Introduction
In the realm of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, the role of a parent advocate is essential. These advocates stand as the connecting link between the child, the therapists, and the educational system. However, understanding and managing the intricacies of ABA therapy can be a daunting task. To navigate these complexities, parent advocates should strive to educate themselves about ABA therapy, comprehend the unique needs of the child, and foster effective collaboration with therapists and educators. This can be achieved by seeking knowledge from reliable sources such as books, articles, websites that specialize in autism and ABA therapy, and even online courses and webinars. Joining support groups and connecting with other parent advocates can also be a rich source of insights and resources. Parent advocates should also actively participate in the child's treatment plan. This involves attending ABA therapy sessions, which enables them to observe the techniques used by the therapist, understand their child's needs better and learn how to reinforce the therapy at home. Being present during therapy sessions also aids in establishing a strong rapport with the therapist, fostering open communication and collaboration. Asking questions is another crucial aspect of a parent advocate's role in ABA therapy. Some suggested questions might include inquiring about the specific ABA program being used, how progress will be measured and tracked, the qualifications of the ABA therapists, the frequency of therapy sessions, and how communication will be maintained. Understanding the unique needs of the child in ABA therapy is vital for providing effective support. As a parent advocate, collaborating with the ABA therapist to gain insights into the child's individual strengths, weaknesses, and specific goals can be very beneficial. This collaborative approach helps develop and implement personalized strategies that cater to the child's unique needs, promoting their progress and success in therapy. Another important aspect for parent advocates is to ensure that the child's rights are being respected. This includes making sure that the therapy is implemented in a way that promotes the child's well-being and respects their rights. Adhering to ethical guidelines and standards of practice in ABA therapy, which prioritize the child's welfare and promote their rights to dignity, autonomy, and self-determination is paramount. Lastly, building a strong partnership with therapists and educators in ABA therapy is essential for the successful implementation of ABA programs. This involves open communication, collaboration, and mutual respect. Regular meetings and discussions can help align goals and strategies, share progress and challenges, and make necessary adjustments to the therapy plan. Ongoing training and support for therapists and educators can also help them stay updated with the latest research and techniques in ABA therapy, further strengthening the partnership.
1. Understanding Autism and the Need for Positive Behavior Support Systems
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that impacts social interaction, communication, interests, and behavior in diverse ways. This spectrum condition affects individuals differently and to varying degrees. One common challenge is managing the behaviors of children with autism.

This need has led to the development and implementation of Positive Behavior Support (PBS) systems.
Learn more about Positive Behavior Support systems and strategies.
PBS is a scientifically validated approach that helps understand what maintains an individual's challenging behavior. It's a collaborative and assessment-based methodology aimed at developing effective, individualized interventions. The goal is to create interventions that are practical, implementable, and enhance the quality of life for individuals and their support providers.
There are effective interventions available for managing challenging behaviors in individuals with ASD. These interventions are designed to address specific needs and challenges, with the ultimate aim of promoting positive behavior and reducing problematic behaviors. One such intervention is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA). ABA uses principles of behavior to teach new skills and reduce problem behaviors. This is achieved by breaking down these behaviors into smaller, manageable steps and providing positive reinforcement for desired behaviors.
Other interventions that have shown effectiveness include social stories, visual supports, structured schedules, and sensory strategies.
