Overview
This article highlights the critical importance of Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) for children with autism, focusing on how they can provide essential, tailored educational support for students. It’s crucial for parents and educators to understand that developing IEPs is a collaborative effort. This process brings together parents, educators, and specialists, all working hand-in-hand to create effective, personalized strategies that cater to the unique needs and strengths of each child. By fostering this teamwork, we can ultimately enhance their academic and social success.
Imagine the difference it makes when everyone involved in a child's education is on the same page, sharing insights and strategies. This collaboration not only addresses the specific challenges faced by students with autism but also celebrates their individual strengths. As we develop these plans, we’re not just creating a document; we’re nurturing a pathway to success for each child.
We encourage parents and educators to actively participate in this process, sharing their experiences and insights. Together, we can create a supportive environment that truly understands and meets the needs of our children. By fostering open communication and collaboration, we can ensure that every student receives the personalized support they deserve.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of education for children with autism can feel overwhelming, but understanding Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) is a crucial first step. These essential frameworks are more than just bureaucratic documents; they embody a personalized approach to learning that honors the unique strengths and challenges of each student on the spectrum. As awareness of autism grows, so does the significance of effectively implementing IEPs, ensuring that every child receives the support they need to flourish both academically and socially.
In this article, we will explore the intricacies of IEPs, including their components, the collaborative process involved in their development, and the vital role parents play in advocating for their children's needs. By examining best practices and innovative strategies, it becomes evident that a strong IEP is not just a plan; it is a pathway to success for students with autism.
Understanding Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) for Autism
An autism individual learning plan is more than just a document; it serves as a legally binding framework that outlines the educational objectives, services, and accommodations tailored to meet the unique needs of students with autism. Developed in accordance with the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), IEPs ensure that individuals receive a free appropriate public education (FAPE). Each IEP is carefully crafted, considering the child's strengths, challenges, and distinct learning requirements.
Recent statistics reveal that during the 2022-2023 school year, a significant percentage of individuals with autism were supported under IEPs, reflecting a growing awareness and implementation of these vital programs. Notably, the percentage of students served under IDEA who were male was higher (18 percent) than that of female students (10 percent). Parents play a crucial role in the IEP process, advocating for their child's needs and ensuring that the plan is effectively executed within the educational setting.
This collaborative approach fosters an inclusive atmosphere where children can thrive both academically and socially. Education specialists emphasize the importance of creating supportive and inclusive environments, essential for enabling individuals on the autism spectrum to develop their individual learning plans and reach their full potential alongside their peers. Jenine Catudio, an education specialist for individuals with mild-moderate needs, beautifully states, "Let us commit to creating supportive and inclusive spaces where those on the autism spectrum can reach their full potential alongside their peers."
Moreover, according to the U.S. Department of Education (2018-2019):
- 74% of autistic individuals in the U.S. graduate with a diploma
- 19% graduate with a certificate
This highlights the pressing need for enhanced support and resources in special education to improve outcomes for these individuals. Together, we can advocate for the necessary changes and ensure that every child receives the support they deserve.
