Overview
The top benefits of an autism DNA test are profound, offering early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and a deeper understanding of family risk factors. Together, these elements support improved care and outcomes for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Imagine having critical insights that lead to timely interventions and tailored educational strategies. This not only empowers families but also fosters informed planning, creating a more supportive environment for those affected by autism. By understanding these benefits, we can collectively work towards nurturing the lives of individuals with ASD and their families.
Introduction
The intersection of genetics and autism is an evolving frontier that holds the promise of unlocking deeper insights into autism spectrum disorder (ASD). As research progresses, autism DNA testing emerges as a vital tool, revealing genetic variants that may inform diagnosis, treatment, and support strategies for individuals affected by ASD. This article explores the multifaceted benefits of genetic testing, from facilitating early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans to understanding family risk factors and enhancing educational strategies.
By delving into the implications of genetic insights, it becomes evident that these advancements not only empower families but also contribute to a broader understanding of autism. Ultimately, they foster improved care and support for those navigating the complexities of this condition. We invite you to join us on this journey of discovery, as we seek to understand and address the emotional and practical concerns surrounding autism, together.
Understanding Autism DNA Testing: An Overview
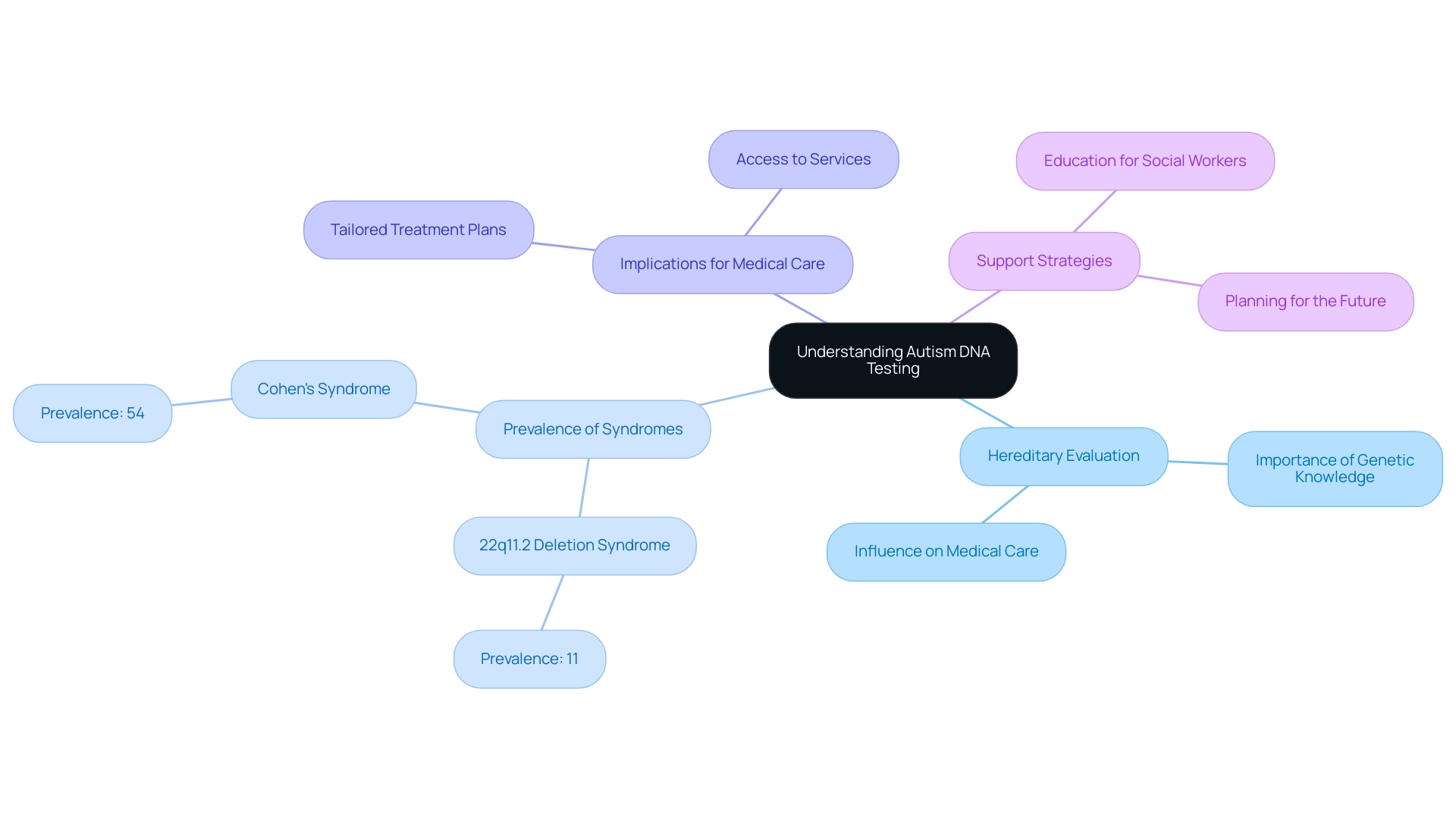
The autism DNA test plays a crucial role in analyzing hereditary material, revealing possible hereditary variants associated with spectrum disorder (ASD). This assessment method not only enhances our comprehension of the biological processes linked to the condition, but also provides families and healthcare providers with important insights. For instance, understanding a hereditary cause can significantly inform medical care, especially for patients whose variations affect multiple organ systems. As Susanna B. Mierau from the Massachusetts General Hospital Lurie Center for Autism highlights, this understanding is vital.