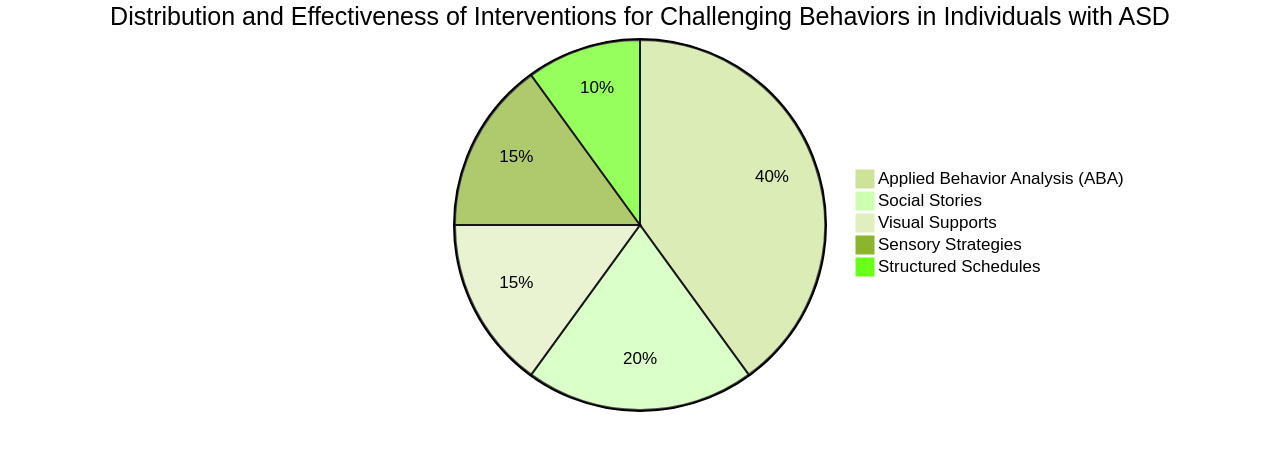
These strategies are best implemented under the guidance of a trained professional or therapist who specializes in ASD interventions. They can develop and implement an individualized intervention plan based on the specific needs and challenges of the individual with ASD.
Developing individualized positive behavior support plans for children with autism often involves focusing on effective strategies for enhancing social skills. Strategies that target specific social behaviors can help children with autism learn and practice appropriate social interactions. Involving parents, teachers, and other professionals in the development and implementation of these behavior support plans ensures consistency and generalization of skills across different settings.
Collaborative assessment methods can be particularly effective in understanding and addressing challenging behaviors in individuals with ASD. These methods involve a team of professionals, including psychologists, educators, and therapists, working together to gather information and develop strategies. By pooling their expertise and perspectives, the team can gain a comprehensive understanding of the individual's behaviors and determine the most effective interventions.
One potential solution to enhance the quality of life for individuals with autism and their support providers is to implement effective strategies for enhancing social skills in children with autism. These strategies can focus on developing communication skills, promoting social interaction, and fostering independence. Providing access to unlimited digital resources and information can also be beneficial for individuals with autism and their support providers to stay informed and connected.
Research-based interventions for improving social interaction and communication skills in children with ASD may include strategies such as social skills training, peer-mediated interventions, and video modeling. Additionally, speech and language therapy can also be effective in targeting communication difficulties in children with ASD. It's important to individualize interventions based on the specific needs and abilities of each child with ASD.
Positive behavior support techniques can be effective in addressing specific challenging behaviors in individuals with autism.
These techniques focus on understanding the function of the behavior and implementing strategies to teach and reinforce more appropriate behaviors. Some examples of positive behavior support techniques include functional behavior assessments, visual supports, social stories, token economies, and structured schedules. These techniques are tailored to the individual's needs and can help promote positive behavior change and improve overall quality of life.
To implement a comprehensive positive behavior support system for individuals with ASD, there are several resources and tools available. These resources can include evidence-based interventions, social skills training programs, visual supports, and behavior management strategies. Additionally, professionals and caregivers can access online platforms and websites that offer educational materials, training modules, and support networks specifically tailored for individuals with ASD and their families. These resources and tools provide valuable guidance and strategies to promote positive behavior and enhance the overall well-being of individuals with ASD.
To find case studies and success stories of using positive behavior support in managing challenging behaviors in individuals with autism, you can explore reputable websites and resources that focus on autism support services. These sources often provide real-life examples and testimonials from professionals, parents, and individuals with autism who have implemented positive behavior support strategies. Additionally, academic journals and research publications may also contain case studies that highlight the effectiveness of positive behavior support in managing challenging behaviors in individuals with autism.
There might be training and professional development opportunities available for professionals working with individuals with ASD and implementing positive behavior support. These opportunities could provide professionals with the necessary knowledge and skills to effectively support individuals with ASD and promote positive behavior. It is important for professionals to stay updated on the latest research and interventions in the field of ASD to ensure they are providing the best possible support.
