Overview
This article highlights nine compassionate strategies aimed at enhancing social skills development in children with autism. It underscores the critical role of early intervention and the power of collaborative efforts between parents and professionals. By exploring methods such as structured playgroups, visual supports, and positive reinforcement, it illustrates how these approaches can nurture essential social abilities. Ultimately, these strategies not only foster growth but also significantly improve the overall quality of life for individuals on the autism spectrum. As you navigate this journey, remember that seeking support and resources can make a meaningful difference in your child's development.
Introduction
The journey to enhance social skills for children with autism is both vital and complex, as it lays the foundation for meaningful interactions and a fulfilling life.
With approximately 1 in 36 children in the U.S. affected by autism spectrum disorder, the quest for effective strategies has never been more urgent.
This article explores nine actionable strategies designed to empower both parents and professionals, providing insights into how targeted interventions can transform social development.
How can these approaches improve communication while fostering a sense of belonging and confidence in young individuals navigating the challenges of autism?
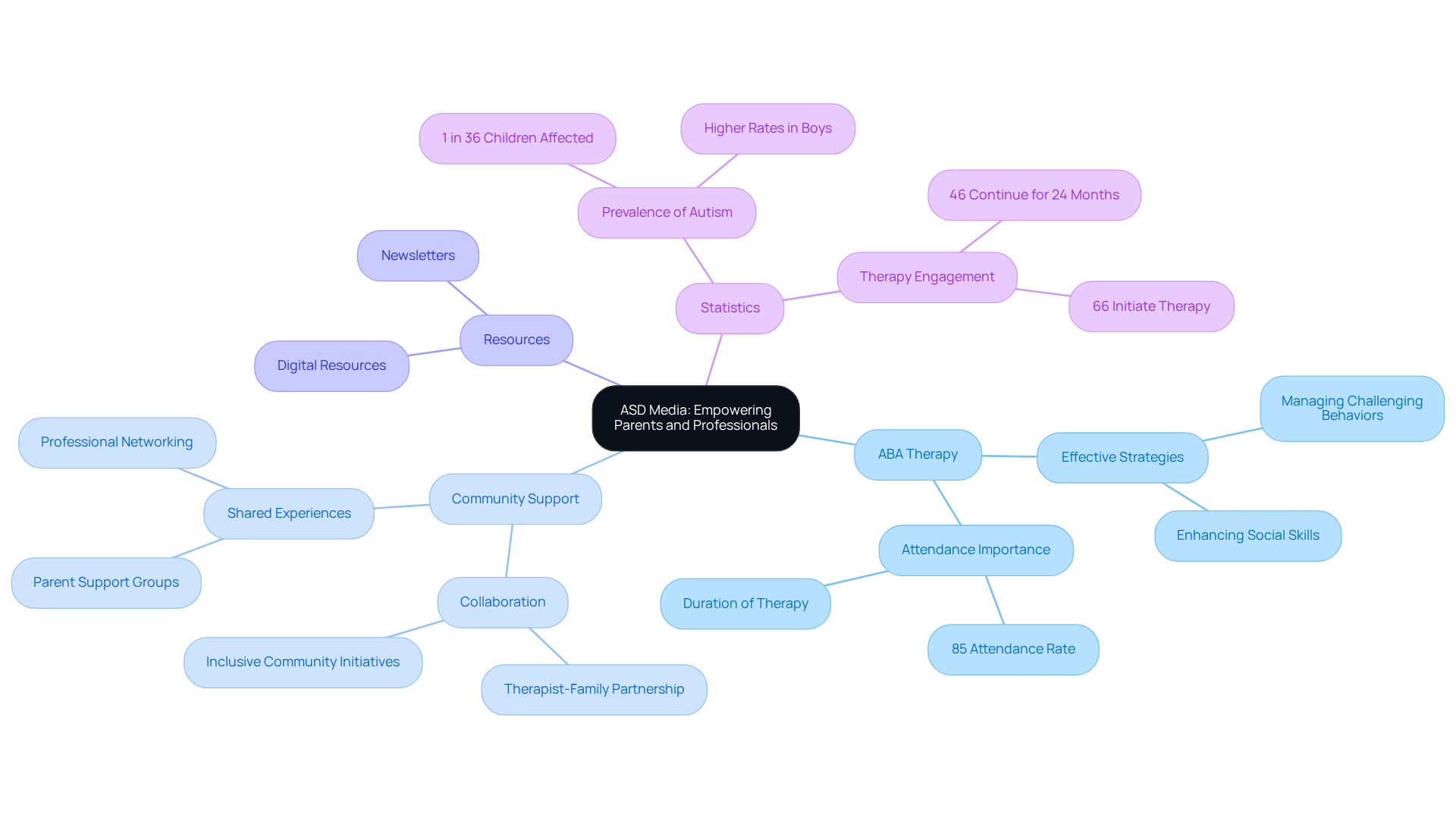
About ASD Media: Empowering Parents and Professionals in Social Skills Development
At ASD Media, we are deeply committed to advancing the implementation of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, offering valuable insights and strategies that address the challenges faced by families and improve outcomes for their children. Our organization provides a wide range of resources designed specifically for parents and professionals in the developmental disabilities sector. Central to our mission is the creation of a supportive and inclusive community where individuals can share experiences, learn from one another, and receive essential support throughout their journeys.
By subscribing to our newsletter, you can gain access to the latest news and unlimited digital resources, empowering you to unlock the potential of children with autism and ADHD. We focus on effective strategies for managing difficult behaviors, navigating support services, and enhancing the development of social abilities.
Research shows that early intervention with ABA therapy can lead to significant improvements in communication and cognitive skills, especially for toddlers starting therapy around age two. Yet, fewer than half (46%) of youth referred for ABA therapy maintain treatment for the recommended 24 months. This statistic underscores the necessity for ongoing community support and involvement. Additionally, autism spectrum disorder affects approximately 1 in 36 youngsters in the U.S., highlighting the importance of ASD Media's efforts in this vital field.
