Overview
Engaging in activities that promote joint attention in children can be a delightful journey for both parents and kids. Interactive experiences like reading together, playing turn-taking games, and utilizing visual supports are not just fun; they are vital in fostering shared focus. These activities are particularly beneficial for children with autism, as they enhance communication and social skills, laying a strong foundation for their developmental journey.
As parents, you may wonder how these simple interactions can make a significant impact. Imagine sitting down with your child, sharing a story, and watching their eyes light up with understanding. Or picture the joy of taking turns in a game, where each moment shared builds not just skills, but also a deeper connection between you and your child.
These experiences are more than just activities; they are stepping stones toward meaningful communication and social interaction. By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you are nurturing your child's development and creating a supportive environment where they can thrive. So, take a moment to explore these engaging activities with your child, and watch as their world expands in wonderful ways.
Introduction
In the intricate tapestry of child development, joint attention emerges as a pivotal thread, weaving together the essential skills of communication and social interaction. This foundational ability, characterized by the shared focus of two individuals on an object or event, holds particular significance for children with autism, who often encounter unique challenges in forming these connections. As children navigate their early years, the emergence of joint attention serves as a gateway to learning. It enables them to interpret social cues, engage with their environment, and foster meaningful relationships.
Imagine the joy of a child discovering a butterfly, pointing excitedly while a parent shares in that moment. This simple act of joint attention not only enhances learning but also strengthens the bond between parent and child. Through a blend of research insights and practical strategies, this article delves into the significance of joint attention, the hurdles faced by children with autism, and the vital role parents play in nurturing this skill. By understanding these dynamics, we can lay the groundwork for a lifetime of effective communication and social engagement. Let’s explore how we can support our children in this journey together.
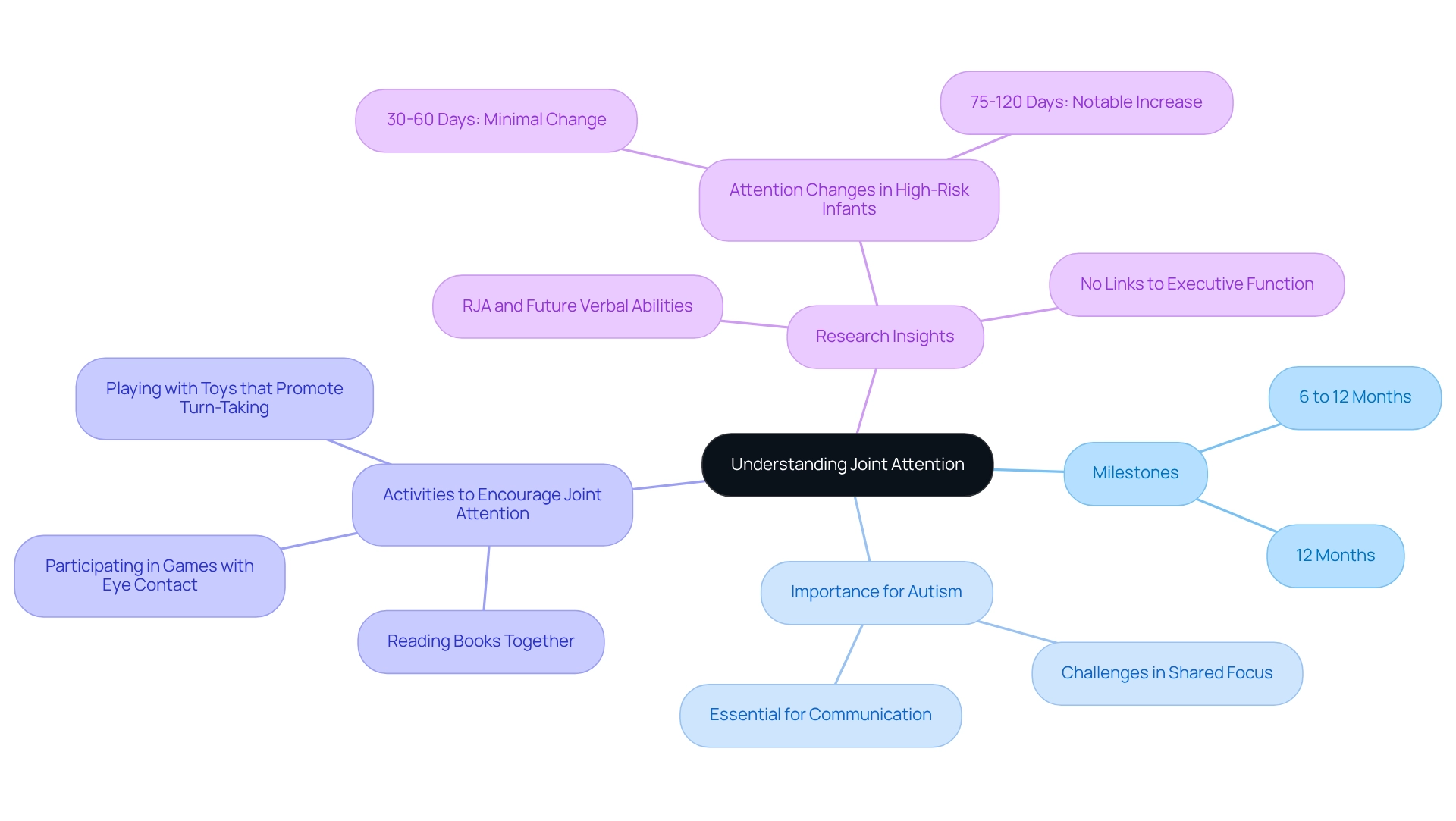
Understanding Joint Attention: A Key Developmental Skill
Joint focus is a beautiful milestone in a child's development, defined as the shared concentration of two individuals on a specific object or event. This ability typically begins to emerge in infancy and is especially crucial for children with autism, who often face challenges in forming this shared focus—an essential component for effective communication and social engagement. It’s not just about looking at the same object; it’s about the mutual understanding that both individuals are engaged in the same experience.
Key milestones for collaborative focus usually occur between 6 to 12 months of age, when infants start tracking the gaze of others and sharing their own focus with caregivers. By 12 months, many children can point to objects to guide others' attention, further enhancing their social engagement. Research indicates that focus at three months is more strongly linked to social-communication abilities than to nonverbal cognitive skills, highlighting the significance of early shared focus development.
