Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects individuals in various ways. Early detection and intervention are crucial for improving outcomes, yet disparities in diagnosis and access to resources persist.
In this article, we will explore the early signs and symptoms of autism, types of testing and diagnosis methods, the role of parents in the diagnosis and treatment process, and accessing local resources and services for autism support. By providing guidance and resources, we aim to empower parents to advocate for their children and ensure they receive the support they need to thrive.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) encompasses a wide range of neurodevelopmental challenges, including difficulties with social interaction, communication, and a tendency for repetitive behaviors. Clinicians rely on the DSM-5 criteria, which state that the core features of Autism must be present from early childhood. However, symptoms may become more apparent as social demands increase.
Some individuals learn coping strategies that mask challenges, making diagnosis complex. It's essential for professionals skilled in evaluating communication and behavioral development to observe individuals for an accurate diagnosis. The rise in awareness and screening has led to more adults recognizing possible undiagnosed ASD in themselves or others.
Recognizing common signs, such as social communication difficulties and repetitive behaviors, is a critical first step. It's important to note that not all symptoms may be present, and life changes can influence these characteristics. Recent advancements in screening technology, like the EarliPointTM Evaluation, are now aiding in the early detection of autism.
This eye-tracking diagnostic tool, validated by research published in JAMA, provides objective measurements for a more accurate and timely diagnosis. Early diagnosis is crucial; children diagnosed by age 4 are fifty times more likely to receive services, leading to better outcomes. Despite improvements in early detection, disparities persist.
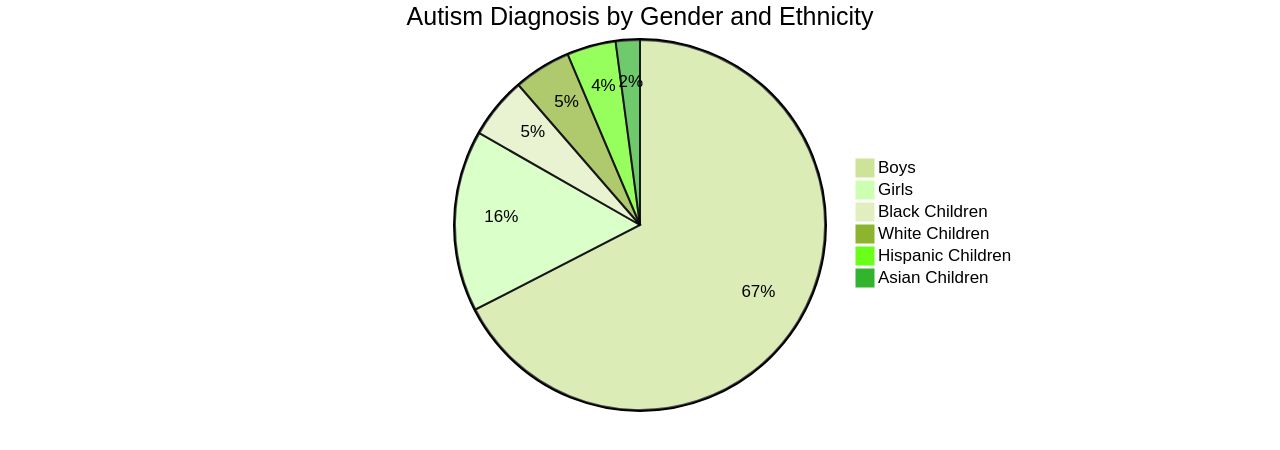
Data shows that White and Black children are more frequently identified with Autism than Hispanic children, who may face barriers such as stigma, access to healthcare, and language differences. Boys are also approximately four times more likely to be diagnosed than girls. These challenges highlight the importance of inclusive and accessible diagnostic services to ensure all children with ASD receive the support they need.
Recognizing the Early Signs and Symptoms of Autism
Early identification of autism can be pivotal for children and their families. At 18 months, subtle signs may begin to surface.
This can include a lack of social interest, difficulties with joint-attention, or challenges in pretend play and protodeclarative pointing. A study utilizing the Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (CHAT) revealed that over 80% of randomly selected toddlers showed none or only one of these signs, whereas toddlers at high genetic risk for autism exhibited two or more of these behaviors.
