Overview
This article highlights the best practices in autism behavioral health, focusing on the importance of tailored interventions and the significant role of various therapies, especially Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), in supporting individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
It illustrates how personalized treatment plans, combined with active family engagement, can profoundly enhance outcomes.
For instance, statistics reveal that children experience improved social skills and overall well-being when their parents are actively involved in their care.
This underscores the vital role families play in the journey of their loved ones with ASD, creating a nurturing environment that fosters growth and development.
Introduction
In the intricate landscape of autism support, understanding the multifaceted nature of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is paramount. With the prevalence of autism on the rise—recent statistics revealing that approximately 1 in 36 children in the U.S. is diagnosed—the urgency for tailored interventions has never been greater.
This article explores the critical components of autism behavioral health, emphasizing the importance of personalized approaches and the diverse therapies available, such as:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
- Occupational therapy
- Speech therapy
By examining individualized treatment plans and the essential involvement of families, it highlights how a collaborative effort can create a nurturing environment for individuals with autism. Together, we can empower them to thrive within their communities.
Understanding Autism Behavioral Health: Key Concepts and Importance
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted developmental condition that presents unique challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior. Understanding autism behavioral health requires recognizing the distinct needs of individuals on the spectrum and the critical role of tailored interventions. Key concepts include:
- The neurodevelopmental basis of the condition
- The wide range of symptoms
- The significant influence of environmental factors on behavior
For instance, recent statistics indicate that approximately 1 in 36 youngsters in the U.S. is diagnosed with spectrum disorder in 2025, underscoring the increasing prevalence of this condition.
The importance of tailored approaches cannot be overstated. Tailored interventions are essential for addressing the diverse needs of autistic individuals, as they can lead to improved outcomes in social skills, communication, and overall well-being. The American Psychological Association recognizes ABA as an evidence-based therapy with demonstrated success, highlighting that understanding the autism behavioral health of individuals is crucial for creating effective assistance strategies.
Moreover, a report from UC San Francisco reveals the mental health challenges faced by families, showing that around 50% of mothers of autistic children experience symptoms of depression, significantly higher than their non-autistic counterparts. This finding points to the urgent need for comprehensive support systems for parents and caregivers.
In addition, the educational landscape for autistic youth highlights disparities, with 8% of autistic students in the U.S. not completing high school, compared to 5% of all students. Furthermore, approximately 50% of autistic youth in the U.S. who receive vocational rehabilitation services begin those services in high school, emphasizing the importance of early intervention.
These statistics underscore the necessity of bridging gaps in healthcare access and ensuring culturally-informed care for diverse communities. By fostering a deeper understanding of autism behavioral health and implementing successful strategies, parents and professionals can create a supportive environment that empowers individuals with developmental disorders to thrive.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): A Cornerstone of Autism Support
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a scientifically validated method that focuses on understanding and modifying behavior through techniques such as reinforcement, prompting, and modeling. This approach is particularly effective for children on the spectrum, as it aligns with autism behavioral health and can be tailored to meet their specific needs. Recent studies show that roughly 36.5% of caregivers for individuals with developmental disorders employ ABA therapy, highlighting its commonality and approval within the community.
Advocacy efforts are underway to enhance access to therapy services for individuals on the spectrum, specifically targeting autism behavioral health. These initiatives include insurance reform and increased public funding, aiming to ensure that more families can benefit from essential autism behavioral health services.
Intensive and long-term ABA therapy has been shown to yield substantial improvements in critical areas such as communication, social skills, and daily living activities. Different types of ABA therapy cater to individual needs, enhancing learning experiences and outcomes. For instance, a significant case study underscores the importance of early diagnosis in autism behavioral health, demonstrating that early intervention through ABA therapy greatly improves outcomes for youngsters.
This aligns with findings that show 90% of youngsters receiving intensive ABA therapy exhibit remarkable progress, frequently attaining developmental levels similar to their peers. Dr. O. Ivar Lovaas observed that '90% of youngsters undergoing intensive ABA therapy displayed significant advancements, with many advancing to levels indistinguishable from their counterparts.'
