Introduction
Children with Level 2 Autism require substantial support due to significant difficulties in social interaction and communication. They often exhibit inflexible behaviors, resistance to change, and a narrow range of interests. Understanding the intricacies of Level 2 Autism is crucial for caregivers and professionals in order to provide suitable support and interventions. In this article, we will explore the challenges faced by children with Level 2 Autism and discuss strategies, such as low-demand parenting and various interventions, that can help support their development and well-being. We will also delve into the role of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy in managing Level 2 Autism and enhancing social skills. Additionally, we will provide guidance on time management and prioritization techniques for parents supporting children with Level 2 Autism, as well as strategies for addressing challenging behaviors. Lastly, we will discuss the importance of navigating support services and provide resources to assist parents in advocating for their child's needs. By understanding and addressing the unique needs of children with Level 2 Autism, we can create a supportive and inclusive environment that promotes their growth and development
1. Understanding Level 2 Autism: A Brief Overview
Level 2 Autism, a categorization under the broader Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is characterized by children who need substantial support due to significant difficulties in social interaction and communication. These children often exhibit inflexible behaviors, resistance to change, and a narrow range of interests. Understanding the intricacies of Level 2 Autism is crucial for caregivers and professionals, as it helps in devising suitable support and interventions.
Level 2 Autism can be metaphorically likened to a building foundation with significant cracks, representing the more severe challenges these children face compared to those with lower-support needs autism. The developmental delays, social skills deficits, sensory processing issues, and restrictive/repetitive behavior they exhibit are the major cracks in their developmental foundation.
Children with Level 2 Autism might experience developmental stagnation, struggle with control and communication, and be hypersensitive to sensory inputs. For them, communication can be likened to being in a foreign country, where the language is comprehensible, but the cultural norms and idioms are confusing. They also grapple with cognitive rigidity, finding it difficult to adapt to changes or switch activities. Sensory issues could be as disorienting as being abruptly awakened after a short sleep and expected to perform a task.
In managing children with Level 2 Autism, traditional parenting techniques may not yield the desired results. Thus, a concept like low-demand parenting, which involves trust, flexibility, collaboration, and a balanced approach to demands, can be effective. This approach aims to reduce stress and anxiety levels in children, fostering a more conducive environment for their growth and development.
Various interventions are available to support individuals with Level 2 Autism. These interventions, including Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), Social Skills Training, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Speech and Language Therapy, and Occupational Therapy, are designed to address the specific needs and challenges of these individuals. They aim to enhance communication skills, social interaction, behavior management, and overall functioning.
To address social interaction challenges, implement strategies that enhance their social skills, such as providing step-by-step tutorials and techniques that encourage social engagement. Similarly, communication difficulties can be mitigated with appropriate strategies and support to enhance their social skills and communication abilities.
Inflexible behaviors can be effectively managed by implementing strategies that promote social skills development.
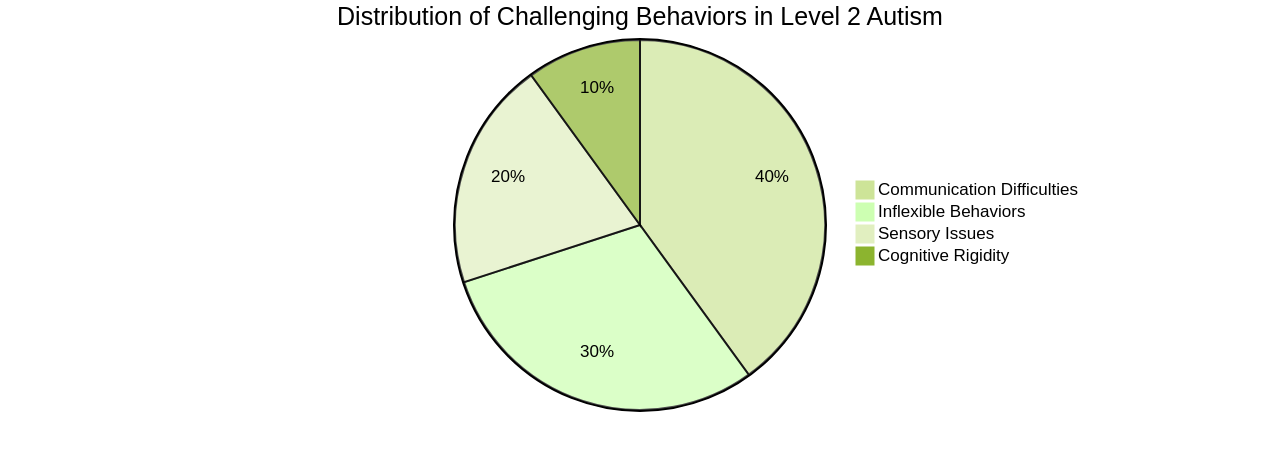
Techniques such as social stories, visual supports, and social skills groups can provide structure, predictability, and opportunities for practice in various social situations. Individualized behavior plans and positive reinforcement techniques can address specific inflexible behaviors and encourage more flexible responses.