Our resources play a crucial role in fostering social skills autism development. We have initiatives designed to promote inclusion and collaboration among families and professionals. We emphasize the importance of maintaining an attendance rate of 85 percent for both parents and children to maximize the effectiveness of therapy. As we know, effective therapy is a collaborative effort among therapists, families, and individuals with developmental differences, all working together towards achieving positive outcomes. By addressing obstacles to access and offering specialized support, ASD Media is dedicated to improving the overall quality of life for individuals on the spectrum and their families. Join us in this journey; together, we can make a difference.
Early Diagnosis: Key to Tailoring Social Skills Training for Autism
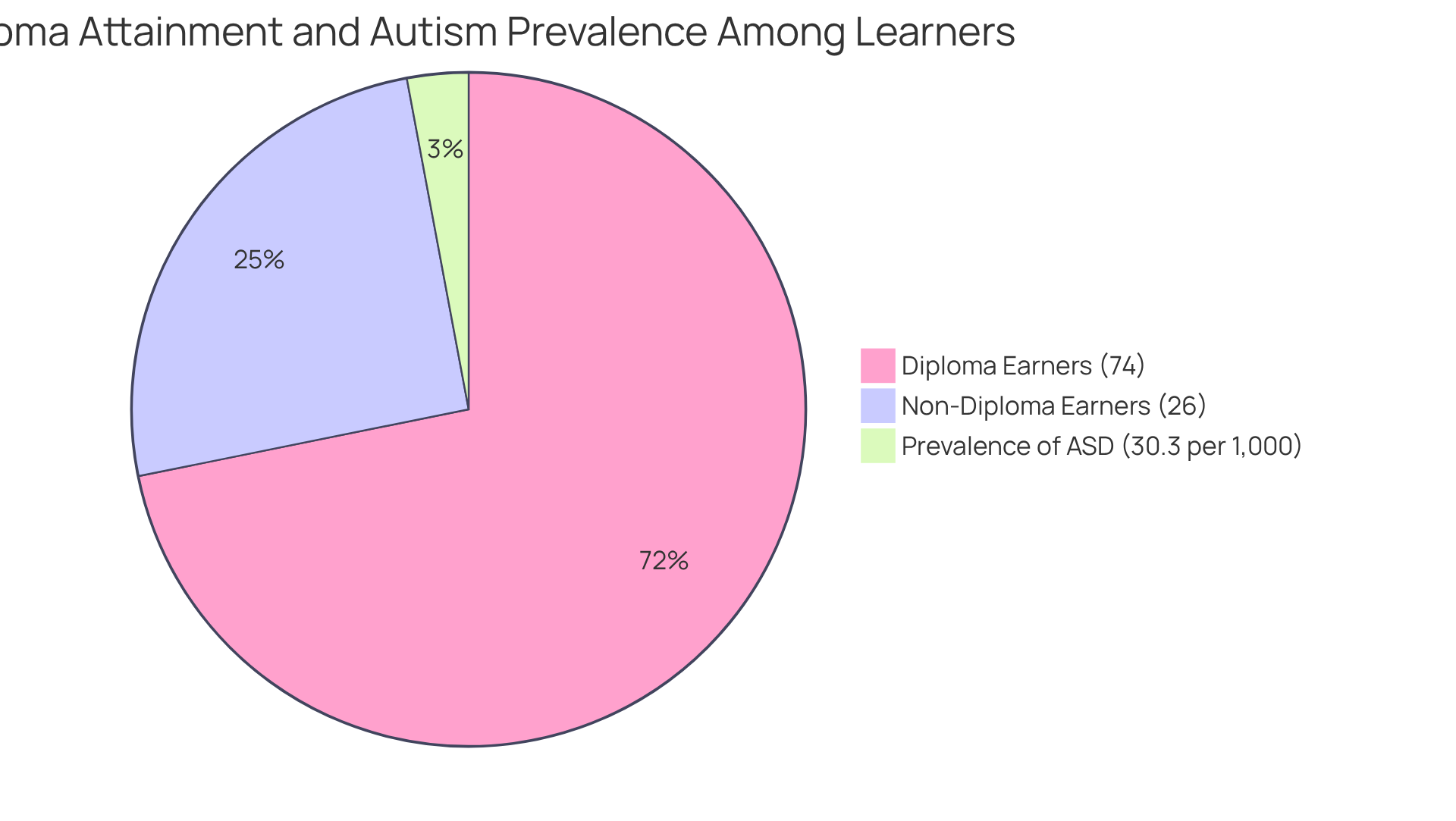
Timely identification of developmental spectrum conditions is vital for implementing effective interpersonal training. Recognizing developmental disorders early allows for customized strategies that specifically address the interpersonal challenges faced by youth. Research shows that autism can often be identified by a specialist by age 2, and those diagnosed early can significantly benefit from targeted therapies, which enhance their social communication skills and lead to better long-term outcomes. For instance, in 2022, the prevalence of ASD among children aged 5 to 8 was 30.3 per 1,000 individuals, underscoring the critical need for early diagnosis.
Case studies, such as 'Exploring Core Strategies for Effective Behavior Intervention,' highlight the positive impact of applied behavior analysis (ABA) techniques on children's adaptability and emotional resilience. It is essential for parents and professionals to prioritize early screening and assessment to ensure timely support. Currently, the average age of diagnosis in the U.S. is around five years, while the average age for first intervention is 4.7 years. By focusing on early identification, we can unlock the potential for improved social skills autism development in young individuals with developmental disorders. This is reflected in the statistic that 74% of autistic learners in the U.S. earn a diploma, illustrating the importance of early intervention and support.
