Overview
This article explores a significant question: Can someone develop autism? It emphasizes that Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition shaped by a unique blend of genetic and environmental factors. Recognizing the signs and symptoms early is crucial, as timely intervention and support can profoundly enhance outcomes for individuals on the spectrum. By understanding these aspects, we can foster a more supportive environment for those affected by ASD.
Introduction
Understanding autism is essential in today's world, where its prevalence continues to rise, igniting vital conversations about its impact on individuals and families. This article takes a compassionate look at the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), exploring its diverse manifestations and the challenges that those affected may encounter.
As the lines blur between awareness and diagnosis, a significant question arises: can someone truly develop autism later in life? Through this exploration, we aim to illuminate the signs, symptoms, and crucial support strategies, empowering you to recognize potential indicators and seek the necessary interventions.
Define Autism and Its Spectrum
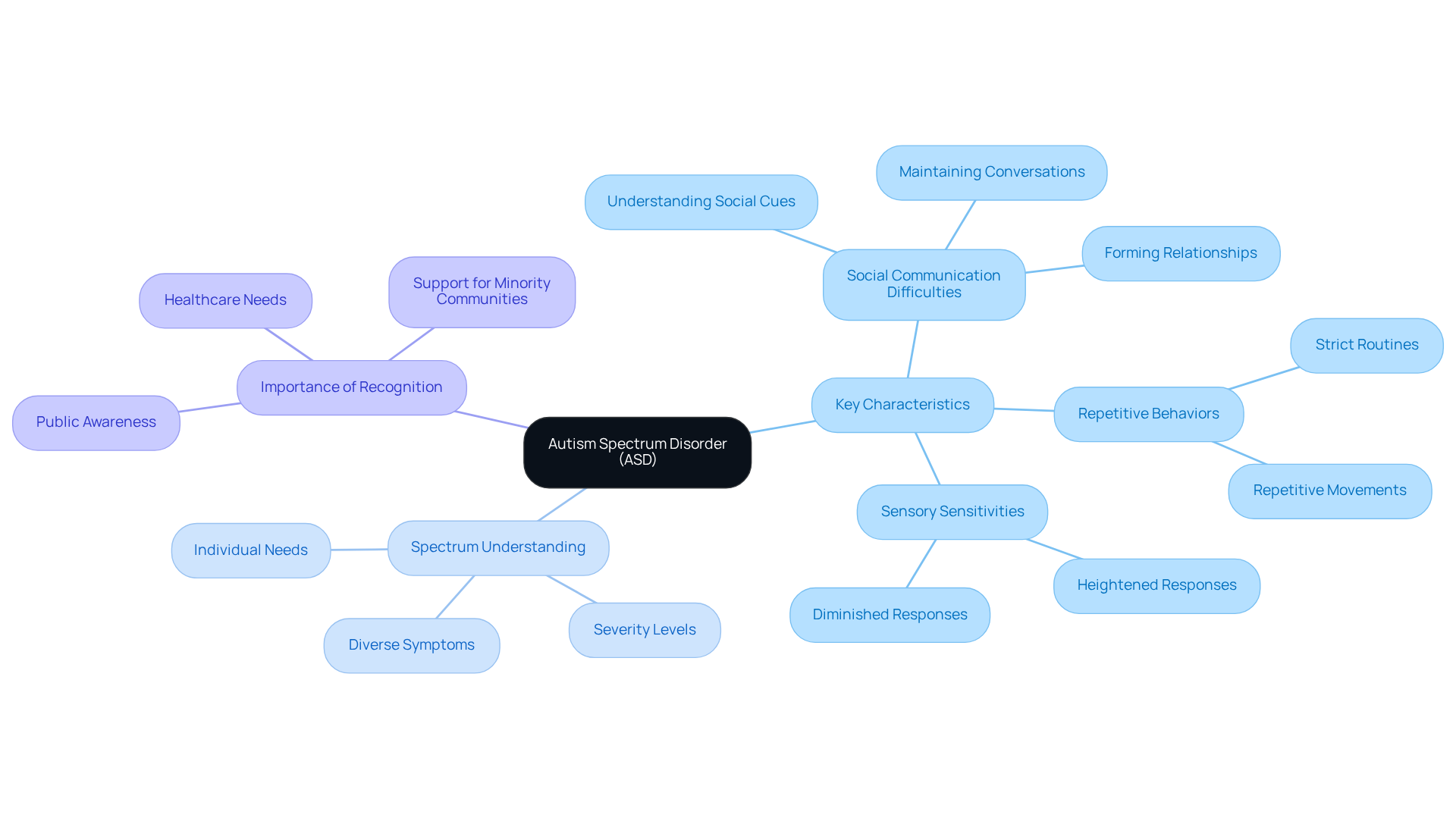
Autism, or Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that presents a range of challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior. The term 'spectrum' beautifully captures the diverse symptoms and severity levels experienced by individuals on the autism spectrum. Some may face significant challenges in daily functioning, while others may exhibit milder symptoms and lead relatively independent lives. Understanding this spectrum is essential for recognizing the varied expressions of the condition and the unique needs of each individual.
