Overview
While babies are not necessarily born with autism, understanding the condition requires us to look at its significant genetic and environmental origins. This can be a complex journey for many parents. It's important to know that genetic factors contribute a large portion of the autism risk, but environmental influences—like prenatal exposure to toxins and maternal health—also play a crucial role. This highlights the intricate interplay between genetics and environment in the emergence of autism symptoms.
As you navigate this path, remember that you are not alone. Many parents face similar concerns and questions. If you find yourself pondering these complexities, consider reaching out for support or sharing your experiences. Connecting with others can provide comfort and insight as you seek to understand your child's unique journey.
Introduction
The origins of autism have been a topic of heartfelt discussion and research, raising important questions about its genetic and environmental influences. As studies reveal that a significant portion of autism cases can be traced to hereditary factors, it becomes crucial for parents and caregivers to understand the delicate balance between genetics and external conditions.
However, with the rising number of autism diagnoses, many parents find themselves wondering: are babies truly born with autism, or do symptoms emerge later in their development? This exploration invites you to delve into the complexities surrounding autism's origins, offering insights that could reshape perceptions and inform vital early intervention strategies.
Explore the Origins of Autism: Are Babies Born with It?
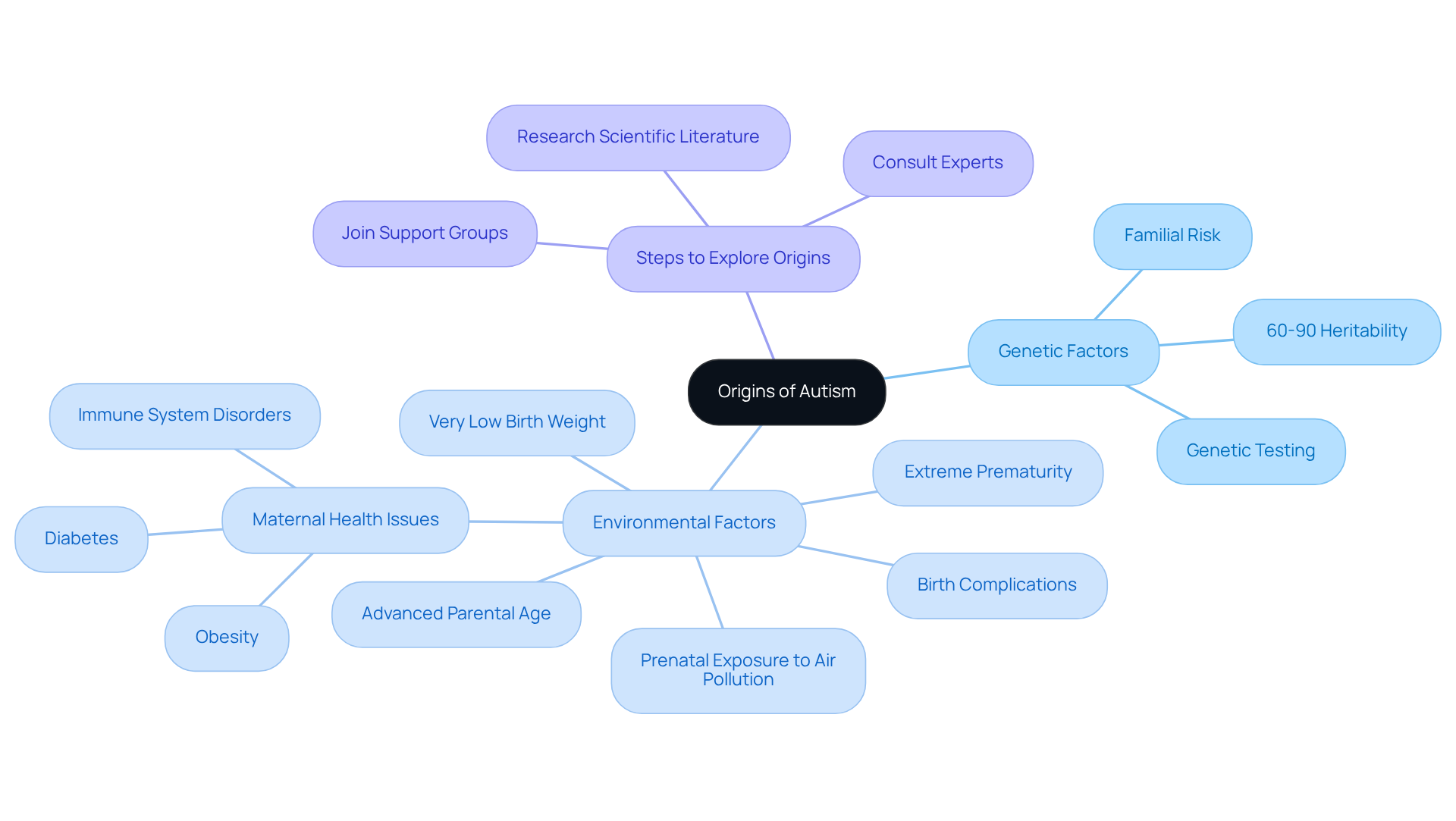
To understand whether babies are born with autism, it is crucial to explore current scientific research. Autism is recognized as a neurodevelopmental condition with significant hereditary components. Studies indicate that 60 to 90% of the likelihood of developing autism can be attributed to genetic factors, with heritability estimates around 