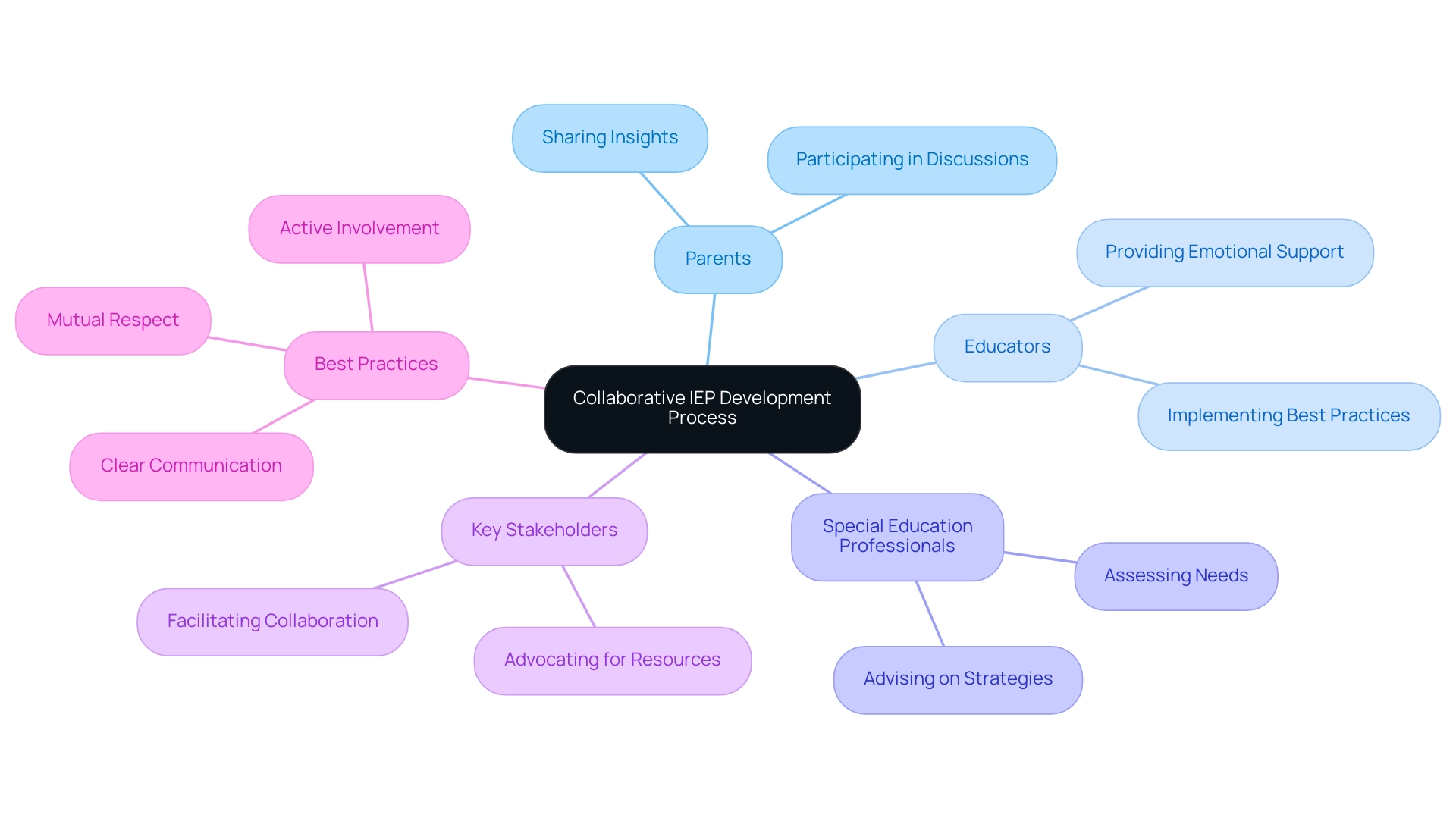
The Collaborative Process of Developing an IEP
The development of an Individualized Education Program (IEP) is fundamentally a collaborative endeavor, engaging parents, educators, special education professionals, and other key stakeholders. Each participant plays a vital role in sharing insights regarding the child's strengths and challenges, which is crucial for crafting a comprehensive plan that encompasses all facets of the child's educational journey.
Statistics indicate that in the 2022-2023 academic year, 4 percent of individuals served under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) experienced emotional disturbances. This underscores the need for tailored support through effective IEPs. The collaborative process not only enhances the quality of the IEP but also fosters a sense of community among team members.