A strategy to help children with Level 2 Autism cope with change involves enhancing their social skills, enabling them to navigate and adapt to changes in their environment. This also contributes to their overall well-being and improves their ability to engage with others. One can also expand their range of interests by exposing them to a variety of activities and experiences, helping them discover new interests and develop a broader range of hobbies.
Supporting parents of children with Level 2 Autism involves providing resources and information to navigate autism support services, including educational materials, workshops, training programs, support groups, and online communities.
This holistic approach helps parents understand the unique needs of their child and equips them with the tools and knowledge to provide the best possible care and support
2. Recognizing Stage 2 Autism Symptoms & Prognosis
Autism, specifically Level 2, can manifest in varied symptoms such as limited social initiation and unusual responses to others' social gestures.
Challenges adjusting to change and rigid adherence to routines are also common. However, it's crucial to understand that the prognosis for Level 2 Autism is not fixed - it can be significantly influenced by early intervention and appropriate support. Each child is unique, and the pace and nature of progress may differ from one child to another.
Level 2 Autism, as defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), is characterized by individuals needing substantial support due to more severe social deficits. Communication can be challenging, and issues with non-verbal communication may arise. Inflexible behaviors that interfere with daily functioning are also common. It's important to remember that these levels are assigned based on the severity of the symptoms. A correct autism diagnosis that includes the levels of severity can help doctors and other specialists work with the individual to provide the right treatment and support.
Autism symptoms can vary, from social difficulties and repetitive behaviors to obsessive interests and difficulty coping with changes. However, early diagnosis is invaluable for treatment and can lead to a better quality of life. There are treatment options available for autism, such as behavioral therapy and medication for related symptoms, along with educational and behavioral therapies, which can help individuals with autism develop the skills necessary for as much independence as possible.
The DSM-5's introduction of autism levels is a significant step towards understanding this disorder's multidimensional nature. From Level 1, needing some support, to Level 3, needing very substantial support, these levels indicate both the disorder's severity and the level of support needed. Other conditions that may coexist with autism must also be considered as they can affect the individual's overall presentation and the level of support needed.
Understanding and addressing an individual's strengths, goals, and priorities is key to providing the right support and therapy. While each child may progress differently, with the right support and treatment, children with Level 2 Autism can lead fulfilling lives. Effective strategies for enhancing social skills in these children include Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, social stories, visual supports, and social skills training groups. ABA therapy, in particular, has been found effective in improving social interaction, communication, and behavior in children with autism. It involves breaking down skills into smaller steps and using positive reinforcement to encourage desired behaviors. These strategies, along with guidance and support of professionals, can greatly benefit children with Level 2 Autism in their social skills development.
Interventions enhancing social interaction focus on teaching social skills and promoting social engagement, including social skills training, peer-mediated interventions, and video modeling. Implementing these interventions can greatly improve social interaction in children with Level 2 Autism.
Supporting children with Level 2 Autism in coping with change involves providing them with strategies and tips to navigate transitions more effectively. This may include creating visual schedules, using social stories, providing advance notice of upcoming changes, and implementing sensory breaks or calming techniques. Consistency in their daily activities provides a sense of predictability and stability.
For children with Level 2 Autism, establishing routines and structure can be highly beneficial. Having a predictable and structured daily schedule can help them feel more secure and reduce anxiety. Providing clear and consistent expectations can also help them understand what is expected of them in different situations. Visual supports such as visual schedules, social stories, and visual cues can be used to enhance communication and understanding.
Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes for children with Level 2 Autism. By providing appropriate support and interventions at an early age, these children can develop important skills and abilities that will benefit them throughout their lives. It is important to implement strategies and interventions that are tailored to the specific needs of each child, focusing on enhancing social skills, communication abilities, and academic progress.
Understanding the unique needs of children with Level 2 Autism is crucial to providing appropriate support and interventions. Children with Level 2 Autism typically require more structured and specialized approaches to address their specific challenges with social interaction, communication, and behavior. Recognizing and addressing these unique needs, professionals and caregivers can create a supportive and inclusive environment promoting the development and well-being of children with Level 2 Autism
3. The Role of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) Therapy in Managing Level 2 Autism
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a well-recognized and scientifically validated approach, particularly beneficial in managing Level 2 Autism, a category within the Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). This therapy diverges from conventional models, which generally involve shorter, monthly or weekly sessions. In contrast, ABA therapy is recommended for an intensive duration of up to 40 hours per week.
Dating back to the late 1980s, research has demonstrated the remarkable influence of early and intensive ABA therapy. Reports indicate that around 50% of children diagnosed with ASD, who underwent intense ABA intervention involving 40 hours per week, showcased significant improvement. After several years, these children were nearly indistinguishable from their peers, unlike only 2% in the group that received non-intensive ABA therapy.
A thorough literature review in 2010 concluded that children receiving 35 or more hours of ABA therapy per week demonstrated the best treatment gains. The intensity or "dosage" of treatment can vary based on each individual's needs. Generally, comprehensive treatment ranging from 25 to 40 hours per week is associated with better outcomes. Focused treatment, involving fewer hours and targeting specific objectives, also plays a vital role, especially for older children or those who have already received early intense ABA therapy.
ABA therapy extends beyond just "table time," where tasks are divided into small behaviors using discrete trial teaching (DTT). Besides DTT, a comprehensive ABA program should also include natural environment teaching (NET), functional communication training (FCT), and other methodologies. It's essential to debunk the myth that a reduced dosage of ABA, say 10-15 hours per week, will yield the same results. Studies have proven that only 2% of children achieved normal intellectual and educational functioning with a 10-hour per week program.
The "gold standard" label for ABA is particularly associated with early intense ABA therapy, not lower intensity treatments. Therefore, the research supports the recommendation of 25 to 40 hours per week of intense comprehensive ABA therapy for young children with ASD. For older children, focused ABA based on their objectives and desired outcomes may be more beneficial. Parents and behavior analysts must consider the research when making treatment recommendations and ensure that the service model aligns with the scientific rigor of ABA.
ABA therapy can yield numerous benefits for children with Level 2 Autism, such as improved social skills, enhanced communication abilities, increased independence, reduced challenging behaviors, and better academic performance. This therapy emphasizes teaching and reinforcing positive behaviors while decreasing problem behaviors, ultimately helping children with autism reach their full potential. The specific benefits of ABA therapy can vary depending on the individual child and their unique needs and strengths.
ABA therapy employs various techniques to teach children with Level 2 Autism how to communicate effectively and appropriately. These techniques may include using visual aids, implementing structured teaching methods, and employing positive reinforcement to encourage desired communication behaviors. Through consistent and individualized ABA therapy sessions, children with Level 2 Autism can make significant improvements in their communication skills, leading to enhanced social interactions and overall quality of life.
There are effective strategies for managing challenging behaviors in children with Level 2 Autism using ABA therapy. These strategies focus on understanding the function of the behavior and implementing appropriate interventions. Common ABA strategies for managing challenging behaviors in children with autism include positive reinforcement, visual supports, social stories, and structured routines.
Parents searching for the right ABA therapy program for a child with Level 2 Autism should consider a few tips. Firstly, parents should research and identify reputable ABA therapy providers in their area. They can look for providers specializing in working with children with autism and having experience with Level 2 cases. Additionally, parents should inquire about the availability of parent training and involvement in the therapy process. This can help ensure that parents are equipped with the knowledge and skills to continue supporting their child's progress outside of therapy sessions.
Positive reinforcement techniques in ABA therapy for children with Level 2 Autism can include strategies such as token economies, where the child earns tokens or points for desired behaviors and can exchange them for preferred items or activities. Another technique is the use of social reinforcement, such as praise or verbal affirmations, to encourage and reinforce positive behaviors. Additionally, behavior contracts may be utilized, where the child agrees to work towards specific goals and is rewarded when those goals are met. The specific techniques used in ABA therapy may vary depending on the individual needs and goals of the child.