80%. Families with one autistic child often find themselves at a higher risk of having another, underscoring the familial nature of this hereditary risk. While some infants demonstrate that babies are born with autism at birth, others might not show symptoms until later in childhood. It's important to recognize that autism arises from a combination of genetic predispositions and environmental influences. The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences has identified several environmental factors, such as advanced parental age, prenatal exposure to air pollution or specific pesticides, maternal obesity, diabetes, immune system disorders, extreme prematurity, very low birth weight, and complications during birth that can lead to oxygen deprivation. Parents are encouraged to reach out to healthcare professionals with any developmental concerns, as early intervention can significantly enhance outcomes. Additionally, it's vital to acknowledge that the increase in autism diagnoses over the years may be linked to heightened awareness and broader diagnostic criteria, influencing perceptions about whether babies are born with autism.
Steps to Explore Origins:
- Research Scientific Literature: Seek peer-reviewed studies that delve into the genetic and environmental factors related to autism.
- Consult Experts: Engage with pediatricians or specialists in child development to gain insights into the latest findings.
- Join Support Groups: Connect with communities focused on developmental disorders to share experiences and gather information from other parents and professionals.
Identify Contributing Factors: Genetics and Environment
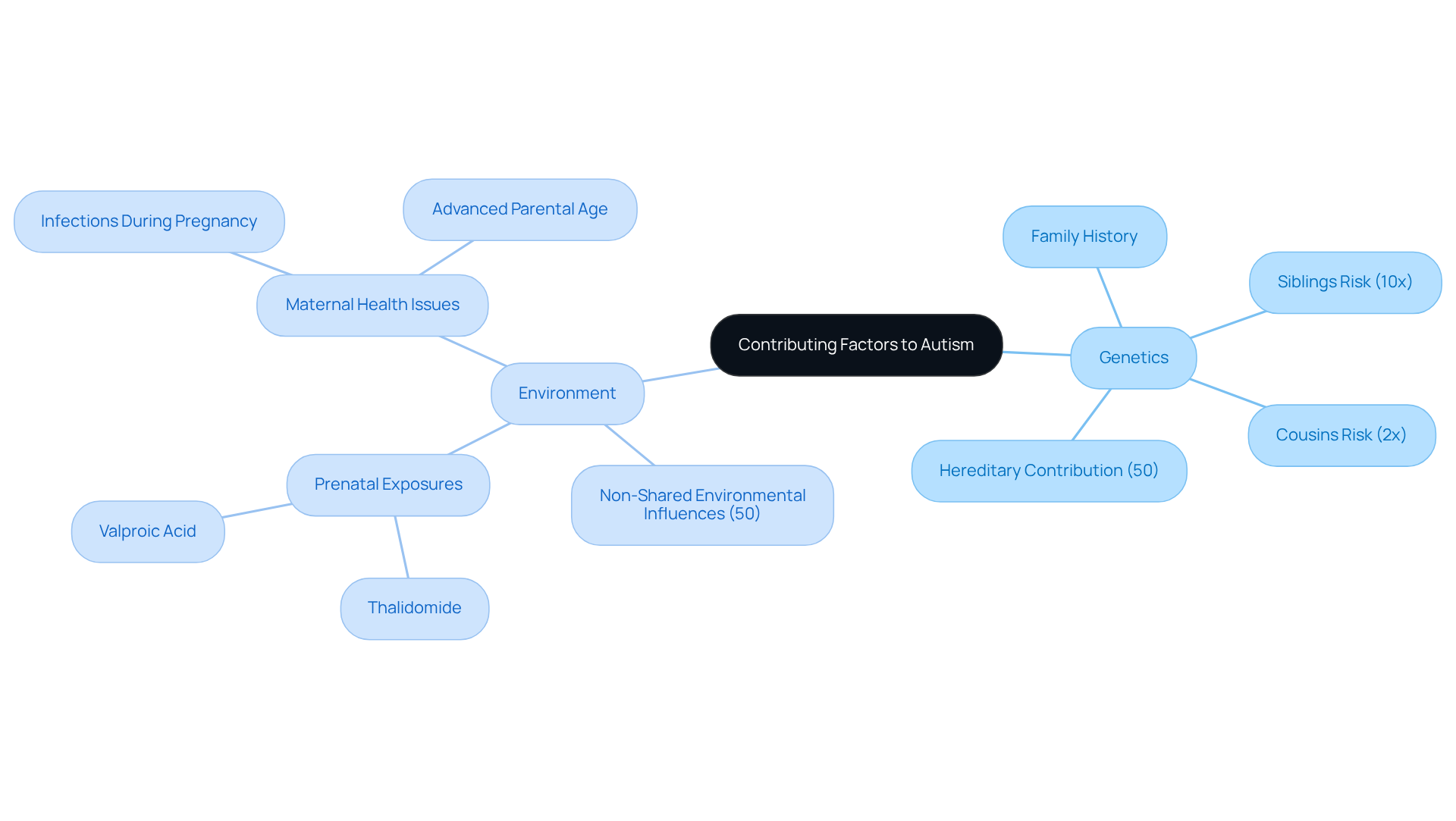
Understanding the role of genetics and environmental factors is vital in addressing this condition. Research shows that children with a family history of developmental disorders face a significantly higher risk; siblings of those affected have a tenfold increased chance of diagnosis, while cousins have double the likelihood. A comprehensive study