By 30 months, those who had shown multiple signs were diagnosed with autism, underscoring the importance of early screening. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has highlighted an increase in autism diagnosis rates, with 1 in 36 children now diagnosed, compared to 1 in 44 two years prior.
The earlier a child is diagnosed, the more likely they are to receive vital services, with those diagnosed by age 4 being fifty times more likely to receive support. However, disparities exist; White and Black children are more frequently identified with autism than Hispanic children, pointing to barriers such as stigma, healthcare access, and language differences. Understanding these early indicators is not just about recognizing symptoms but also about connecting with the right support systems and interventions. With the right approach, including family involvement and a focus on generalization, children with autism can thrive. As research continues to evolve, it's clear that early detection and intervention are key to providing children with autism the best possible outcomes.
Types of Autism Testing and Diagnosis
Understanding the journey of autism diagnosis is pivotal for parents who suspect their child may be on the spectrum. It begins with routine health checkups where pediatricians monitor developmental milestones, including those that could indicate autism, which is characterized by unique social interactions, communication patterns, and behaviors.
Notably, advancements in early detection mean that signs can now be spotted in children as young as 12-14 months. This early identification is crucial, as it facilitates timely intervention, enhancing a child's developmental trajectory.
The Marcus Autism Center has revolutionized this process by introducing EarliPointTM Evaluation, an eye-tracking technology for children aged 16-30 months. This tool objectively assesses a child's gaze patterns, providing valuable data that aligns with expert clinical evaluations.
Such innovations underscore the importance of objective, evidence-based diagnostic methods in the absence of medical tests for autism. Diagnosis is typically based on the DSM-5 criteria, which necessitate the presence of autism's core features in early childhood.
However, these symptoms might not become apparent until a child faces social challenges beyond their coping abilities. A multidisciplinary team of specialists, including neurologists, psychologists, and speech therapists, is essential to ensure a comprehensive evaluation. Recent data underscores the urgency of early intervention, with a diagnosis by age 4 significantly increasing the likelihood of receiving necessary services. Yet, disparities persist, with children of color often diagnosed later than their white peers, highlighting the need for equitable access to diagnostic resources. Boys are also diagnosed more frequently than girls, pointing to a gender gap in autism recognition. These insights propel the continuous search for better diagnostic strategies, aiming to connect every child with the support they need as early as possible.
The Role of Parents in the Diagnosis and Treatment Process
The journey of supporting a child with autism is multidimensional, involving a blend of medical, behavioral, and educational interventions. As the latest statistics from the CDC indicate, autism diagnoses have risen to 1 in 36 children, underscoring the urgency for parents to be well-informed and proactive in seeking support. With a consensus on the importance of treatment intensity, family involvement, and a focus on generalizing skills, it's crucial for parents to collaborate closely with healthcare professionals from the initial screening, which can often take over two years to result in a diagnosis, to the selection of appropriate therapies.
Navigating the healthcare system can be daunting, especially as many programs are tailored for preschool-aged children and may not be widely accessible or known. Parents often find themselves advocating fiercely to secure the support their child needs, as reported by autistic mothers with children in mainstream education. These challenges are compounded for parents who are themselves autistic, as they confront a system that is complex and not always accommodating.