Furthermore, the latest research emphasizes the long-term advantages of ABA therapy. Individuals who participate in these interventions not only enhance their immediate abilities but also experience enduring positive impacts as they mature. Success stories from families illustrate how ABA therapy has transformed communication skills, enabling young individuals to express themselves more effectively and interact socially with their peers.
Considering its demonstrated effectiveness and the ongoing advocacy for enhanced access, parents and professionals should regard ABA therapy as a fundamental element of support for individuals with developmental disorders. It is vital to ensure that young ones receive the customized interventions essential for their growth.
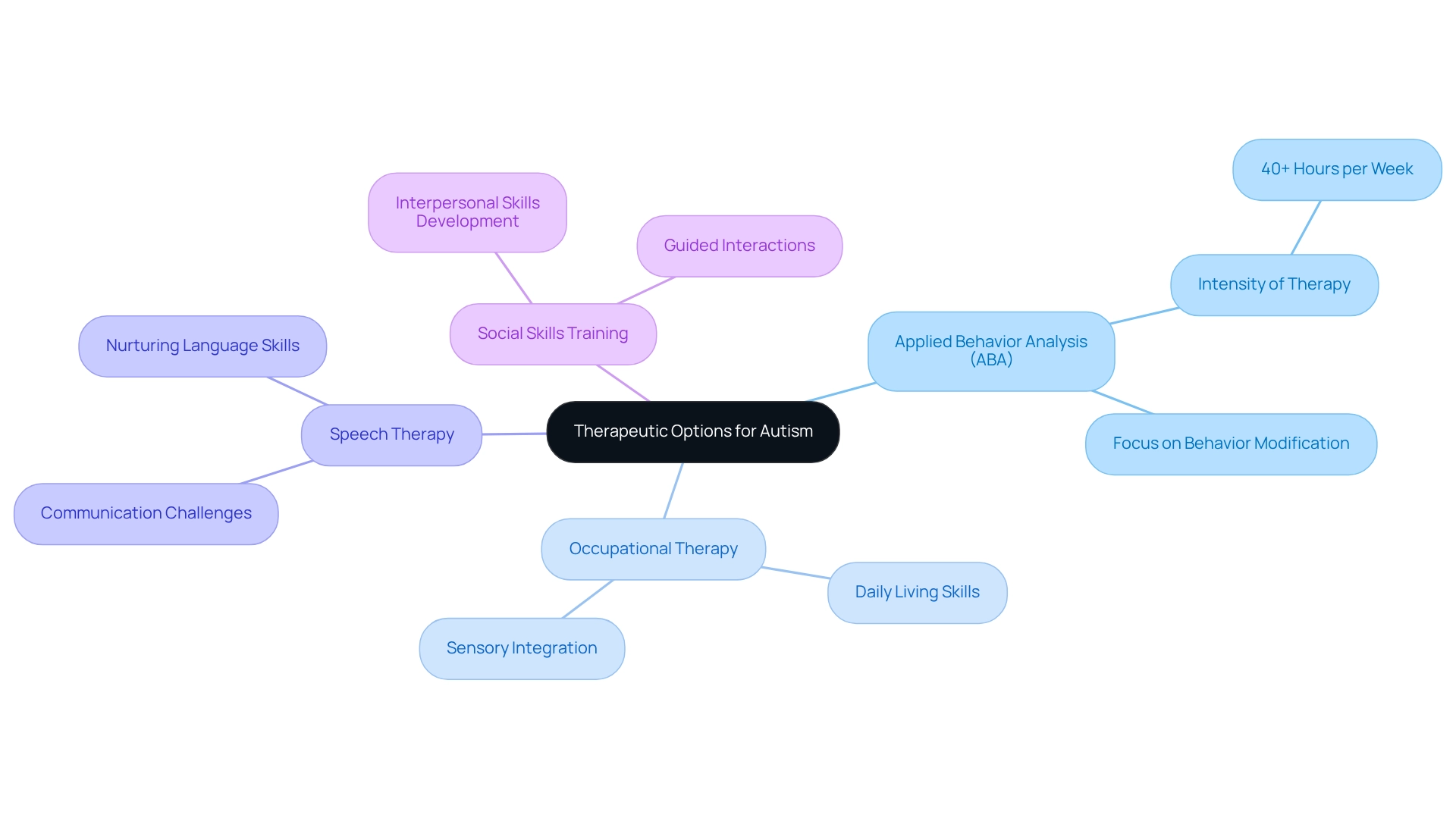
Exploring Therapy Options: From ABA to Occupational Therapy
Beyond Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), there exists a range of therapeutic options designed to support individuals with autism, each offering distinct benefits.