Experts in special education emphasize the significance of teamwork during IEP meetings, advocating for ongoing learning and adaptation to improve services for individuals with disabilities. Ben Tillotson, the 2025 President Elect of the Council for Exceptional Children, shares his vision: 'As the CEC looks ahead, we must prioritize collaboration to enhance education for exceptional learners.' Best practices for these meetings include:
- Establishing clear communication channels
- Setting mutual respect as a priority
- Actively involving parents in discussions
This approach ensures that every voice is heard, ultimately enriching the educational experience for the child. Case studies, such as 'Reaping the Rewards of Teacher Collaboration,' have shown that institutions that prioritize teacher collaboration, especially in the wake of challenges posed by the pandemic, have witnessed improved student outcomes. By sharing best practices and providing emotional support, educators can cultivate an environment conducive to creative idea generation and professional growth.
In summary, the collaborative development of autism individual learning plans for individuals with autism is not just beneficial; it is essential. By effectively collaborating in IEP meetings, stakeholders can create a robust framework that includes the autism individual learning plan to support the unique needs of each student, paving the way for their success in the educational landscape.
Key Components of Effective IEPs for Autistic Students
Creating effective individual learning plans (IEPs) for autistic students is vital for ensuring that their educational experiences are tailored to their unique needs. These plans incorporate several essential components that help in this endeavor.
- Present Levels of Performance: This crucial section offers a comprehensive assessment of the individual's current academic and functional abilities. It serves as a solid foundation for establishing realistic and achievable goals, ensuring that every student can thrive.
- Measurable Goals: By employing the SMART criteria—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound—these goals clearly outline what the individual is expected to accomplish. For example, a long-term goal could focus on enhancing social skills to enable independent participation in group activities. Research supports that IEPs with SMART goals lead to significantly better outcomes, showing that students who engage with measurable objectives often see improvements in both social skills and academic performance.
- Specialized Services: This component identifies the specific special education services, therapies, or accommodations that are essential to support the individual's unique learning needs. It is important for these services, such as those outlined in the autism individual learning plan, to align with measurable goals, creating a cohesive educational approach.
