Overview
The article "Caring Insights on Joint Attention and Autism: A Guide for Caregivers" emphasizes the vital role caregivers play in nurturing joint attention skills in children with autism. These skills are essential for fostering communication and social interactions. By employing strategies such as visual supports and engaging in interactive play, caregivers can significantly enhance their child’s social abilities and language development. Research supports these methods, indicating their effectiveness in promoting growth in children with autism.
For caregivers, understanding how to support these skills can feel overwhelming at times. It’s important to recognize that you are not alone in this journey. Many parents face similar challenges, and sharing experiences can be incredibly beneficial. By using visual aids and incorporating play into daily routines, you can create a nurturing environment that encourages your child to engage and connect.
As you explore these strategies, consider reaching out to local support groups or online communities where you can share your experiences and learn from others. Together, we can foster a supportive network that empowers caregivers and enriches the lives of children with autism. Remember, your efforts make a difference, and every small step counts in this journey.
Introduction
In the intricate landscape of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), joint attention stands out as a cornerstone of effective communication and social interaction. This vital skill, where two individuals focus on the same object or event, lays the groundwork for meaningful connections and language development in children with autism. As research continues to unveil the profound impact of joint attention on social engagement, caregivers are increasingly recognizing its significance. By implementing targeted strategies and interventions, they can create an environment that nurtures joint attention and enhances their child's overall developmental journey.
This article delves into the multifaceted role of joint attention, exploring its implications and challenges. We will discuss effective approaches to support children with autism as they navigate their path toward improved communication and social skills. Together, let’s uncover how fostering joint attention can lead to brighter connections and a deeper understanding of our children’s needs.
Understanding Joint Attention: A Key Component in Autism
Joint focus is the remarkable ability of two individuals to concentrate on the same object or event, sharing their awareness for meaningful social interaction. This skill is particularly vital for effective communication and social engagement, especially for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), as it is closely tied to joint attention and autism. For caregivers, understanding shared focus is essential, as it lays the groundwork for nurturing social skills and language development in their children.
Research shows that difficulties in mutual awareness can significantly impede a young person's ability to connect with others, underscoring the importance of joint attention and autism in support strategies. A study utilizing eye-tracking technology revealed that specific signals can enhance joint attention and autism in youth with ASD during virtual games. This suggests that targeted interventions can foster social involvement. Similarly, a case study titled 'The Impact of Cues on Collaborative Focus in Youth with Autism Spectrum Disorder' demonstrated that particular cues can greatly improve joint attention and autism, pointing to potential methods for increasing social engagement among youth with autism.
Moreover, expert opinions emphasize the critical role of shared focus in child development, highlighting its contribution to improving communication skills. Recent findings indicate that the left thalamus is a significant predictor of ASD, reinforcing the relevance of joint attention and autism, with a p-value of 0.019, which points to the neurological underpinnings of shared focus deficits. Caregivers can adopt effective collaborative focus strategies, such as utilizing visual signals and engaging in shared activities, to enhance interaction and communication.
By prioritizing shared focus, caregivers can cultivate enriching environments that support their children's social and communicative growth, ultimately fostering their overall development. Future research should aim to validate measurement tools and explore the effectiveness of interventions in natural settings to further refine collaboration strategies.
The Importance of Joint Attention in Child Development
Shared focus is a fundamental component in youth development, playing a crucial role in language learning, social abilities, and cognitive advancement. For youngsters with autism, developing joint attention can significantly enhance their communication skills and interactions with peers and caregivers. In fact, statistics show that 94% of researchers evaluate the effectiveness of collaborative strategies as excellent or good in improving communication skills among children with autism. This underscores how vital joint attention is in enriching these interactions.
Participating in collaborative focus activities not only promotes shared experiences but also enhances joint attention, which is essential for understanding social signals and forming meaningful relationships. Caregivers can enhance implicit learning by directing focus to illustrations, making it crucial to prioritize shared focus in daily interactions.
Activities that encourage joint attention, such as:
- Shared reading
- Interactive play
- Responsive communication
can significantly influence a child's developmental path. For example, a study analyzing shared focus performance in preschool-aged boys with autism and fragile X syndrome revealed that while overall performance was similar, boys with fragile X syndrome exhibited higher shared focus scores when accounting for age, non-verbal IQ, and autism symptom severity. This highlights the subtle connections between joint attention and language skills.
Experts emphasize that joint attention is not merely a skill but an essential element of social learning. As development expert Angela John Thurman observed, "Although overall shared focus performance was similar across the groups, shared focus scores were higher for boys with fragile X syndrome when controlling for the influences of age, non-verbal IQ, and autism symptom severity." This insight underscores the importance of shared focus, particularly in the context of joint attention for social learning.
