Overview
The article "9 Strategies for Effective Autism Behavior Support" aims to provide practical approaches for supporting individuals with autism through various strategies. It highlights the significance of tailored interventions, such as:
- Positive Behavior Support
- Functional Behavior Assessments
- Applied Behavior Analysis
These methods are backed by research showcasing their effectiveness in enhancing social skills, communication, and overall development in children with autism.
As a parent, understanding these strategies can feel overwhelming, but you are not alone. Each intervention is designed to cater to the unique needs of your child, fostering an environment where they can thrive. Imagine the joy of seeing your child develop meaningful connections and communication skills—this is the goal of these approaches.
Research has shown that when these strategies are implemented thoughtfully, they can lead to remarkable improvements in a child's life. Consider reaching out to professionals who can guide you through the process, ensuring that the support you provide is both effective and nurturing. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of children with autism.
Introduction
In a world where understanding autism and providing effective support is more crucial than ever, a wealth of resources and strategies has emerged to empower families and professionals alike. The transformative power of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) and the collaborative efforts of interdisciplinary teams illustrate how the landscape of autism support is rich with innovative approaches tailored to individual needs. This article delves into various evidence-based techniques, including:
- Positive Behavior Support
- Functional Behavior Assessments
- Natural Environment Teaching
Each of these methods aims to foster meaningful engagement and development for children with autism.
As we explore these techniques, we not only highlight the challenges faced by families but also present promising solutions that pave the way for improved outcomes and greater understanding within our communities. Together, we can create a supportive environment where every child has the opportunity to thrive.
About ASD Media: Comprehensive Resources for Autism Behavior Support
At ASD Media, we are deeply committed to advancing the implementation of ABA therapy by providing a comprehensive array of resources and insights specifically designed for parents and professionals. Our extensive offerings include informative articles, practical toolkits, and interactive community forums that promote knowledge sharing and support. This inclusive environment empowers individuals to effectively navigate the complexities of autism behavior support for those on the spectrum while addressing critical disparities in access to care—an essential need given the rising demand for these services.
Recent statistics highlight the challenges many face in obtaining sufficient treatment. For instance, a study released by the NCBI revealed that only 15% of insured youth referred for ABA-based behavioral health treatment received 80% or more of the suggested hours. This underscores the urgent need for advocacy in insurance reform and increased public funding to improve access to therapy services—a cause that ASD Media actively supports through community engagement initiatives.
Moreover, case studies illustrate the tangible benefits of ABA therapy, particularly in enhancing social skills among youths with developmental disorders. One case study, for example, demonstrated that youngsters who participated in ABA therapy showed significant improvements in their ability to interact positively with peers. This highlights the profound impact that effective autism behavior support can have on their lives.
By fostering a supportive community, ASD Media not only enhances the implementation of ABA therapy but also plays a pivotal role in empowering families and professionals to unlock the potential of children with autism and ADHD. Additionally, we provide a wealth of resources, including webinars, guides, and forums, to further assist families in accessing the support they need.
We invite you to join us in this journey, sharing your experiences and insights as we work together to make a difference.
Positive Behavior Support: Techniques to Encourage Desired Behaviors
Positive conduct support (PBS) is all about nurturing a positive environment for our children. It involves proactive strategies that encourage desired behaviors while gently guiding away from challenging ones. Think of it as setting clear expectations, providing consistent feedback, and using reinforcement techniques to foster growth. Research shows that these approaches can lead to remarkable improvements in behavior. For example, a study compared 474 students from four primary schools using PBS with 83 students from two control schools, clearly demonstrating the effectiveness of these methods.
However, it's important to recognize that not every child responds to the universal model of School-Wide Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (SWPBIS). Some may need additional support tailored to their unique needs. Celebrating even the smallest achievements can be incredibly uplifting; it encourages our young ones to engage in positive actions and helps them understand what is expected of them. As Robert Horner, a leading expert in this field, emphasizes, effective PBS incorporates evidence-based practices that prioritize prevention and teaching social expectations, creating a supportive environment for children with developmental disorders and those needing autism behavior support.
The benefits of these behavioral strategies extend far beyond immediate improvements. They can positively influence students' academic, social, and daily living skills. A longitudinal study titled 'Behavioral Outcomes Over Time' followed students for four years, revealing that those in schools implementing SWPBIS experienced lasting gains in social-emotional development. This underscores the long-term advantages of such interventions. Together, we can foster a nurturing atmosphere that empowers our children to thrive.