Key characteristics of autism include:
- Social Communication Difficulties: Many individuals may struggle with understanding social cues, maintaining conversations, and forming relationships. For example, they might find it challenging to interpret body language or tone of voice, which can lead to misunderstandings in social situations.
- Repetitive Behaviors: It is common for many to engage in repetitive movements or speech, or to adhere to strict routines. This might manifest as hand-flapping, rocking, or a strong preference for following specific patterns in daily activities.
- Sensory Sensitivities: Autistic individuals often experience heightened or diminished responses to sensory input, such as sounds, lights, or textures. For instance, a young person might feel overwhelmed by loud noises or actively seek out particular textures for comfort.
Recent research emphasizes that this condition leads to questions about how can someone develop autism from a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors during early brain development. The prevalence of autism in the U.S. has notably increased, with the CDC reporting a rise from 1 in 36 children to 1 in 31, highlighting a pressing public health concern. Furthermore, autistic individuals frequently face intricate healthcare needs that require coordinated services spanning health, education, and social care sectors.
Experts stress the importance of recognizing the variety within autism to foster an inclusive environment that meets the needs of all individuals on the spectrum. Additionally, collaboration among various sectors is crucial for effective interventions and support. As we deepen our understanding of this condition, it's vital to address the specific challenges faced by minority communities, who may experience a higher prevalence and severity of this disorder.
By outlining the condition and its spectrum, we empower readers to recognize potential signs and consider whether can someone develop autism in themselves or others, opening the door for further exploration of symptoms and support options. We invite you to share your experiences and thoughts in the comments or through our newsletters, as together we can create a more understanding and supportive community.