- Progress Monitoring: Regularly assessing the individual's progress toward established goals is vital for a robust plan. This ongoing evaluation allows for timely adjustments to the IEP, ensuring that it remains relevant and effective as the individual grows. Federal laws, including the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), mandate regular reviews to adapt the autism individual learning plan to meet evolving educational needs.
- Transition Planning: For older individuals, a well-structured IEP includes a transition plan that outlines necessary steps for moving into post-secondary education or employment. This planning is essential for fostering autonomy and preparing individuals for life after school.
Incorporating these key elements not only enhances the effectiveness of autism individual learning plans but also empowers caregivers to engage actively in goal-setting discussions and track their child’s progress. As highlighted by the US Surgeon General, participating in this collaborative process allows parents to provide valuable insights, leading to meaningful adjustments to the IEP that ultimately support their child’s educational journey. Furthermore, it is crucial to revisit and enhance the IEP regularly, integrating innovative teaching methods and strategies that truly engage students.
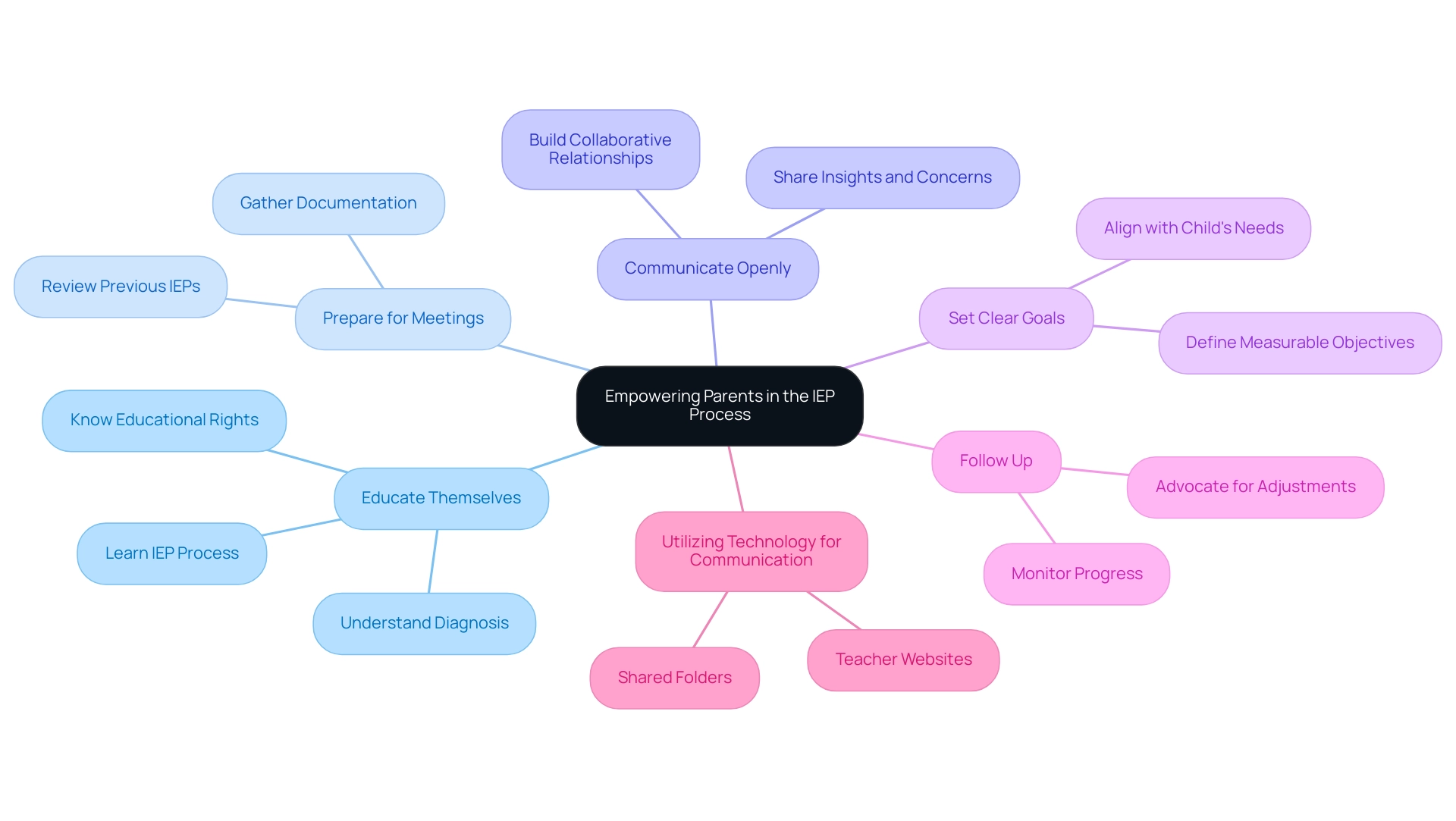
Empowering Parents: Advocacy and Participation in the IEP Process
Parents play a crucial role as advocates in the autism individual learning plan process, and their active involvement can significantly enhance outcomes for their children with autism. Research highlights that having an advocate present at IEP meetings is essential for many guardians, ensuring that their voices are heard and their children's needs are met. Indeed, the active participation of an advocate is seen as a necessity for many guardians, facilitating meaningful engagement in the IEP process.
To effectively navigate this journey, parents might consider the following strategies:
- Educate Themselves: Familiarizing themselves with their child's diagnosis, educational rights, and the intricacies of the IEP process is vital. Understanding these elements empowers caregivers to advocate effectively.
- Prepare for Meetings: Gathering relevant documentation, such as assessments, observations, and previous IEPs, is key. This preparation allows guardians to present a comprehensive view of their child's needs during meetings.
- Communicate Openly: Building a collaborative relationship with educators and specialists is essential. Open lines of communication ensure that parents' insights and concerns are acknowledged, fostering a team-oriented approach to their child's education.
- Set Clear Goals: Working with the IEP team to define specific, measurable objectives that align with the child's unique needs and aspirations is important. Clear objectives help in tracking progress and ensuring accountability.
- Follow Up: Regularly monitoring the child's progress and the implementation of the IEP is crucial. Proactive follow-ups enable guardians to advocate for necessary adjustments, ensuring that the educational plan remains effective.