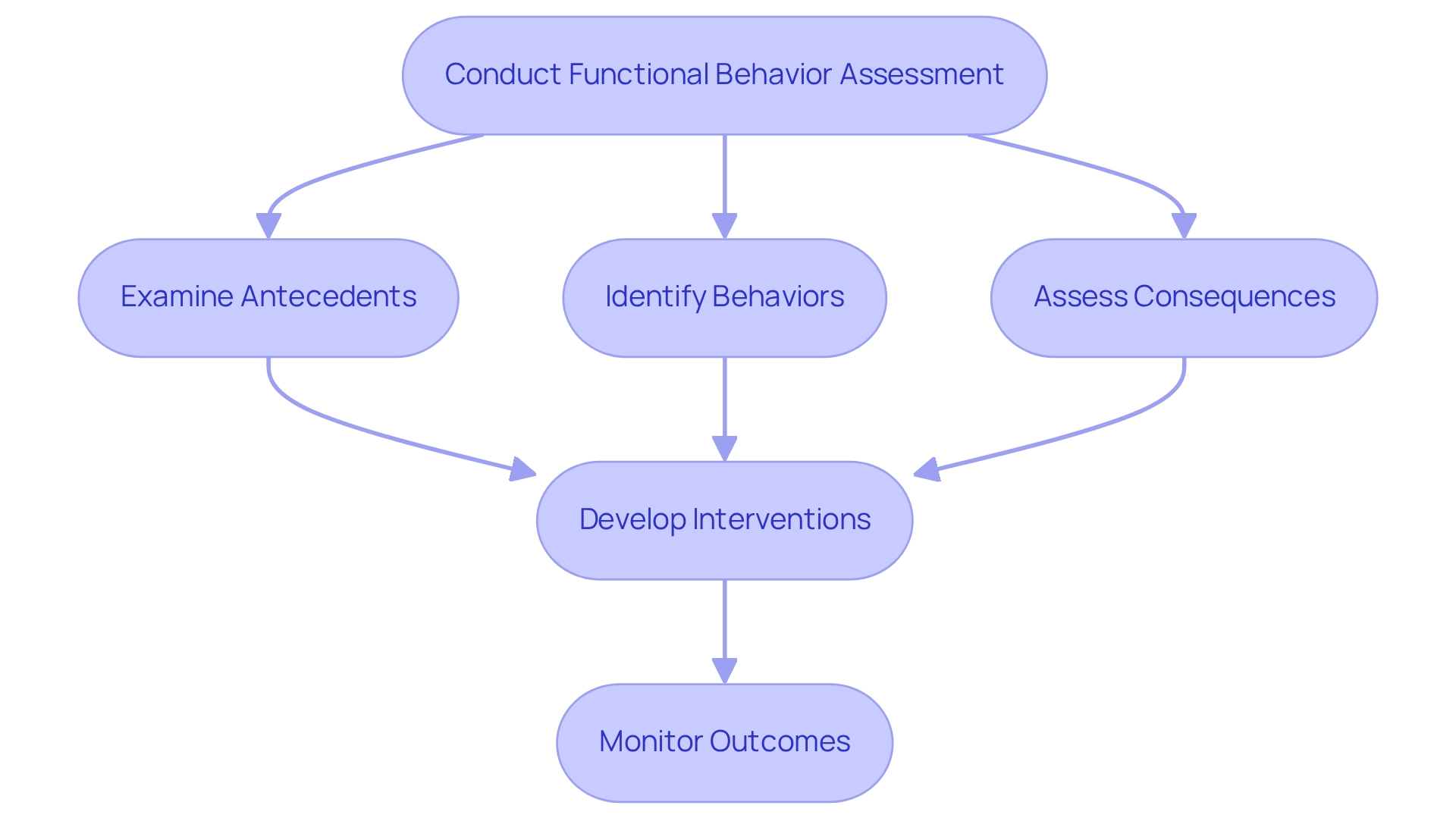
Functional Behavior Assessment: Understanding Behavior Functions for Effective Interventions
Functional behavior assessments (FBAs) play a vital role in understanding the underlying reasons behind challenging behaviors in youth receiving autism behavior support. By carefully examining antecedents, behaviors, and consequences, practitioners can develop tailored interventions that meet individual needs. For instance, if a young person acts disruptively to seek attention, practitioners can implement strategies that reinforce positive behaviors, effectively redirecting the need for attention in a constructive manner.