Recognize Signs and Symptoms of Autism
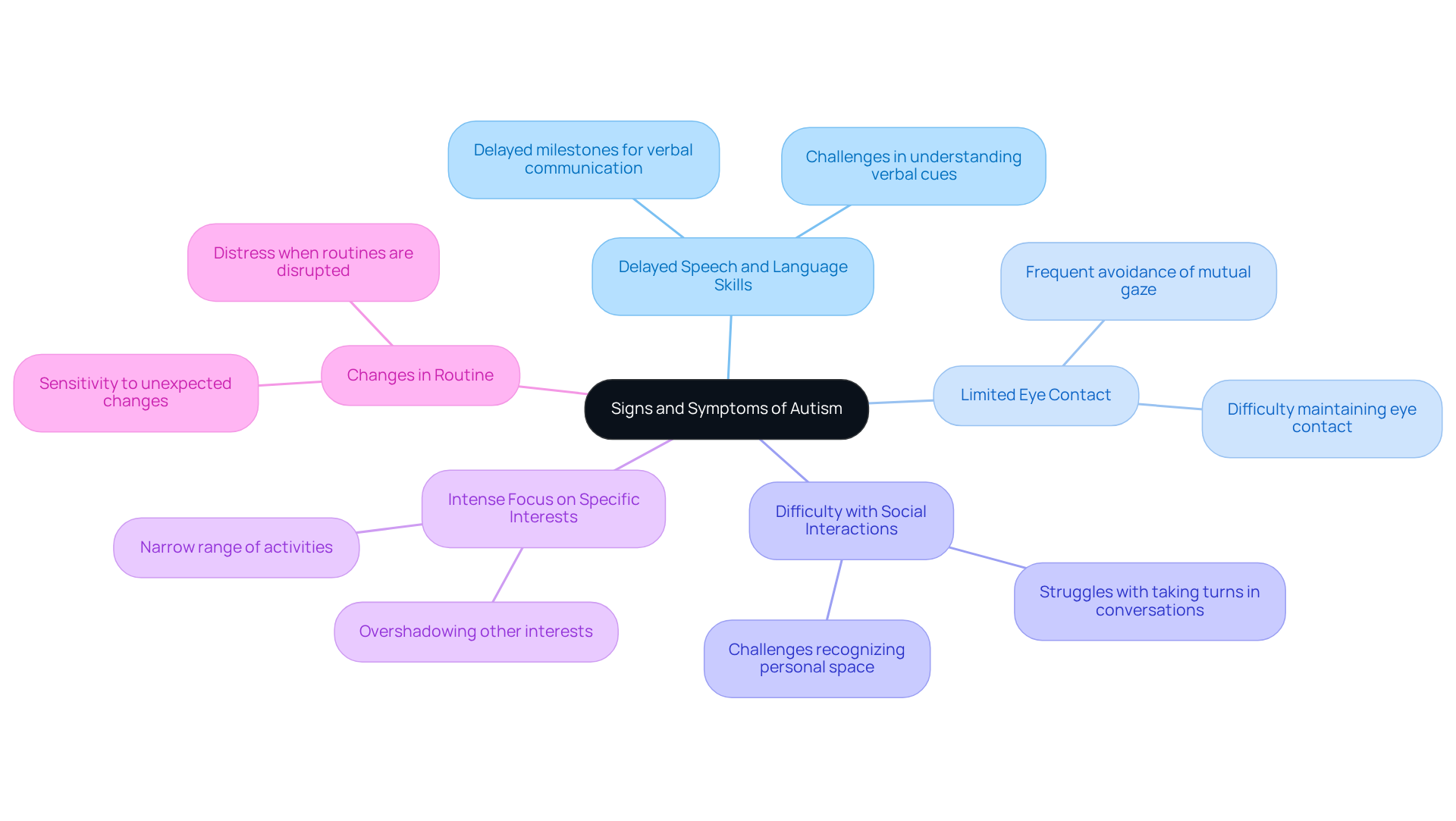
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of autism can someone develop autism, as they often differ significantly from one individual to another. Yet, there are some common indicators that parents and caregivers can look out for:
- Delayed Speech and Language Skills: Many children with autism experience delays in their speech development. Studies indicate that up to 40% may not reach expected milestones for verbal communication. This can manifest as challenges in both developing spoken language and understanding verbal cues.
- Limited Eye Contact: A significant number of young individuals on the spectrum struggle with maintaining eye contact. They may frequently avoid it or find it difficult to engage in mutual gaze. Current data suggests that difficulties with eye contact remain a prevalent concern in 2025, underscoring the importance of awareness.
- Difficulty with Social Interactions: Navigating social norms can be a challenge for children with autism. They may struggle with taking turns in conversations or recognizing personal space, which can lead to misunderstandings in social settings and hinder their ability to form friendships.
- Intense Focus on Specific Interests: It is common for children with autism to exhibit an intense interest in particular subjects or activities. This focused engagement can sometimes overshadow other interests, resulting in a narrower range of activities.
- Changes in Routine: Many young individuals with developmental disorders experience distress when their routines are disrupted or when they encounter unexpected changes. This sensitivity to routine can serve as a significant indicator of autism.
Parents and caregivers are encouraged to observe these behaviors over time, as early recognition can help determine if can someone develop autism, paving the way for timely intervention and support. Recent case studies emphasize the importance of monitoring these signs, as they can provide crucial insights into a young person's developmental journey. Consulting with developmental specialists can further aid in understanding these symptoms and determining the most appropriate course of action.