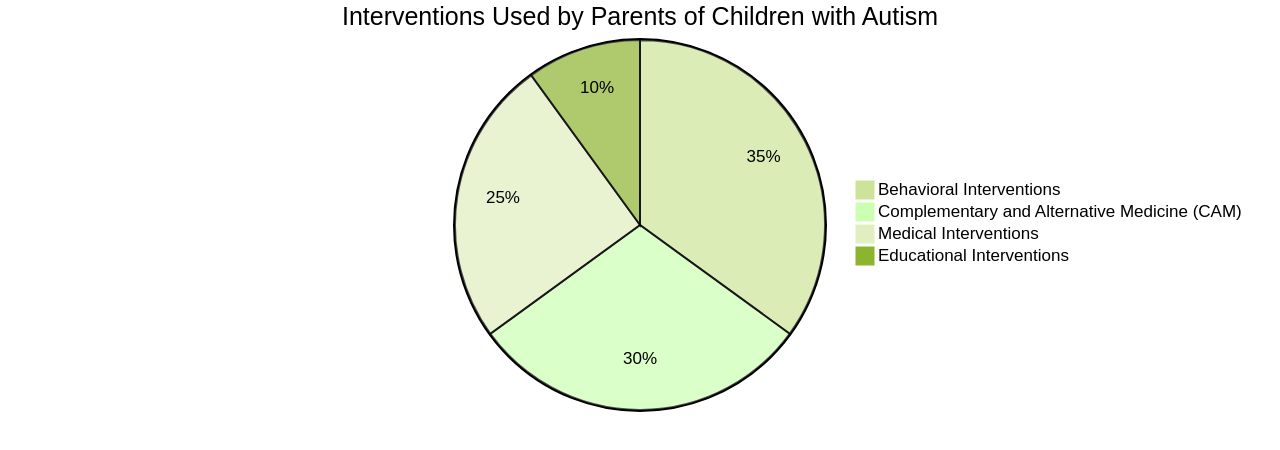
To bolster a child's development, addressing co-occurring medical conditions is essential. Organizations like The Autism Community in Action (TACA) emphasize the synergy of medical and targeted therapy to enhance a child's health and ability to communicate and socialize. Parents utilize a variety of interventions, with 95% engaging in complementary and alternative medicine (CAM), often on the recommendation of a healthcare provider.
Amidst these challenges, hope remains a constant companion. As one author puts it, "Every day brings a new beginning and a new ending." This sentiment captures the evolving nature of autism and the daily renewals it brings, reminding parents and children alike that each day is a fresh opportunity for growth and improvement.
Accessing Local Resources and Services for Autism Diagnosis and Treatment
Navigating the healthcare landscape is crucial for parents of children with autism, as early diagnosis and intervention can significantly affect a child's development. With autism currently diagnosed in approximately 1 in 36 children, it's essential to understand the available resources and services to support these children and their families.
Recent studies, such as those published in The Journal of Pediatrics, Perinatology and Child Health, highlight the challenges faced by many due to limited access to trained professionals and resources, particularly in regions like Africa. This situation often leads to delayed diagnoses, which can hinder the potential benefits of early therapeutic interventions.
Access to local support is a cornerstone for managing autism. Therapies aimed at enhancing communication, social interactions, and sensory processing can foster independence and improve quality of life.
It's imperative that parents are equipped with knowledge on how to find and utilize these services effectively. Understanding the societal and psychological challenges that come with an autism diagnosis, particularly for adults diagnosed later in life, is also vital.
A collaborative study, co-designed with autistic adults, revealed that personalized support plans and access to local support are among the top priorities post-diagnosis. Parents must also be aware of the disparities in healthcare access and diagnosis rates. Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show that while boys are about four times more likely to be diagnosed with autism than girls, girls may present symptoms differently, leading to potential underdiagnosis. Additionally, children of color and those from low-income or non-English speaking families face barriers to early identification and support. Therefore, parents must advocate for their children and seek out culturally competent care that addresses these disparities, ensuring their children receive the support they need to thrive.
Conclusion
In conclusion, early detection and intervention are crucial for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) to thrive. Recognizing the early signs, such as social communication difficulties and repetitive behaviors, is essential in initiating the diagnostic process. Advancements in screening technology, like the EarliPointTM Evaluation, have improved the accuracy and timeliness of diagnoses.
However, disparities in diagnosis still exist. Parents play a vital role in advocating for their children and collaborating with healthcare professionals. Navigating the healthcare system can be challenging, but seeking support from local resources is crucial for accessing appropriate therapies.
Addressing co-occurring medical conditions is also important for enhancing a child's development. By understanding available resources and services, parents can ensure their child receives necessary support to improve communication, social interactions, and sensory processing. Together, we can support children with ASD on their journey towards growth and improvement.