involving over 2 million participants revealed that hereditary factors contribute to 50% of the risk associated with autism spectrum disorder, with non-shared environmental influences accounting for the remaining half. This underscores the importance of recognizing both genetic predispositions and environmental contexts.
Environmental influences are equally critical in the prevalence of this condition. Prenatal exposure to substances like thalidomide and valproic acid has been linked to a greater likelihood of autism. Moreover, maternal health issues, such as infections during pregnancy and advanced parental age, can further heighten this risk. As noted by Autism Speaks, "One significant area of research relates to how environmental factors interact with hereditary vulnerability." Understanding how these environmental factors and genetic susceptibilities interact is essential for developing effective prevention strategies and enhancing diagnosis and treatment.
To help identify contributing factors, consider these steps:
- Review Family History: Look into any relatives with autism or similar developmental disorders.
- Monitor Environmental Influences: Assess prenatal exposures to toxins or infections and evaluate the child's early environment for potential hazards.
- Consult Genetic Counseling: If you have concerns about genetic predisposition, reaching out to a genetic counselor for testing and guidance can be beneficial.
Grasping these elements is crucial for parents and advocates navigating the complexities of risk. It fosters informed conversations about prevention and support, empowering families to seek the help they need.
Recognize Early Signs: Importance of Timely Diagnosis and Support
Early signs of autism can present in various ways, often encompassing challenges in communication, social interactions, and repetitive behaviors. Recognizing these indicators swiftly is crucial, as it can lead to timely diagnoses and access to essential support services that significantly enhance outcomes for young individuals.
