Overview
This article explores an important question: Can individuals be both bipolar and autistic? It highlights that these dual diagnoses can indeed coexist, often presenting overlapping symptoms like mood swings and emotional dysregulation. For parents and caregivers, this understanding is crucial.
Statistics on prevalence and insights into misdiagnosis underscore the importance of accurate diagnosis and specialized care. Tailored support strategies become essential for those navigating both conditions. By recognizing these complexities, we can foster a more compassionate approach to care.
If you or someone you know is facing these challenges, seeking support and resources can make a significant difference.
Introduction
The intersection of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Bipolar Disorder presents a complex landscape that calls for thoughtful exploration. As the prevalence of these conditions continues to rise, it becomes increasingly important to understand their unique characteristics and overlapping symptoms. This understanding is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Individuals navigating both disorders often encounter distinct challenges, such as emotional dysregulation and impulsivity, which can complicate their care.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of ASD and Bipolar Disorder, illuminating their co-occurrence and the pressing need for accurate assessments. We will also discuss the importance of tailored support strategies. By examining these critical aspects, we aim to empower caregivers and clinicians to foster a more informed approach to navigating dual diagnoses. Ultimately, our goal is to enhance the quality of life for those affected, ensuring they receive the compassionate care they deserve.
Define Autism Spectrum Disorder and Bipolar Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that can be challenging for both children and their families. It is characterized by persistent difficulties in social communication, along with restricted interests and repetitive behaviors. Symptoms typically emerge in early childhood and vary widely in severity, impacting each person in unique ways. On the other hand, Bipolar Disorder presents significant mood fluctuations, featuring manic episodes filled with heightened energy and euphoria, as well as depressive episodes marked by low energy and sadness.
Understanding these definitions is vital, particularly in relation to whether can you be bipolar and autistic, as both conditions can coexist and influence individuals in different ways. Current statistics reveal that approximately 1 in 44 children are diagnosed with ASD, while Bipolar Disorder affects around 2.8% of adults in the U.S. This dual diagnosis can complicate care and support strategies, highlighting the importance for caregivers and clinicians to be well-informed about both conditions.
As noted by Hyman, S. L., Levey, S. E., & Myers, S. M., "Research into these types of interventions continues, and parents/caregivers interested in them should discuss them with their child's treating clinician." This insight underscores the need for open communication between caregivers and healthcare providers. Additionally, the Autism Centers of Excellence Program, supported by NIMH, funds extensive studies aimed at enhancing understanding and developing innovative treatment and support methods for ASD.
