Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that presents unique challenges and strengths in individuals. From difficulties in social interaction to repetitive behaviors and communication challenges, ASD manifests in a highly individualized manner.
Recent studies have shed light on the implications of late diagnoses and the changing landscape of autism diagnoses in adults, calling for a broader understanding and acceptance of autism across the lifespan. While the precise causes of autism are still being researched, it is clear that it is not linked to vaccines, parenting styles, or nutrition.
Genetic factors and hereditary components play a role, and researchers continue to seek out specific genetic patterns. With increased awareness and understanding, society is making strides in accommodating the needs of individuals with autism, but challenges remain, including systemic issues in providing adequate support and addressing racial disparities in diagnosis. Advocating for inclusive policies and practices is crucial to ensure the well-being of the autistic community.
Autismo: Definición y Características
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition with hallmarks that include difficulties in social interaction, repetitive behaviors, and challenges in both verbal and non-verbal communication. Its manifestation is highly individualized, with a spectrum that reveals the vast diversity in the experiences and abilities of those affected.
Some individuals may indeed face significant obstacles in language and social engagement, while others might exhibit exceptional skills in certain domains. Recent studies, including one from the University of Bath and King's College London, have investigated the implications of late diagnoses, revealing that the timing of when one learns they are autistic does not necessarily correlate with their quality of life.
This is a critical insight, especially considering the rising recognition of ASD in adults, including women, and the changing landscape of autism diagnoses over the years. The increase in adult diagnoses calls for a broader understanding and acceptance of autism across the lifespan.
Understanding autism goes beyond recognizing symptoms. Brain imaging studies show structural differences in autistic brains compared to neurotypical development.
While the precise causes of autism are still being researched, what is clear is that it is not linked to vaccines, parenting styles, or nutrition. Instead, there is evidence of genetic patterns within families, suggesting a hereditary component. Researchers continue to seek out specific genetic factors that contribute to the condition. With increased awareness and understanding, society is slowly making strides in accommodating the needs of individuals with autism. However, challenges remain, such as systemic issues in providing adequate support and services, as well as addressing the long-standing racial disparities in diagnosis. It is essential to continue advocating for inclusive policies and practices that recognize the unique needs and contributions of the autistic community.
Causas y Factores de Riesgo del Autismo
Understanding the intricate nature of autism is a complex endeavor, with researchers delving into the interplay between genetics and environmental influences. Brain imaging studies have revealed that individuals with autism possess distinctive brain shapes and structures when compared to neurotypical development.
While the specific origins of autism remain elusive, the scientific community is actively exploring theories that include hereditary, genetic, and medical components. Genetic research has yet to pinpoint a singular gene responsible for autism; however, patterns within families suggest a strong genetic underpinning.
Additionally, some individuals may be born with a predisposition to autism, but a singular "trigger" for the condition has not been identified. Environmental factors, such as exposure to certain toxins during pregnancy or premature birth, may also contribute to the development of autism.
Importantly, it has been established that vaccinations, parenting styles, or nutritional choices do not cause autism. Recent data from the CDC underscores a significant rise in autism diagnoses, with current figures indicating that 1 in every 36 children is affected, a stark increase from 1 in 125 in 2004. This rise in diagnoses is not evenly distributed across demographics, with disparities evident in the timing and frequency of diagnoses among Hispanic children and children of color, potentially due to barriers such as stigma, healthcare access, and language differences. These findings emphasize the need for heightened awareness and resources to support early identification and intervention for all children, irrespective of background.