By integrating practices that promote joint attention into daily activities, caregivers can greatly impact their child's ability to navigate social exchanges and develop important language skills. This nurturing approach can make a significant difference in their developmental journey.
Challenges in Joint Attention for Children with Autism
Children with autism often face significant challenges in developing joint attention and autism skills, which are essential for effective communication and social interaction. These challenges can manifest as difficulties in initiating or responding to collaborative engagement requests, such as making eye contact or indicating objects of interest. Research indicates that a considerable percentage of individuals with autism struggle with skills related to joint attention, contributing to social isolation and communication barriers.
For instance, a longitudinal study highlighted the limited research focusing on infants at familial risk for autism, emphasizing the need for further exploration into collaborative development over time. This research included 101 infants, with 20 later identified with ASD, employing MRI scans and behavioral evaluations to examine the connection between brain volumes and ASD diagnosis.
Recognizing these difficulties is crucial for caregivers who seek to implement effective methods that enhance their children's collaborative focus development. Timely assistance that emphasizes joint attention has been shown to improve social abilities and the overall quality of life for vulnerable youth. Experts in the field stress that nurturing joint attention can lead to better outcomes in social interaction and communication.
To address shared focus challenges, caregivers can utilize several techniques:
- Modeling Behavior: Demonstrating shared focus through common activities can encourage children to engage.
- Using Visual Supports: Incorporating visual aids, such as images or videos, can help children understand and respond to shared focus signals.
- Creating Engaging Environments: Establishing play scenarios that naturally foster shared focus can enhance interaction.
Statistics reveal that the net dwell time of toddlers with autism is significantly higher in settings that promote shared focus, underscoring the importance of context in developing these abilities. As Valsamma Eapen noted, the authors acknowledge the financial support of the Cooperative Research Center for Living with Autism (Autism CRC), which emphasizes the significance of the research findings discussed. By understanding and addressing the common challenges associated with joint attention, caregivers can play a pivotal role in their children's development, paving the way for enhanced social interactions and communication skills.
Effective Strategies to Enhance Joint Attention Skills
Improving shared focus abilities in children with autism can be achieved through several effective strategies that caregivers can easily implement.
- Follow the Youngster's Lead: Begin by paying close attention to your child's interests and activities. Engaging with what captivates them fosters a natural connection that encourages shared attention.
- Use Visual Supports: Visual aids, such as pictures or objects, can significantly enhance focus and facilitate shared experiences. These supports guide your child's attention and make interactions more engaging.
- Model Shared Focus: Actively demonstrate shared focus behaviors. This includes pointing to objects of interest and maintaining eye contact during play. By modeling these behaviors, you provide a clear example for your child to follow.
- Engage in Interactive Play: Choose games that promote turn-taking and shared experiences, such as rolling a ball back and forth. These activities not only improve shared focus but also strengthen social skills through collaborative play.
- Narrate Actions: As you engage in activities, narrate your actions to your child. This verbal interaction encourages them to respond and participate, enhancing their understanding of mutual focus.
Research indicates that incorporating parent-mediated collaborative focus interventions into early support programs can lead to significant improvements in children's language and social skills, especially in the realm of joint attention and autism. For instance, studies have shown a strong positive correlation between these interventions and learning outcomes, with Pearson Phi coefficients reflecting a robust association. Antonio Ferrer notes that enhancing joint attention in children on the autism spectrum can be effectively supported through interventions mediated by augmented reality technology.
Moreover, case studies underscore the importance of visual aids in enhancing mutual focus, demonstrating their practical application in everyday interactions. The evaluation titled 'Implications for Future Research' highlights the necessity of integrating collaborative focus training into early assistance programs and involving parents in the intervention process.
By implementing these approaches, caregivers can make a meaningful difference in improving collaborative focus abilities, ultimately supporting their child's growth and social interaction.
Therapeutic Approaches to Support Joint Attention Development
A variety of therapeutic methods can significantly support the development of focus in children with autism, particularly those that emphasize joint attention. Among these, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy stands out with its structured interventions aimed at enhancing these vital skills. Research indicates that ABA therapy not only improves focus but also fosters greater social involvement, which is essential for understanding joint attention in autism, as highlighted by experts in the field. McAuliffe et al. observed that Relationship Development Intervention (RDI) is beneficial in enhancing the social engagement of autistic youth, including parent-child interactions, while also enriching the parenting experience.