Seek Professional Evaluation and Diagnosis
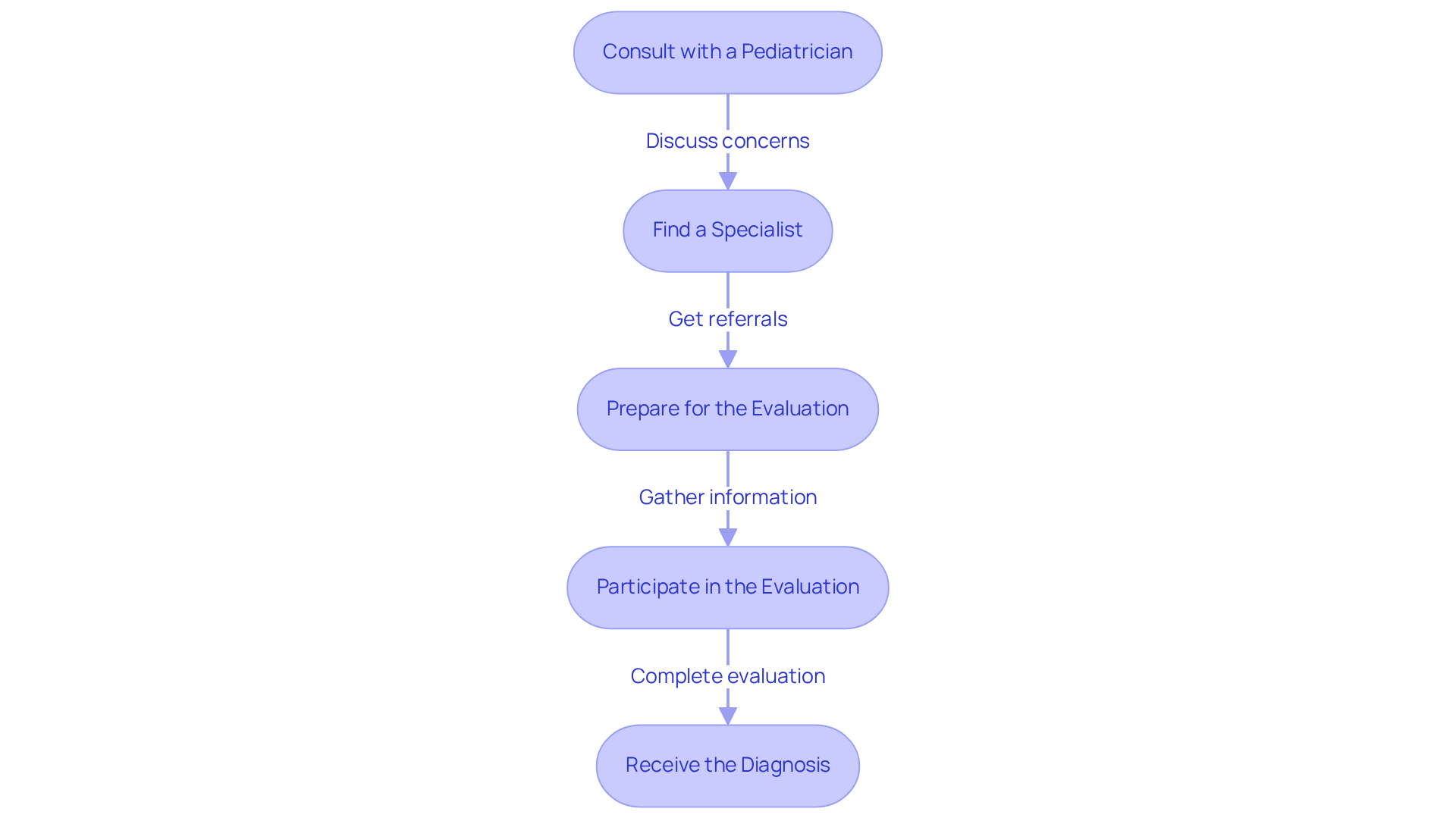
If you suspect that someone may be displaying signs of a developmental disorder, seeking a professional evaluation is essential. It’s a crucial step that can lead to the support and resources needed for the individual. Here’s how to navigate this process effectively:
- Consult with a Pediatrician: Start by discussing your concerns with a pediatrician. They can provide initial guidance and refer you to specialists who can conduct further evaluations.
- Find a Specialist: Look for professionals who specialize in autism assessments, such as child psychologists, developmental pediatricians, or neurologists. Their expertise is vital for an accurate diagnosis and understanding of the situation.
- Prepare for the Evaluation: Gather information about the person’s developmental history, behaviors, and specific concerns you’ve noticed. This information will be invaluable during the assessment process, helping to paint a complete picture.
- Participate in the Evaluation: The evaluation may involve interviews, questionnaires, and direct observations. Be prepared to respond to inquiries and share detailed insights about the person’s behavior and development, as this will aid the specialists in their assessment.
- Receive the Diagnosis: After the evaluation, the specialist will provide feedback and, if applicable, a diagnosis. This diagnosis is crucial for accessing appropriate resources and support services, ensuring that the individual receives the tailored assistance they need.