Diagnóstico del Autismo
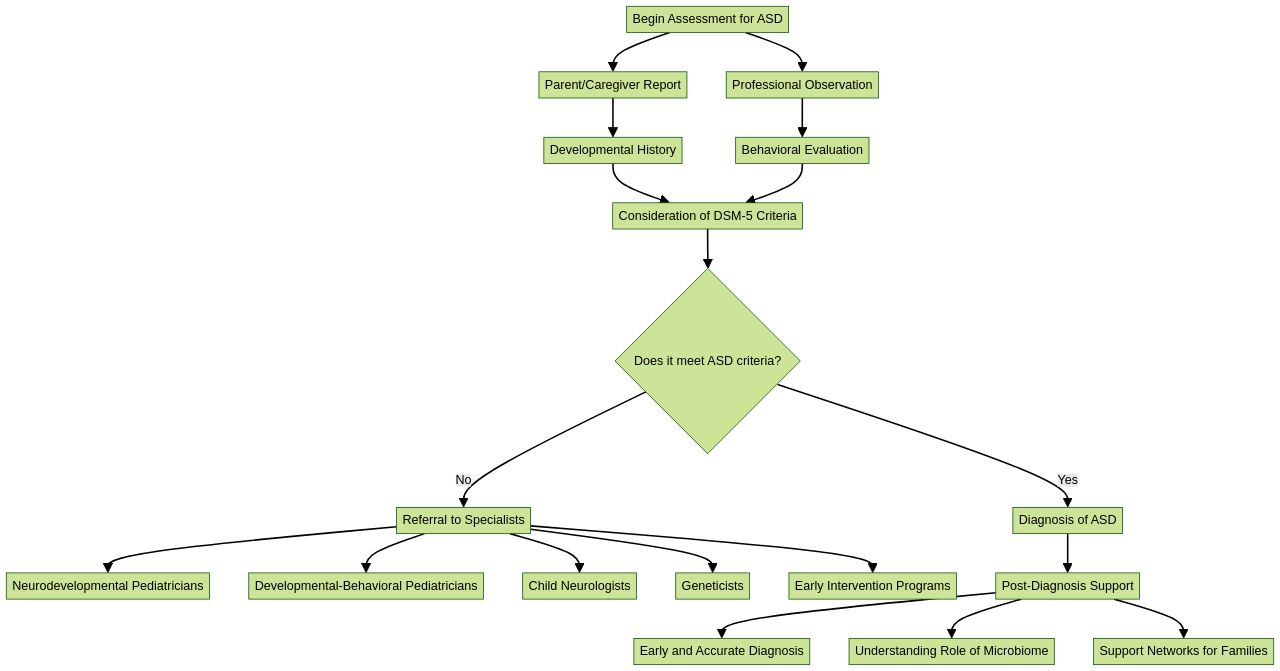
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that presents a growing challenge for families and health professionals alike, with diagnoses occurring typically in childhood but sometimes later in life. A nuanced and multifaceted approach is crucial for accurate assessment, which involves clinical observations, developmental tests, and understanding a child's behavior from caregiver reports.
It's important to note that no single tool can define the diagnosis; instead, a combination of assessments is key to forming a comprehensive understanding of each child's unique needs. A reliable diagnosis paves the way for tailored early intervention services, which are critical for the child's development and greatly improve the quality of life for both the child and their family.
Nevertheless, the journey to diagnosis can be arduous and fraught with miscommunication and delays, underscoring the need for clear information and strong support networks. Recent research emphasizes the importance of early and accurate diagnosis, and the potential role of the microbiome in ASD, indicating a shift towards understanding environmental influences. Furthermore, with the right support, individuals with ASD can navigate their diagnosis and find community, as evidenced by the increasing resources available, such as books, podcasts, and organizations dedicated to ASD support. Ensuring a personalized, supportive, and informed diagnostic process is essential for the well-being of individuals with ASD and their families.
Tratamiento y Terapias para el Autismo
Autism therapy is not a one-size-fits-all remedy; it's a spectrum of strategies tailored to enrich the lives of individuals with autism by enhancing communication, fostering social connections, addressing sensory issues, and nurturing independence. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), a widely recognized approach, emphasizes skill development through positive reinforcement.
Nevertheless, it's crucial to acknowledge that ABA's intensity, which can require upwards of 30 hours per week, raises significant concerns regarding family dynamics, privacy, and the balance of therapy with everyday life. The Council of Autism Service Providers' new ABA Practice Guidelines underscore the necessity of high-quality, individualized care.
This aligns with the Autism Community in Action's advocacy for early and effective treatments that are responsive to the diverse needs and circumstances of families. Moreover, recent research confirms the efficacy of targeted behavioral interventions in improving language, cognitive abilities, and adaptive behavior, while also noting that parents can be instrumental in implementing these strategies. The nuanced needs of those with autism demand that we consider the entire ecosystem of care, ensuring that interventions do not just cater to children, but also respect and support the well-being of their families.