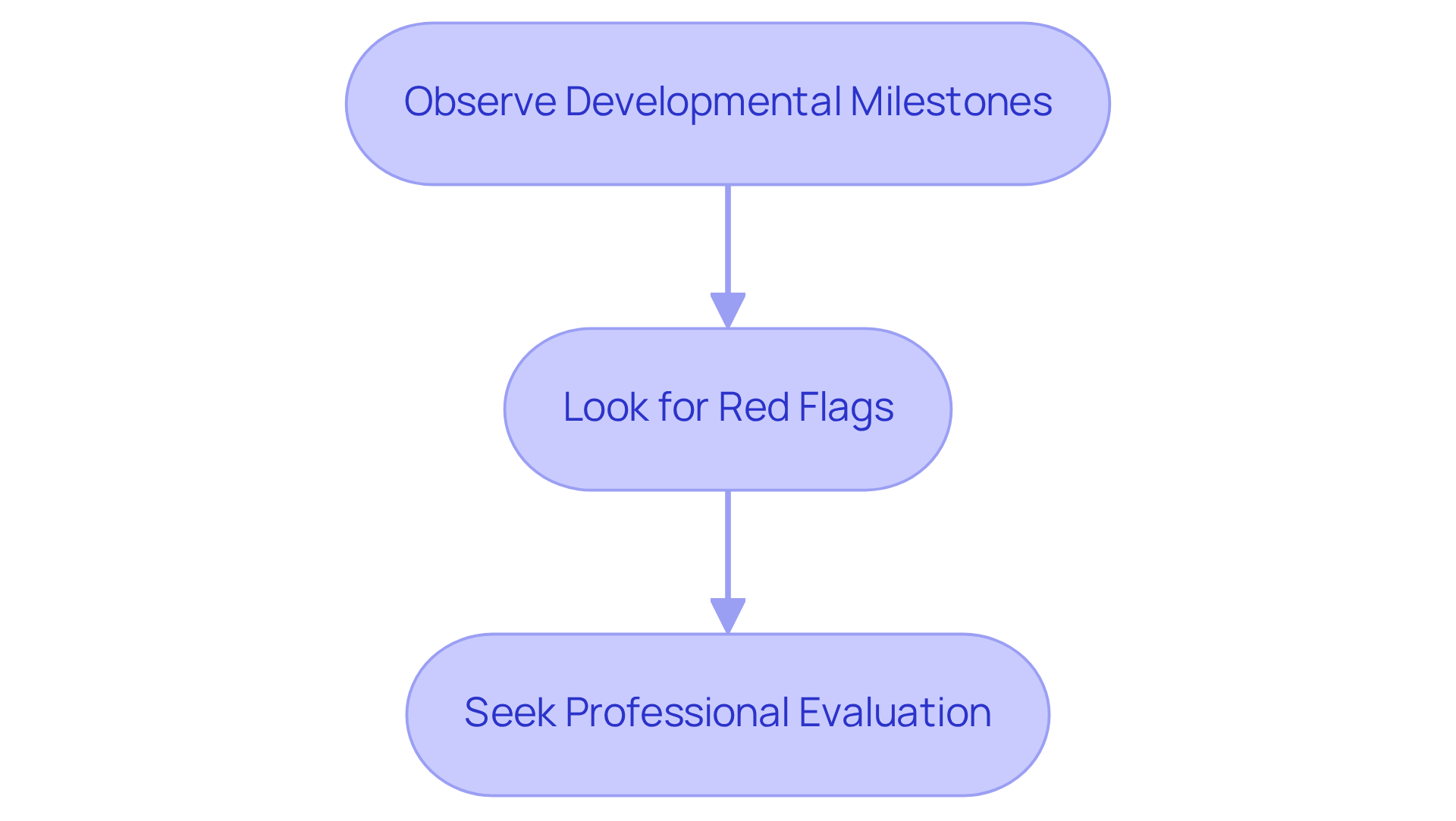
To help you recognize these signs, consider the following steps:
-
Observe Developmental Milestones: Regularly monitor your child's progress in communication, social skills, and play activities. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends developmental and behavioral evaluations for developmental disorders at key milestones: 9 months, 18 months, 24 months, and routine assessments at 30 months. While most children typically achieve milestones such as sitting, crawling, and walking on schedule, they may show delays in social communication and joint attention.