It's important to note that prevalence estimates for developmental disorders fluctuate greatly among hereditary syndromes, with 11% in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome and 54% in Cohen's syndrome. This variation underscores the significance of hereditary evaluation in recognizing these conditions. By investigating specific genes, healthcare providers can gather critical information that may influence diagnosis, treatment plans, and support strategies tailored to individual needs. Moreover, recognizing the foundational aspects of autism DNA test analysis is essential for both parents and professionals, as it establishes a framework for appreciating its potential benefits in effectively managing autism.
The implications of these advancements are profound, highlighting the urgent need to improve awareness and access to hereditary assessments, particularly among adults with ASD. This effort is crucial to enhance care and support throughout their lives. By clearly linking these advantages to the enhancement of medical care and access to services for adults with ASD, we emphasize the importance of hereditary analysis in meeting their specific requirements. Together, we can foster a deeper understanding and create a more supportive environment for those affected by autism.
1. Early Diagnosis: Unlocking Timely Interventions
One of the most significant benefits of hereditary testing for developmental disorders is its ability to facilitate early diagnosis. By identifying hereditary markers associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) through an autism DNA test, healthcare professionals can accelerate assessments and interventions. Early diagnosis is essential, as it enables families to access vital therapies and support services sooner, ultimately improving developmental outcomes.
Research findings highlight that children diagnosed early often show enhancements in communication, social skills, and behavioral management, which can lead to a notably improved quality of life. Furthermore, a 2013 study indicated that children diagnosed with ASD at an early stage are less likely to receive a subsequent ADHD diagnosis, underscoring the importance of timely intervention. According to Luke Grosvenor, PhD at Kaiser Permanente Northern California, 'Your final point about social work interventions and holistic care highlights an important opportunity for future researchers to use our findings to motivate greater evaluation of the many types of services that can be provided, including outside of the traditional healthcare setting.'
This illustrates that early recognition through an autism DNA test not only paves the way for prompt interventions but also nurtures a more holistic approach to care, ensuring that families receive the varied support they need. Additionally, utilizing effective screening tools and methods, as discussed in case studies on ASD diagnosis, can further enhance the likelihood of timely referrals for formal evaluations, ensuring that children receive appropriate diagnosis and interventions.
2. Personalized Treatment Plans Based on Genetic Insights
DNA analysis offers invaluable insights into hereditary variants that can significantly influence how a child responds to various therapeutic methods. For example, the estimated values of Θ opt were -0.842 with a 95% CI of (-2.657, -0.441), while Θ alt was -0.765 with a 95% CI of (-2.362, 0.134). These findings highlight the nuanced understanding that testing provides for treatment planning. This information empowers healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans that cater to the unique needs and strengths of each child diagnosed with a developmental disorder, such as through the use of an autism DNA test.
By understanding a child’s hereditary profile, professionals can better identify which behavioral therapies or educational strategies will yield the most favorable outcomes. In line with this, Jeon et al. (2018) reported the use of expanded risk prediction models, which can be tailored to effectively personalize autism therapies.
