Introduction
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a methodical approach that aims to enhance positive behaviors and mitigate problematic ones in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and developmental disabilities. However, recent research has highlighted design flaws in some ABA studies, raising questions about their effectiveness and ethical conduct.
This article explores the different types of ABA therapies, the evolution of ABA over the years, the use of positive reinforcement, the integration of artificial intelligence, the importance of cultural values, and practical examples and applications of ABA in daily life. By critically analyzing ABA interventions and considering the voices of the autism community, we can ensure that these therapies are not only effective but also respectful and ethically conducted.
What is Applied Behavior Analysis?
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) stands as a methodical approach that delves into behavior and its environmental influences, founded on behaviorism principles. This therapy is pivotal for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and varying developmental disabilities, as it employs strategic interventions to enhance beneficial social behaviors while mitigating those that are problematic.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge that not all ABA research is flawless. Recent research syntheses aimed at critically evaluating non pharmacological interventions for autistic children and youth highlight a prevalent issue: many studies come with design flaws that obscure the true impact of these interventions.
These flaws raise questions about the effectiveness, the breadth of change expected, potential harms, and the involvement of community members in the research process. Furthermore, there is a growing movement, led by individuals with autism, to improve the quality and reporting of intervention research. Their advocacy underscores the importance of respectful and ethical research conduct as a fundamental component of interventions. As we navigate the landscape of ABA therapy, it's essential to scrutinize these interventions with a critical eye, ensuring that they are not only effective but also ethically conducted and reported with the utmost respect for the autism community.
How Does ABA Work?
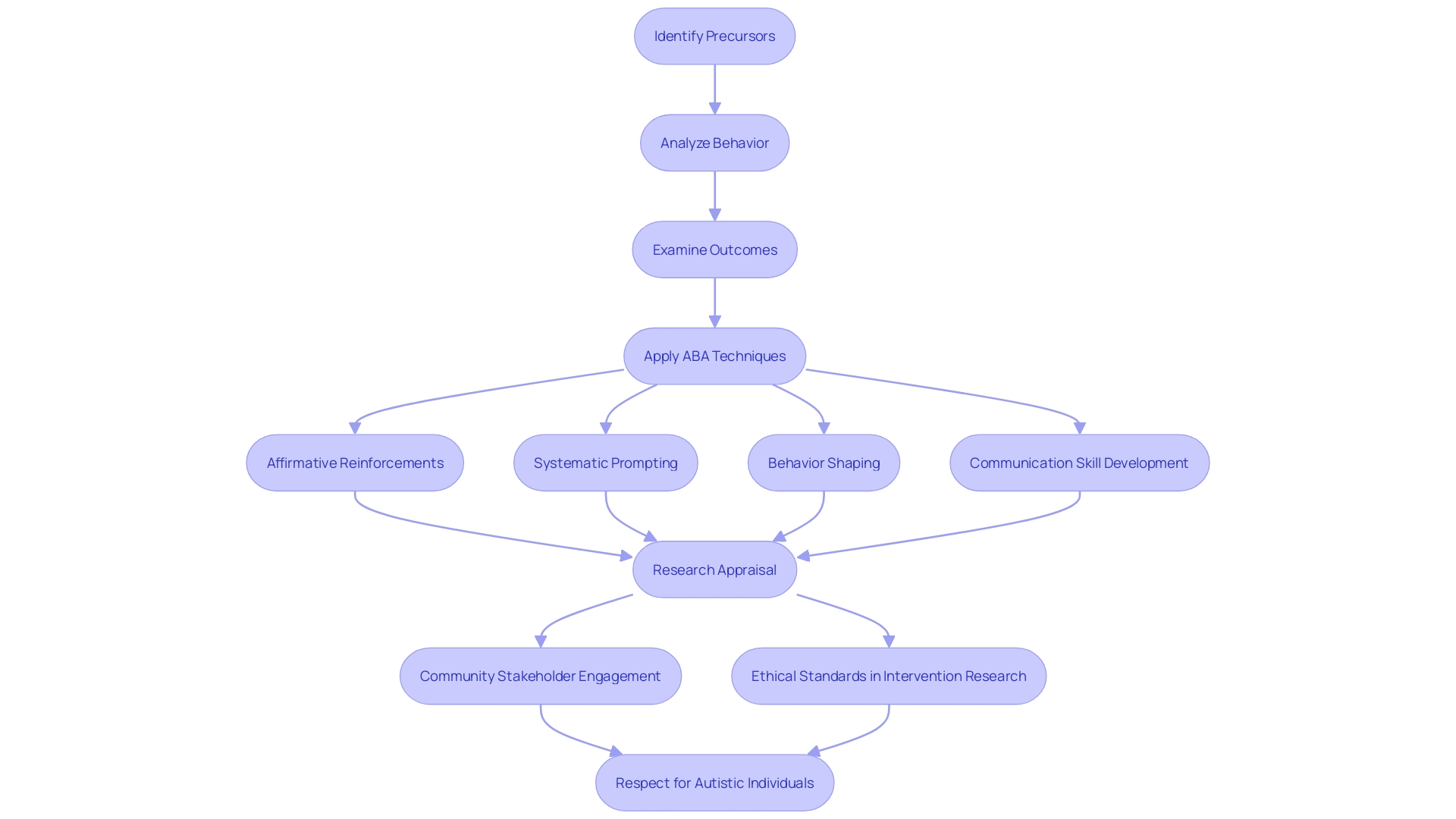
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy stands out as a meticulous, evidence-based method designed to enhance positive behaviors and diminish those that may be harmful or impede learning. It meticulously dissects behavior into manageable units for analysis, scrutinizing the precursors, the behavior itself, and its subsequent outcomes.