-
Look for Red Flags: Stay alert for indicators like lack of eye contact, delayed speech, limited interest in social interactions, and unusual responses to sensory stimuli. For example, children on the autism spectrum may not respond to their name or may display repetitive movements.
-
Seek Professional Evaluation: If you observe concerning behaviors, it’s vital to consult a pediatrician or child psychologist for a comprehensive assessment. Early identification through recommended screenings at critical ages can lead to better access to interventions, enhancing communication skills, socialization, and behavioral growth.
Research underscores the importance of early intervention, showing that children receiving prompt assistance can experience significant advancements in their development. For instance, those who begin intervention programs soon after an autism diagnosis may see an average increase of 17 IQ points. Additionally, early diagnosis can lead to reduced long-term healthcare costs and improved academic achievement, making it essential for parents to effectively advocate for their child's needs. It's also important to recognize that about 9% of individuals diagnosed with ASD in early childhood may not retain the diagnosis into young adulthood, highlighting the complexities of the diagnostic process.
Navigate the Evaluation Process: Steps for Parents Seeking Support
Navigating the assessment procedure for developmental disorders can feel overwhelming, but understanding the steps involved can empower parents. This journey typically involves a series of evaluations by professionals to determine if a child meets the criteria for the condition, particularly focusing on whether babies are born with autism.
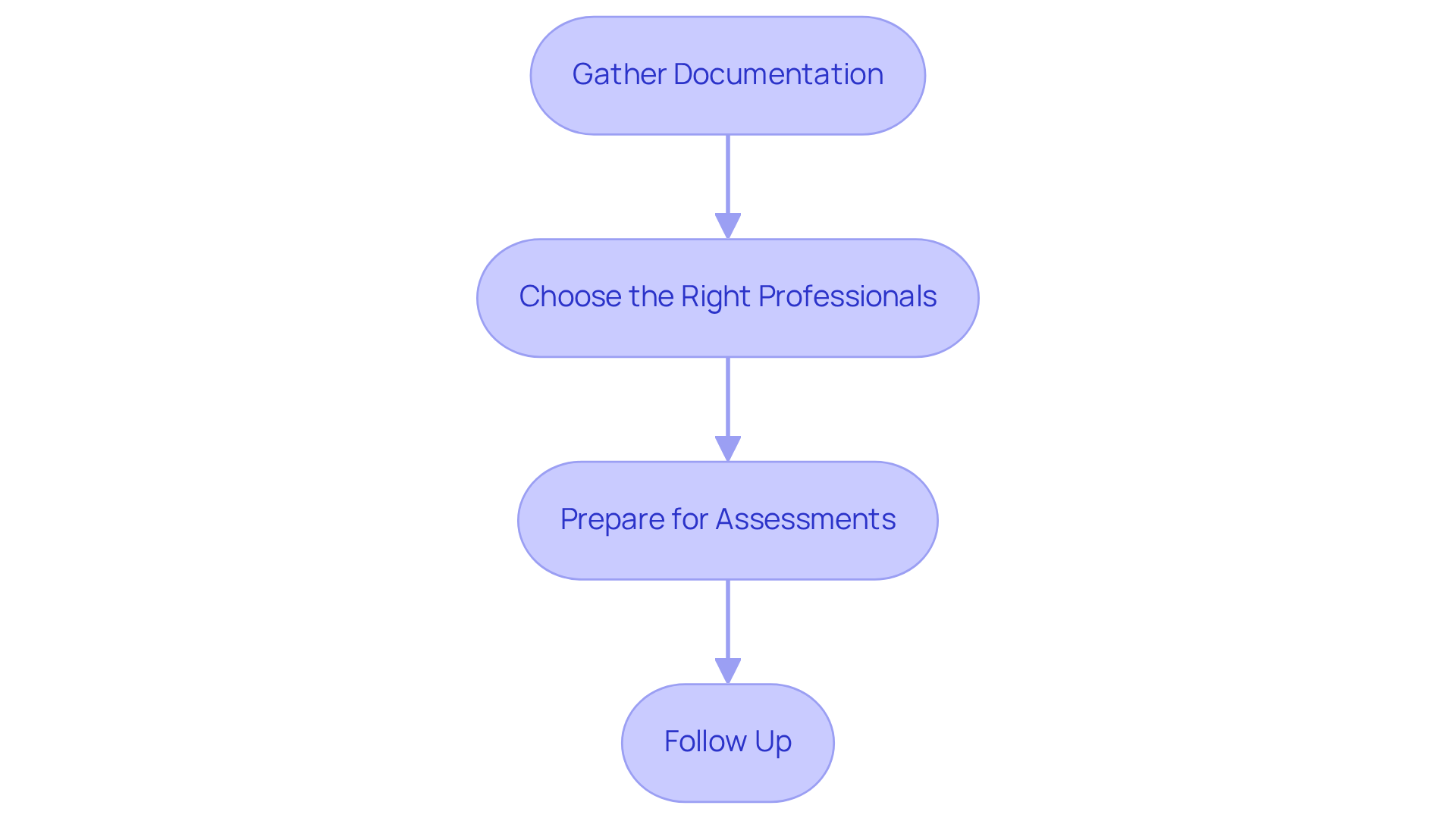
-
Gather Documentation: Start by compiling any relevant medical records, developmental history, and observations of your child's behavior. This information will be crucial in providing a comprehensive view of your child's needs.
-
Choose the right professionals: Take the time to research and select qualified professionals, such as pediatricians, psychologists, or developmental specialists, who can help determine if babies are born with autism. Finding the right expert can make a significant difference in the assessment experience.
-
Prepare for Assessments: Familiarize yourself with the types of assessments that will be conducted. Preparing your child for the process can help ease their anxiety and make them feel more comfortable.
-
Follow Up: After the evaluation, it’s important to discuss the results with the professionals involved. Explore available support options together, including therapy and educational resources, to ensure your child receives the help they need.
Conclusion
Understanding whether babies are born with autism is a journey that involves a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. While there is significant evidence pointing to a hereditary component, it's essential to recognize that autism is not solely determined by genetics. Often, the condition emerges from both inherited traits and the environment in which a child develops, highlighting the multifaceted nature of autism spectrum disorder.
