Overview
The article discusses the significant increase in autism diagnosis rates from 1 in 150 in 2000 to 1 in 36 in 2023, attributing this rise to improved diagnostic practices, greater awareness, and socio-environmental factors. This trend underscores the need for enhanced resources and support systems for families, as well as the importance of addressing disparities in diagnosis and treatment across different socioeconomic backgrounds.
Introduction
The landscape of autism diagnoses has undergone a remarkable transformation over the past two decades, revealing a surge in prevalence that reflects both heightened awareness and evolving diagnostic criteria. With approximately 1 in 36 children diagnosed with autism in 2023, the implications of this trend extend far beyond mere statistics; they touch the lives of families, educators, and communities alike.
As parents navigate the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder, understanding the factors driving this increase becomes crucial. From the impact of socioeconomic disparities to the evolving educational landscape, the challenges are significant but not insurmountable.
This article delves into the multifaceted nature of autism diagnoses, exploring the underlying factors and their implications for society, while empowering parents with the knowledge needed to advocate effectively for their children’s needs.
Trends in Autism Rates: A 23-Year Overview
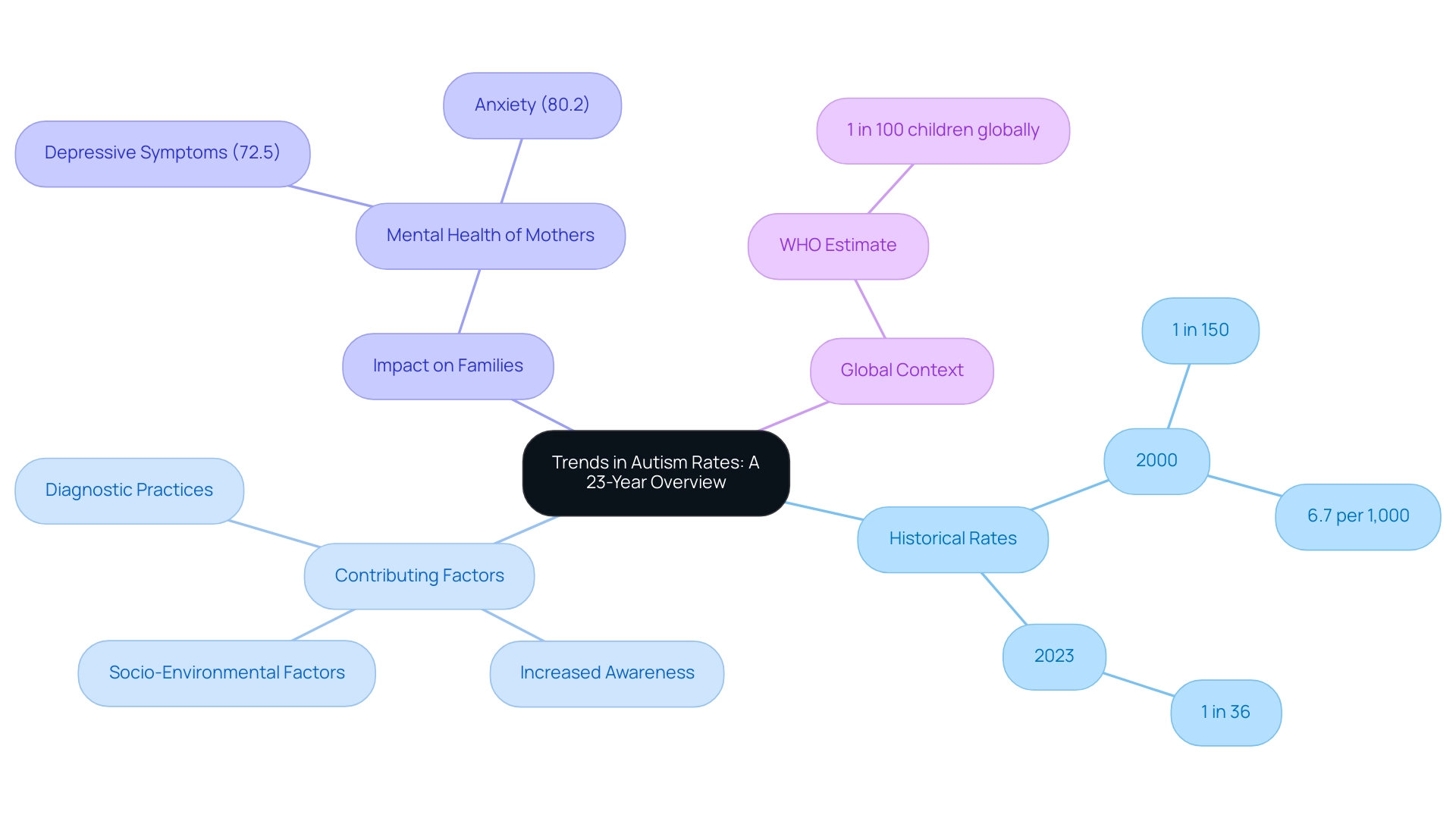
Over the past 23 years, the diagnosis of the condition has surged dramatically, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has reported autism rates by year, showing a prevalence of approximately 1 in 36 youths diagnosed in 2023, which is a marked increase from 1 in 150 in 2000, translating to 6.7 per 1,000 youths. This upward trend can be largely attributed to advancements in diagnostic practices, increased awareness among parents and professionals regarding the signs and symptoms of the condition, and various socio-environmental factors. As the World Health Organization estimates that 1 in every 100 youths globally has autism, this highlights a critical need for increased resources and support systems tailored for families navigating the complexities of autism.
Notably, a recent study emphasizes what many parents instinctively understand: it is indeed possible for individuals to thrive even while continuing to meet the criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). However, the journey can be challenging, as demonstrated by a case study revealing that mothers of autistic individuals report high levels of anxiety and depressive symptoms, with:
- 72.5% experiencing depressive symptoms
- 80.2% experiencing anxiety
This encouraging perspective reinforces the importance of fostering supportive environments for our children and advocating for the necessary resources to help them succeed.
Factors Driving the Increase in Autism Diagnoses
The terrain of developmental disorders has changed considerably, shaped by numerous interrelated elements. A pivotal change occurred with the introduction of the DSM-5 in 2013, which streamlined previous diagnostic categories into a unified Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) classification. This evolution in criteria has broadened the spectrum of individuals identified with the condition, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of it.
Moreover, heightened awareness and advocacy initiatives have empowered parents to actively pursue evaluations for their offspring, resulting in earlier and more frequent diagnoses. As Murphy D. from the NIHR Journals Library notes,
Nearly half of young adults with an ASD do not meet DSM-V criteria, according to ICD-10,
emphasizing the importance of understanding these diagnostic nuances. Notably, one-quarter of individuals diagnosed with an ICD-10 AND would not qualify for either AND or SCD under the DSM-V, highlighting inconsistencies in diagnostic criteria.
Recent research also indicates potential genetic and environmental influences on the prevalence of this condition, inviting further investigation into these factors. Additionally, a case study examining demographic variability revealed critical insights:
- Individuals with intellectual disabilities and those experiencing developmental regression are more likely to meet DSM-5 criteria,
- Variations observed based on sex and race/ethnicity.
This underscores the significance of considering demographic factors in prevalence estimates and diagnostics, ultimately guiding effective treatment planning by BCBA or qualified Program Supervisors through targeted interviews and observations.
Furthermore, the review offers suggestions for future research designs for ASD prevalence studies, ensuring ongoing advancements in understanding the condition. Such thorough comprehension not only guides assessment but also aids the endeavors of Parent Advocates in navigating the intricacies of the condition for their children.