As we look ahead to 2025, the significance of guardian advocacy in the IEP process is underscored by numerous case studies showcasing successful outcomes when guardians actively participate. For example, the integration of technology, such as teacher websites and shared folders, has proven effective in enhancing communication between families and educators, leading to improved transparency and collaboration. This illustrates how technological tools facilitate efficient communication and the sharing of student artifacts, which is vital for tracking progress.
Experts emphasize that an autism individual learning plan necessitates parental involvement, which is not just beneficial but essential. Grace Eunjung Kim, Principal Attorney at The Law Office of Grace E. Kim, P.C., who has supported individuals with disabilities since 2002, states, "The active involvement of guardians in IEP meetings can result in more customized educational strategies that better serve the autism individual learning plan for individuals with autism." By embracing their role as advocates, caregivers can profoundly influence their children's educational journeys, ensuring they receive the support necessary to thrive.
Moreover, it is essential to recognize that school districts have faced repercussions for retaliating against advocates or parents involved in the IEP process, underscoring the importance of parental involvement and the protections available to them.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting IEPs for Optimal Outcomes
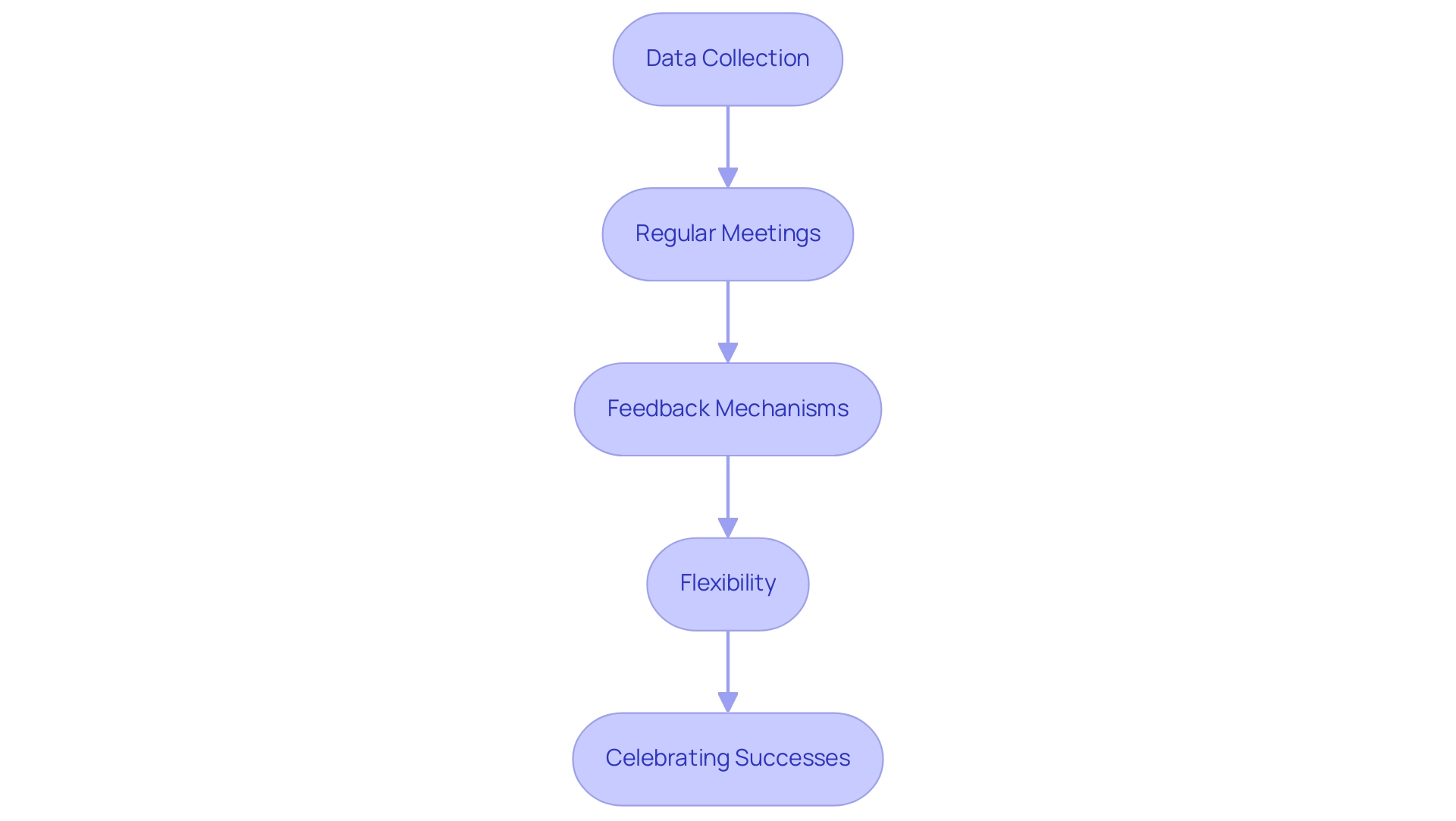
Monitoring progress is a vital part of the autism individual learning plan process, particularly for students with autism. Regular assessments play a crucial role in evaluating a child's journey toward their goals, and several effective strategies can enhance this important process:
- Data Collection: Gathering both quantitative and qualitative data on the young individual's performance across various domains is essential. This data should align with the performance criteria outlined in the IEP's annual goals, such as reading speed and accuracy, enabling informed instructional decisions.
- Regular Meetings: Scheduling periodic IEP meetings is necessary to review progress comprehensively. These meetings create opportunities to discuss the young person's development, assess the effectiveness of current strategies, and make necessary adjustments to the plan.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing strong communication channels between parents and educators is critical. This feedback loop allows both parties to share insights regarding the student's progress and any challenges faced, fostering a collaborative approach to support.