Several key methods complement ABA therapy in promoting shared focus:
- Natural Language Acquisition (NLA) emphasizes natural interactions, encouraging communication and shared focus—both crucial for joint attention in autism. By embedding learning within familiar contexts, children are more likely to generalize these skills.
- The Developmental, Individual Difference, Relationship-Based (DIR) Model focuses on the emotional and relational aspects of development, particularly in joint attention. By engaging children in play, the DIR model nurtures joint attention, fostering deeper connections and more meaningful interactions.
- Parent-Mediated Interventions train parents to encourage shared focus during everyday activities, showing great promise. These interventions empower parents to create opportunities for collaborative engagement, effectively enhancing their children's skills in joint attention within a supportive environment.
A systematic review registered with PROSPERO (CRD42020206439) synthesizing findings from 27 studies underscores the effectiveness of these interventions, particularly those that utilize play as a context and involve natural communication partners. The review emphasizes the importance of aligning shared focus behaviors with natural contingencies, indicating that tailored strategies can lead to improved outcomes in joint attention for individuals with autism. As the field evolves, ongoing research will be crucial in refining these strategies to meet the diverse needs of young people and their families.
Additionally, a recent article titled 'Interventions for Preschoolers with ASD,' published on January 15, 2024, highlights the latest advancements in joint attention and autism, ensuring the content remains timely and relevant. Together, these insights provide a pathway for parents seeking effective strategies to support their children’s development.
The Link Between Joint Attention and Communication Skills
Shared focus is a cornerstone of joint attention and autism, playing a vital role in the development of communication skills in young children. Research indicates that children with strong shared focus abilities are significantly more likely to cultivate effective verbal and non-verbal communication skills, especially within the context of joint attention and autism. This connection appears in various forms, such as sharing information, taking turns in conversations, and interpreting social cues.
For instance, studies have shown that toddlers with autism exhibit longer net dwell durations in environments that foster shared focus. Notably, net dwell durations were significantly higher in Conditions 4 and 3 compared to Condition 1. This suggests that these interactions enhance their engagement and learning.
Caregivers can actively nurture shared focus through engaging play and attentive interactions, which are essential for developing communication skills. Activities that encourage turn-taking or shared focus not only strengthen the bond between caregiver and child but also promote improved social engagement and language development. Furthermore, specialists emphasize that early skills in joint attention and autism are crucial in shaping the initial signs of autism. As Maite Montagut-Asuncion aptly noted, 'In conclusion, early abilities in joint attention and autism played a crucial role in defining early signs of ASD.' This underscores the importance of targeted interventions.
Case studies reveal significant positive associations between visual focus and various clinical traits, including cognitive and language abilities in toddlers with autism. Specifically, the study titled "Correlations Between Visual Focus and Clinical Characteristics" found that enhancements in visual focus were linked to improvements in cognitive and language skills. These findings suggest that fostering joint attention and autism can lead to advancements in both visual perception and overall communication skills.
By prioritizing joint attention and autism in therapeutic settings, caregivers can unlock the potential for better communication outcomes in children with autism. Additionally, future research should aim to explore larger samples and incorporate advanced techniques for early detection, highlighting the ongoing need for research in this area. As discussions about autism prevalence trends in Georgia continue, the importance of early identification and intervention regarding shared focus becomes increasingly relevant.
The Role of Parents in Fostering Joint Attention
Parents play an essential role in nurturing joint attention and autism skills in their children, particularly those on the autism spectrum. By actively engaging in play and everyday routines, they not only model behaviors related to joint attention but also create shared experiences that are vital for development. Research indicates that increased parental involvement is linked to significant improvements in children's social abilities and a reduction in behavioral issues.
Specifically, teacher-reported increases in parent involvement correlate with a 0.12 enhancement in social skills and a 0.08 decrease in behavioral problems.
As Vito Borrello, Executive Director of the National Association for Family, School, and Community Engagement, wisely points out, "If the school is not welcoming and families don’t feel welcome at the school, then you’re not going to get them to come to school no matter what you do." This insight underscores the critical role of family engagement in educational settings.
To effectively support your child's development of joint attention, consider adopting these strategies:
- Engaging in Play: Participate in activities that promote turn-taking and shared focus, such as board games or interactive storytelling.
- Utilizing Support: Acknowledge and reinforce collaborative behaviors when they occur, helping your child recognize and imitate these interactions.
- Establishing a Vibrant Linguistic Setting: Use expressive language and engage in discussions that foster shared focus, enhancing both vocabulary and comprehension.
- Being Present: Reduce distractions during interactions to boost focus and engagement, ensuring that your child feels valued and understood.