As parents, you can effectively encourage joint engagement by incorporating captivating activities that require shared focus. Simple yet interactive activities, such as:
- Reading books together
- Playing with toys that promote turn-taking
- Participating in games that involve eye contact and shared laughter
These can significantly enhance this ability. Recent studies reveal that high-risk infants show minimal change in focus from 30 to 60 days, followed by a notable increase from 75 to 120 days, underscoring the dynamic nature of developmental progress during early infancy.
Moreover, a research project focusing on babies aged 8 to 15 months confirmed the importance of responding to shared focus capabilities and their connection to future verbal abilities and social responsiveness. While the research did not establish definitive links between early reactive joint attention (RJA) and executive function capabilities, it emphasized that RJA is an evolving ability, essential for young individuals' social-cognitive development. As C. Lasch beautifully noted, "Lastly, we are indebted to the ELAB members for their dedication to the broader project, specifically Elayne Vollman, Rachel Roisum, Sharlotte Irwin, and Kristen Gault."
By actively engaging in activities that promote joint attention, you can play a vital role in your child’s developmental journey. This involvement lays the groundwork for effective communication and social skills that will benefit them throughout their lives. What activities have you found helpful in fostering joint attention with your little ones? Share your experiences in the comments; your insights could be invaluable to other parents navigating this journey.
The Importance of Joint Attention in Communication and Social Skills
Shared focus serves as a vital foundation for effective communication and the development of social skills in children. This interactive process allows young learners to share experiences, which is crucial for language acquisition. When children engage in shared focus, they begin to understand social signals, appreciate others' perspectives, and cultivate empathy.
Consider a moment when a parent points to a bird and exclaims, 'Look at that!' In this scenario, the child not only learns about the bird but also practices responding to social signals, reinforcing their grasp of communication dynamics.
Research underscores the importance of shared focus in early social-cognitive development, particularly regarding autism spectrum disorder. A case study titled 'Language Groups Categorization' explored the effects of collaborative engagement and expressive language ratings, revealing significant differences in language development among various diagnostic groups, including ASD, developmental delays (DD), and typically developing (TD) individuals. This study highlighted how shared focus effectively promotes communication skills, indicating that children who partake in shared focus activities tend to show improved language outcomes.
The findings of this research emphasize the need to recognize these differences to tailor interventions effectively.
Statistics reveal a strong correlation between shared focus and language growth; children who actively engage in shared focus situations often exhibit enhanced vocabulary and social skills. Notably, family income distribution shows that 28.1% of families earn between $100K and $150K, which may influence their access to resources that facilitate collaborative activities. Experts agree that shared focus not only boosts communication but also plays a crucial role in developing social skills.
As Mundy noted, it involves 'the social use of executive focus abilities,' highlighting its essential role in effective communication.