This granular approach helps in unveiling the underlying patterns and stimuli that provoke certain behaviors, equipping therapists with the insight to tailor precise interventions. ABA employs a variety of techniques, such as affirmative reinforcements, systematic prompting and gradual withdrawal, behavior shaping, and the cultivation of functional communication skills.
Despite its widespread application, it is crucial to acknowledge that research on non pharmacological interventions for autistic individuals often features methodological limitations. This highlights the necessity for a discerning appraisal of such research, particularly in its ability to effectively drive change, its potential for unintended consequences, and the degree of community stakeholder engagement. Moreover, the autistic community has played a pivotal role over recent years in spotlighting the importance of quality and ethical standards in intervention research, advocating for practices that fundamentally respect individuals with autism.
Types of ABA Therapies
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a versatile treatment approach, with various methods such as Discrete Trial Training (DTT), which breaks down skills into simple steps. Naturalistic Teaching Strategies (NTS) integrate learning in natural settings.
Pivotal Response Training (PRT) focuses on key behaviors that affect a wide range of social and cognitive skills. Early Intensive Behavioral Intervention (EIBI) is designed for young children and can have a significant impact on their development.
While these therapies aim to enhance communication, social skills, and reduce problematic behaviors, it's crucial to acknowledge that research on ABA interventions often encounters methodological challenges. These challenges can obscure the effectiveness, potential risks, and the true breadth of change ABA can bring. It highlights the necessity for rigorous evaluation to respect the needs and voices of the autism community, as they have been pivotal in advocating for quality in research and ethical considerations in interventions.
The Evolution of ABA
ABA has evolved over the years, influenced by advancements in research and technology. It originated in the 1960s and focused primarily on treating individuals with autism.
Since then, ABA has expanded its applications to various settings and populations, including schools, homes, and workplaces. The field continues to grow and adapt, incorporating new evidence-based strategies and technologies to improve outcomes for individuals with behavioral challenges.
