Overview
This article serves as a compassionate guide for parents and advocates, helping them understand and support individuals with high-functioning Asperger's syndrome. It emphasizes the unique traits and challenges that come with the condition, fostering a deeper awareness of the emotional landscape these individuals navigate. Tailored support strategies, such as establishing routines and promoting interpersonal skills, are highlighted as essential tools for enhancing the quality of life for those affected. Backed by research and real-life case studies, the article illustrates effective interventions that can make a meaningful difference. Together, let’s explore these insights and create a nurturing environment for those we care about.
Introduction
As awareness of autism spectrum disorders continues to grow, understanding Asperger's Syndrome—often viewed as a high-functioning form of autism—becomes increasingly vital. This condition is characterized by unique challenges in social interaction and specific behavioral patterns. Individuals with Asperger's often navigate a world that may not fully recognize their strengths or struggles. With statistics revealing a significant prevalence of developmental disabilities among children, the importance of early identification and tailored support strategies cannot be overstated.
This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of Asperger's Syndrome, exploring its historical context and symptom recognition. We will also discuss effective support strategies for parents and advocates. Our aim is to foster an environment where individuals can thrive amidst their challenges. Together, we can create a supportive community that understands and values the unique experiences of those with Asperger's Syndrome.
Understanding Asperger's Syndrome: A Comprehensive Overview
Asperger's syndrome high functioning, often recognized as a high-functioning variant of the spectrum, presents unique traits that can significantly impact individuals and their families. Notable challenges in social interactions, alongside restricted and repetitive behaviors and interests, are key traits of this condition. Unlike other autism spectrum disorders, individuals with Asperger's typically do not experience delays in language development, which can make their struggles more challenging to identify and understand.
Recent statistics reveal that approximately 1 in 6 children, or 17%, are diagnosed with a developmental disability. This highlights the critical importance of awareness and early identification efforts, as emphasized by the CDC. According to the CDC, the overall ASD prevalence is lower among non-Hispanic White children (24.3) and children of two or more races (22.9) compared to non-Hispanic Black or African American (29.3), Hispanic (31.6), and non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander (33.4) children. Understanding these statistics is crucial for parents and advocates, as it lays the groundwork for effective support strategies tailored to the specific needs of individuals with Asperger's syndrome high functioning on the autism spectrum.
Furthermore, a case study titled 'Future Predictions for Autism Awareness and Planning' indicates that while awareness is improving, parents often express concerns about planning for their child's future and their ability to provide care as their child ages. This underscores the need for social workers to assist parents in breaking down future planning into manageable steps and providing ongoing support. Additionally, the CDC's monitoring methods have become more consistent, aiding in case identification.
By recognizing these core characteristics and challenges, caregivers can better navigate the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder. This understanding fosters an environment where children can thrive, and we encourage parents to share their experiences and seek support as they embark on this journey together.
The Historical Context of Asperger's Syndrome
Initially recognized by Hans Asperger in the 1940s, Asperger's syndrome high functioning was identified as a distinct diagnosis within the spectrum of autistic disorders. This condition is characterized by specific traits that set it apart from other types of autistic conditions. However, significant advancements in our understanding of autism have led to the incorporation of this specific condition into the broader category of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) with the adoption of the DSM-5 in 2013. This crucial change reflects an evolving recognition that the symptoms related to Asperger's condition are, in fact, part of a broader spectrum. Such an evolution promotes more inclusive diagnostic practices and enhances the support available for individuals and families navigating these challenges.
In the 2010s, the classification of Asperger's syndrome high functioning was eliminated as a separate diagnosis. This change has understandably raised concerns among families and professionals regarding the adequacy of support for those previously diagnosed. Many families expressed fears that the new criteria might exclude them from receiving appropriate services, as noted in the case study 'Impact of DSM-5 Changes on AS Diagnosis.' Simon Baron-Cohen emphasizes the importance of recognizing the unique strengths of individuals on the spectrum. He states, 'In the communal realm, there is no substantial advantage to a precise eye for detail, but in the fields of maths, computing, cataloging, music, linguistics, engineering, and science, such an eye for detail can lead to success rather than failure.' This perspective highlights the value that individuals on the spectrum bring to various fields.