Research indicates that a well-structured functional analysis often leads to a reduction in the severity of problematic behaviors compared to those observed outside of an analytic context. This underscores the value of FBAs in enhancing treatment outcomes. Experts emphasize the necessity of conducting functional assessments promptly, particularly in cases of severe challenges, to leverage existing knowledge for immediate improvements in the lives of those affected. As Bowman et al. (1997) pointed out, effective analysis methods are essential for grasping and addressing the complexities of behaviors in children with pervasive developmental disorders.
Successful interventions following FBAs depend on a clear understanding of behavior functions. By identifying the factors that contribute to challenging behaviors, professionals can design approaches that not only address the issues but also foster the individual's overall development. For example, interventions that focus on teaching alternative skills can significantly reduce the frequency of challenging behaviors, creating a more positive environment for learning and social interaction. Data shows that challenging behaviors are common among individuals with autism, highlighting the urgent need for effective FBAs and autism behavior support.
In conclusion, functional assessment tools are indispensable in providing autism behavior support. They empower practitioners to comprehend behavior functions and implement effective interventions, leading to meaningful improvements in the lives of young individuals. If you’re a parent or caregiver, consider reaching out to professionals who can guide you through this process, ensuring your loved one receives the support they deserve.
Applied Behavior Analysis: Tailoring Interventions for Individual Needs
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a compassionate, data-driven approach that focuses on modifying behavior through thoughtful reinforcement strategies. Each intervention is carefully tailored to meet the unique strengths and challenges of individuals, ensuring that therapeutic goals are not only relevant but also achievable. For example, when a child faces difficulties in social interactions, a successful ABA program might include organized playdates designed to foster social skills in a nurturing environment.
As highlighted by the apricoott team, "ABA therapy can be utilized to instruct individuals with developmental disorders on how to engage with their peers and family members," showcasing the benefits of personalized interventions. Research indicates that ABA therapy significantly enhances language, social, adaptive, and educational skills in individuals with developmental disorders, underscoring its effectiveness.
Moreover, case studies reveal that families often invest an average of six hours each week in non-drug treatments, reflecting the dedication required from caregivers for effective autism management. Yet, caregivers frequently face logistical hurdles, such as waiting lists and insurance coverage challenges, which can hinder access to these essential services.
