hiring practices, providing job readiness training and ongoing support, and partnering with community organizations, employers can foster a work environment that embraces neurodiversity and promotes diversity, innovation, and growth.
Targeted job readiness training is crucial to bridge the employment gap for autistic individuals. This includes developing essential skills and providing practical experience.
Fostering connections within the workplace is vital for social integration. Creating inclusive hiring practices involves clear job descriptions and reasonable adjustments during recruitment.
By adopting these practices, employers can benefit from a neurodiverse workforce that drives innovation. Partnering with community organizations provides valuable resources in building inclusive workplaces.
These efforts help dismantle barriers to employment and create a more diverse workforce. Supporting autistic employees requires understanding their unique needs and providing necessary accommodations. Individualized support plans, mentoring relationships, and assistive technologies enable their success. In conclusion, embracing neurodiversity benefits both autistic individuals and businesses. By recognizing talents, offering support, and creating an inclusive environment, employers tap into untapped potential while driving innovation. It's time to break down barriers, challenge misconceptions, and provide equal opportunities for autistic individuals to thrive in the workplace.