2. The Role of ABA Therapy in Building Positive Behavior Support Systems
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a widely recognized and effective strategy for treating individuals with autism. The therapy is rooted in the principles of behavior analysis and is tailored to the unique needs and abilities of each individual. It is crucial in establishing Positive Behavior Support (PBS) systems, as it emphasizes the enhancement of specific behaviors like social skills, communication, academic capabilities, and adaptive learning skills, such as fine motor dexterity, hygiene, grooming, domestic capabilities, punctuality, and job competence.
The effectiveness of ABA therapy lies in its focus on teaching and reinforcing positive behaviors, a process that is systematic and structured to foster skill development and generalization. Techniques used in ABA therapy are varied and can be adapted to the individual's requirements. For example, social skills such as turn-taking, initiating conversations, and understanding social cues can be learned through ABA therapy. This is often supplemented with other techniques like social stories, video modeling, and social skills groups to further enhance social interaction and communication skills.
Positive reinforcement strategies are a key component of ABA therapy, particularly for enhancing communication skills. Rewards and praise for desired behaviors motivate individuals to improve their communication abilities. This can include token systems, social praise, or small tangible rewards to reinforce and encourage effective communication.
ABA therapy also plays a significant role in building PBS systems. It focuses on behavior analysis and modification, which can help individuals with autism develop appropriate social and communication skills.
Explore the impact of ABA therapy on building positive behavior support systems.
By identifying and addressing problem behaviors, ABA therapy helps individuals with autism learn new behaviors and reduce challenging behaviors. This, in turn, contributes to the development of a positive behavior support (PBS) system that supports individuals with autism in various settings such as homes, schools, and communities.
Within the realm of adaptive learning skills, ABA therapy targets a variety of skills, including fine motor dexterity, hygiene, grooming, and more. By breaking down skills into smaller steps and providing positive reinforcement, ABA therapy can help individuals develop and improve their skills in various areas.
ABA therapy is also effective in improving academics and job competence. Techniques such as positive reinforcement and shaping can help children improve their academic skills and develop the necessary job-related competencies. This can include skills such as following instructions, staying on task, problem-solving, and social interactions, all of which are important for success in academics and future employment.
In the context of punctuality, implementing ABA therapy techniques involves creating a structured schedule and routine with visual schedules, timers, and prompts to help individuals with autism understand and follow a set schedule. Positive reinforcement can be used to motivate and encourage punctuality, such as providing rewards or praise for being on time.
Finally, ABA therapy is considered the gold-standard treatment for autism and related disorders. It unlocks the potential of individuals with autism by using strategies and interventions based on the principles of behavior analysis. These strategies and interventions aim to teach and reinforce desired behaviors while reducing challenging behaviors. Through consistent and structured implementation of ABA therapy, individuals with autism can develop and acquire essential skills across different domains, including communication, social, academic, and daily living skills.
3. Strategies for Parent Advocates: Navigating the Challenges of ABA Therapy
In the realm of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, the role of a parent advocate is essential. These advocates stand as the connecting link between the child, the therapists, and the educational system. However, understanding and managing the intricacies of ABA therapy can be a daunting task.
To navigate these complexities, parent advocates should strive to educate themselves about ABA therapy, comprehend the unique needs of the child, and foster effective collaboration with therapists and educators. This can be achieved by seeking knowledge from reliable sources such as books, articles, websites that specialize in autism and ABA therapy, and even online courses and webinars. Joining support groups and connecting with other parent advocates can also be a rich source of insights and resources.
Parent advocates should also actively participate in the child's treatment plan. This involves attending ABA therapy sessions, which enables them to observe the techniques used by the therapist, understand their child's needs better and learn how to reinforce the therapy at home. Being present during therapy sessions also aids in establishing a strong rapport with the therapist, fostering open communication and collaboration.
Asking questions is another crucial aspect of a parent advocate's role in ABA therapy. Some suggested questions might include inquiring about the specific ABA program being used, how progress will be measured and tracked, the qualifications of the ABA therapists, the frequency of therapy sessions, and how communication will be maintained.
Understanding the unique needs of the child in ABA therapy is vital for providing effective support. As a parent advocate, collaborating with the ABA therapist to gain insights into the child's individual strengths, weaknesses, and specific goals can be very beneficial. This collaborative approach helps develop and implement personalized strategies that cater to the child's unique needs, promoting their progress and success in therapy.