Experts suggest that customizing ABA interventions not only meets individual needs but also encourages meaningful engagement and progress in various life skills. By focusing on personalized strategies, ABA practitioners can make a positive impact on behaviors, helping young individuals navigate their social worlds.
Parents and professionals are warmly encouraged to explore tailored ABA programs that recognize individual strengths and challenges. This approach promises a more effective pathway to autism support, ensuring that every child receives the understanding and guidance they deserve.
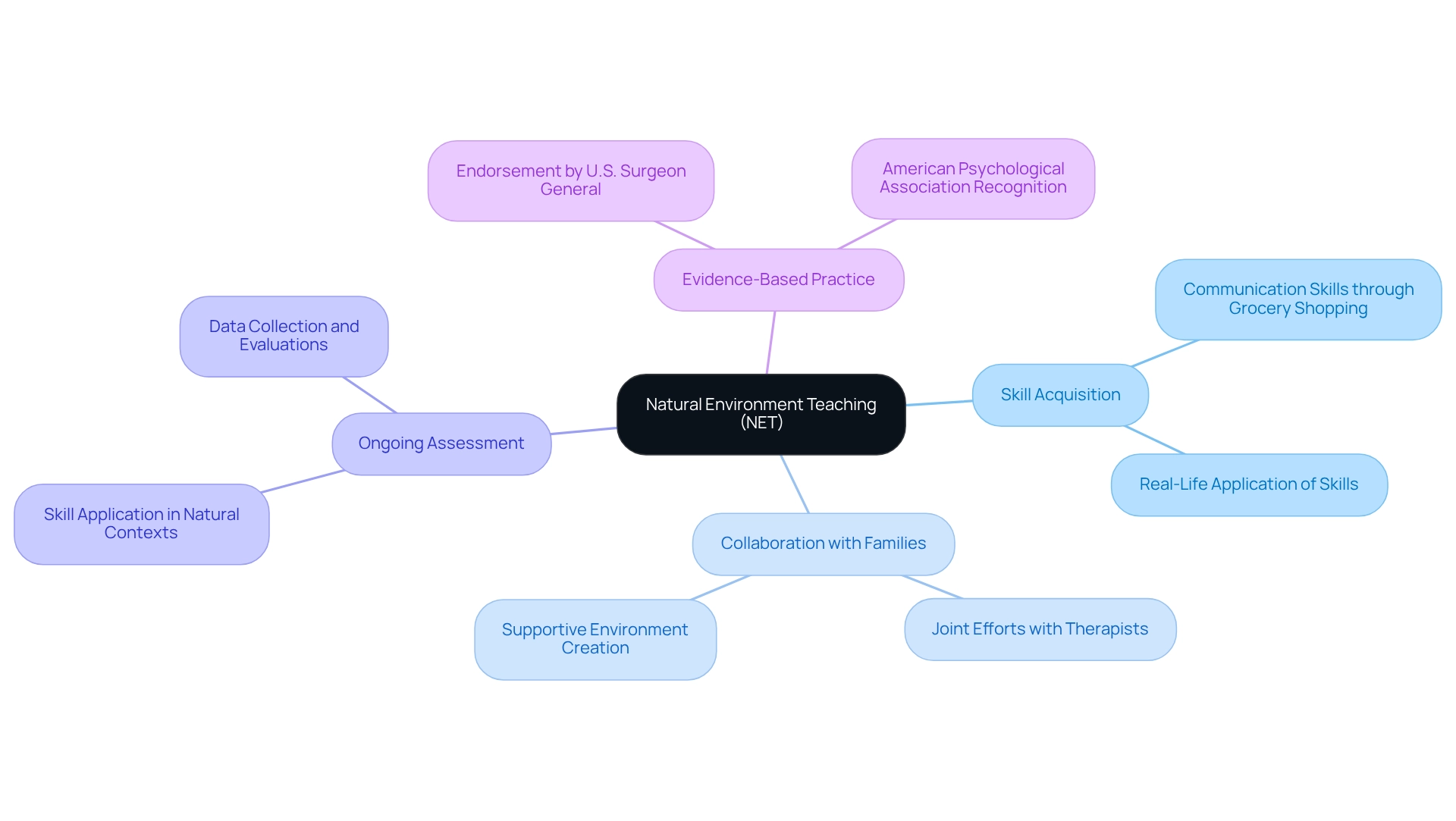
Natural Environment Teaching: Learning in Everyday Contexts
Natural Environment Teaching (NET) highlights the importance of learning within a young person's everyday surroundings, such as home and community settings. This nurturing approach fosters the development of skills through play and daily activities, making the learning experience both relevant and impactful. For instance, when a young person learns to ask for items while grocery shopping, they not only enhance their communication skills but also find opportunities to apply these skills in real-life situations.
Research indicates that NET significantly boosts skill acquisition, with young individuals demonstrating an increased ability to utilize learned skills across various natural environments. The effectiveness of this approach is further validated by its recognition as an evidence-based best practice for autism behavior support in relation to autism spectrum disorder (ASD) by the U.S. Surgeon General and the American Psychological Association.
Moreover, it is crucial to engage in ongoing conversations about therapeutic methods that honor neurodiversity, highlighting the necessity of tailoring strategies to meet individual needs. The collaborative efforts between skilled therapists and dedicated families create a supportive environment where young individuals can thrive and reach their fullest potential. As emphasized, "The joint endeavors between skilled therapists and committed families foster an atmosphere where young individuals can flourish and achieve their utmost potential."
Successful implementation of NET strategies reveals that when children learn during everyday activities, they are more likely to retain and generalize these skills, paving the way for greater independence and community integration. Progress in NET is assessed by observing how individuals apply their skills in diverse natural contexts, with data collection and regular evaluations ensuring ongoing improvements. Furthermore, insights from the case study titled 'The Future of ABA in Autism Behavior Support' underscore the ongoing evolution of ABA therapy as vital in providing autism behavior support for skill development in individuals with developmental disorders. Regular evaluations ensure that the strategies employed are effective and tailored to each individual's unique needs.