Recent advancements in hereditary research underscore the importance of continuous health monitoring. When combined with hereditary assessments, this approach can lead to timely interventions that enhance the developmental trajectory of children. For instance, a case study comparing treatment allocation strategies demonstrated the clinical effectiveness of individualized treatment approaches over standard methods. This provides valuable insights into the potential benefits of tailored interventions. By aligning strategies with these biological insights, families can improve their methods of supporting their child's development and education.
As specialists in the field continue to advocate for the integration of hereditary data, such as the autism DNA test, into developmental disorder therapy, the path toward more efficient, personalized treatment strategies becomes increasingly clear. Together, we can foster a supportive environment that nurtures every child's unique journey.
3. Understanding Family Risk Factors for Informed Decisions
Genetic testing for conditions like autism, such as an autism DNA test, offers invaluable insights into family risk factors. By identifying genetic predispositions, these tests can inform parents about the likelihood of this disorder manifesting in future children. Current statistics reveal that the familial recurrence rate for a new baby boy is notably higher at 25%, compared to 13% for a baby girl. This disparity aligns with observations made by Sally Ozonoff, a distinguished professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, who notes:
This is in line with the fact that boys are diagnosed with this condition about four times as often as girls in general.
Additionally, children undergo routine developmental assessments, with diagnostic information reported to the Patient Register, ensuring comprehensive tracking of ASD diagnoses. A recent case study highlighted a significant increase in diagnosis rates of developmental disorders, with current estimates showing about 1 in 36 children diagnosed, compared to 1 in 68 in 2011. This trend underscores the importance of understanding the factors that affect autism diagnosis and recurrence among relatives.
Moreover, results indicate that both hereditary and non-hereditary elements play a role in the risk of developing ASD, offering essential insights for parental guidance. With this knowledge, parents can make informed planning decisions, preparing for potential challenges while ensuring they provide the necessary support for all siblings. Understanding these hereditary risk factors not only aids in predicting developmental disorders but also emphasizes the importance of resources and focus for each child within the family structure. Ultimately, this fosters an atmosphere of support and empathy, nurturing the well-being of every family member.
4. Guiding Educational Strategies for Enhanced Learning
The autism DNA test serves as a vital resource in crafting effective educational strategies for children with autism. By exploring a child's hereditary profile, educators can customize their teaching methods to align more closely with the individual's unique strengths and challenges. For instance, research shows that certain genetic variants are linked to specific learning difficulties, underscoring the importance of personalized education.
In Arizona, a monitoring site reported a prevalence of 26.8 per 1,000 for ASD among children aged 8 years in the American Indian/Alaska Native population. This statistic highlights the urgent need to address these challenges. By understanding these connections, educators can implement targeted interventions that directly tackle these issues. This personalized approach not only enriches the overall learning experience but also fosters a more inclusive educational environment.
Moreover, the complexities surrounding autism are reflected in case studies like 'The Indiana Autism Puzzle,' which illustrate rising prevalence rates and the critical need for tailored support systems. As Jakob Grove, an associate professor in biomedicine, notes, both autism and related conditions frequently involve social inhibition and communication difficulties. This emphasizes the necessity for strategies that incorporate biological insights, particularly when tailoring educational approaches.
By integrating the autism DNA test into educational frameworks and recognizing the effectiveness of ABA interventions through social validity assessments, we can pave the way for more effective, individualized learning strategies that address the diverse needs of autistic children. Together, let’s create a supportive environment that nurtures every child's potential.
5. Emotional Support: Reducing Uncertainty for Families
Navigating the intricacies of neurological differences can feel overwhelming for families, often filled with uncertainty and anxiety. However, DNA analysis through an autism DNA test offers a pathway to understanding by identifying possible hereditary factors of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). This newfound clarity can significantly ease parental anxiety, empowering families with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
Research indicates that:
- 48% of parents believe extensive DNA analysis should occur when a child’s development diverges.
- 36% advocate for evaluation before pregnancy.
Importantly, four studies were categorized as favorable regarding the effectiveness of hereditary analysis, while 26 showed mixed outcomes; none were deemed unfavorable. As Katerina Dounavi from the School of Social Sciences, Education & Social Work at Queen's University of Belfast notes, parents generally view the autism DNA test positively, appreciating its capacity to clarify the reasons for ASD, assist in family planning, and facilitate early access to interventions.