Another important aspect for parent advocates is to ensure that the child's rights are being respected. This includes making sure that the therapy is implemented in a way that promotes the child's well-being and respects their rights. Adhering to ethical guidelines and standards of practice in ABA therapy, which prioritize the child's welfare and promote their rights to dignity, autonomy, and self-determination is paramount.
Lastly, building a strong partnership with therapists and educators in ABA therapy is essential for the successful implementation of ABA programs. This involves open communication, collaboration, and mutual respect. Regular meetings and discussions can help align goals and strategies, share progress and challenges, and make necessary adjustments to the therapy plan. Ongoing training and support for therapists and educators can also help them stay updated with the latest research and techniques in ABA therapy, further strengthening the partnership.
4. Empowering Parents: Effective Communication and Time Management Techniques
As primary caregivers, parents are instrumental in a child's development, and this role is even more critical when it comes to managing Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy for children with autism or ADHD. This journey, while rewarding, can be demanding and sometimes overwhelming.
A key part of this journey is effective communication. Parents need to maintain open, regular communication with therapists and educators. This ensures they stay informed about their child's progress and promptly address any concerns. By implementing clear and concise instructions, using visual supports, and providing positive reinforcement, parents can foster effective communication. It's also crucial that parents actively involve themselves in their child's therapy sessions. This not only improves parent-child communication but also ensures consistency and collaboration in implementing ABA techniques.
Similarly, time management is a vital skill for parents navigating ABA therapy. A structured routine, setting realistic goals, and efficiently prioritizing tasks are strategies that can help parents manage their time effectively. To create a structured routine, break down therapy sessions and tasks into smaller, manageable steps. Use visual aids, such as a visual schedule or task cards, to provide a visual representation of the routine. Consistent reinforcement and rewards for completing tasks can help motivate individuals to stick to the routine.
Setting realistic goals is an integral part of managing ABA therapy. Parents should work closely with therapists and professionals to understand their child's abilities and needs, which can inform the development of appropriate goals. Celebrating small victories along the way can encourage both the parent and child and instill a sense of accomplishment.
Prioritizing tasks is another essential time management technique. By organizing tasks based on their importance and deadline, parents can ensure that the most important and time-sensitive tasks are completed first. When needed, delegating tasks or seeking assistance can lighten the workload and ensure that all responsibilities are being addressed effectively.
Lastly, self-care should not be forgotten. Taking time for relaxation, exercise, and activities that help recharge can reduce stress levels. Having a support system in place, such as other parents who have gone through similar experiences or joining support groups, can offer much-needed respite and advice.
Remember, every child is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. As a parent, trust your instincts and collaborate with professionals to provide the best possible support for your child's ABA therapy.
5. Unlocking Potential: Strategies for Managing Challenging Behaviors in Children with Autism
Addressing challenging behaviors in children with autism may seem overwhelming, yet with the right approaches and tools, parents and advocates can guide these children towards unlocking their potential. ABA therapy, a cornerstone in managing challenging behaviors, offers a variety of strategies. Among them are positive reinforcement, which rewards good behavior to promote its repetition, and antecedent-based interventions, where triggers for challenging behaviors are identified and modified.
However, it's not only about ABA therapy. Creating a predictable and structured environment for the child can significantly reduce anxiety and minimize challenging behaviors. Visual supports such as visual schedules and social stories can also be instrumental in helping children grasp expectations and routines, further reducing challenging behaviors.
Positive reinforcement techniques, like rewards and praise, can be effective in promoting desired behaviors. It's crucial to identify specific behaviors to reinforce and maintain a consistent reinforcement schedule. This consistency is the key to managing challenging behaviors. Consistently applying behavior management strategies across different settings helps children with autism understand expectations, develop appropriate behaviors, and generalize these behaviors across various environments.
In addition to the above-mentioned strategies, focusing on the child's strengths and interests plays a crucial role. Providing opportunities for them to engage in activities they enjoy and excel at can help them feel more secure and confident in their abilities.