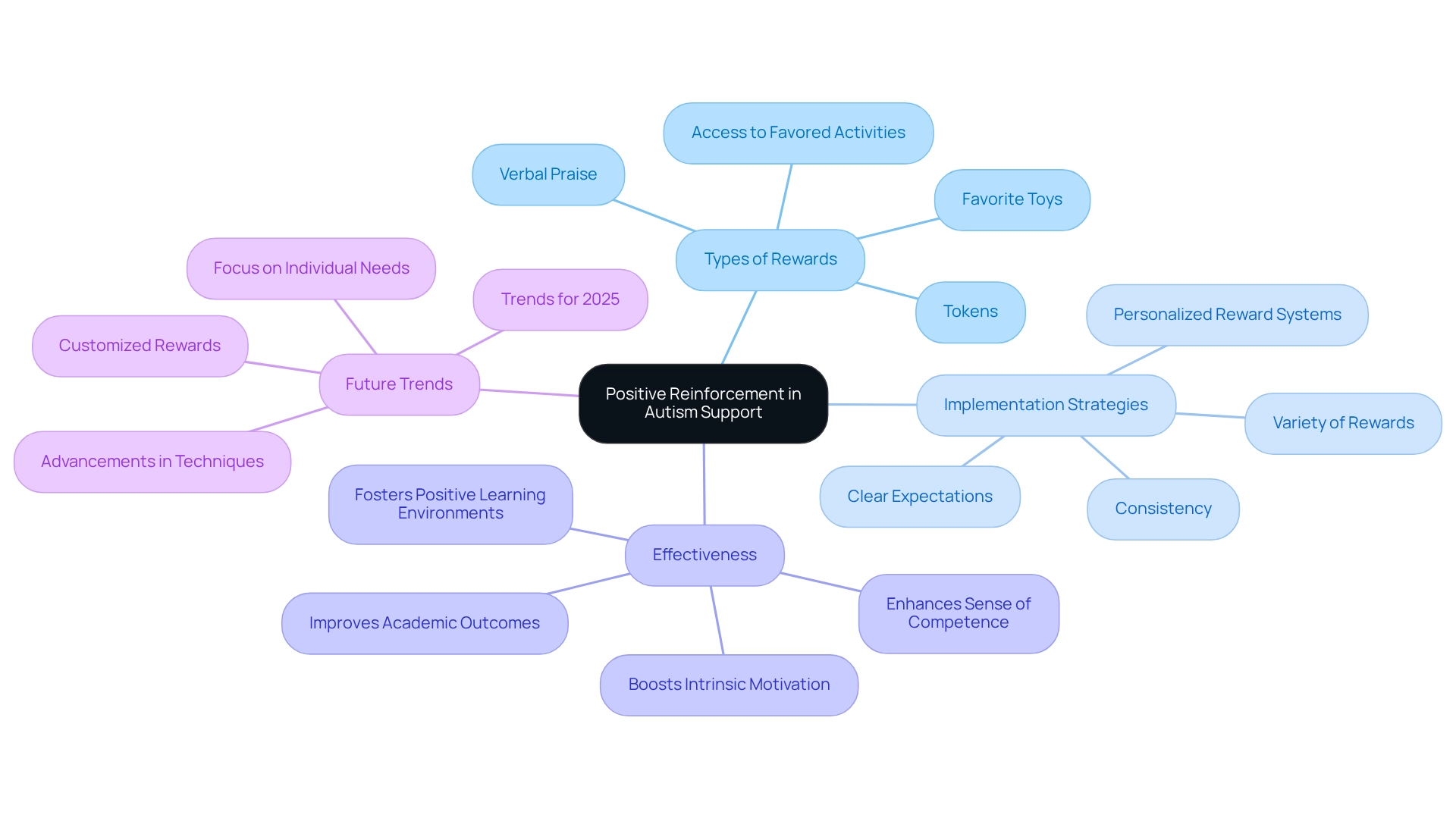
Positive Reinforcement: Encouraging Desired Behaviors Through Rewards
Positive reinforcement serves as a vital approach in autism behavior support to nurture desired actions among youth with autism. This compassionate method involves offering rewards or incentives—like verbal praise, tokens, or access to favored activities—to encourage young individuals. For example, a child who completes their homework might earn extra playtime, effectively reinforcing the practice of finishing tasks. Research indicates that positive reinforcement can significantly boost young people's intrinsic motivation and sense of competence, thereby increasing the likelihood of their future engagement in preferred activities.
To implement effective reinforcement strategies, consistency is key. By establishing clear expectations and consistently applying rewards, children can better understand the connection between their actions and the outcomes. Current strategies for positive reinforcement in autism behavior support emphasize the importance of using a variety of rewards tailored to individual preferences, such as favorite toys or activities, which can greatly enhance motivation. Statistics reveal that positive reinforcement is particularly effective in behavior management, with studies underscoring its role in fostering positive learning environments. For instance, educators trained in positive reinforcement techniques, like those from Eastern Washington University's M.Ed. program, have reported improved academic, emotional, and social outcomes for their students. This program equips educators with the skills necessary to create supportive learning environments, ultimately leaving a lasting impact on the development of young individuals. By nurturing motivation and curiosity, these educators empower young learners to explore their interests and face challenges with confidence.