For those seeking more information, brochures and fact sheets regarding ASD are available for free in print and online, offering valuable resources for parents and advocates. We encourage you to explore these materials and share your experiences or questions in the comments or through our newsletters. Together, we can foster a supportive community for those navigating these complex conditions.
Explore Overlapping Symptoms and Challenges
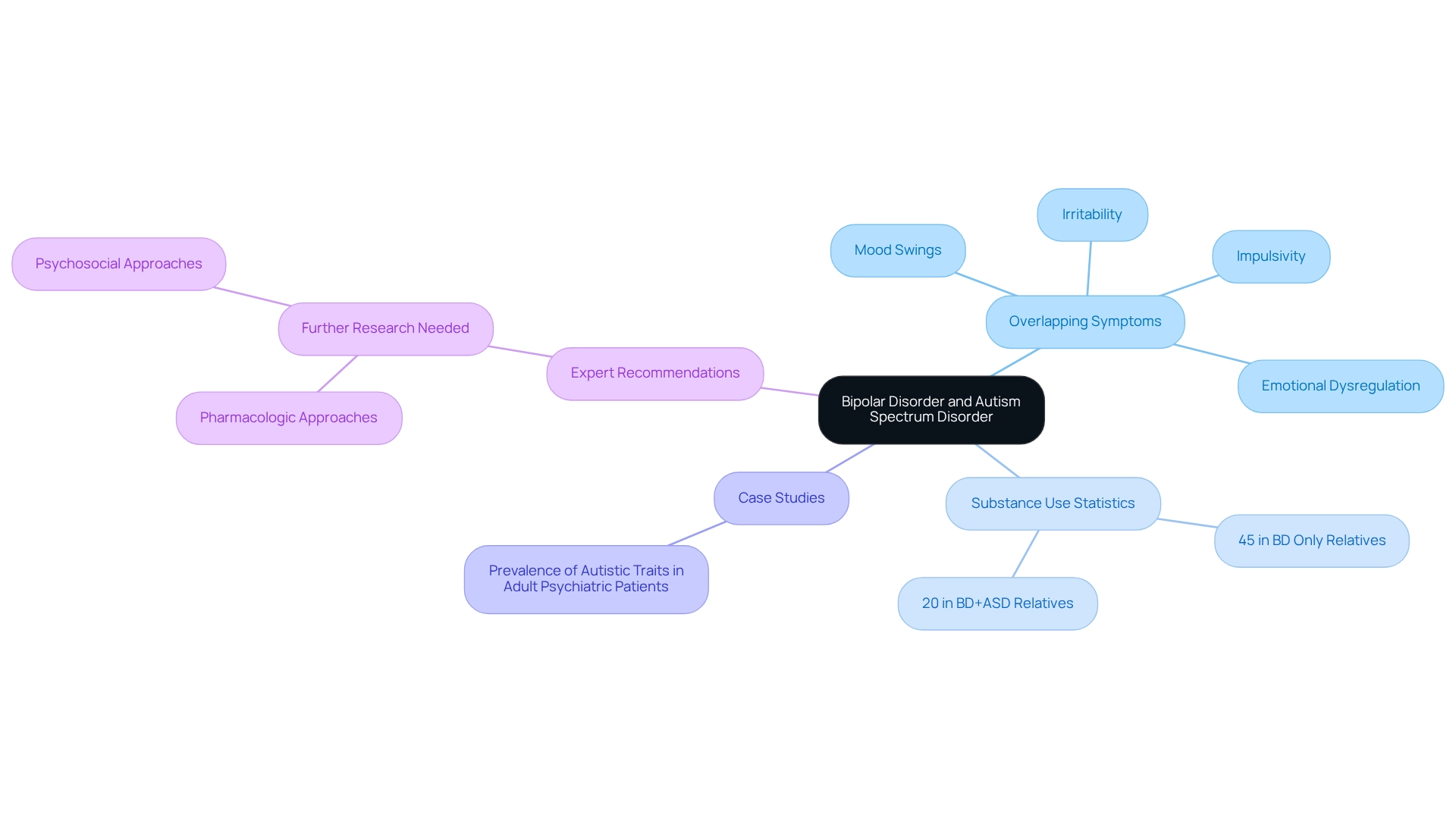
A common question is, can you be bipolar and autistic, as individuals diagnosed with both conditions often face overlapping symptoms, such as mood swings, irritability, and impulsivity. Emotional dysregulation is particularly common, manifesting as difficulties in managing emotions effectively. For example, during manic episodes of bipolar disorder, behaviors like pacing or rapid speech may emerge. However, these same actions can also be triggered in individuals with sensory processing issues due to sensory overload or heightened anxiety. Understanding these nuances is vital for accurate diagnosis and the development of effective management strategies.
Research reveals that youth with both bipolar disorder and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) raise the question of can you be bipolar and autistic, and they show a significantly lower rate of substance use issues in first-degree relatives—20% compared to 45% in youth with bipolar disorder alone. This statistic underscores the unique family dynamics associated with these dual diagnoses, suggesting that recognizing these patterns can inform intervention strategies.
Case studies, such as 'Prevalence of Autistic Traits in Adult Psychiatric Patients,' highlight the prevalence of autistic traits among adult psychiatric patients and explore the question of can you be bipolar and autistic, as they reveal notable overlaps with conditions like bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. These findings stress the importance of identifying autistic characteristics to tailor strategies that meet the specific needs of individuals, particularly regarding the question of can you be bipolar and autistic.
Experts emphasize the need for further research into the impacts of pharmacologic and psychosocial approaches on the clinical progression of bipolar disorder in youth with ASD. As Dr. Xenia Borue notes, "Future work is needed to explore the effect of specific pharmacologic and psychosocial approaches on the clinical course of BD in youth with ASD." This highlights the ongoing necessity for research in understanding these complexities. It becomes increasingly clear that a nuanced understanding of emotional dysregulation and overlapping symptoms is crucial for improving outcomes for those managing both conditions. If you or someone you know is concerned about these symptoms, seeking a comprehensive diagnosis from a physician is essential to ensure appropriate support and care.