This evolution in classification underscores the pressing need for interprofessional coordination in healthcare. It is vital to ensure that all individuals on the spectrum receive the comprehensive care they deserve. Together, we can foster a supportive environment that acknowledges and nurtures the strengths of every individual.
Recognizing Symptoms of Asperger's Syndrome in Adults
Adults with high-functioning Asperger's Syndrome often face a unique set of challenges that can significantly impact their interactions with others. Many struggle with interpersonal engagement, which may manifest as limited eye contact and difficulties in interpreting non-verbal cues. Additionally, behavioral patterns such as a strict adherence to routines, an intense focus on specific interests, and a tendency to miss subtle social cues are frequently observed.
For instance, Mr. M, a patient, shared that 'the biggest strain for the patient was participating in life outside his own private sphere.' This statement highlights the isolation that can stem from these challenges. In professional environments, individuals with ASD-AS may communicate in a formal manner and experience cognitive inflexibility, which can complicate job acquisition, despite their valuable qualities.
Understanding the symptoms of high-functioning Asperger's syndrome is crucial for parents and advocates. This knowledge enables them to provide tailored support and interventions that meet the individual's specific needs. Notably, neuroscientific studies indicate reduced activity in brain areas linked to empathy and social cognition among those with the condition, underscoring the importance of awareness and informed advocacy. Approximately 9% of children diagnosed with ASD at an early age may no longer meet the diagnostic criteria in adulthood, highlighting the evolving nature of these challenges.
Obtaining an adult diagnosis of ASD can be complex due to coping mechanisms that may mask symptoms. However, recognizing these patterns is vital for accessing the necessary support. By leveraging the community and resources available through ASD Media, parents and advocates can facilitate better access to interventions, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for those navigating this condition. Together, we can foster understanding and support for individuals with Asperger's Syndrome and their families.
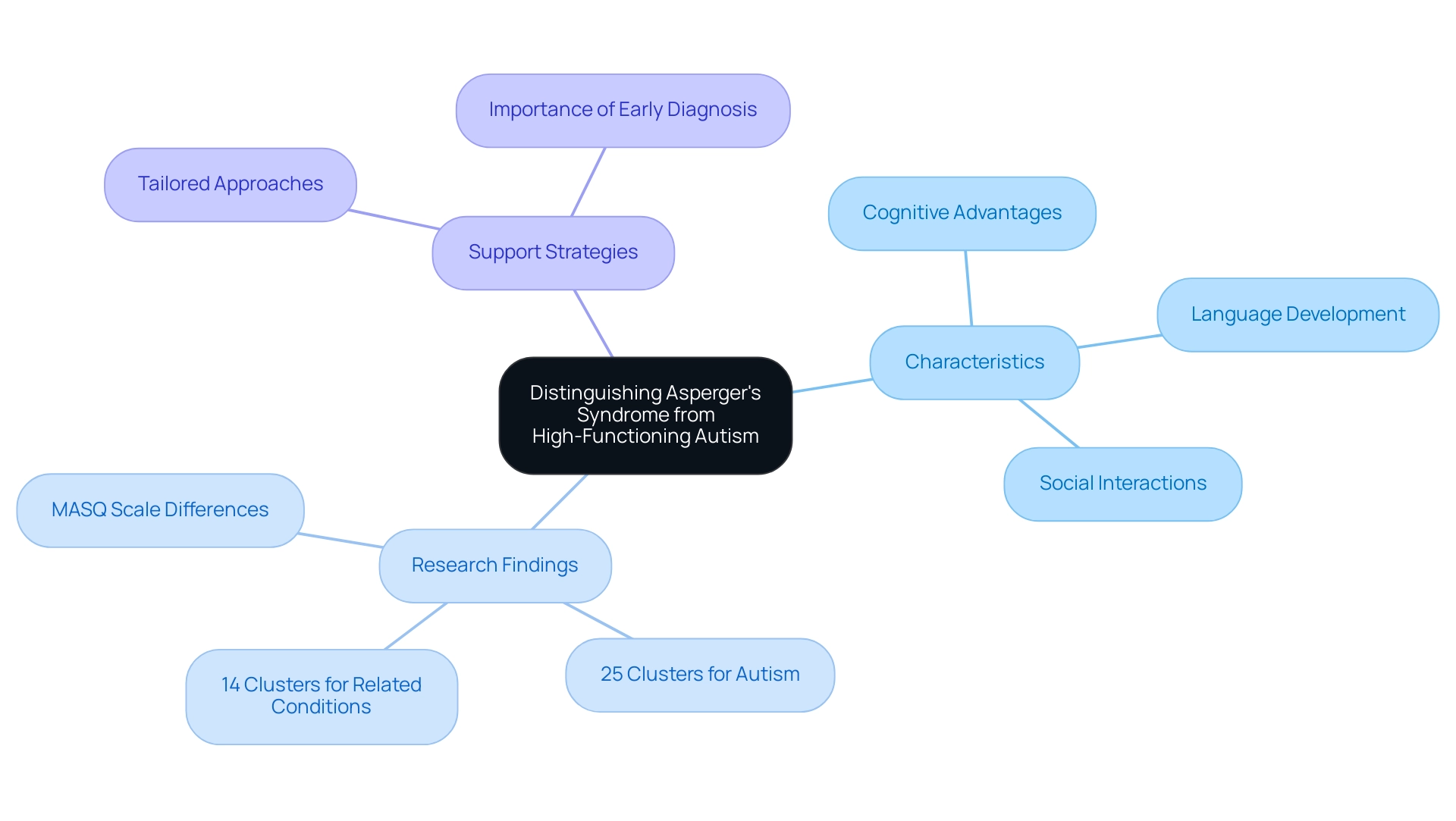
Distinguishing Asperger's Syndrome from High-Functioning Autism
Understanding high-functioning neurodevelopmental disorders, including Asperger's syndrome and related conditions, is essential for parents and advocates. These individuals often display unique traits that can significantly impact their lives. Typically, those with autism spectrum disorder show no substantial delays in language development and frequently exhibit a higher level of cognitive functioning compared to their peers. This cognitive advantage may present itself through advanced vocabulary or strong analytical skills, which can be both a gift and a challenge.