Apoyo y Recursos para Personas con Autismo
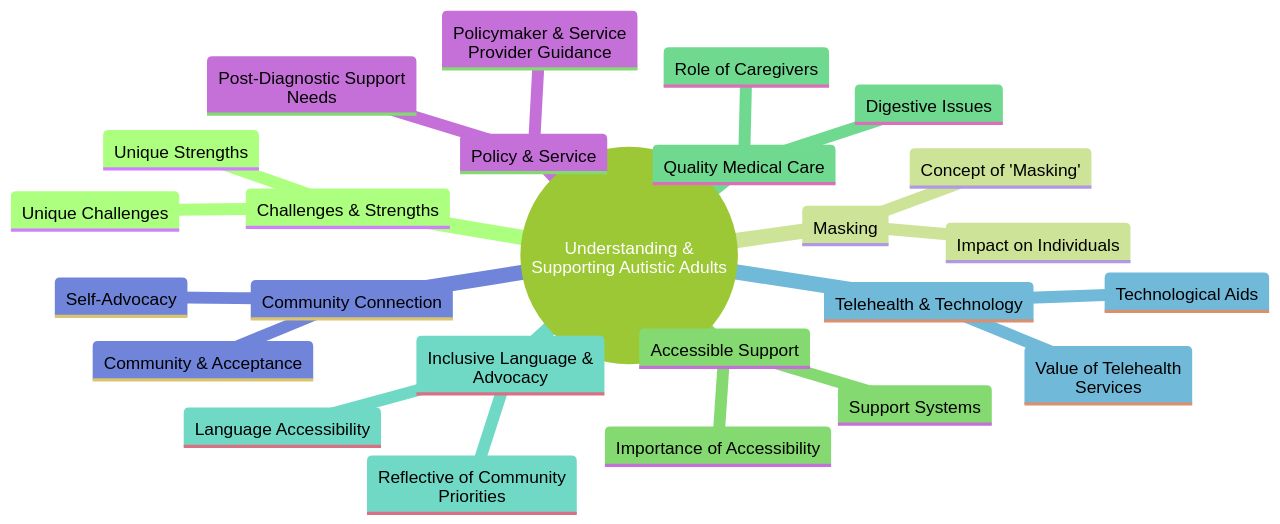
Autism presents unique challenges and strengths that persist into adulthood, requiring a nuanced understanding and approach to care. Adults with autism may exhibit a strong sense of justice, remarkable attention to detail, and deep expertise in specific areas, which can be advantageous in various settings.
However, societal pressures often lead to 'masking,' a coping strategy where autistic individuals adopt behaviors to blend in, which can be a response to stigmatization and past traumas. This underscores the necessity for accessible and tailored support systems.
Harvard Medical School's Adult Autism Health Resources initiative, backed by the Nancy Lurie Marks Family Foundation, seeks to educate clinicians and caregivers about the specific needs of autistic adults, who may face challenges once they age out of school-based services. The project emphasizes the importance of quality medical care for autistic adults, comparable to that for neurotypical individuals.
The Autistic Self Advocacy Network and other resources stress the importance of inclusive language and advocate for equal access and opportunities for autistic individuals. They encourage the autistic community to take an active role in shaping the discourse about autism. Moreover, telehealth services and technological aids, including assistive technologies and mobile apps, are invaluable for facilitating communication and skill development for those unable to access in-person care. It's imperative for autistic adults and their families to connect with the autism community and leverage these resources for necessary support and information.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that presents unique challenges and strengths in individuals. Recent studies have highlighted the importance of early diagnosis and the changing landscape of autism diagnoses in adults.
While the exact causes of autism are still being researched, it is clear that it is not linked to vaccines, parenting styles, or nutrition. Increased awareness and understanding have led to progress in accommodating the needs of individuals with autism.
However, systemic issues in providing support and addressing racial disparities in diagnosis still exist. Advocating for inclusive policies and practices is crucial.
Parents play a vital role as advocates for their children with autism. Access to accurate information, resources for diagnosis and intervention, and support networks are essential.
Early identification and intervention greatly improve outcomes for children with ASD. It's important to recognize that autism extends into adulthood, requiring tailored support systems. Inclusive language, equal access to healthcare services, and opportunities for employment and education are necessary for the well-being of autistic individuals throughout their lives. By fostering understanding, providing resources, advocating for inclusive policies, and supporting individuals with autism at every stage of life, we can create a more accepting and supportive society. Together, we can empower parents as advocates for their children with autism and ensure their well-being and success.