Structured Playgroups: Facilitating Social Interaction in Autism
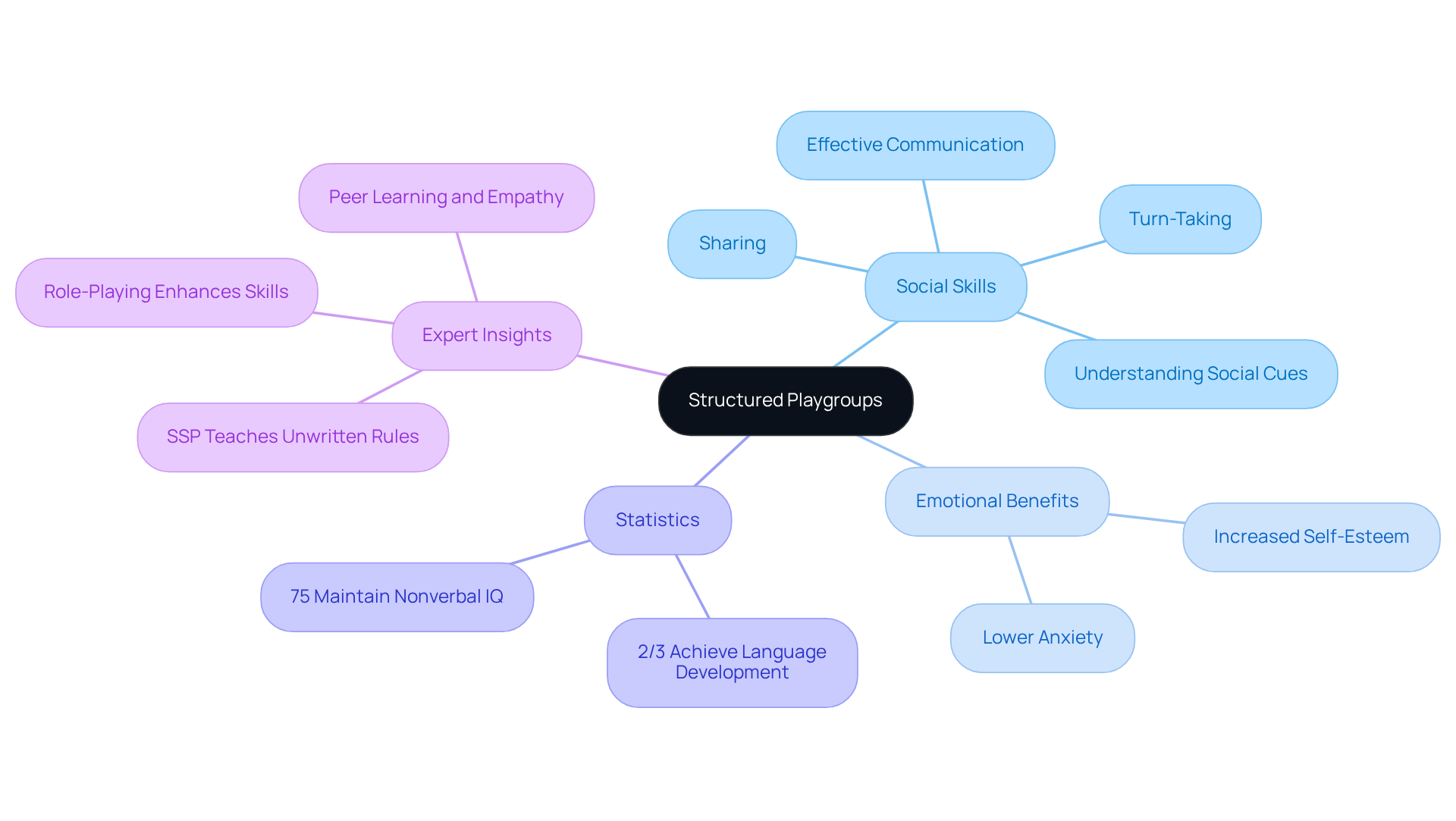
Organized playgroups serve as a powerful way to foster social skills autism through interaction among children. These environments are designed to be safe and supportive, allowing young ones to cultivate essential social skills autism through structured activities. Research indicates that participation in integrated playgroups can lead to significant improvements in social skills, with studies revealing that two out of three children in these settings achieve notable language development. It's also crucial to recognize that two-thirds of children with autism face bullying, highlighting the importance of social skills autism in preventing such challenges. Through organized play, children learn critical social skills autism, including sharing, turn-taking, and effective communication, which are vital for their growth. SSP teaches children the unspoken rules of social behavior, further enhancing their interaction abilities.
Parents and professionals can tailor playgroups to focus on specific social goals related to social skills autism, ensuring that every child has the opportunity to enhance their social skills in an enjoyable and engaging manner. The benefits of these playgroups extend beyond immediate social skills; they also contribute to long-term academic success and emotional well-being. For example, research shows that 75% of integrated playgroup participants maintained an average nonverbal IQ into grade school, emphasizing the academic advantages of these programs. Children who participate in organized playgroups often experience lower anxiety and increased self-esteem, which are essential for navigating social situations both inside and outside the classroom.
Moreover, expert insights highlight that organized playgroups not only teach children the unwritten rules of interaction but also help them develop empathy and understand social cues. Children learn to interpret facial expressions, body language, and tone of voice, which are crucial elements of social interaction. Through role-playing and collaborative activities, young individuals gain the ability to initiate and sustain conversations, fostering meaningful peer relationships. Overall, organized playgroups are vital strategies that significantly enhance social skills autism and improve the overall quality of life for individuals on the autism spectrum.