Research has shown that the MASQ scale reveals significant differences among high-functioning conditions on the spectrum, highlighting the necessity for tailored approaches. Asperger's syndrome encompasses a broader range of characteristics, which can vary in severity and influence social interactions and behavioral responses. Notably, studies have identified 25 clusters summarizing autism research and 14 clusters for related conditions, underscoring the complexity of these experiences.
Recognizing these differences is vital for developing effective support strategies. This understanding empowers parents and advocates to address the unique needs and challenges faced by individuals. As Kimberly Holland wisely pointed out, 'However, many children, and even some adults, may not be diagnosed until much later.' This statement sheds light on the diagnostic challenges that can hinder timely intervention, which is crucial for fostering growth.
By embracing these nuances, we can create a more supportive environment that nurtures development and encourages open dialogue. We invite you to share your experiences and insights in the comments or through our newsletter, as together, we can foster understanding and support for all.
Effective Support Strategies for Parents and Advocates of Individuals with Asperger's Syndrome
Supporting individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a journey that requires understanding and compassion. As parents and advocates, you can implement several key strategies that not only foster growth but also create an environment of security and connection.
- Establish Routines: Consistent routines are vital for individuals on the autism spectrum. They offer a sense of security and predictability, which can significantly reduce anxiety and improve behavioral outcomes. Research shows that structured environments are beneficial. Additionally, the FDA has approved risperidone for treating behavioral issues in children with high-functioning Asperger's syndrome, underscoring the importance of addressing these challenges effectively.
- Promote Interpersonal Skills: Engaging in role-playing exercises can greatly enhance social interactions and understanding of social cues. According to the American Psychiatric Association, targeted efforts in interpersonal skills training are crucial for fostering effective communication. It’s also important to clarify that there is no evidence linking ASD to immunization as an environmental risk factor, helping to dispel common misconceptions.