ABA Therapy Programs
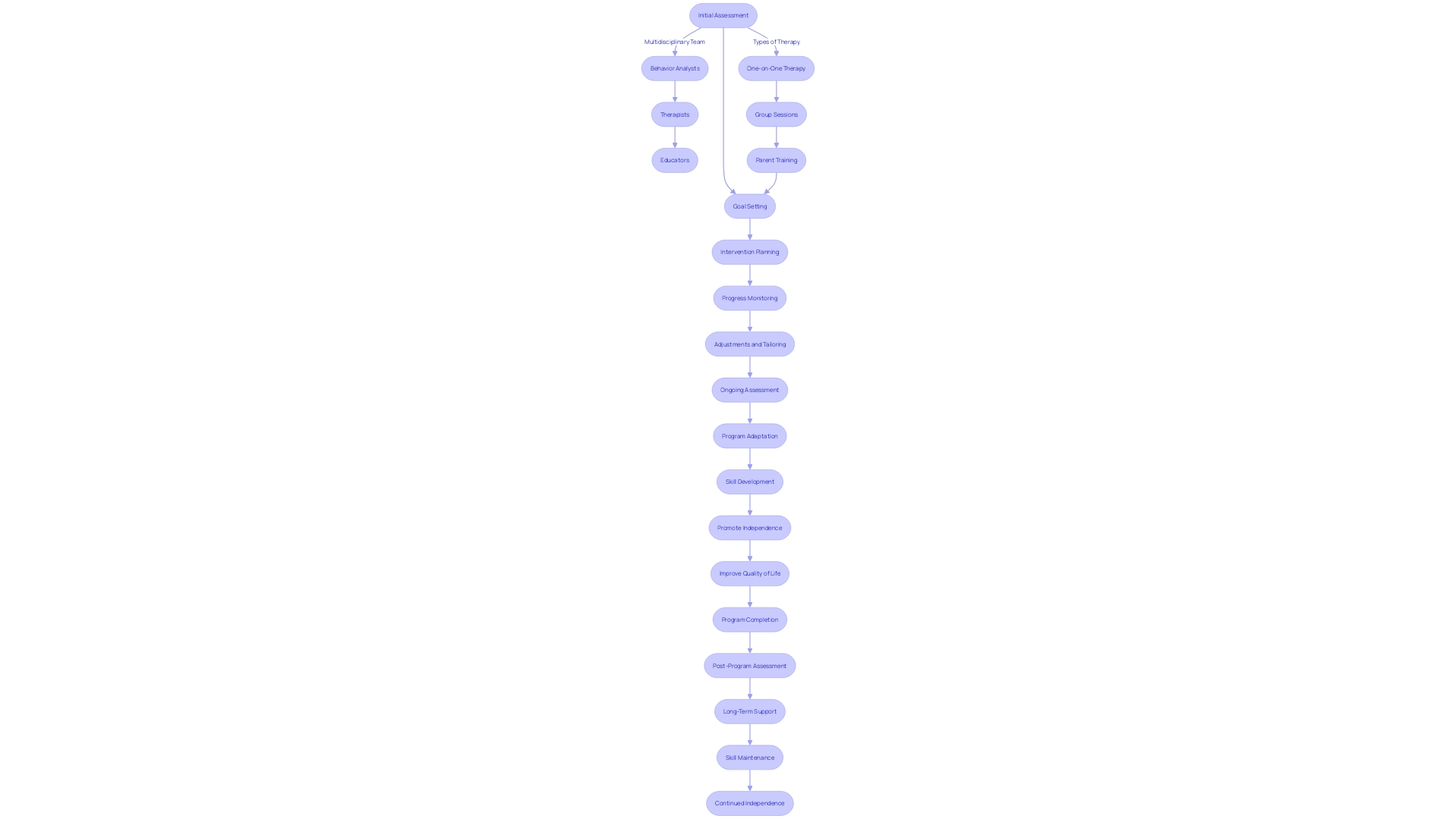
ABA therapy programs are designed to provide comprehensive interventions and support for individuals with autism and other developmental disabilities. These programs typically involve a multidisciplinary team of professionals, including behavior analysts, therapists, and educators.
The programs are tailored to meet the unique needs of each individual and may include a combination of one-on-one therapy, group sessions, and parent training. The goal is to promote skill development, independence, and overall quality of life.