The emotional reassurance gained from understanding hereditary factors can cultivate a sense of control, allowing families to focus on effective support strategies rather than feeling overwhelmed by the unknown. This empowerment is vital for mental health, as it can lead to improved coping strategies and proactive approaches to managing the condition within the family. Future research should aim to capture diverse parental perspectives and enhance healthcare professionals' knowledge on ASD screening.
A compelling case study titled 'Advantages of Genetic Analysis for ASD' illustrates that parents firmly believe an autism DNA test could enhance family planning and early intervention strategies, reinforcing the theme of emotional support.
6. Contributing to Autism Research: The Bigger Picture
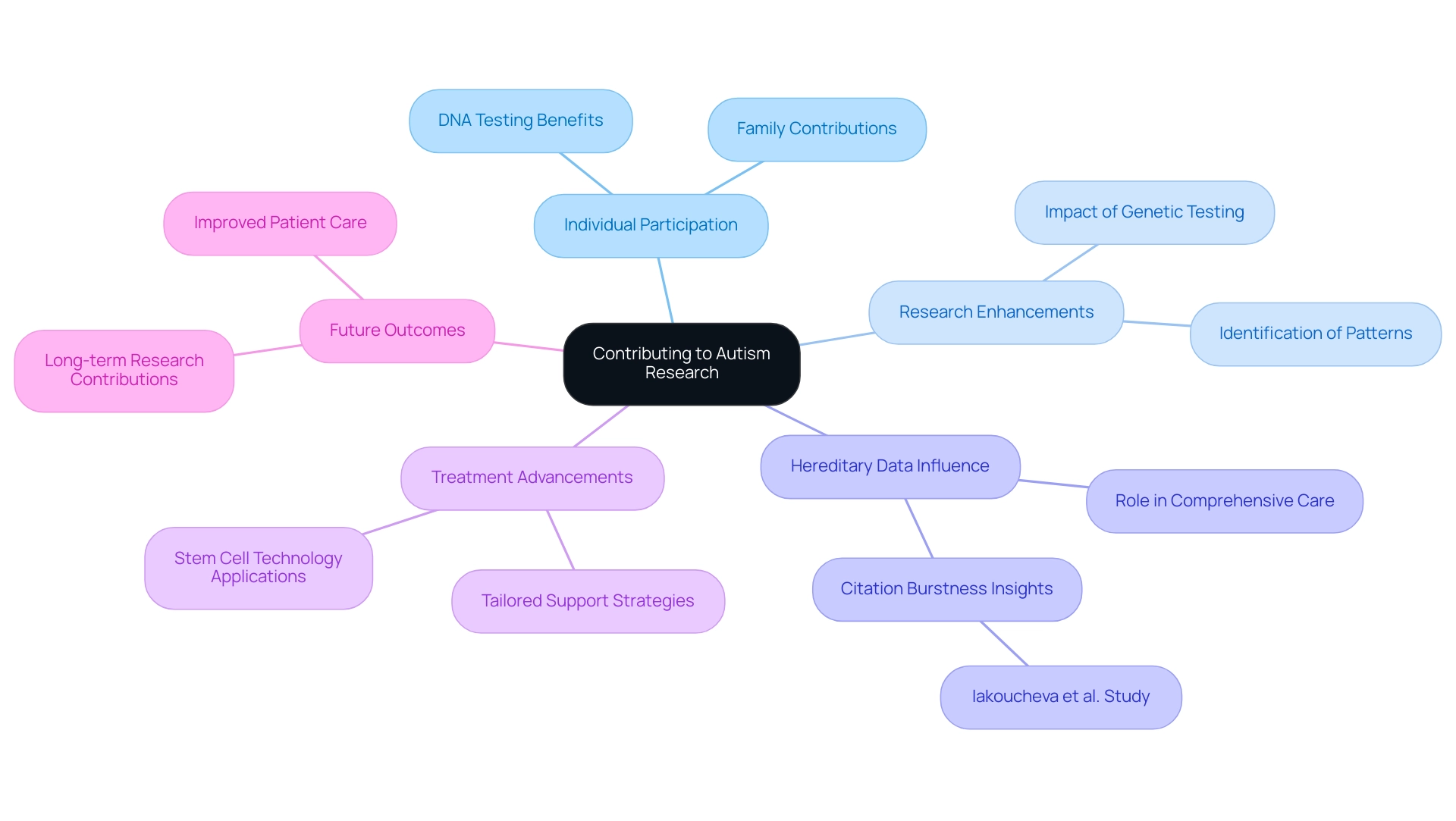
Participating in an autism DNA test related to developmental disorders brings significant advantages, not just for individual families but also for the broader research community. Each hereditary test result, including the autism DNA test, enhances our collective understanding of autism's biological foundations. This knowledge enables researchers to identify critical patterns and potential risk factors associated with the condition. Recent findings reveal that patients without hereditary examination information had fewer years documented by ASD clinic records compared to those who underwent assessment. This underscores the vital role of hereditary data in providing comprehensive care.