- Flexibility: Adapting goals, services, and strategies based on the individual's evolving needs is paramount. As David Bateman, a Principal Researcher, emphasizes, "We need to provide appropriate supports for this." Flexibility ensures that the autism individual learning plan remains relevant and effective in meeting the individual's unique requirements.
- Celebrating Successes: Recognizing and celebrating milestones achieved can significantly motivate both the child and the educational team. Acknowledging progress, no matter how small, reinforces positive behaviors and encourages continued effort.
As we look toward 2025, the emphasis on accurate documentation during progress monitoring has become increasingly important. Advanced districts are utilizing IEP data collection tools to enhance data management for autism individual learning plans, ensuring that IEP teams can effectively demonstrate their efforts in helping individuals achieve their goals. Statistics also indicate that regular reviews of the autism individual learning plan are essential, focusing on the frequency of these evaluations to ensure optimal outcomes for autistic students.
Parents can access a range of supports, including free or low-cost legal representation, if disagreements arise regarding evaluations or the IEP itself. Additionally, the MTSS Center provides guidance on implementing Multi-Tiered Systems of Support for early intervention. By implementing these strategies, parents and educators can collaborate to create a supportive environment that fosters growth and development for individuals with autism.
Incorporating Therapeutic Approaches into Individual Learning Plans
Incorporating therapeutic approaches into the autism individual learning plan is essential for effectively addressing the diverse needs of individuals with autism. A comprehensive strategy includes several key components that resonate deeply with families.
- Behavioral Interventions: Implementing Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) techniques is crucial for fostering positive behaviors and mitigating challenging ones. Research indicates that these interventions can lead to significant improvements in behavior and learning outcomes, providing hope and progress for many families.
- Social Skills Training: Programs designed to enhance social interaction skills are vital. These initiatives assist young individuals in developing the ability to navigate peer relationships, which is often a challenge for those on the autism spectrum. Imagine the joy of a child making friends and feeling included!
- Speech and Language Therapy: Addressing communication difficulties through targeted speech and language therapy can significantly enhance a young person's ability to express themselves, thereby improving their overall quality of life. This is a journey towards finding their voice.