By incorporating joint attention activities into daily routines, parents can significantly improve their children's ability to communicate effectively and forge meaningful social connections. Examples of engaging collaborative activities for joint attention include interactive games like 'I Spy,' where children are encouraged to observe and discuss items together, or shared reading sessions that prompt them to point out pictures and talk about the story. These joint attention activities not only enhance social skills but also lay the groundwork for robust language development, making shared focus an essential aspect for parents eager to support their children's growth.
Challenges in Joint Attention for Children with Autism
Children with autism often face challenges with joint attention, manifesting as limited eye contact, difficulty in following another person's gaze, or struggles in sharing experiences. These hurdles can significantly impede their ability to engage in social interactions and develop essential language skills. For instance, a child may become so engrossed in a toy that they overlook a parent's attempts to connect or involve them.
Understanding these challenges is vital, as it lays the groundwork for implementing effective strategies centered around activities that promote joint attention.
Research indicates that shared focus challenges are prevalent among children with autism, with many exhibiting a mean nonverbal mental age of just 17.75 months when demonstrating responsive shared focus (RJA) skills. This statistic underscores the importance of early intervention, as addressing these issues can lead to improved social skills and a better quality of life for these vulnerable children.
Experts emphasize the need to recognize signs of shared focus challenges. Common indicators include:
- A lack of shared gaze
- Minimal interest in social interactions
- Difficulties in responding to social cues
As Charman points out, "Tools like the CHAT have high positive predictive value, but their sensitivity is only moderate," highlighting the necessity of using effective assessment tools to identify these difficulties.