ABA therapy is a commonly used intervention for children with autism. It focuses on teaching skills and reducing problem behaviors through the use of systematic and evidence-based strategies. One of the goals of ABA therapy is to promote independence in children with autism. This can be achieved by implementing strategies that target specific skills such as self-care, communication, social skills, and academic skills. Strategies may include breaking down tasks into smaller steps, providing visual supports, using positive reinforcement, and teaching self-monitoring techniques. With consistent and individualized ABA therapy, children with Level 2 Autism can make significant progress in developing independence and functional skills
4. Strategies for Addressing Challenging Behaviors in Children with Level 2 Autism
Managing challenging behaviors in children diagnosed with level 2 autism necessitates a multi-pronged approach. A pivotal element is pinpointing the 'function' or the rationale behind the behavior, which can offer insights into the child's actions. Understanding the function of the behavior helps in devising strategies to effectively manage it. These strategies could include positive reinforcement to foster appropriate behaviors, teaching alternate behaviors to replace challenging ones, and modifying the environment to minimize potential triggers.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a crucial tool in this process, providing a structured method to manage these behaviors. This therapeutic approach aids in systematically addressing the behaviors and promoting positive behavioral changes.
In the context of managing challenging behaviors in children with level 2 autism, a case study underscoring the transformation of autism treatment through a goal-led approach is worth mentioning. This approach highlights the significance of early diagnosis, access to services, and the role of parents in providing care and advocating for their children.
The goal-led approach is designed to tackle subgoals, such as insurance authorization and early diagnosis, to ultimately enhance outcomes for individuals with autism and their families. The case study also underlines the benefits of goal-led collaboration and continuous optimization in achieving superior results. The potential impact of this transformation on the health and therapy industries is noteworthy.
Managing challenging behaviors in children with level 2 autism is a complex task. It requires a comprehensive understanding of the child's behavioral patterns and the implementation of effective strategies. ABA therapy, combined with a goal-led approach, can make a significant difference in this endeavor.
Implementing ABA therapy techniques can be effective in addressing challenging behaviors. These techniques involve using evidence-based strategies to modify behavior and teach new skills. ABA therapy focuses on breaking down behaviors into smaller components and using positive reinforcement to encourage desired behaviors. It also involves identifying antecedents and consequences that may be influencing the challenging behaviors.
Positive reinforcement strategies can be effective for managing challenging behaviors in children with level 2 autism. By providing rewards or incentives for desired behaviors, such as following instructions or using appropriate social skills, children with level 2 autism can be motivated to engage in more appropriate behaviors. This can help reduce the occurrence of challenging behaviors and promote positive behavior change.
To address challenging behaviors, it can be helpful to teach replacement behaviors. By teaching alternative behaviors that are more appropriate and functional, children with autism can learn to replace challenging behaviors with more acceptable ones. This can be done through various strategies such as visual supports, social stories, and positive reinforcement.
Managing challenging behaviors using ABA therapy involves implementing various best practices. These may include creating a structured environment, using visual supports and schedules, providing clear and consistent expectations, using positive reinforcement, and utilizing behavior intervention strategies such as functional behavior assessments and behavior plans. Regular monitoring and data collection can help track progress and make necessary adjustments to the intervention strategies.
In essence, ABA therapy, or Applied Behavior Analysis therapy, is commonly used to address challenging behaviors in children with autism. It focuses on understanding the function of these behaviors and developing strategies to modify them. By identifying the underlying reasons for challenging behaviors, such as communication difficulties or sensory issues, ABA therapists can design individualized interventions to teach more appropriate behaviors and reduce problem behaviors. Through consistent implementation of ABA strategies, children with level 2 autism can learn new skills and improve their overall behavior and functioning
5. Time Management and Prioritization Techniques for Parents Supporting Children with Level 2 Autism
Efficient time management and prioritization techniques are key to handling the multiple responsibilities entailed in supporting children with Level 2 Autism. Structuring each day with a well-devised routine, setting clear and achievable objectives, and ensuring time for self-care are fundamental aspects of this task. Flexibility is crucial, given that the effectiveness of strategies may vary from day to day.