- Occupational therapy is essential for enhancing daily living skills and sensory integration, helping children navigate their environments more effectively.
- Conversely, speech therapy specifically tackles communication challenges, nurturing vital language skills that facilitate social interactions.
- Moreover, social skills training programs present structured opportunities for individuals to cultivate interpersonal skills through guided interactions, significantly boosting their ability to connect with peers.
The integration of these therapies can culminate in a holistic treatment plan tailored to the individual's unique needs. For instance, children with substantial developmental disabilities may require over 40 hours of ABA therapy each week, underscoring the intensity of this approach compared to other alternatives. However, incorporating occupational and speech therapy can address broader developmental objectives.
As Catherine Lord, a pioneering autism researcher, notes, "What a good therapist does... is try to figure out ways that build on an individual’s strengths, that use their interests, but that allow them to participate in society and that will give them the most choices." This viewpoint resonates with the growing acknowledgment of neurodiversity, highlighting the importance of recognizing each individual’s unique strengths throughout the therapeutic journey.
Parents are encouraged to explore these diverse options, considering their child’s age, developmental level, and specific challenges. This comprehensive approach not only nurtures the young person's development but also underscores the importance of therapist approachability and adaptability. Case studies reveal that inconsistency and inflexibility can hinder a young individual’s engagement and progress during therapy sessions. By fostering an environment of support and understanding, we can help pave the way for meaningful growth.
Individualized Treatment Plans: Tailoring Support to Unique Needs
Personalized treatment plans are vital for effectively supporting children with autism, as they cater to each child’s unique needs. These plans should stem from thorough evaluations that highlight the individual’s strengths, challenges, and preferences. It is crucial to involve parents in the planning process; this ensures that the interventions align with family goals and values, fostering a collaborative atmosphere.
Research shows that when parents actively engage in treatment planning, the chances of positive outcomes rise significantly. Statistics reveal that parent involvement can enhance both engagement and skill acquisition in children.
José Fernández Cerero highlights the importance of investing in educational materials tailored for students with ASD, underscoring the need for customized resources in treatment planning. Regular monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan are essential to meet the evolving needs of the individual. A recent study categorized patients into three age groups—2-5 years, 6-12 years, and 13-22 years—to assess progress in skill acquisition.
The findings indicated that the middle age cohort (6-12 years) demonstrated the most significant growth in skill acquisition, while the youngest cohort faced challenges with executive functioning skills. This emphasizes the importance of age-appropriate treatment strategies in ABA therapy. Moreover, the K coefficient surpassed 0.8 for 11 of the 12 selected experts, reflecting a highly satisfactory level of competence in treatment planning.
This personalized approach not only enhances involvement but also fosters a sense of ownership and empowerment for both the youth and their families, ultimately leading to more effective support and improved outcomes.
Engaging Families: The Role of Parents and Caregivers in Autism Support
Family participation is vital for providing effective support to individuals with developmental disorders. Parents and caregivers serve as the primary advocates for their children, and their unique insights can significantly shape treatment strategies. Therefore, their engagement is essential. To foster this involvement, professionals should prioritize regular communication and offer comprehensive education about autism.
Equally crucial is training parents on how to reinforce therapeutic skills at home.
Successful approaches to involving families include:
- Therapy sessions
- Group meetings
- Workshops
These methods not only empower families to tackle challenges but also cultivate a supportive community where they can celebrate achievements together. Research indicates that participation in support groups has been particularly beneficial; a significant majority of parents have reported gaining valuable information and emotional support from these networks.
A case study titled "Support Groups for Parents of Children with ASD" highlights this, showing that many parents found these groups instrumental in sharing experiences and resources.