As we look ahead to 2025, the focus on positive reinforcement methods continues to evolve, with experts advocating for personalized reward systems that cater to the unique needs of each child. Current trends highlight the importance of customizing rewards to align with personal preferences, which not only encourages desired behaviors but also fosters a nurturing environment where young individuals can truly flourish.
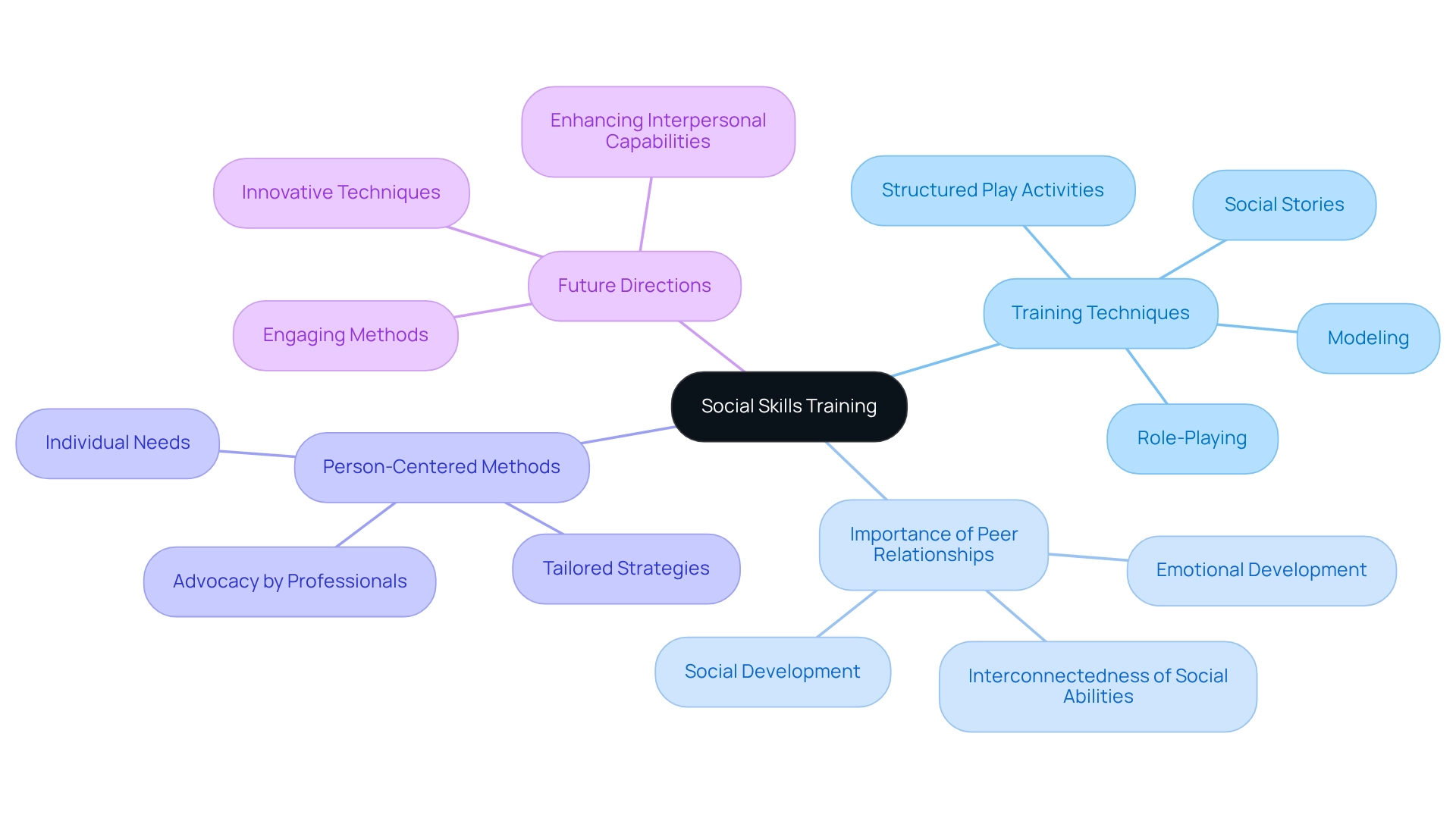
Social Skills Training: Building Interpersonal Skills for Better Interactions
Training in social interaction is essential for guiding young individuals on how to engage appropriately with their peers. Effective techniques, such as role-playing, modeling, and using social stories, can illustrate various social scenarios. For example, structured play activities that emphasize greetings and turn-taking significantly enhance children's understanding of social cues, fostering better interactions with their peers.