Positive Reinforcement in ABA
Positive reinforcement is a fundamental principle of ABA therapy. It involves providing rewards or incentives to reinforce desired behaviors and increase the likelihood of their recurrence.
Positive reinforcement can take various forms, such as verbal praise, tokens, or access to preferred activities or items. By using positive reinforcement strategies, therapists can motivate individuals to engage in positive behaviors and make progress in their therapy goals.
ABA and Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize ABA therapy by providing innovative tools and technologies to support behavior analysis and intervention. AI-powered systems can assist in data collection, analysis, and decision-making processes, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of ABA therapy programs. These technologies can also facilitate remote therapy delivery and provide real-time feedback and recommendations to therapists and parents.
ABA and Cultural Values
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is not a one-size-fits-all approach; it deeply values the cultural and individual uniqueness of each person. Research has highlighted the necessity of tailoring interventions to accommodate the diverse cultural backgrounds and personal experiences of individuals with autism. ABA professionals are well-aware that the success of an intervention greatly hinges on its cultural relevance and sensitivity.
They are committed to fostering an inclusive environment that resonates with the individual's own cultural beliefs and practices. This thoughtful consideration is not just about respect—it's about ensuring that behavior changes are not only positive but also lasting and meaningful within the context of the individual's life. By aligning ABA strategies with the family's values and aspirations, therapists support the creation of positive outcomes that are both significant and sustainable.
ABA in Practice: Examples and Applications
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy extends its reach into numerous aspects of daily life for individuals with autism and ADHD. It's a multifaceted approach that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of each person.
Within educational environments, ABA principles are instrumental in teaching foundational academic competencies, such as literacy and numeracy, while simultaneously addressing disruptive behaviors that could hinder a student's academic progression. The therapy's adaptability allows educators to start with small, manageable goals, building upon the learner's strengths and positive relationships with specific subjects or instructors.
ABA's influence continues into the realm of social skills, where it provides structured strategies to enhance communication, such as practicing conversation turns and understanding others' viewpoints. This not only fosters better social interactions but also equips individuals with the necessary skills for community involvement and successful employment. By starting with a solid foundation and gradually scaling up interventions based on individual needs, ABA therapy proves to be a powerful tool in promoting independence and quality of life across various life domains.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a methodical approach aimed at enhancing positive behaviors and mitigating problematic ones in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and developmental disabilities. Recent research has raised concerns about the effectiveness and ethical conduct of some ABA studies. The voices of the autism community have emphasized the need for respectful and ethically conducted research in interventions.
It is crucial to critically evaluate ABA interventions, considering the limitations of nonpharmacological intervention research for autistic individuals. ABA therapy utilizes techniques like positive reinforcement, systematic prompting, behavior shaping, and functional communication skills to tailor interventions. Rigorous evaluation is essential to ensure effective interventions that respect the needs and voices of the autism community.
Different types of ABA therapies, such as Discrete Trial Training (DTT), Naturalistic Teaching Strategies (NTS), Pivotal Response Training (PRT), and Early Intensive Behavioral Intervention (EIBI), aim to improve communication, social skills, and reduce problematic behaviors. It is important to evaluate these therapies rigorously to understand their true impact. ABA has evolved over the years, incorporating advancements in research and technology.
It provides comprehensive support for individuals with autism and other developmental disabilities in various settings. Positive reinforcement is a fundamental principle of ABA therapy that motivates individuals to engage in positive behaviors. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize ABA therapy by providing innovative tools for data collection, analysis, remote therapy delivery, and real-time feedback.
ABA therapy values cultural diversity and individual uniqueness. By aligning strategies with cultural values and aspirations, therapists can foster meaningful behavior changes within an individual's life context. In practice, ABA therapy promotes academic competencies while addressing disruptive behaviors in educational environments.
It enhances social skills for better interactions within communities and equips individuals with skills for successful employment. By critically analyzing ABA interventions and considering the voices of the autism community, we can ensure effective and ethically conducted therapies. With careful evaluation and consideration, we can improve the quality of life for individuals with autism spectrum disorder and developmental disabilities through ABA therapy.