The Family Involvement Questionnaire-Short Form (FIQ-SF) has demonstrated high reliability in measuring parental involvement across different contexts, emphasizing the significance of family engagement in educational outcomes. By implementing these strategies, you can profoundly impact your child's ability to develop joint attention and autism skills, ultimately enhancing their communication and social interactions. The FIQ-SF serves as a valuable resource for assessing how these strategies relate to your child's educational success.
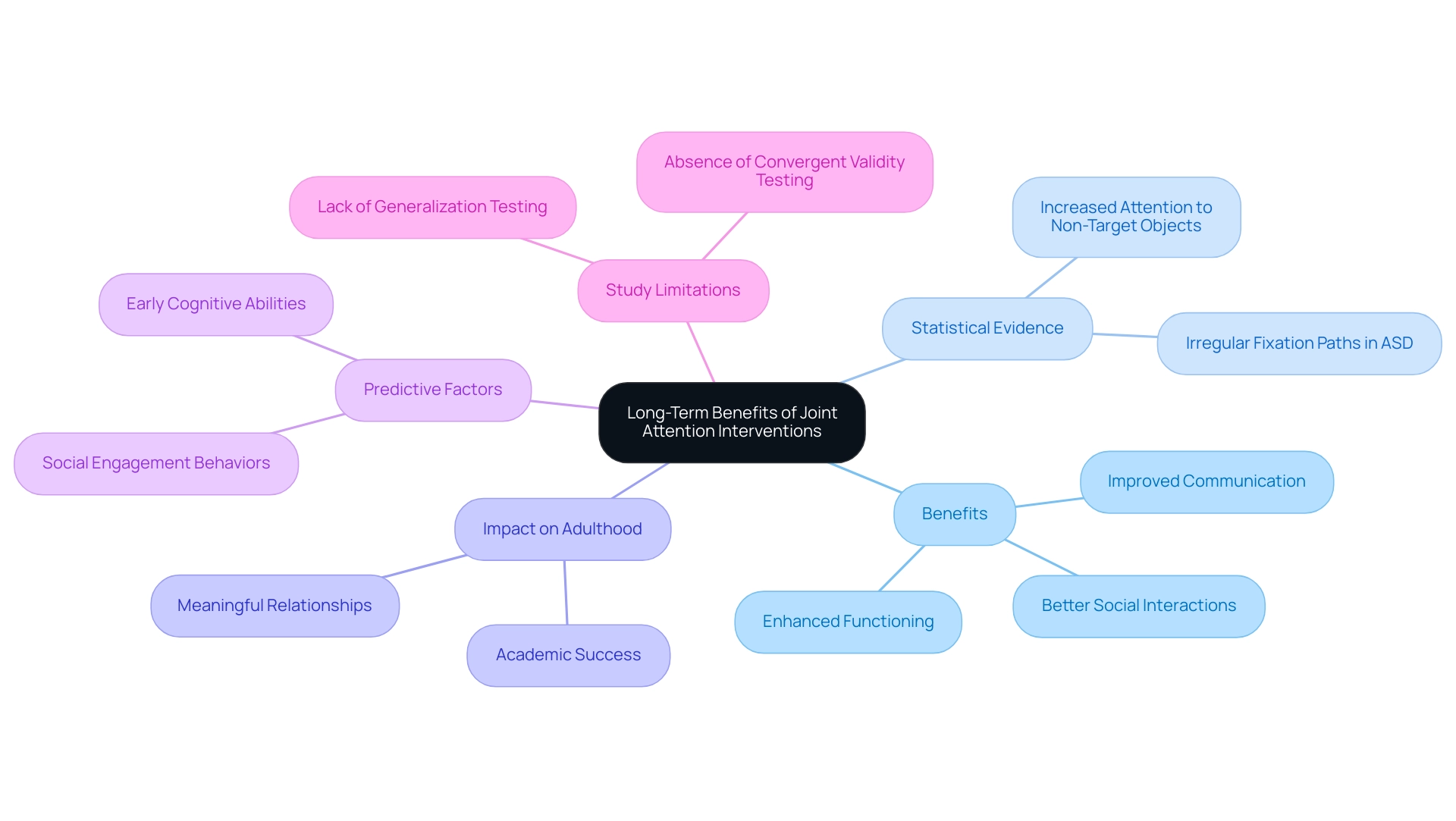
Long-Term Benefits of Joint Attention Interventions
Interventions designed to enhance cooperative focus abilities offer significant, lasting benefits for individuals with autism. Research consistently shows that children who cultivate strong focus skills are more likely to see improvements in communication, social interactions, and overall functioning. Notably, statistics reveal that individuals with ASD exhibit irregular fixation paths and heightened attention to non-target objects compared to typically developing individuals (TDC). This underscores the critical need to enhance skills related to joint attention and autism.