By identifying these signs early on, parents and caregivers can adopt targeted strategies through activities for joint attention, ultimately enhancing their child's social engagement and communication skills.
Furthermore, recent research findings stress the need for culturally relevant studies in autism research, as shared focus difficulties may manifest differently across various socio-linguistic contexts. However, it’s crucial to approach these findings with caution, as limitations such as small sample sizes have been noted, indicating the need for more extensive research to validate findings in larger populations.
Effective Activities to Enhance Joint Attention at Home
To enhance joint focus at home, parents can engage in several effective activities that nurture connection and understanding.
- Turn-Taking Games: Consider playing games that require taking turns, such as stacking blocks or rolling a ball back and forth. These activities not only foster focus but also create shared moments of joy.
- Interactive Storytime: Reading books together can be a delightful experience. Encourage your young reader to point at pictures and discuss them, making the story come alive and strengthening your bond.
- Use of Visual Supports: Incorporating visual aids, such as pictures or symbols, can be incredibly helpful. They guide your child's focus on specific objects or actions, making learning more engaging.
- Play with Bubbles: What could be more fun than blowing bubbles? Encourage your little one to pop them, fostering shared excitement and focus.
These activities not only encourage mutual focus but also enhance the parent-child connection, creating cherished memories together.
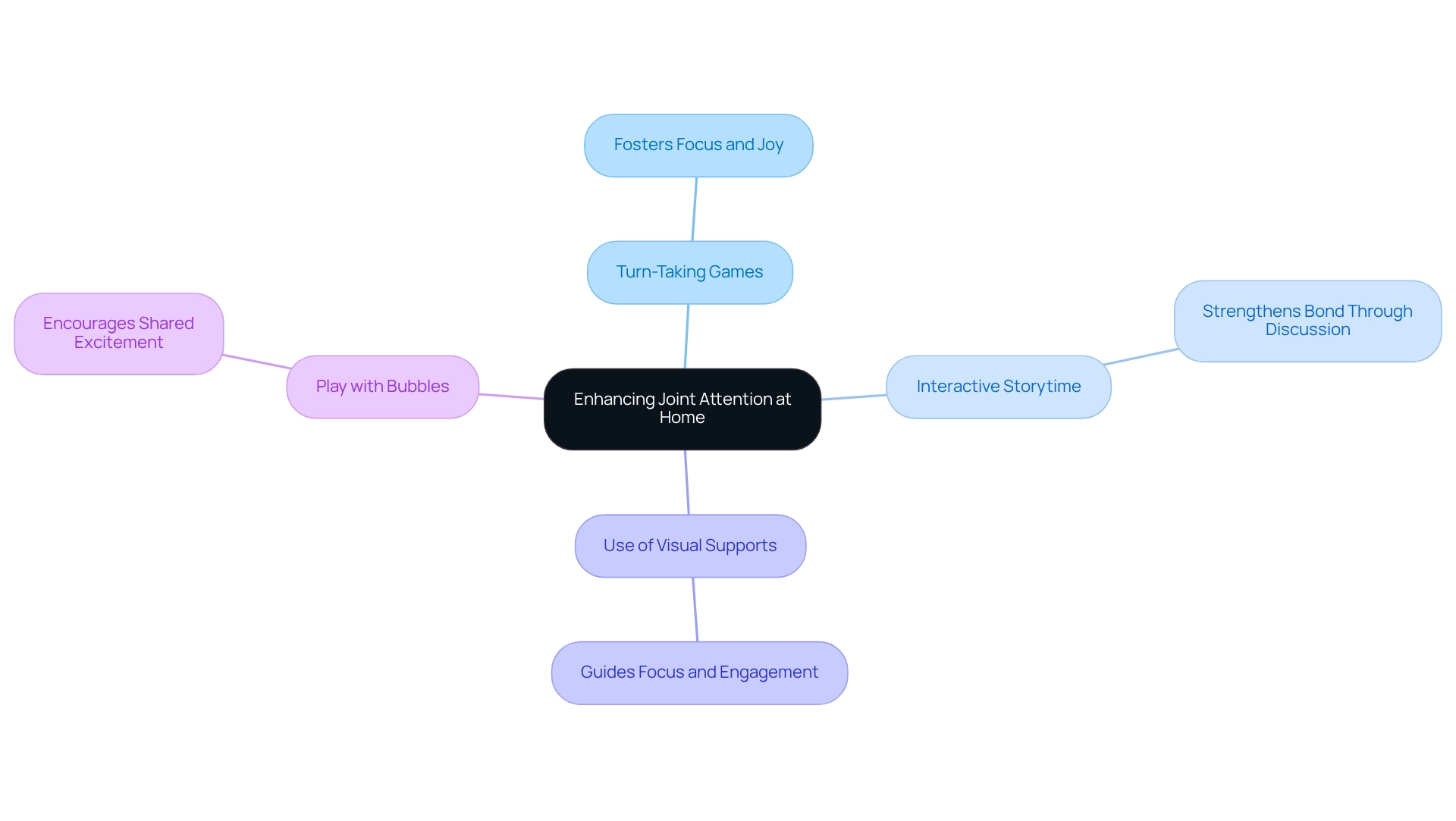
Play-Based Techniques to Promote Joint Attention
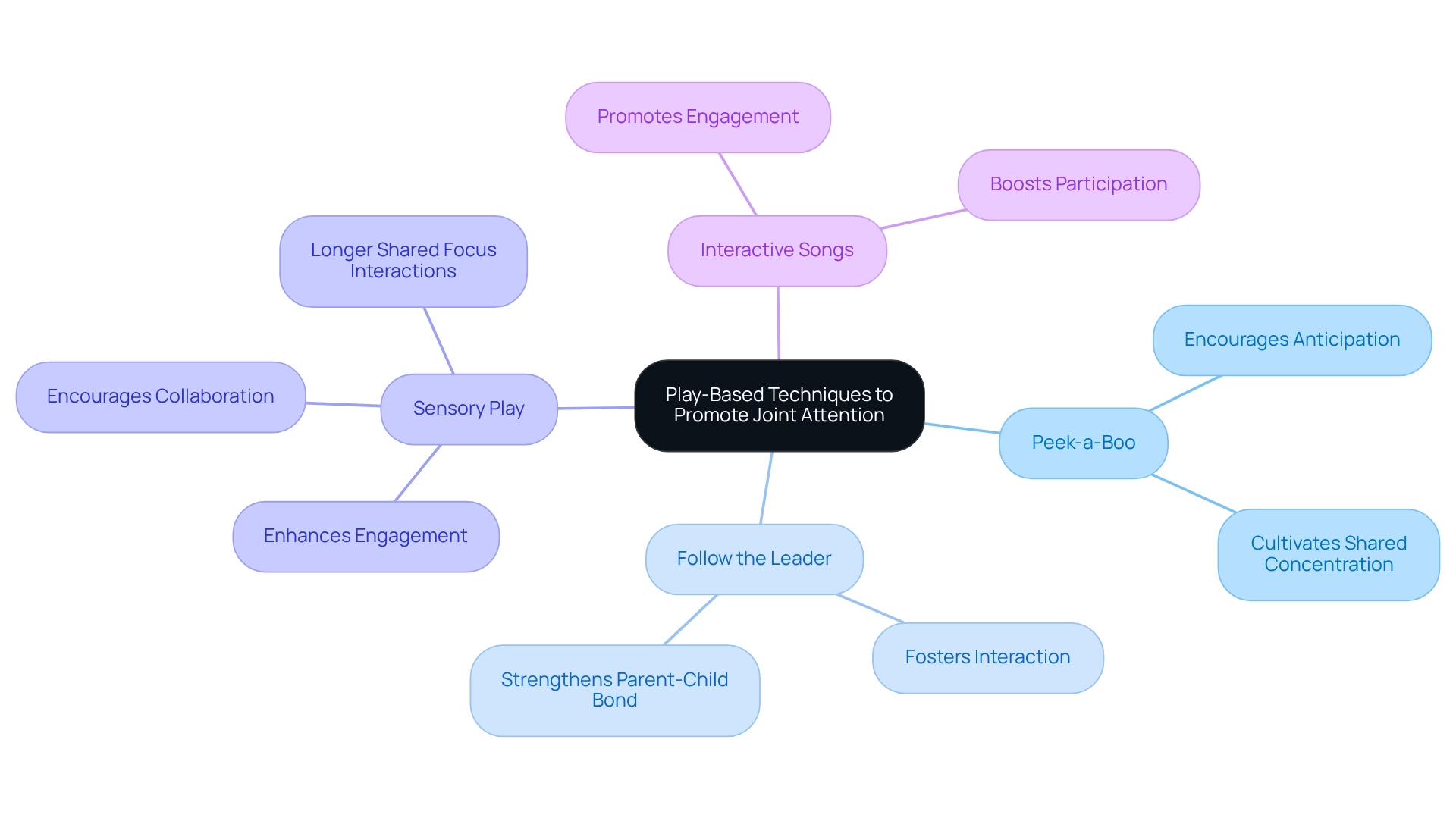
Play-oriented methods are incredibly effective in nurturing shared focus abilities in young children. Here are several strategies that you can seamlessly integrate into your daily activities:
- Peek-a-Boo: This timeless game not only sparks joy but also cultivates anticipation and shared concentration—key elements of mutual engagement.
- Follow the Leader: Engage your little one in activities where they imitate your actions. This not only fosters interaction but also strengthens the bond between you and your child, enhancing their ability to share focus.
- Sensory Play: Utilizing materials like sand, water, or playdough creates immersive experiences that naturally encourage collaboration. Research suggests that sensory play can significantly enhance focus skills, as children become more engaged and responsive to their surroundings. Notably, studies have shown that shared focus interactions tend to last longer and synchronize more effectively during the latter part of play sessions compared to the beginning.
- Interactive Songs: Singing songs that incorporate actions promotes engagement and helps children concentrate on your movements. This interactive approach not only makes learning fun but also boosts their ability to participate in shared focus.
These techniques not only encourage activities for joint attention but also enrich the learning experience, making it enjoyable and engaging for young learners. A case study titled 'Behavioral Profiles of Responders to Pivotal Response Training' found that children with more advanced toy play skills before treatment exhibited greater improvements in language, play, and social abilities during the intervention. This indicates that toy play skills may significantly influence the effectiveness of language acquisition strategies.
Moreover, Karen Toth from the University of Washington noted that among various language factors, initiating protodeclarative shared focus was most closely associated with concurrent language skills in 3–4-year-old children with autism. By weaving these strategies into everyday routines, parents can effectively support their children's development in a meaningful and enjoyable way. The research backing these insights was funded by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institute of Mental Health, highlighting the credibility of these findings.