As stated by the American Academy of Pediatrics, all young children should be assessed for developmental disorders at 18 and 24 months. In 2025, 1 in 36 U.S. youngsters are expected to be identified with a developmental disorder, highlighting the importance of early assessment. The median age of diagnosis is around 4 years and 1 month, underscoring the need for timely intervention. Taking these steps can make a significant difference in the life of a child and their family.
Access Resources and Support Strategies
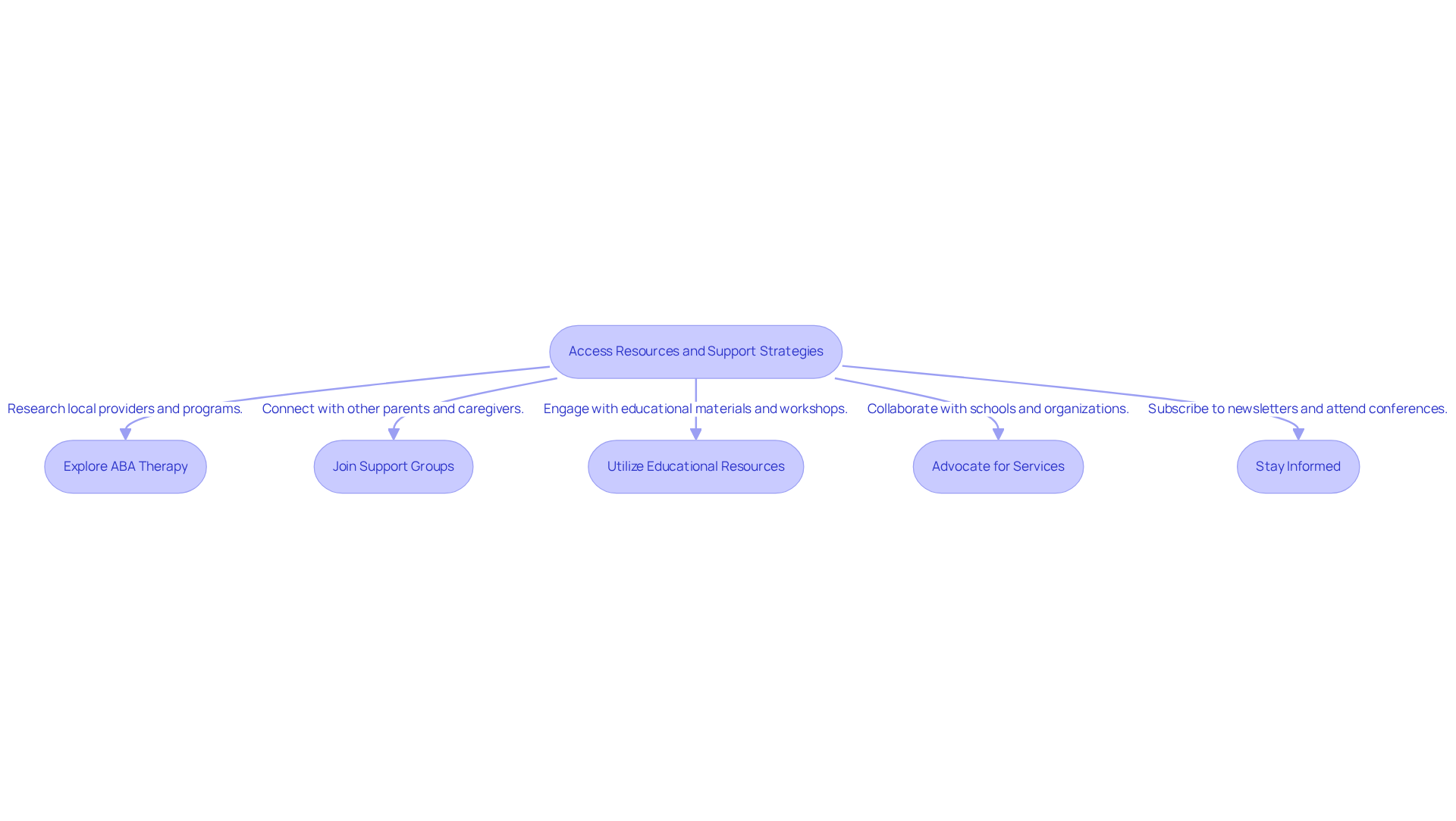
Once a diagnosis has been made, accessing resources and support strategies becomes essential for fostering growth and development. Here are some thoughtful steps to consider:
-
Explore ABA Therapy: Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is recognized as a gold standard for supporting individuals with developmental disorders. Take the time to research local providers and consider enrolling in programs that focus on skill development and behavior management. Studies indicate that children receiving at least 25 hours of ABA therapy weekly show significant improvements in communication and social skills, making it advisable to aim for this baseline to achieve optimal benefits.