Implications of Rising Autism Rates on Society and Education
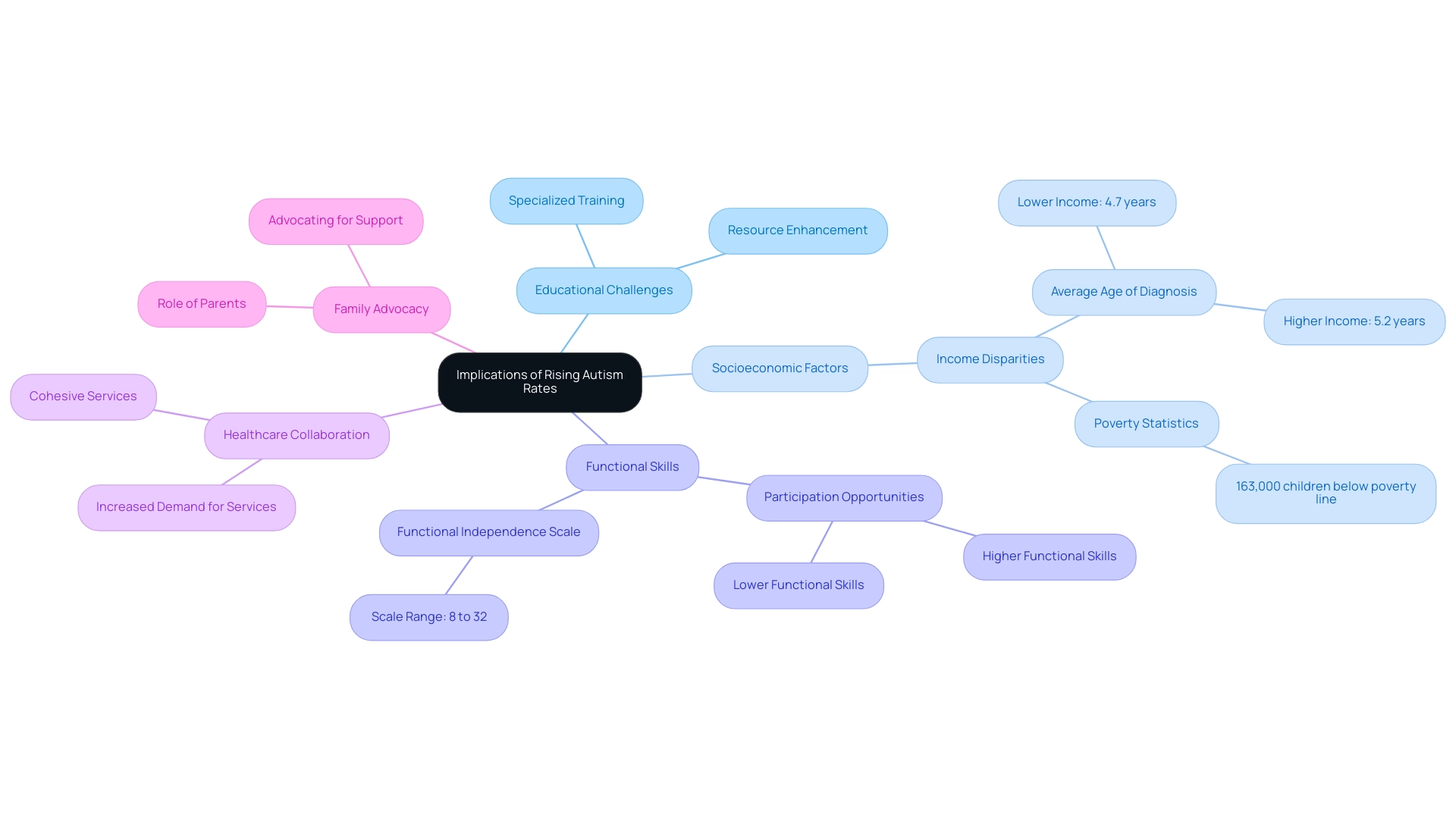
The rising prevalence of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) presents profound implications for both society and educational systems. As the number of assessments rises, schools are faced with the challenge of accommodating a broader range of learning needs. This necessitates not only specialized training for educators but also a significant enhancement of resources dedicated to support services.