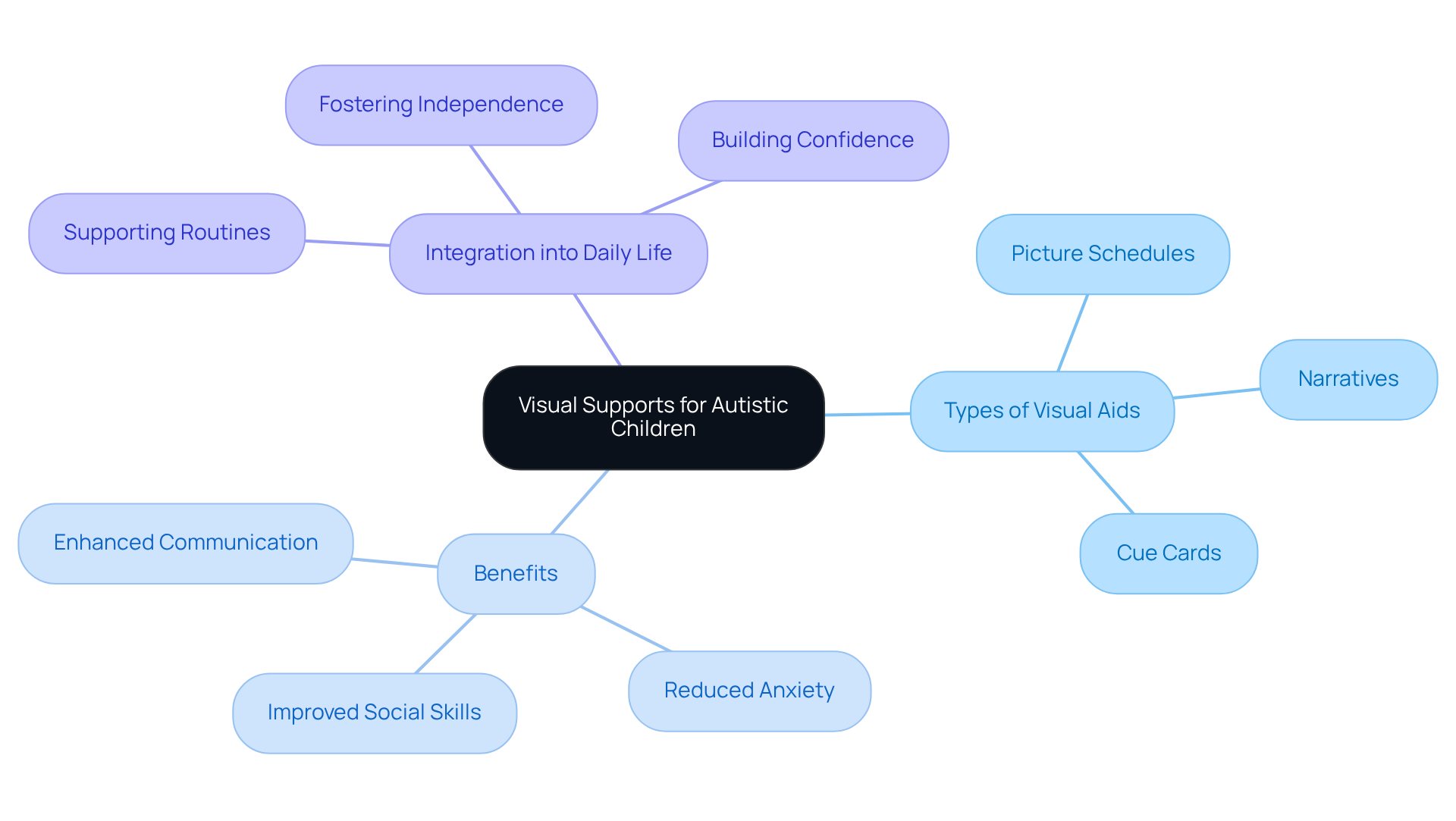
Visual Supports: Enhancing Understanding and Communication for Autistic Children
Visual aids, such as picture schedules, narratives, and cue cards, are invaluable tools that can significantly enhance comprehension and communication for children with autism. These resources help clarify societal expectations and daily routines, making it easier for young ones to develop social skills and navigate social interactions. By weaving visual supports into everyday activities, parents and professionals can provide essential guidance that not only boosts interpersonal skills but also supports the development of social skills and alleviates anxiety in social settings.
Imagine a child feeling more at ease during a family gathering, equipped with a simple picture schedule that outlines what to expect. This small adjustment can make a world of difference, fostering confidence and reducing stress. As caregivers, we have the power to create supportive environments that empower our children to thrive.
Consider integrating these visual aids into your daily life. How might they transform your child's experience in social situations by improving social skills? Sharing your stories and insights can inspire others in our community. Together, we can cultivate a nurturing atmosphere that supports our children’s growth and development.