-
Join Support Groups: Connecting with other parents and caregivers can offer invaluable emotional support and practical advice. Look for local or online support groups dedicated to developmental disorders. These communities often share resources and strategies that can enhance your journey.
-
Utilize Educational Resources: Many organizations provide educational materials, workshops, and training sessions for parents and professionals. Engaging with these resources can deepen your understanding of developmental disorders and effective support strategies, empowering you to advocate for your child more effectively.
-
Advocate for Services: Work collaboratively with schools and community organizations to ensure that individuals with autism receive the necessary accommodations and support services. Familiarize yourself with your rights and available resources to advocate effectively for your child's needs. It’s important to note that only 15% of insured minors referred for ABA treatment receive the recommended hours of therapy, underscoring the challenges in accessing adequate support.
-
Stay Informed: Subscribe to newsletters, such as those from ASD Media, attend conferences, and engage in online communities to stay updated on the latest research and strategies in supporting individuals with developmental differences. Continuous learning is vital, as it enables you to adapt to new findings and approaches that can benefit your child. Additionally, being aware of the financial burden of autism therapy, which can average around $60,000 per year, is crucial for planning and accessing necessary services.
Conclusion
Understanding autism and its spectrum is essential for recognizing its signs and seeking the right support. The complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) reveal the diverse experiences individuals may encounter, from significant challenges in social interaction to milder symptoms that allow for greater independence. By raising awareness of these variations, we enhance the potential for early recognition and intervention, paving the way for tailored support that addresses each individual's unique needs.
Key insights highlight the importance of recognizing common symptoms, such as:
- Delayed speech
- Limited eye contact
- Intense focus on specific interests
These indicators serve as critical signals for parents and caregivers to seek professional evaluation and diagnosis. Engaging with specialists and accessing resources like ABA therapy and support groups can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with autism and their families, ensuring they receive the necessary assistance to thrive.
Ultimately, the call to action is clear: fostering a more inclusive and supportive community begins with awareness and understanding. By sharing experiences, seeking knowledge, and advocating for resources, we can all contribute to a world where individuals on the autism spectrum are acknowledged for their strengths and supported in their challenges. Embracing this journey together not only enriches the lives of those affected by autism but also cultivates a society that values diversity and promotes acceptance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by a range of challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior. The term 'spectrum' reflects the diverse symptoms and severity levels experienced by individuals with autism.
What are the key characteristics of autism?
Key characteristics of autism include social communication difficulties, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities. Individuals may struggle with understanding social cues, engage in repetitive movements or speech, and have heightened or diminished responses to sensory input.
How does autism affect social communication?
Many individuals with autism may find it challenging to understand social cues, maintain conversations, and form relationships. They might have difficulty interpreting body language or tone of voice, leading to misunderstandings in social situations.
What are some examples of repetitive behaviors in autistic individuals?
Repetitive behaviors can include movements such as hand-flapping or rocking, as well as adhering to strict routines or specific patterns in daily activities.
What are sensory sensitivities in autism?
Autistic individuals often experience heightened or diminished responses to sensory input. For example, they may feel overwhelmed by loud noises or may seek out certain textures for comfort.
What factors contribute to the development of autism?
Autism is thought to develop from a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors during early brain development.
What is the prevalence of autism in the U.S.?
The prevalence of autism in the U.S. has increased, with the CDC reporting a rise from 1 in 36 children to 1 in 31, indicating a significant public health concern.
What challenges do autistic individuals face in healthcare?
Autistic individuals often have intricate healthcare needs that require coordinated services across health, education, and social care sectors.
Why is it important to recognize the variety within autism?
Recognizing the variety within autism is essential for fostering an inclusive environment that meets the needs of all individuals on the spectrum and for effective interventions and support.
How can minority communities be affected by autism?
Minority communities may experience a higher prevalence and severity of autism, highlighting the need to address specific challenges they face regarding the disorder.