It's been observed that children and teens on the autism spectrum often face challenges in their academic performance and motivation. High-functioning autistic children respond best when they are personally invested or interested in a task. Therefore, leveraging their unique interests can serve as a powerful motivator. Changing the perception around schoolwork can also make a significant difference. For instance, replacing the term "homework" with "study" can help reduce resistance.
Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) are known to experience boredom and anxiety, which can impact their motivation and engagement in schoolwork. To counter these challenges, teaching organizational skills and time management is of paramount importance. Breaking down tasks into smaller, manageable steps and setting achievable goals can make the workload less daunting. Implementing a token economy system, where desired actions are rewarded with tokens that can later be exchanged for preferred activities, can motivate children with ASD.
Visual aids like calendars or charts can be beneficial, helping children visualize their progress and achievements. However, it's essential to remember that some days may be more challenging than others, and patience and understanding are crucial. As one article aptly puts it, "The amount of benefit a daughter gets from finishing a homework assignment never outweighs the importance of the relationship." The parent-child relationship should always be prioritized above all.
In the context of low demand parenting, it's important to understand that traditional parenting techniques may not always be effective for children with pathological demand avoidance (PDA), a profile of autism. PDA is characterized by a strong drive for autonomy, and demands are often perceived as threats, triggering a fight, flight, or freeze response. Low demand parenting is a low arousal approach that focuses on reducing stress and anxiety levels in children with PDA. This strategy emphasizes trust, flexibility, collaboration, and a balanced approach to demands.
In summary, managing time effectively and prioritizing tasks can go a long way in supporting children with Level 2 Autism. Using their personal interests as motivators, teaching them organizational skills, implementing a token economy system, and using visual aids can significantly improve their academic performance and motivation. However, the parent-child relationship should always be the priority. Additionally, understanding the unique needs of children with PDA and adopting a low demand parenting approach can be beneficial in managing challenging behaviors
6. Enhancing Social Skills Development in Children with Level 2 Autism Using ABA Therapy
ABA therapy plays a vital role in enhancing social skills in children with level 2 autism. The therapy employs various methods like role-playing, social stories, and video modeling. These techniques aim to foster the understanding and navigation of social scenarios, enhance communication skills, and promote the formation of meaningful relationships.
Role-playing activities provide a safe and controlled environment for children to practice social interactions. They get to learn and practice skills such as turn-taking, initiating conversations, understanding non-verbal cues, and problem-solving. This hands-on approach builds their confidence and improves their social skills in real-life situations.
Social stories are another effective strategy in ABA therapy. These are short narratives providing information about specific social situations and the appropriate behaviors expected. By reading and discussing these stories, ABA therapists help children understand social cues, develop social skills, and improve their social interactions.
Video modeling, another widely used tool in ABA therapy, involves showing children a video of a desired social behavior or skill and encouraging them to imitate it. This method helps children learn and generalize social skills in a structured environment. By watching and imitating the modeled behaviors, they can develop new social skills and improve their social interactions.
Programs like Peers® for Preschoolers (P4P) are specially designed for young children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Studies have shown that these programs significantly improve the social skills of children with ASD. They underscore the importance of evidence-based interventions targeting social skill development in young children with ASD.
Caregiver-implemented interventions also play a vital role in enhancing social communication skills in toddlers and young children with autism. These involve a 4-week program offering individual coaching for caregivers and active engagement with the children. The results have shown improvements in social communication, receptive and expressive language, caregiver knowledge, and engagement.
ABA therapy emphasizes consistent practice and repetition, along with positive reinforcement, to help children with level 2 autism develop and improve their social skills. It creates a structured and supportive environment that encourages social interactions and provides opportunities for social skill development.
To sum up, ABA therapy, with its focus on behavior analysis and modification techniques, offers effective strategies for enhancing social skills in children with level 2 autism. These strategies and techniques, when implemented as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, can lead to improved social skills and increased social integration for children with level 2 autism
7. Navigating Support Services for Children with Level 2 Autism
For parents of children with Level 2 Autism, the journey towards securing the right support services can seem like a daunting maze. The path to success lies in understanding your child's rights, standing up for their needs with conviction, and seeking guidance from professionals and communities. A valuable resource in this journey can be found in ASD Media, which offers a wealth of information aimed at guiding parents through this intricate labyrinth.