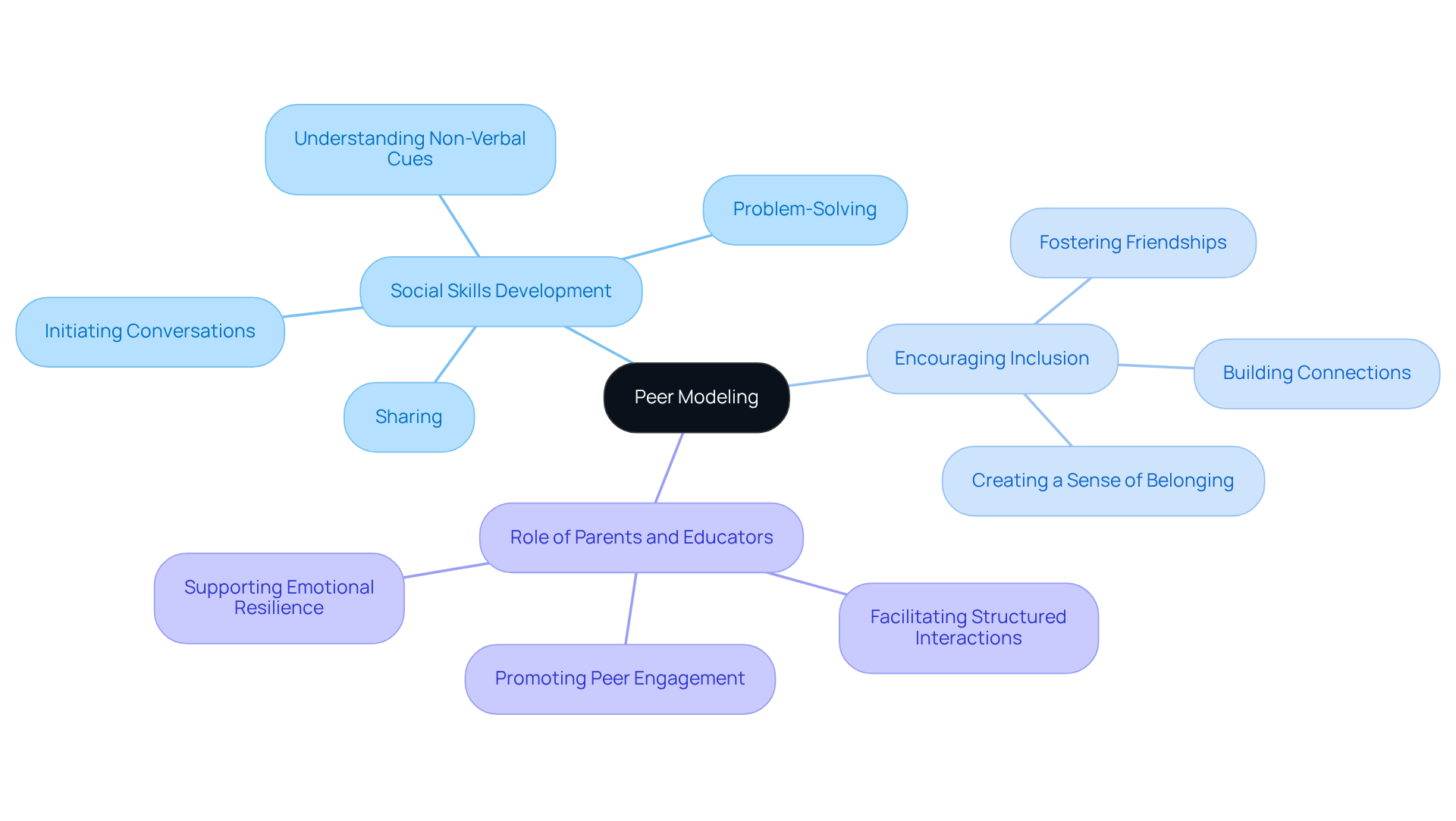
Peer Modeling: Leveraging Social Learning for Skill Development
Peer modeling is a wonderful approach that involves using typically developing peers to demonstrate appropriate interpersonal behaviors. This practice can significantly enhance the social skills of children with autism. By observing and imitating their classmates, these children learn to engage in interactions more effectively. Not only does this method foster vital social skills in autism, but it also encourages inclusion and friendship among all children.
As parents and educators, we can actively promote peer modeling by creating opportunities for young individuals to interact with their peers in structured environments. Imagine the joy of watching children learn from one another, building connections that last a lifetime. By facilitating these interactions, we can help nurture a sense of belonging and camaraderie, paving the way for a more inclusive community. Let's work together to support our children in their social journeys.
Social Stories: Guiding Autistic Children Through Social Situations
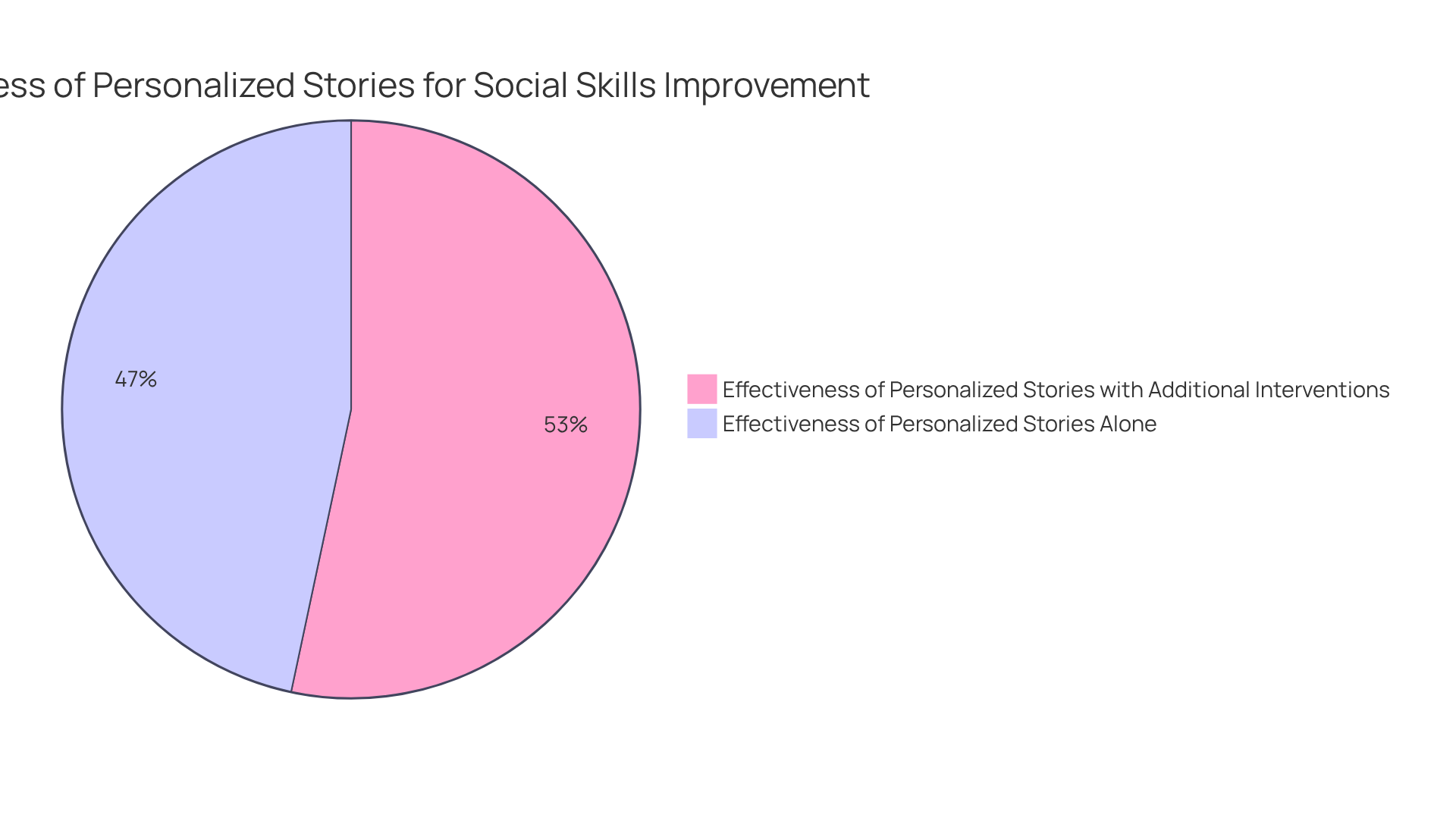
Personalized stories serve as tailored narratives designed to help children with autism improve their social skills, allowing them to navigate interpersonal situations and understand expectations. By outlining specific scenarios and appropriate responses, these narratives create a structured framework for managing interactions. Customized to address individual challenges, they become a versatile tool for both parents and professionals.