Moreover, expert opinions underscore the importance of parental involvement in autism therapy. Involving family members in the therapeutic process has been shown to improve intervention outcomes in autism behavioral health. Statistics reveal that children whose guardians are actively engaged in their therapy exhibit enhanced behavioral and social skills. Notably, the K coefficient exceeded 0.8 for 11 of the 12 selected experts, reinforcing the credibility of these findings.
As we look toward 2025, the emphasis on parent training continues to grow, with effective strategies emerging to equip parents with the resources they need to support their children successfully.
Additionally, mindfulness-based interventions have proven effective in reducing parental distress, further promoting involvement and well-being. By fostering a collaborative environment, professionals can significantly enhance the overall effectiveness of interventions, ultimately leading to better outcomes for children with autism. This commitment to involvement not only strengthens the therapeutic connection but also creates a robust network that benefits the entire family.
Furthermore, increased funding for educational materials and training initiatives for school personnel is crucial to address the systemic challenges families face, ensuring they have the support necessary to thrive.
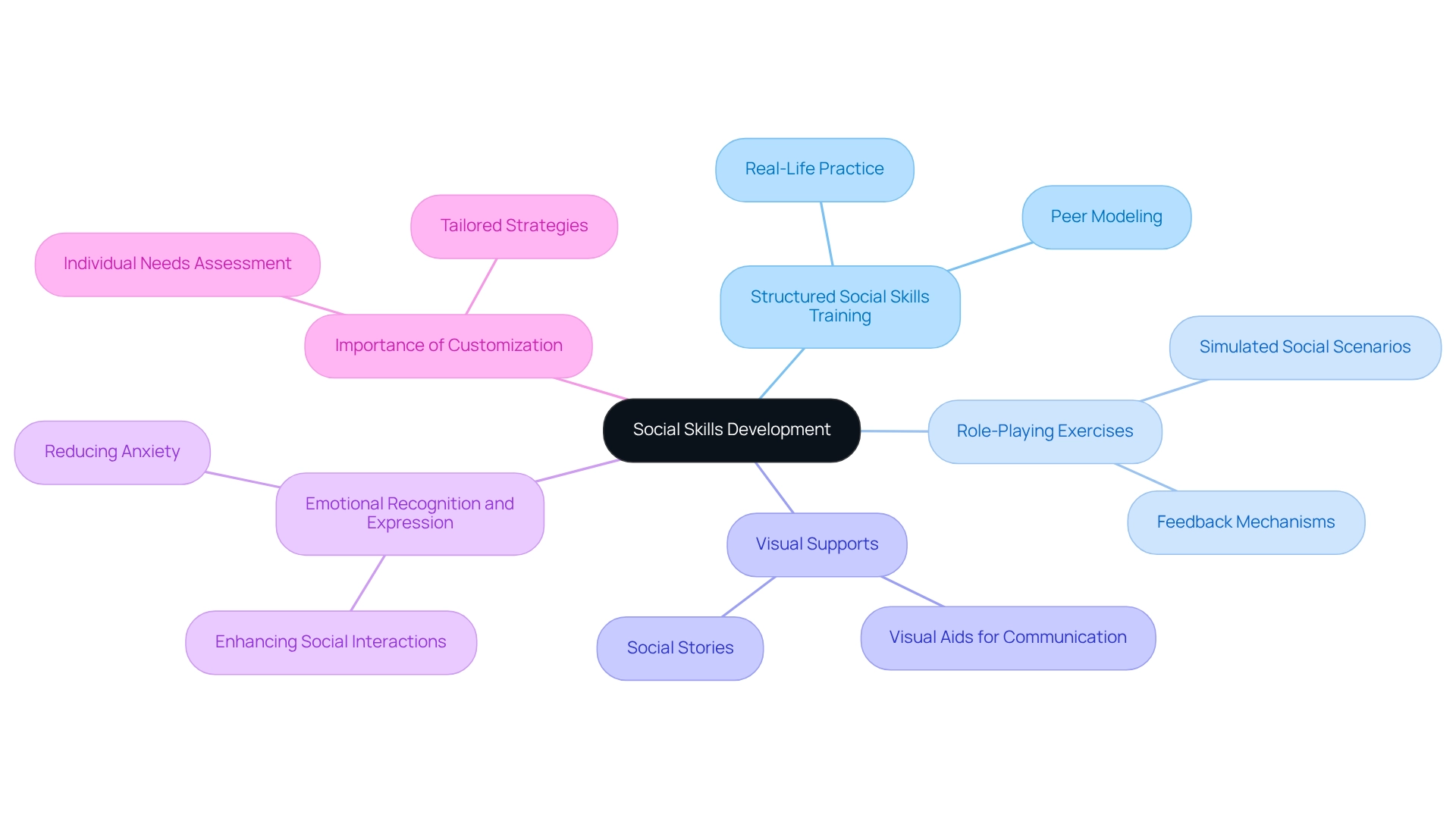
Social Skills Development: Strategies for Enhancing Communication
The development of social skills is crucial for individuals with autism, as it greatly impacts their ability to connect with peers and navigate various social situations. By implementing effective strategies such as:
- Structured social skills training
- Role-playing exercises
- Visual supports
we can foster a nurturing environment that encourages meaningful communication. Programs that incorporate peer modeling and real-life practice provide essential support, allowing individuals to learn and apply appropriate social behaviors in a safe space.