Research shows that peer relationships are vital for emotional and social development. A notable study reveals significant correlations among different centrality metrics in peer relationships, such as degree and closeness centrality (p<0.01). Specifically, a significant change in closeness centrality for female students was noted (t=-4.413, p=0.001). This indicates that advancements in one area can lead to improvements in others, highlighting the interconnected nature of social abilities.
Moreover, 91% of specialists in the field advocate for person-centered methods as the most effective way to promote social abilities. Successful programs often incorporate techniques tailored to individual needs, underscoring the importance of personalized strategies in achieving positive outcomes. As Dr. Brenda Smith Myles aptly states, 'Autism is a part of the youth, not something that occurred to them or that can be detached from their identity.' This emphasizes the necessity of understanding autism in relation to social abilities training.
Looking ahead to 2025, innovative social abilities training techniques continue to evolve, focusing on enhancing interpersonal capabilities through engaging methods. Instructors highlight the effectiveness of role-playing in imparting these abilities, as it allows youngsters to engage in real-life interactions within a secure setting. By utilizing these strategies, parents and professionals can significantly improve the social competence of youth with autism behavior support, paving the way for more fulfilling peer relationships. Successful social skills training programs often integrate these techniques, providing a comprehensive approach to developing interpersonal skills.
Parent Training Programs: Empowering Parents with Effective Strategies
Parent training programs play a vital role in equipping caregivers with essential strategies to promote their children's development. These programs typically cover a range of topics, including:
- Behavior management
- Communication techniques
- Effective reinforcement strategies
By providing parents with valuable information and practical skills, these initiatives significantly enhance the overall effectiveness of autism behavior support interventions, leading to improved outcomes for individuals with autism.
Research shows that parent training can lead to sustainable solutions, especially in low-resource settings where tailored approaches are crucial. For instance, successful outcomes from these programs have been documented, demonstrating that parents who engage in training are better equipped to manage challenging behaviors and foster their children's social skills development.
Statistics reveal that the overall effectiveness of parent training programs is impressive, with studies indicating a significant positive impact on both child behavior and family dynamics. Specifically, the between-group heterogeneity for active control studies was χ (1) = 0.067, p = 0.80, highlighting the robust effect of these programs. By prioritizing education and enhancing family capabilities, these programs not only tackle immediate behavioral issues but also nurture long-term growth and resilience within families.
As we look towards 2025, the emphasis on parent training programs continues to grow, reflecting a broader recognition of their importance in supporting individuals with developmental disorders. Experts advocate for these programs as foundational interventions, stressing their role in empowering parents to implement practical and effective autism behavior support techniques. The case study titled "Recommendations for Policy Makers in LMICs" underscores the urgent need for culturally relevant and economically viable services in low-resource settings, reinforcing the sustainability of parent training programs.
Through collaborative efforts and shared experiences, parent training programs create a nurturing environment that benefits both children and their families. As Naoufel Gaddour poignantly stated, "To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/", highlighting the significance of empowering parents through effective strategies. It is also essential to recognize potential biases in the studies included in the meta-analysis, which adds layers of complexity to the research landscape surrounding parent training programs.
Visual Supports: Enhancing Communication and Understanding
Visual aids, including picture schedules, social narratives, and graphic organizers, are valuable tools for enhancing communication and providing autism behavior support to young individuals on the spectrum. These resources clarify expectations and provide a structured framework, helping to foster a better understanding of routines. For instance, using a visual timetable allows children to anticipate daily transitions, significantly reducing anxiety and promoting greater independence.
Recent statistics reveal that employing visual schedules can lead to long-term improvements in both independence and confidence among young individuals with developmental disorders. Moreover, expert opinions emphasize the effectiveness of picture schedules and social stories in providing autism behavior support. As Strive ABA Consultants note, 'Contact us today for assistance and resources related to developmental support to help your young one excel in their daily activities and beyond.' This highlights the importance of utilizing these visual supports.