Research reveals that genetic predispositions account for a substantial portion of autism risk. However, environmental influences—such as prenatal exposures and maternal health—also play a critical role. Early detection of autism signs is paramount; timely intervention can lead to improved developmental outcomes. Parents are encouraged to closely monitor their child's progress, seek professional evaluations, and advocate for necessary support services to nurture their child's growth and development.
Ultimately, understanding the origins of autism is profoundly significant. By recognizing the interplay of genetics and environmental factors, and by promoting early diagnosis and intervention, families can better navigate the challenges associated with autism. Empowering parents with knowledge and resources enhances their ability to support their children and contributes to a broader understanding of autism within society. Taking proactive steps today can indeed pave the way for brighter futures for children on the autism spectrum.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are babies born with autism?
Some studies suggest that babies may be born with autism, while others may not show symptoms until later in childhood. Autism is a neurodevelopmental condition influenced by both genetic and environmental factors.
What role do genetics play in the development of autism?
Genetic factors contribute significantly to the likelihood of developing autism, with estimates suggesting that 60 to 90% of autism cases can be attributed to hereditary components. The heritability estimates are around 80%, indicating a strong familial risk.
What environmental factors are associated with autism?
Several environmental factors may contribute to the risk of autism, including advanced parental age, prenatal exposure to air pollution or specific pesticides, maternal obesity, diabetes, immune system disorders, extreme prematurity, very low birth weight, and complications during birth that can lead to oxygen deprivation.
How can parents address developmental concerns regarding autism?
Parents are encouraged to consult healthcare professionals if they have developmental concerns about their child. Early intervention can significantly enhance outcomes for children with autism.
Why has there been an increase in autism diagnoses over the years?
The rise in autism diagnoses may be linked to increased awareness and broader diagnostic criteria, which have influenced perceptions about the condition and its prevalence.
What steps can be taken to explore the origins of autism?
To explore the origins of autism, individuals can research scientific literature, consult experts such as pediatricians or specialists in child development, and join support groups to connect with communities focused on developmental disorders.