Moreover, the citation burstness by Iakoucheva et al., with a strength of 8.080, highlights the substantial influence and originality of hereditary examination research in the field. As Ann M Neumeyer observes,
Awareness of a hereditary cause of ASD can inform medical care, particularly for patients in which the hereditary variant affects multiple organ systems.
This wealth of knowledge, combined with research on stem cell technology, showcases the practical applications and advancements arising from hereditary analysis. Such progress paves the way for significant developments in treatment methods and support strategies tailored for individuals with developmental disorders.
By participating in the autism DNA test and genetic testing, families not only contribute to ongoing research but also help shape the future of autism studies. This involvement ultimately fosters improved outcomes for generations to come. Together, we can make a difference.
Conclusion
The exploration of autism DNA testing reveals its transformative potential in understanding and addressing autism spectrum disorder (ASD). By facilitating early diagnosis, genetic testing allows for timely interventions that can significantly enhance developmental outcomes for children. This ability to identify specific genetic variants empowers healthcare professionals to tailor personalized treatment plans, ensuring that each child receives the most effective support based on their unique needs.
Moreover, genetic insights into family risk factors provide parents with critical information that aids in informed decision-making regarding family planning and resource allocation. This understanding not only prepares families for potential challenges but also fosters a supportive environment for all children. In educational settings, the integration of genetic testing can guide the development of customized teaching strategies, enhancing the learning experience for children with autism.
The emotional support provided by genetic testing cannot be overstated, as it alleviates uncertainty and empowers families to take proactive steps in managing autism. This sense of control promotes mental well-being and encourages families to focus on effective support strategies. Lastly, the contributions of genetic testing extend beyond individual families, enriching the broader autism research community. Each test result adds to the collective understanding of autism's genetic landscape, paving the way for future advancements in treatment and care.
In summary, the multifaceted benefits of autism DNA testing underscore its crucial role in improving diagnosis, treatment, and support for individuals with ASD and their families. As research continues to evolve, embracing genetic insights will only enhance the care and understanding of autism, ultimately fostering a more inclusive and supportive society for those affected by this complex condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of the autism DNA test in understanding autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
The autism DNA test analyzes hereditary material to reveal possible hereditary variants associated with ASD, enhancing our understanding of the biological processes linked to the condition and providing important insights for families and healthcare providers.
How does hereditary evaluation impact medical care for individuals with ASD?
Understanding hereditary causes can significantly inform medical care, especially for patients whose variations affect multiple organ systems, allowing for tailored diagnosis, treatment plans, and support strategies.
What are the prevalence rates of developmental disorders among hereditary syndromes?
Prevalence estimates for developmental disorders vary significantly, with 11% in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome and 54% in Cohen's syndrome, highlighting the importance of hereditary evaluation in recognizing these conditions.
Why is early diagnosis crucial for children with autism spectrum disorder?
Early diagnosis through hereditary testing can facilitate quicker assessments and interventions, allowing families to access vital therapies and support services sooner, which ultimately improves developmental outcomes.
What improvements can be seen in children diagnosed early with ASD?
Research indicates that children diagnosed early often show enhancements in communication, social skills, and behavioral management, leading to a notably improved quality of life.
How does early diagnosis affect the likelihood of receiving a subsequent ADHD diagnosis?
A 2013 study found that children diagnosed with ASD at an early stage are less likely to receive a subsequent ADHD diagnosis, emphasizing the importance of timely intervention.
What is the significance of holistic care in the context of autism?
Early recognition through an autism DNA test nurtures a holistic approach to care, ensuring that families receive varied support beyond traditional healthcare settings.
How can effective screening tools enhance the diagnosis process for ASD?
Utilizing effective screening tools and methods can improve the likelihood of timely referrals for formal evaluations, ensuring that children receive appropriate diagnosis and interventions.