As the prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder continues to rise, with 1 in 31 youngsters recognized by age 8, the implications for parents and educators become increasingly vital. This growing occurrence underscores the necessity for effective communication strategies, making visual aids essential in promoting understanding and autism behavior support for youth experiencing this condition.
Collaboration with Professionals: Partnering for Comprehensive Support
Teamwork among specialists—therapists, educators, and healthcare providers—is vital for delivering comprehensive support to youth with developmental disorders. With 1 in 36 children in the United States diagnosed with these disorders, the effectiveness of interventions is significantly enhanced through regular communication and shared goals among team members.
When teachers actively participate in behavior plans, it creates consistency between home and school environments, which is essential for achieving positive outcomes. Statistics indicate that interdisciplinary approaches can lead to improved behavioral and developmental results, underscoring the importance of collaboration in interventions for individuals with developmental disorders.
As one parent insightfully remarked, "I don’t always have all the answers, but I do have Google," reflecting the challenges parents encounter in navigating support systems. By partnering with educators and therapists, parents can establish a strong support network that not only tackles immediate issues but also fosters long-term growth and success for their children.
Moreover, sharing the unique perspectives of autistic voices can cultivate understanding and teamwork, dismantling stereotypes and promoting empathy, respect, and acceptance for individuals on the autism spectrum. By utilizing quotes and insights, parents can fortify their support network and encourage societal acceptance.
Conclusion
The conversation around autism support underscores the essential role of various evidence-based techniques, including:
- Positive Behavior Support
- Functional Behavior Assessments
- Applied Behavior Analysis
Each of these approaches offers unique strategies tailored to meet the individual needs of children with autism, creating an environment that nurtures growth and development. By implementing customized interventions, caregivers and professionals can greatly improve behavioral outcomes and encourage meaningful engagement in daily activities.
Furthermore, the significance of collaboration among professionals is paramount. A cohesive approach that includes therapists, educators, and families guarantees consistency and continuity in support, ultimately leading to better outcomes for children. As the landscape of autism support evolves, initiatives such as parent training programs and the use of visual supports are vital in equipping families with the necessary tools and knowledge to navigate the intricacies of autism.
In the end, fostering a supportive community where every child can flourish demands persistent advocacy, education, and collaboration. By embracing the diverse strategies available and nurturing partnerships among all stakeholders, we can strive toward a future where children with autism are empowered to realize their full potential and lead fulfilling lives. The collective effort to comprehend and support individuals on the autism spectrum is crucial in cultivating a more inclusive and compassionate world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the mission of ASD Media?
ASD Media is committed to advancing the implementation of ABA therapy by providing resources and insights for parents and professionals, promoting knowledge sharing and support to navigate autism behavior support complexities.
What types of resources does ASD Media offer?
ASD Media offers informative articles, practical toolkits, interactive community forums, webinars, and guides to assist families and professionals in accessing the support they need.
What does recent research say about access to ABA therapy?
Research indicates that only 15% of insured youth referred for ABA-based behavioral health treatment received 80% or more of the recommended hours, highlighting the need for advocacy in insurance reform and increased public funding for therapy services.
How does ASD Media support advocacy for better access to therapy?
ASD Media actively supports advocacy efforts through community engagement initiatives aimed at improving access to therapy services.
What are the benefits of ABA therapy for youths with developmental disorders?
Case studies have shown that youths participating in ABA therapy experience significant improvements in social skills, enhancing their ability to interact positively with peers.
What is Positive Behavior Support (PBS)?
PBS involves proactive strategies that encourage desired behaviors while guiding away from challenging ones, using clear expectations and reinforcement techniques to foster growth.
How effective is School-Wide Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (SWPBIS)?
Research demonstrates that schools implementing SWPBIS have seen lasting gains in social-emotional development among students, proving the long-term advantages of these interventions.
What role do Functional Behavior Assessments (FBAs) play in autism behavior support?
FBAs help understand the underlying reasons for challenging behaviors, allowing practitioners to develop tailored interventions that meet individual needs.
How can interventions following FBAs improve behavior outcomes?
By identifying the factors contributing to challenging behaviors, professionals can design interventions that teach alternative skills, significantly reducing the frequency of those behaviors.
Why are functional assessment tools important in autism behavior support?
Functional assessment tools empower practitioners to understand behavior functions and implement effective interventions, leading to meaningful improvements in the lives of young individuals.