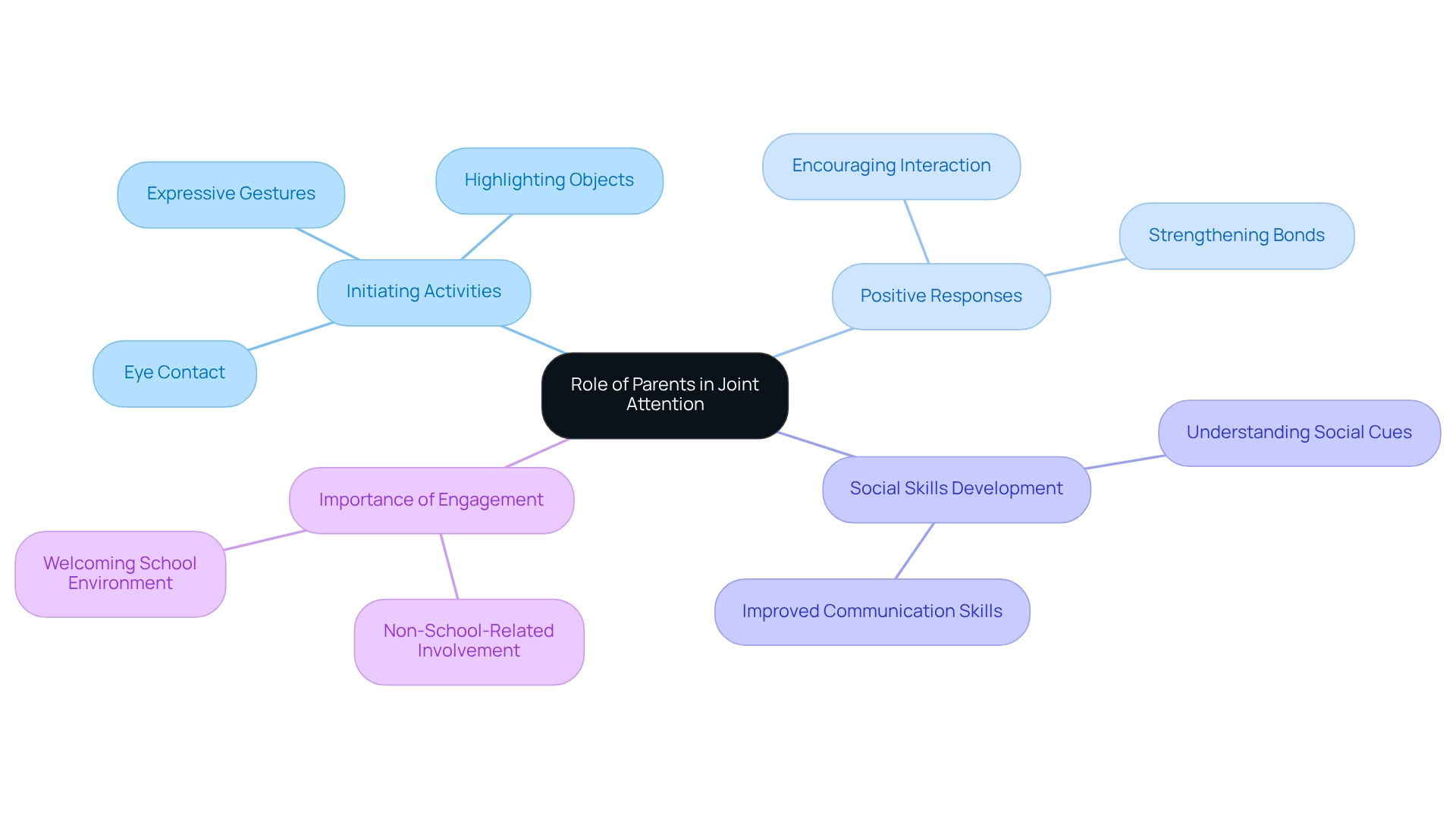
The Role of Parents in Facilitating Joint Attention
Parents play a crucial role in fostering activities for joint attention in their children. They can effectively initiate these activities by highlighting intriguing objects, using expressive gestures, and maintaining consistent eye contact. For instance, when a parent spots a dog outside, they might exclaim, 'Look at the dog!' while pointing towards it. This simple action not only captures the child's interest but also exemplifies the practice of sharing focus. It's essential for parents to respond positively to their child's efforts in these activities, thereby strengthening their interactions.
Such mutual exchanges help children understand the significance of joint attention while significantly enhancing their social abilities. Research indicates that parental involvement is vital in nurturing these activities, with studies showing that children with engaged parents exhibit improved communication skills. One study revealed that parental touch was coded frame-by-frame, achieving a high inter-coder reliability of 0.90, highlighting the importance of parental engagement in these interactions.
Furthermore, the case study titled 'Indicators of Joint Attention Deficits' points out typical signs such as limited eye contact and lack of gestures, which can hinder young people's social and communication skills. Recognizing these signs early can aid in addressing focus challenges through joint attention activities, ultimately improving communication. The value of non-school-related parental involvement is also emphasized, suggesting that such engagement is just as important as school-related participation.
As Vito Borrello, Executive Director of the National Association for Family, School, and Community Engagement, wisely states, 'If the school is not welcoming and families don’t feel welcome at the school, then you’re not going to get them to come to school no matter what you do.' By actively engaging in these interactions, parents can create a nurturing environment that fosters their child's social growth and communication skills.
Collaborating with Professionals: Support for Parents
Collaborating with experts is crucial for enhancing shared focus abilities in young children. ABA therapists play an essential role by providing tailored strategies and support that empower parents to implement effective techniques at home. For example, therapists may recommend specific activities that resonate with a child's interests, making the journey of fostering shared focus both engaging and enjoyable.