Moreover, teaching emotional recognition and expression plays a vital role in enhancing social interactions. Research from the Nehemiah Autism Center utilized a pre-test, post-test control group design to assess the effectiveness of social skills training, revealing positive changes in the social competencies of youth. This training not only alleviates anxiety related to social interactions but also enhances overall communication, paving the way for more fulfilling relationships.
As noted by March-Miguez, social skills training significantly boosts the social competence of youth with developmental disorders, which is essential for their growth and well-being. It’s important for parents and professionals to prioritize social skills training as a core element of a comprehensive treatment plan. This approach not only promotes better socialization but also supports emotional regulation and communication abilities. Insights from social skills trainers emphasize the importance of customizing these strategies to meet individual needs, ensuring that every young person can thrive in social environments.
Lastly, the overall between-group heterogeneity for treatment type was 0.28 with p = 0.59, highlighting the ongoing need to focus on effective social skills training interventions. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of those we support, fostering a brighter future for individuals with autism.
Navigating Challenges: Common Obstacles and Solutions for Parents
Parents of children facing autism behavioral health issues often encounter numerous challenges, such as communication barriers, behavioral problems, and the need for specialized education. Navigating the healthcare system can feel overwhelming; many parents share their struggles in accessing appropriate therapies and services. This journey often takes an emotional toll, with studies revealing that most caregivers, especially mothers, experience mild to moderate levels of burden.
This reality underscores the urgent need for improved support systems. To effectively address these challenges, parents can adopt various strategies. Building a strong support network is vital; engaging with local resources and connecting with other families can provide invaluable insights and encouragement.
Advocacy is equally important, empowering parents to articulate their children's needs and secure necessary services. Additionally, prioritizing self-care is crucial in preventing burnout and sustaining overall well-being. Respite care, which offers temporary relief for primary caregivers, serves as an essential resource that can help ease some of the continuous caregiving responsibilities.
Mindfulness-based approaches have shown promise in strengthening parent-child connections, suggesting that parents should explore methods that foster emotional resilience. Upcoming studies emphasize the potential benefits of these practices.
As Juliann Garey notes, navigating the healthcare system can be challenging, but sharing experiences and strategies can cultivate a sense of community. This not only supports individual journeys but also fortifies collective resilience. Such a collaborative approach is vital in managing the complexities of autism behavioral health assistance, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for children and their caregivers.
Building Community: The Power of Collaboration in Autism Support
Creating a nurturing community is vital for those impacted by autism. It encourages cooperation among parents, professionals, and organizations, ultimately leading to enhanced outcomes and a deeper sense of belonging. Research indicates that siblings of autistic children can significantly benefit from social assistance, highlighting the broader impact of community involvement on family dynamics. A 2020 study reveals that these siblings often experience improved social skills and emotional resilience when engaged in supportive environments.
Community resources, such as assistance groups, educational workshops, and social events, serve as essential platforms for families to access valuable information and forge meaningful connections.