Lastly, it's vital to work closely with professionals, such as therapists and educators, who can provide guidance and support in implementing these strategies. Their expertise can offer valuable insights on behavior management strategies, ensuring that the child's unique needs are met and that they have the best chance at reaching their full potential.
6. Enhancing Social Skills Development in Children with Autism through ABA Therapy
Social interactions form the crux of relationships, and mastering social skills is crucial for successful communication. This can be a challenge for children diagnosed with autism, but, thankfully, tools such as ABA therapy can provide significant assistance. This therapy uses evidence-based strategies to break down complex social skills into smaller, manageable steps, making it easier for children to grasp and practice these skills.
One such strategy involves role-play. This technique creates a simulated environment where children can practice their social skills in a controlled setting. It provides opportunities for them to learn and apply social behaviors like turn-taking, active listening, and conversation initiation. Through repeated role-play exercises, children can gain confidence and improve social competence; they can even apply these learned skills to real-life social interactions.
ABA therapy also employs narrative-based interventions, known as social stories, to provide children with specific information about social situations. These stories include details about appropriate behaviors and responses to different social cues. By incorporating social stories, ABA therapists can help children navigate social interactions, understand social cues, and develop appropriate social skills.
Another strategy used in ABA therapy for teaching social behavior is video modeling. Here, videos demonstrating appropriate social skills and behaviors are shown to the children. By observing these videos, children can learn how to engage in social interactions, communicate effectively, and respond appropriately to social cues.
Group ABA therapy sessions are also beneficial for children to practice their social skills with peers. These sessions can be designed and planned using insights from various resources, combined with the expertise of an ABA therapist. This creates a comprehensive plan that focuses on practicing social skills with peers.
Remember, the ultimate goal of ABA therapy is to enhance the overall social abilities of children with autism and promote their integration into social settings. By using a combination of strategies, such as visual supports, social stories, and structured routines, ABA therapy creates a positive learning environment. Clear and consistent instructions help children develop social skills, improve communication, and build relationships with others.
While each child with autism is unique, the teaching strategies and interventions can be tailored to meet their specific needs and abilities. With the right support, they can learn to navigate the complex world of social interactions, leading to a more fulfilling and independent life.
7. Building an Inclusive Community: Collaborative Approaches to Support Services
Creating a community that includes and supports children with autism and their families is a pivotal step. This task requires nurturing a collaborative spirit amongst parents, therapists, educators, and other contributors. The implementation of a collaborative approach to support services can significantly improve the effectiveness of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy and promote positive results.
One beneficial strategy in building this inclusive community within ABA therapy is to focus on promoting social skills development in children with autism. By ensuring unlimited digital access to resources and materials, ABA therapy practitioners can help these children develop their social skills, contributing to the establishment of a more inclusive community within the therapy setting.
The collaborative approach extends beyond just the therapy setting. It involves therapists, educators, and parents working together to create a comprehensive treatment plan that caters to the unique needs of the individual. Regular communication, coordination, and sharing of resources and strategies between all parties involved can maximize the effectiveness of autism therapy and support services.
Joint decision-making is another aspect of this collaborative approach that can enhance the effectiveness of ABA therapy. By involving multiple stakeholders in the treatment process, a more comprehensive understanding of the individual's needs and goals can be achieved. This approach allows the identification of potential barriers and the development of solutions while considering the perspectives and expertise of parents, therapists, and other professionals.
Coordinated service delivery is also of paramount importance in an inclusive community. This approach ensures that all relevant organizations, professionals, and resources work together in a cohesive and collaborative way, providing comprehensive and holistic support that addresses the unique needs of individuals with autism. This coordination can include healthcare providers, educators, therapists, and community organizations, and the implementation of evidence-based practices and interventions.
The provision of a platform for parents and advocates to share experiences is also crucial. This can be achieved through setting up a website or online community dedicated to this purpose. Such a platform can facilitate communication and information exchange, empowering parents and advocates in navigating ABA therapy and improving outcomes for individuals with autism.
In an inclusive community, a spectrum of support is necessary. This spectrum can include various services and resources aimed at empowering parents and promoting social skills in children with autism. Specialized therapies, educational interventions, and community programs that foster inclusion and understanding can all contribute to this spectrum of support.