- Encourage Special Interests: Harnessing a person’s specific interests can serve as a powerful motivational tool. This approach not only promotes passion but also facilitates learning and community engagement, helping individuals connect with peers who share similar interests.
- Provide Clear Communication: Using straightforward and literal language is essential to prevent misunderstandings. Clarity in communication helps individuals navigate social interactions more effectively, reducing frustration and confusion. For instance, individuals with impaired pragmatic language skills may find it challenging to express their abilities during job interviews, as highlighted in case studies on the professional challenges faced by those with ASD.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Collaborating with therapists and educators who specialize in autism ensures that interventions are tailored to meet unique needs. Recent case studies demonstrate that such collaboration leads to more effective behavior support plans, enhancing overall well-being. By implementing these strategies, you can create a nurturing environment that promotes the development and success of individuals with high-functioning Asperger's syndrome. Together, we can make a meaningful difference in their lives.
Conclusion
Understanding Asperger's Syndrome is essential for fostering a supportive environment where individuals can thrive despite their unique challenges. This article highlights the distinct characteristics of Asperger's, such as difficulties in social interaction and specific behavioral patterns, which set it apart from other forms of autism. With the increasing prevalence of developmental disabilities among children, early identification and tailored support strategies have never been more critical.
The historical context of Asperger's Syndrome illustrates the evolving understanding of autism and the importance of inclusive diagnostic practices. Recognizing symptoms in adults, along with distinguishing Asperger's from high-functioning autism, emphasizes the need for targeted interventions that address individual needs. Effective support strategies, such as establishing routines and promoting social skills, can significantly enhance the quality of life for those navigating Asperger's Syndrome.
Ultimately, creating a compassionate and informed community is vital in ensuring that individuals with Asperger's are recognized for their strengths and supported in overcoming their challenges. By embracing awareness, understanding, and proactive advocacy, we can foster an environment where every individual has the opportunity to succeed and contribute meaningfully. Let us work together to build this supportive community, where every voice matters and every journey is valued.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Asperger's syndrome high functioning?
Asperger's syndrome high functioning is recognized as a high-functioning variant of the autism spectrum, characterized by unique traits such as challenges in social interactions and restricted, repetitive behaviors and interests. Unlike other autism spectrum disorders, individuals with Asperger's typically do not experience delays in language development.
How common is Asperger's syndrome high functioning among children?
Approximately 1 in 6 children, or 17%, are diagnosed with a developmental disability, highlighting the importance of awareness and early identification efforts for conditions like Asperger's syndrome.
What are the prevalence statistics for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) among different racial groups?
According to the CDC, the overall ASD prevalence is lower among non-Hispanic White children (24.3) and children of two or more races (22.9) compared to non-Hispanic Black or African American (29.3), Hispanic (31.6), and non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander (33.4) children.
What concerns do parents have regarding their child's future with Asperger's syndrome?
Parents often express concerns about planning for their child's future and their ability to provide care as their child ages. This emphasizes the need for social workers to assist parents with manageable steps for future planning.
What changes occurred in the classification of Asperger's syndrome in the 2010s?
In the 2010s, Asperger's syndrome was eliminated as a separate diagnosis and incorporated into the broader category of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) with the adoption of the DSM-5 in 2013. This change reflects an evolving recognition that Asperger's symptoms are part of a broader spectrum.
What are the implications of the DSM-5 changes for families previously diagnosed with Asperger's syndrome?
The elimination of Asperger's syndrome as a distinct diagnosis has raised concerns among families and professionals about the adequacy of support for those previously diagnosed. Many families fear that the new criteria might exclude them from receiving appropriate services.
What strengths do individuals on the autism spectrum possess?
Individuals on the autism spectrum, including those with Asperger's syndrome, often have unique strengths, particularly in fields such as mathematics, computing, cataloging, music, linguistics, engineering, and science, where attention to detail can lead to success.
Why is interprofessional coordination important in healthcare for individuals on the spectrum?
Interprofessional coordination in healthcare is vital to ensure that all individuals on the spectrum receive the comprehensive care they deserve, fostering a supportive environment that acknowledges and nurtures their strengths.