Moreover, professionals can offer training sessions for parents, equipping them with vital skills to consistently participate in joint attention activities across different environments. Research shows that nearly all mental health professionals acknowledge the significance of partnering with parents for successful therapeutic outcomes. This collaboration not only promotes individual development but also strengthens the overall well-being of the family. Parents frequently express the benefits of working alongside mental health professionals, such as receiving encouragement about their child's progress and practical advice tailored to their unique circumstances.
However, it's important to consider potential challenges, such as instances of dishonesty or insensitivity from professionals, which can impede the therapeutic journey. As one parent shared, while professional support can be invaluable, there are moments when communication falters, leading to frustration.
Expert insights highlight that ongoing education, active listening, and collaborative goal-setting are essential strategies for nurturing inclusivity in this partnership. By working together, parents and therapists can create a supportive environment that enhances the ability to foster shared focus skills.
Effective ABA therapy techniques aimed at improving mutual engagement at home often require consistent communication and feedback between parents and therapists. This synchronization ensures that both parties are aligned in their approach. Ultimately, this joint effort leads to more effective outcomes for youth with autism, paving the way for improved communication and social skills. The benefits of this collaboration are evident, but it is equally important to remain mindful of the potential drawbacks, as illustrated in the case study on the advantages and disadvantages of working with mental health professionals.
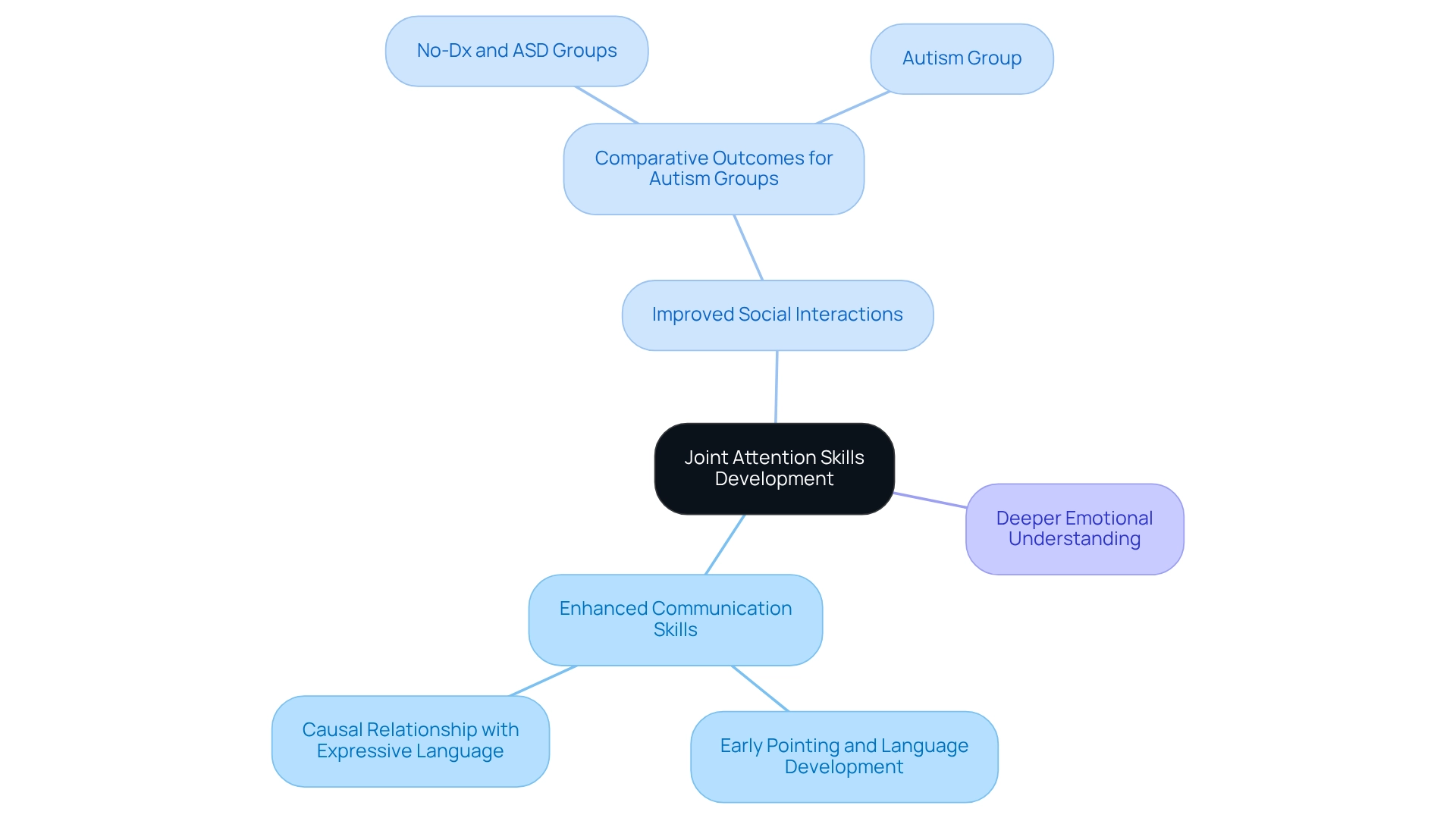
Long-Term Benefits of Joint Attention Skills Development
Cultivating shared focus abilities offers numerous lasting advantages that can significantly impact a young person's growth. Mastering these abilities is linked to enhanced communication skills, improved social interactions, and a deeper emotional understanding. Research indicates that children who exhibit strong collaborative focus abilities, particularly through early pointing, experience notable benefits in language development and social skills as they grow.