Finally, to enhance positive outcomes through collaboration in ABA therapy, it is important for professionals to work together and share their expertise. This collaboration can involve multidisciplinary teams, such as behavior analysts, speech therapists, occupational therapists, and educators. Moreover, collaboration with parents and caregivers is crucial as they play a vital role in implementing strategies and interventions outside of therapy sessions.
8. Staying Updated: The Importance of Continuous Learning and Improvement in ABA Therapy
Keeping abreast of the latest research and techniques in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is pivotal for ensuring the highest quality of care for children with autism. One way to stay current is by regularly engaging with reputable sources in the field. This includes reviewing scholarly journals, attending professional conferences, and consulting with field experts. Moreover, engaging in discussions and sharing insights on online communities and forums dedicated to ABA therapy can offer valuable perspectives on the latest research and techniques.
An effective way to receive regular updates on ABA therapy is by subscribing to relevant newsletters. For instance, the website https://www.asd.media/news/enhancing-aba-therapy-implementation-industry-insights-for-overcoming-challenges-and-improving-outcomes provides options for unlimited digital access, with subscription options ranging from 5-7 months to a yearly subscription.
Additionally, this website provides access to a wealth of digital content, including industry insights that can aid in overcoming challenges and enhancing the implementation of ABA therapy. This resource also gives access to workshops and seminars, providing an opportunity for continuous learning and professional development.
Participation in online forums and communities dedicated to ABA therapy is another effective way to stay updated. These platforms offer a space for sharing information, posing questions, and engaging in discussions about the latest updates and advancements in the field. Joining these communities not only allows for connection with like-minded individuals, but also provides opportunities to learn from their experiences and stay informed about new developments in ABA therapy.
Continuous learning is essential in ABA therapy, as it allows for staying updated with the latest industry insights, overcoming challenges, and improving outcomes. By continually learning and adapting techniques, practitioners can provide the best possible care for individuals with autism.
Staying informed about the latest advancements in ABA therapy can lead to numerous benefits. It allows for access to new techniques, strategies, and interventions that can improve the implementation of ABA therapy. This knowledge can help overcome challenges and improve outcomes for individuals receiving ABA therapy. Moreover, staying updated allows individuals to stay current with evolving standards and best practices in the field, ensuring that they are providing the most effective, evidence-based interventions.
In conclusion, continuous learning is paramount for maximizing the benefits of ABA therapy. By staying updated with industry insights and overcoming challenges, practitioners can improve outcomes for individuals receiving ABA therapy. Ongoing professional development and education play a crucial role in enhancing the implementation of ABA therapy techniques and strategies.
Staying informed about advancements in ABA therapy allows professionals and parents to access the latest industry insights, overcome challenges, and improve outcomes. By staying updated about new techniques, strategies, and research findings, individuals involved in ABA therapy can enhance the implementation of therapy and provide better support to individuals with autism. Moreover, staying updated on advancements helps professionals and parents navigate autism support services more effectively, empowering them to play an active role in their child's therapy journey.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ABA therapy is a crucial tool in building positive behavior support systems for individuals with autism. It focuses on teaching and reinforcing positive behaviors, breaking down complex skills into manageable steps, and promoting generalization across different settings. By incorporating strategies such as positive reinforcement, visual supports, and social stories, ABA therapy helps individuals develop essential skills in areas like communication, social interaction, academics, and adaptive learning. The collaborative approach between therapists, educators, and parents is vital in creating effective treatment plans that cater to the unique needs of each individual. With continuous learning and improvement in ABA therapy techniques, individuals with autism can unlock their potential and lead fulfilling lives.
To support individuals with autism and enhance the effectiveness of ABA therapy, it is important for parent advocates to educate themselves about ABA therapy and collaborate with therapists and educators. They should actively participate in their child's treatment plan by attending therapy sessions and asking questions to gain insights into the specific ABA program being used. Parent advocates should also strive to understand the unique needs of their child in ABA therapy by collaborating with the therapist to develop personalized strategies. Ensuring that the child's rights are respected and building strong partnerships with therapists and educators are also crucial. By taking these steps, parent advocates can create a supportive environment that promotes the progress and success of their child in ABA therapy.