Research shows that interpersonal narratives can significantly reduce inappropriate behaviors and improve communication skills. The mean percentage of non-overlapping data (PND) indicates a 57.46% effectiveness when used alone, suggesting low or questionable effectiveness, and 65.66% when combined with additional interventions, which also reflects low or questionable effectiveness.
It's essential to recognize that the effectiveness of narrative stories may vary among participants, and they have not yet been classified as evidence-based practices. This flexibility empowers children to develop social skills and approach interpersonal situations with increased confidence and understanding, making narrative techniques a valuable resource in therapeutic practices for developmental disorders. By exploring these narratives, parents can find supportive ways to help their children thrive in social interactions.
Emotional Recognition: Building Blocks for Social Skills in Autism
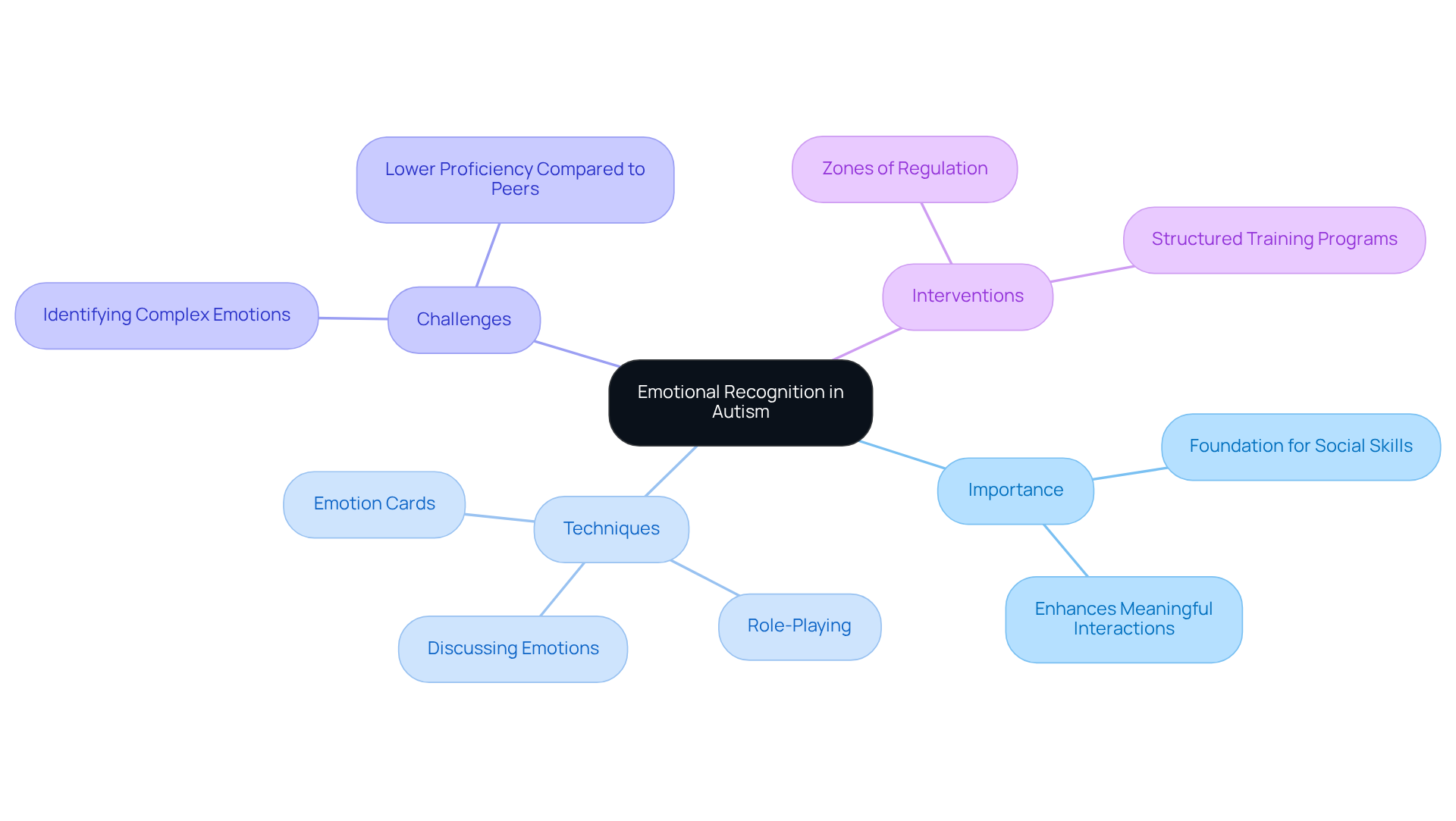
Emotional recognition is an essential skill and a part of social skills autism for children, serving as a cornerstone for meaningful interactions. By teaching young ones to recognize and understand feelings—both their own and those of others—we can significantly enhance their social skills. Effective techniques, such as using emotion cards, role-playing, and discussing emotions in context, play a crucial role in developing this vital ability. For instance, role-playing allows children to practice emotional responses in simulated scenarios, fostering a deeper understanding of social cues.