For instance, a cross-lagged panel analysis reveals a causal relationship between early pointing behaviors and subsequent expressive language development. This highlights the importance of nurturing these abilities from a young age.
Moreover, children with well-developed collaborative focus skills often show quicker expressive language advancement compared to their peers with autism. Notably, the No-Dx and ASD groups exhibited faster expressive language development than the autism group, underscoring the critical role of shared focus in immediate communication and its influence on future social skills. As Angela John Thurman notes, while general joint attention performance was similar among groups, scores improved for boys with FXS when considering various factors, illustrating the nuanced outcomes based on joint attention abilities.
By prioritizing joint attention activities, parents can lay a strong foundation for their children's interactions and relationships, leading to more effective social engagements in the future. Investing time and effort into these developmental strategies can yield significant rewards, paving the way for a brighter, more connected future for children. In the broader context of autism discussions, as seen in the case study titled 'Dive into the Autism Meme Controversy,' recognizing the importance of communication and social interactions is essential for fostering a supportive community.
Conclusion
The exploration of joint attention highlights its vital role in child development, particularly for children with autism. This foundational skill not only enhances communication and social interaction but also serves as a gateway for learning and emotional engagement. By understanding the milestones of joint attention, parents can nurture this ability through interactive and engaging activities, ultimately fostering a supportive environment for their child's growth.
Challenges in joint attention, especially for children with autism, emphasize the necessity of early intervention and tailored strategies. Recognizing signs of difficulty and implementing targeted activities can significantly enhance social engagement and communication skills. With the right support, parents can facilitate joint attention in ways that resonate with their child's unique needs, paving the way for meaningful connections and effective communication.
Collaboration with professionals adds another layer of support, enabling parents to access tailored strategies and resources that enhance joint attention skills at home. This partnership not only benefits the child’s development but also strengthens family dynamics, ensuring a holistic approach to growth and learning.
Ultimately, prioritizing joint attention lays the groundwork for immediate communication and social skills while fostering long-term benefits that can profoundly influence a child's developmental trajectory. By investing in these strategies, parents can help their children navigate the complexities of social interactions, leading to a more connected and fulfilling life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is joint focus in child development?
Joint focus is defined as the shared concentration of two individuals on a specific object or event. It typically begins to emerge in infancy and is crucial for effective communication and social engagement, particularly in children with autism.
When do key milestones for joint focus typically occur?
Key milestones for joint focus usually occur between 6 to 12 months of age, when infants start tracking the gaze of others and sharing their own focus with caregivers. By 12 months, many children can point to objects to guide others' attention.
Why is joint focus important for children with autism?
Joint focus is especially important for children with autism as they often face challenges in forming this shared focus, which is essential for effective communication and social engagement.
How can parents encourage joint engagement in their children?
Parents can encourage joint engagement by incorporating captivating activities that require shared focus, such as reading books together, playing with toys that promote turn-taking, and participating in games that involve eye contact and shared laughter.
What does research indicate about the development of joint focus in infants?
Research shows that high-risk infants show minimal change in focus from 30 to 60 days, followed by a notable increase from 75 to 120 days, indicating a dynamic nature of developmental progress during early infancy.
What is the relationship between joint attention and language development?
Studies indicate that children who engage in joint focus activities tend to show improved language outcomes, with a strong correlation between shared focus and language growth.
What activities can promote joint attention and social skills?
Engaging activities that promote joint attention include interactive games like 'I Spy' and shared reading sessions that encourage children to observe, discuss, and point out pictures together.
How does shared focus impact a child's understanding of social dynamics?
Shared focus helps children understand social signals, appreciate others' perspectives, and cultivate empathy, which reinforces their grasp of communication dynamics.