In fact, data reveals that in 2009, approximately 163,000 individuals with ASD lived below the federal poverty line, indicating that socioeconomic factors compound the difficulties faced in educational settings. Furthermore, insights from the National Survey of Children’s Health (2016-2019) indicate that the average age of diagnosis for youths from lower-income households is 4.7 years, in contrast to 5.2 years for those from higher-income families, emphasizing disparities that must be tackled.
Furthermore, it is important to consider the functional independence scale, which ranged from 8 to 32 and was quartiles for analysis. This scale helps to clarify the relationship between functional skills and participation in education and employment among youth with ASD. Research indicates a strong correlation between family income, functional skills, and participation.
The case study titled 'Influence of Family Income and Functional Skills on Participation' illustrates this correlation, demonstrating that youth with higher functional skills and family income have greater participation opportunities, while those with lower resources and skills face significant barriers.
Moreover, the healthcare system must evolve to meet the increasing demand for autism-related services, which calls for cohesive collaboration between healthcare providers, educators, and families. Parents play a crucial role in advocating for their offspring's needs, ensuring they receive the necessary support to thrive in both educational and social environments. By understanding these dynamics and actively participating in discussions about educational policies and resource allocation, parents can help secure the interventions that will enable their children to succeed.
It is also essential to acknowledge the data limitations, including the small number of students from jurisdictions outside the 50 states and the District of Columbia, which may impact the generalizability of findings. By addressing these limitations, we can enhance the credibility and transparency of our discussions regarding the implications of autism rates by year.
Conclusion
The significant rise in autism diagnoses over the past two decades underscores a critical need for comprehensive understanding and support for affected families. With the prevalence now at approximately 1 in 36 children, it is evident that increased awareness, evolving diagnostic criteria, and socio-environmental factors play vital roles in this trend. Parents are not only navigating the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder but are also empowered to advocate for their children’s needs, fostering environments where children can thrive despite the challenges they may face.
The interconnected factors influencing autism diagnoses highlight the importance of adapting educational and healthcare systems to better serve families. The shift to a unified Autism Spectrum Disorder classification has broadened the understanding of autism, yet disparities in diagnosis and support remain, particularly among different socioeconomic groups. As educators and healthcare providers work collaboratively to enhance resources and training, parents are encouraged to actively participate in discussions that shape policies and interventions, ensuring that their children's unique needs are met.
In conclusion, the implications of rising autism rates extend beyond statistics; they demand a collective response from society, educators, and families. By advocating for equitable access to resources and support, parents can play a pivotal role in creating a future where children with autism are recognized for their potential and provided with the opportunities necessary to succeed. Embracing this journey together fosters a more inclusive society, benefiting not only children with autism but also the communities they enrich.
Frequently Asked Questions
What has been the trend in autism diagnoses over the past 23 years?
The diagnosis of autism has surged dramatically, with the CDC reporting a prevalence of approximately 1 in 36 youths diagnosed in 2023, up from 1 in 150 in 2000.
What factors contribute to the increasing rates of autism diagnoses?
The upward trend in autism diagnoses can be attributed to advancements in diagnostic practices, increased awareness among parents and professionals regarding the signs and symptoms, and various socio-environmental factors.
How does the global prevalence of autism compare to the rates in the U.S.?
The World Health Organization estimates that 1 in every 100 youths globally has autism, which highlights the need for increased resources and support systems for families affected by autism.
Can individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) thrive despite their diagnosis?
Yes, it is possible for individuals to thrive while continuing to meet the criteria for ASD, although the journey can be challenging for both the individuals and their families.
What mental health challenges do mothers of autistic individuals face?
A recent study found that mothers of autistic individuals report high levels of anxiety and depressive symptoms, with 72.5% experiencing depressive symptoms and 80.2% experiencing anxiety.
Why is it important to foster supportive environments for children with autism?
Fostering supportive environments is crucial for helping children with autism succeed and for advocating for the necessary resources to assist families navigating the complexities of autism.