Research suggests that children with developmental disorders often struggle to identify emotional expressions, particularly complex feelings. Studies show that these children face considerable challenges with emotions like 'angry' and 'afraid.' By ages 5 to 7, many individuals with developmental disorders exhibit lower proficiency in recognizing emotional expressions compared to their neurotypical peers. This gap highlights the importance of targeted interventions to boost emotional awareness, especially since children with autism may only reliably recognize 'afraid' and 'angry' at the most basic level of emotional expression.
Effective programs, such as those utilizing the Zones of Regulation framework, help children recognize and manage their emotional states, which enhances their social skills autism and leads to improved interactions. Moreover, research indicates that structured emotional recognition training can yield significant advancements in both accuracy and processing speed when identifying emotions. For example, young individuals engaged in emotion recognition activities demonstrated a remarkable improvement in their ability to identify and replicate facial expressions, with accuracy rates improving significantly over time.
Experts emphasize the necessity of consistent practice and reinforcement in nurturing emotional awareness. Bruce William highlights the need for targeted interventions that enhance emotion recognition skills in children with ASD. Visual aids, like emotion charts, can support young individuals in articulating their feelings, while narratives prepare them for various social situations through simple stories. By fostering emotional awareness, parents and professionals can empower children with autism to form meaningful connections, ultimately enhancing their overall social skills autism and quality of life.
Positive Reinforcement: Encouraging Social Skills Through Reward Systems
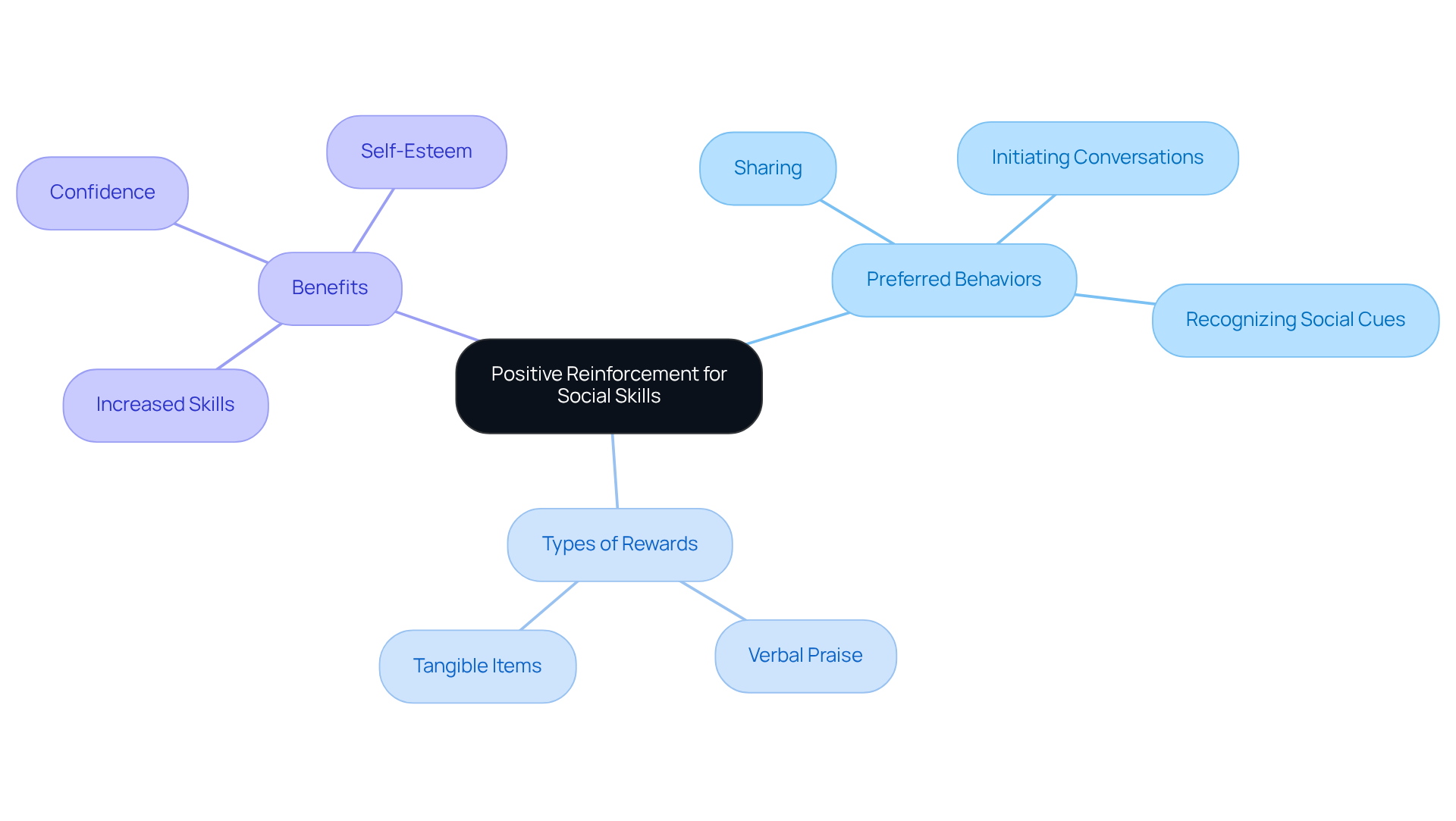
Positive reinforcement serves as a powerful tool in nurturing the growth of social skills autism among youth. By rewarding preferred behaviors—such as sharing, initiating conversations, or recognizing social cues—parents and professionals can encourage young individuals to develop social skills autism. Rewards can vary widely, from verbal praise to tangible items, and should be customized to align with each child's unique interests and preferences.