- Occupational Therapy: This therapy focuses on sensory processing issues and daily living skills, equipping youngsters with the tools they need to manage everyday tasks and interactions effectively.
- Collaboration with Therapists: Engaging therapists in the IEP process ensures that their expertise informs the development of a holistic educational plan. This collaboration is essential for customizing interventions to address each person's unique needs.
Investing in these early intervention programs not only supports individual growth but also results in long-term savings for families and society. The average cost of therapeutic behavioral services in the U.S. is approximately $175.44, underscoring the financial implications of effective early intervention.
Moreover, ongoing research in autism emphasizes the importance of incorporating personal experiences from individuals with autism and their families. This community involvement is crucial for developing more effective treatments and understanding the condition better. As highlighted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), many individuals with autism possess unique talents and interests, such as in music, math, or art, which can be leveraged in educational settings to enhance engagement and learning outcomes.
Additionally, vital neurodiverse community support resources are available for individuals and families, offering tools, networks, and guidance for success. By integrating these therapeutic approaches into the autism individual learning plan, educators and parents can create a supportive framework that not only addresses the immediate educational needs of children with autism but also fosters their long-term development and success. Together, we can make a difference in their lives.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) for children with autism is not just important; it's essential for their success. This article highlights the critical role of collaboration among parents, educators, and specialists in crafting tailored IEPs that truly reflect each child's unique strengths and challenges. Key elements such as measurable goals, specialized services, and regular progress monitoring are vital for creating effective educational experiences.
Parents are not just participants; they are vital advocates in the IEP process. Their active involvement significantly enhances the quality of the educational plan. By preparing for meetings and understanding their rights, parents can effectively influence their child's educational outcomes, ensuring that their voices are heard.
Moreover, integrating therapeutic approaches—like behavioral interventions and speech therapy—is crucial for addressing the diverse needs of autistic students. Flexibility in adapting IEPs allows for ongoing support as children grow and develop, ensuring that their educational journey is responsive to their evolving needs.
In conclusion, a well-crafted IEP is a powerful tool that empowers children with autism to reach their full potential. By fostering collaboration, advocating for individual needs, and incorporating therapeutic strategies, the educational community can create inclusive environments where every child can thrive both academically and socially. A commitment to these principles will not only help students with autism succeed in school but also prepare them for a fulfilling life beyond the classroom.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Individualized Education Program (IEP) for individuals with autism?
An IEP is a legally binding framework that outlines the educational objectives, services, and accommodations tailored to meet the unique needs of students with autism, ensuring they receive a free appropriate public education (FAPE) in accordance with the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA).
How are IEPs developed?
IEPs are developed collaboratively by parents, educators, special education professionals, and other key stakeholders who share insights about the child's strengths and challenges to create a comprehensive educational plan.
What statistics highlight the importance of IEPs for students with autism?
During the 2022-2023 school year, a significant percentage of individuals with autism were supported under IEPs, with 74% graduating with a diploma and 19% graduating with a certificate, indicating a need for enhanced support in special education.
What roles do parents play in the IEP process?
Parents play a crucial role in advocating for their child's needs and ensuring that the IEP is effectively executed within the educational setting.
What is the significance of collaboration in the IEP development process?
Collaboration among stakeholders enhances the quality of the IEP, fosters a sense of community, and ensures that every voice is heard, ultimately enriching the educational experience for the child.
What best practices are recommended for IEP meetings?
Best practices include establishing clear communication channels, prioritizing mutual respect, and actively involving parents in discussions to ensure effective collaboration.
What percentage of individuals served under IDEA experienced emotional disturbances during the 2022-2023 academic year?
Statistics indicate that 4 percent of individuals served under IDEA experienced emotional disturbances, highlighting the need for tailored support through effective IEPs.
How does creating supportive and inclusive environments benefit students with autism?
Supportive and inclusive environments enable individuals on the autism spectrum to develop their individual learning plans and reach their full potential alongside their peers.