Emphasize the Need for Accurate Diagnosis and Tailored Support
Understanding the precise identification of developmental disorders and the concept of can you be bipolar and autistic is essential, as misdiagnosis can significantly hinder effective care strategies. The overlap of symptoms between these conditions raises the question, can you be bipolar and autistic, which complicates the diagnostic process and often leads to inappropriate interventions. For instance, a review highlighted the challenges in diagnosing psychiatric comorbidities in individuals with autism, including the question of can you be bipolar and autistic, and emphasized the need for specialized diagnostic tools tailored for this group. Alarmingly high misdiagnosis rates underscore the urgency for accurate assessments.
It is crucial for professionals to evaluate the full spectrum of symptoms and their interactions to ensure appropriate treatment. Support strategies should be tailored to address the question of can you be bipolar and autistic, and may include:
- Behavioral therapies
- Medication management
- Family counseling
All designed to meet the unique needs of individuals facing both conditions. Neuroleptics, for example, have shown effectiveness in reducing stress levels and impulsivity, illustrating the potential benefits of specific pharmacological treatments. Additionally, melatonin is often recommended for addressing sleep issues in children and teenagers with ASD, which can be particularly relevant for managing symptoms associated with both the spectrum condition and bipolar illness.
By fostering a collaborative approach among healthcare providers, families, and educators, we can create a supportive environment that enhances treatment outcomes. Insights from mental health professionals highlight the importance of obtaining evaluations from specialists experienced in both spectrum conditions and exploring the question of can you be bipolar and autistic. As Dr. Jessica Hellings wisely states, "If you or your child has autism and you’re concerned about the possibility of can you be bipolar and autistic, we recommend that you seek assessment from a mental health provider with experience in autism spectrum disorders and co-occurring psychiatric disorders." This comprehensive strategy not only improves the accuracy of diagnoses but also empowers families to navigate the complexities of dual diagnoses effectively. At ASD Media, we are dedicated to fostering collaboration and growth in the ABA therapy industry, reinforcing the community aspect that is vital for supporting individuals with these dual diagnoses.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate relationship between Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Bipolar Disorder is crucial for improving the quality of care for individuals facing these dual challenges. The complexities of both conditions, from their overlapping symptoms such as emotional dysregulation and impulsivity to the unique diagnostic hurdles they present, highlight the necessity for accurate assessments. Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatment plans, making it imperative for caregivers and clinicians to be well-informed and vigilant in their approach.
Equipped with a deeper understanding of these disorders, tailored support strategies can be developed to meet the specific needs of those affected. This includes integrating behavioral therapies, medication management, and family counseling, which are essential in addressing the multifaceted nature of co-occurring conditions. Collaborative efforts among healthcare providers, families, and educators play a vital role in creating an environment conducive to effective treatment and support.
Ultimately, fostering a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of ASD and Bipolar Disorder can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions. By prioritizing accurate diagnosis and tailored support, we can navigate the journey towards compassionate care and improved outcomes more effectively, ensuring that those impacted receive the understanding and assistance they truly deserve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by persistent difficulties in social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. Symptoms typically emerge in early childhood and vary widely in severity.
What are the key characteristics of Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar Disorder is marked by significant mood fluctuations, including manic episodes with heightened energy and euphoria, as well as depressive episodes characterized by low energy and sadness.
Can someone be diagnosed with both Autism Spectrum Disorder and Bipolar Disorder?
Yes, both conditions can coexist, and understanding their definitions is vital as they can influence individuals in different ways.
What are the statistics regarding ASD and Bipolar Disorder?
Approximately 1 in 44 children are diagnosed with ASD, while Bipolar Disorder affects around 2.8% of adults in the U.S.
Why is it important for caregivers and clinicians to be informed about both conditions?
A dual diagnosis can complicate care and support strategies, making it essential for caregivers and clinicians to understand both conditions to provide effective support.
What resources are available for parents and caregivers regarding ASD?
Brochures and fact sheets about ASD are available for free in print and online, offering valuable information for parents and advocates.
How can caregivers communicate with healthcare providers about interventions for ASD?
Caregivers are encouraged to discuss potential interventions with their child's treating clinician, as ongoing research into these types of interventions continues.
What is the Autism Centers of Excellence Program?
The Autism Centers of Excellence Program, supported by NIMH, funds extensive studies aimed at enhancing understanding and developing innovative treatment and support methods for ASD.