Research indicates that structured incentive programs can lead to remarkable improvements in social skills autism, with studies showing an 85% increase in skills among children receiving ABA therapy. It’s important to consistently apply these reinforcement strategies, as this not only promotes the repetition of positive behaviors but also helps build confidence and self-esteem.
By establishing clear, measurable goals and regularly assessing progress, caregivers can create an environment that fosters interpersonal growth and enhances overall communication skills. As you embark on this journey, remember that each small step counts, and your efforts can make a significant difference in your child's social development.
Parental Involvement: Essential Support for Social Skills Growth
Parental engagement plays a crucial role in the development of social skills in youth with autism. By practicing skills learned in therapy at home and during everyday activities, parents can reinforce these abilities. Engaging in play, modeling interactions with others, and providing constructive feedback can help children apply their skills in various situations. When parents actively participate in their child's development of social skills in autism, they create a nurturing environment that fosters confidence and proficiency in interactions. This supportive atmosphere not only enhances their child's development but also strengthens the bond between parent and child, making the journey together even more meaningful.
Collaboration with Professionals: Enhancing Social Skills Training Outcomes
Collaboration among professionals—therapists, educators, and healthcare providers—is essential for enhancing social skills training outcomes for youth with autism. By uniting their expertise, parents and professionals can craft personalized intervention plans that cater to each child's unique needs. This teamwork not only fosters regular communication and feedback but also ensures that strategies are effectively implemented and adjusted as necessary.
Such a collaborative approach not only enriches the child's development but also empowers families to actively participate in the process. By reinforcing their role as integral partners in their child's growth, we can create a nurturing environment that supports both the child and the family. Together, we can make a meaningful difference in the lives of these children and their families.
Conclusion
The journey towards enhancing social skills in children with autism is truly multifaceted, requiring a comprehensive approach that integrates various strategies and resources. By focusing on:
- Early diagnosis
- Structured playgroups
- Visual supports
- Peer modeling
- Social stories
- Emotional recognition
- Positive reinforcement
- Parental involvement
- Professional collaboration
we can make significant strides in developing effective social skills. Each of these strategies plays a vital role in creating an environment where children can thrive both socially and emotionally.
Throughout this discussion, we must highlight the importance of timely interventions and the collaborative efforts of families and professionals. Early diagnosis paves the way for tailored social skills training, while structured playgroups provide safe spaces where children can practice and refine their interactions. Visual aids and social stories serve as essential tools for enhancing understanding, while emotional recognition training empowers children to navigate complex social situations. Positive reinforcement encourages the repetition of desirable behaviors, and active parental involvement fosters a nurturing atmosphere for growth.
Ultimately, we cannot overstate the significance of these strategies. They not only improve social skills but also enhance the overall quality of life for children with autism and their families. By embracing these approaches and fostering a supportive community, we can make a meaningful difference in the lives of those on the autism spectrum. Let us continue to advocate for resources, share our experiences, and collaborate with professionals to ensure that every child has the opportunity to develop essential social skills and thrive in their interactions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ASD Media's mission?
ASD Media is committed to advancing the implementation of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy by providing resources and support for parents and professionals in the developmental disabilities sector, fostering a supportive community for sharing experiences and improving outcomes for children.
How can I access resources from ASD Media?
By subscribing to the ASD Media newsletter, individuals can gain access to the latest news and unlimited digital resources aimed at empowering parents and professionals in unlocking the potential of children with autism and ADHD.
Why is early intervention important in autism treatment?
Early intervention with ABA therapy can lead to significant improvements in communication and cognitive skills, especially for toddlers starting therapy around age two. However, fewer than half of youth referred for ABA therapy maintain treatment for the recommended 24 months, highlighting the need for ongoing community support.
What is the prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in the U.S.?
Autism spectrum disorder affects approximately 1 in 36 youngsters in the U.S., emphasizing the critical importance of initiatives like those offered by ASD Media.
What role do structured playgroups play in social skills development for children with autism?
Organized playgroups provide a safe and supportive environment for children to cultivate essential social skills through structured activities, leading to improvements in social interaction, language development, and overall emotional well-being.
What are the benefits of participating in integrated playgroups?
Research shows that participation in integrated playgroups can lead to significant improvements in social skills, with studies indicating that two out of three children in these settings achieve notable language development and experience lower anxiety and increased self-esteem.
How can parents and professionals tailor playgroups for children with autism?
Parents and professionals can customize playgroups to focus on specific social goals related to social skills, ensuring that each child has the opportunity to enhance their social abilities in an enjoyable and engaging manner.
What are some key skills children learn in organized playgroups?
Children learn critical social skills such as sharing, turn-taking, effective communication, interpreting facial expressions, body language, and tone of voice, which are essential for successful social interactions.
What impact does early diagnosis have on children with autism?
Timely identification of developmental disorders allows for customized strategies that address interpersonal challenges, leading to enhanced social communication skills and better long-term outcomes for children diagnosed early.