Fostering open conversation and sharing experiences cultivates a culture of understanding and support, which is crucial for navigating the complexities of developmental disorders. As Hartman notes, "What is truly significant is the information provided to parents during the evaluation — that this condition is presented as a distinct neurotype and a legitimate way to exist in this world." Each autistic individual is unique and requires tailored support levels, and collaboration within the autism behavioral health community can effectively address these diverse needs.
By working together, families can advocate for improved services and create inclusive environments that benefit not only individuals with developmental disorders but also enhance the lives of their families.
Moreover, recent studies have uncovered disparities in the identification of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) among youth from various racial and ethnic backgrounds. A new pattern in racial and ethnic differences has emerged in the identification of ASD among 8-year-old children, indicating disparities in diagnosis and access to services. Understanding these distinctions is essential for developing targeted approaches that improve access to services and support for all families.
As ASD Media strives to build a supportive community, it emphasizes the importance of collaboration among autism experts and caregivers, ensuring that everyone has access to the resources they need to thrive. Effective community initiatives and workshops play a crucial role in empowering families, equipping them with the tools and networks necessary to navigate their journeys with confidence. Additionally, subscribing to ASD Media's newsletter allows families to stay informed about the latest news and gain unlimited access to valuable resources.
Conclusion
The exploration of autism behavioral health highlights the essential need for personalized interventions that address the unique challenges faced by individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). As autism diagnoses continue to rise, the significance of tailored therapies—such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), occupational therapy, and speech therapy—becomes increasingly clear. When these approaches are integrated into individualized treatment plans, they empower autistic individuals to enhance their social skills, communication abilities, and overall quality of life.
Engaging families in the therapeutic process stands out as another crucial element of effective autism support. Research shows that active parental involvement leads to improved outcomes for children, underscoring the necessity of collaborative efforts in treatment planning. By fostering open communication and providing educational resources, professionals can equip families to advocate for their children and navigate the complexities of autism support systems.
Furthermore, developing social skills and emotional regulation is vital for facilitating meaningful interactions and alleviating anxiety in social contexts. Strategies such as structured social skills training and peer modeling can significantly enhance communication competencies, further supporting the growth of autistic individuals.
In summary, a comprehensive approach to autism support that prioritizes individualized treatment, family engagement, and community collaboration creates an inclusive environment where individuals with autism can truly thrive. By recognizing the diverse needs of those on the spectrum and advocating for accessible resources, society can unite to build a supportive framework that empowers families and enriches the lives of individuals with autism.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted developmental condition characterized by unique challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior.
What are the key concepts related to autism behavioral health?
Key concepts include the neurodevelopmental basis of the condition, the wide range of symptoms, and the significant influence of environmental factors on behavior.
How prevalent is Autism Spectrum Disorder in the U.S.?
As of 2025, approximately 1 in 36 youngsters in the U.S. is diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder, indicating an increasing prevalence.
Why are tailored interventions important for individuals with autism?
Tailored interventions are essential for addressing the diverse needs of autistic individuals, leading to improved outcomes in social skills, communication, and overall well-being.
What is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)?
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a scientifically validated method that focuses on understanding and modifying behavior through techniques such as reinforcement, prompting, and modeling, particularly effective for children on the spectrum.
How common is the use of ABA therapy among caregivers of individuals with developmental disorders?
Recent studies show that approximately 36.5% of caregivers for individuals with developmental disorders employ ABA therapy.
What are the benefits of intensive and long-term ABA therapy?
Intensive and long-term ABA therapy has been shown to yield substantial improvements in critical areas such as communication, social skills, and daily living activities.
What impact does early intervention through ABA therapy have on children with autism?
Early intervention through ABA therapy significantly improves outcomes for children, with findings showing that 90% of youngsters receiving intensive ABA therapy exhibit remarkable progress.
What long-term advantages does ABA therapy provide?
Individuals who participate in ABA therapy not only enhance their immediate abilities but also experience enduring positive impacts as they mature.
What are the advocacy efforts related to autism behavioral health?
Advocacy efforts include insurance reform and increased public funding to enhance access to therapy services for individuals on the spectrum, ensuring more families can benefit from essential services.