These benefits extend well into adulthood, profoundly impacting academic success and the ability to form meaningful relationships. For example, a long-term study titled "From Toddlerhood to Adolescence, Trajectories and Predictors of Outcome: Long‐Term Follow‐Up Study in Autism Spectrum Disorder" found that early cognitive abilities and social engagement behaviors were strong predictors of positive outcomes. Mikhail Kissine, a writer in this field, notes, 'our review indicates that shared focus plays a crucial role in the development of language,' further supporting the claims about improvements in communication.
By prioritizing shared focus in therapeutic settings, caregivers can empower their children to reach their full potential and navigate social environments with greater ease. Additionally, research suggests that integrating behavioral and developmental approaches in interventions can effectively promote skills related to joint attention and autism. This highlights the importance of these strategies in fostering long-term success. However, it is essential to acknowledge the study's limitations, including the lack of generalization testing in natural environments and the absence of convergent validity testing, which should be considered when interpreting the findings.
Conclusion
The exploration of joint attention reveals its foundational significance in the development of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). This vital skill is not just a developmental milestone; it is a bridge that connects isolated interactions to meaningful social engagement. Throughout this article, we have highlighted the critical role of joint attention in fostering communication and social skills, as well as the challenges children face in mastering this essential ability.
Caregivers are instrumental in nurturing joint attention through targeted strategies such as:
- Modeling behaviors
- Utilizing visual supports
- Engaging in interactive play
These approaches not only enhance a child's ability to share focus but also create enriching environments that promote overall developmental growth. Research suggests that early intervention and active parental involvement can lead to significant improvements in social interactions and communication skills, ultimately paving the way for better long-term outcomes.
As our understanding of joint attention evolves, it becomes increasingly clear that fostering this skill is paramount for children with autism. By prioritizing joint attention in daily interactions and therapeutic settings, caregivers and professionals can equip children with the tools they need to navigate their social worlds more effectively. The long-term benefits of these interventions extend far beyond childhood, influencing future academic success and the ability to form meaningful relationships.
Emphasizing joint attention not only supports immediate developmental goals but also lays the groundwork for a brighter, more connected future for children with autism. Let us commit to nurturing this essential skill, ensuring that every child has the opportunity to thrive in their social interactions and build lasting connections.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is joint focus and why is it important?
Joint focus is the ability of two individuals to concentrate on the same object or event, allowing for meaningful social interaction. It is crucial for effective communication and social engagement, particularly for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), as it is closely linked to joint attention.
How does joint attention relate to autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Difficulties in mutual awareness can hinder a young person's ability to connect with others, making joint attention a vital component for support strategies in individuals with ASD. Research indicates that enhancing joint attention can improve social involvement and communication skills in these individuals.
What research findings support the importance of joint attention in youth with autism?
Studies utilizing eye-tracking technology have shown that specific signals can improve joint attention during virtual games for youth with ASD. Additionally, a case study indicated that particular cues could enhance collaborative focus, suggesting targeted interventions can foster social engagement.
What role do caregivers play in developing joint attention in children with autism?
Caregivers can adopt collaborative focus strategies, such as using visual signals and engaging in shared activities, to enhance interaction and communication. By prioritizing shared focus, they can create enriching environments that support their children's social and communicative growth.
What activities can help promote joint attention in children?
Activities that encourage joint attention include shared reading, interactive play, and responsive communication. These activities can significantly influence a child's developmental path and improve their ability to navigate social exchanges.
What statistics highlight the effectiveness of collaborative strategies in improving communication skills among children with autism?
Statistics show that 94% of researchers evaluate the effectiveness of collaborative strategies as excellent or good in enhancing communication skills among children with autism, underscoring the vital role of joint attention in enriching interactions.
How does joint attention impact language learning and social abilities?
Joint attention is a fundamental component of youth development, playing a crucial role in language learning, social abilities, and cognitive advancement. For children with autism, developing joint attention can significantly enhance their communication skills and interactions with peers and caregivers.
What neurological insights are related to joint attention and autism?
Recent findings indicate that the left thalamus is a significant predictor of ASD, highlighting the neurological underpinnings of shared focus deficits. This reinforces the relevance of joint attention in understanding and addressing autism.
What future research directions are suggested regarding joint attention?
Future research should aim to validate measurement tools and explore the effectiveness of interventions in natural settings to further refine collaboration strategies that enhance joint attention and social skills in children with autism.