Autism is a complex spectrum disorder, characterized by developmental delays, social skills deficiencies, sensory processing issues, and restrictive or repetitive behavior. Think of it as cracks in the foundation of a building; low support needs autism represents smaller cracks, while high support needs autism symbolizes larger, more significant cracks.
Children with Level 2 Autism face a variety of challenges such as developmental stagnation, difficulties with control and communication, cognitive rigidity, and sensory issues. Communication can often be a significant hurdle, akin to cultural and language differences when traveling to a foreign country. Sensory issues can also be a major concern, often feeling like one has been abruptly awakened after a mere three hours of sleep and expected to function normally.
Comprehending autism can be likened to understanding different languages or cultural norms. Individuals with high needs autism may struggle with being understood by others or understanding them. As stated, "Autism is like cracks in the foundation of a building, and we're trying to make the low support needs cracks smaller, but it's still important to recognize that high support needs cracks are large parts of the foundation crumbling."
ASD Media is a platform committed to providing resources and insights for high support needs autistic individuals. It offers an opportunity for these individuals to share their stories and experiences. This not only allows for a deeper understanding of what it's like to have high needs autism, but also facilitates more effective navigation of support services for children with Level 2 Autism.
Speech therapy can be beneficial for children with autism, aiding in the improvement of their communication skills, including speech and language development. Speech therapists employ various techniques and exercises to address specific communication challenges faced by children with autism. The ultimate goal of speech therapy for children with autism is to enhance their overall communication abilities and improve their quality of life.
To better understand your child's rights in autism services, it's important to access reliable information. Reputable websites provide resources and guidance for parents navigating autism support services.
They offer detailed information on the rights and entitlements of children with autism, including educational accommodations, therapy options, and advocacy resources. Connecting with local support groups or organizations that specialize in autism services can provide tailored information and support specific to your region. Professionals in the field, such as doctors or therapists, can offer expert advice and guidance on your child's rights in autism services.
Actively engaging with service providers, educators, and healthcare professionals allows parents to play a crucial role in advocating for their child's individual needs. This may involve attending meetings, voicing concerns, and requesting specific accommodations or interventions. Being well-informed about your child's rights and available services enables parents to effectively advocate for their child's needs in the context of autism services.
The ASD Media website contains resources related to autism support services. The site offers information on "unlocking the potential" and empowering parents to navigate autism support services. By accessing these resources, parents can empower themselves with knowledge and information to make informed decisions and access the appropriate support for their children.
Digital platforms providing unlimited access to information and resources related to autism support services can be a valuable tool. Subscribing to these platforms can provide valuable insights and resources that can assist individuals in their journey of navigating autism services
Conclusion
Children with Level 2 Autism require substantial support due to significant difficulties in social interaction and communication. They often exhibit inflexible behaviors, resistance to change, and a narrow range of interests. Understanding the intricacies of Level 2 Autism is crucial for caregivers and professionals in order to provide suitable support and interventions.
Throughout this article, we have explored the challenges faced by children with Level 2 Autism and discussed strategies such as low-demand parenting and various interventions that can help support their development and well-being. We have also delved into the role of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy in managing Level 2 Autism and enhancing social skills. Additionally, we have provided guidance on time management and prioritization techniques for parents supporting children with Level 2 Autism, as well as strategies for addressing challenging behaviors.
It is important to recognize that each child with Level 2 Autism is unique, and their needs may vary. However, by understanding their strengths, goals, and priorities, we can provide the right support and therapy to help them thrive. By implementing evidence-based strategies like ABA therapy, social stories, visual supports, and social skills training groups, we can enhance their social skills development and improve their overall quality of life.
Navigating support services for children with Level 2 Autism can be overwhelming for parents. However, there are resources available to guide them through this complex journey. Platforms like ASD Media offer valuable information and insights that can assist parents in advocating for their child's needs.
By understanding and addressing the unique needs of children with Level 2 Autism, we can create a supportive and inclusive environment that promotes their growth and development. It is important for parents, professionals, and communities to work together to ensure that these children receive the appropriate support services they need.
To learn more about supporting children with Level 2 Autism and accessing valuable resources, visit ASD Media. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of children with Level 2 Autism by providing the support they need to thrive




