Overview
The article presents four compassionate strategies aimed at enhancing the eating habits of children with autism. It emphasizes the importance of:
- Establishing routines
- Gradually introducing new foods
- Using positive reinforcement
- Modifying food textures
Research supports these approaches, highlighting that structured methods not only alleviate mealtime anxiety but also promote a diverse and nutritious diet. This is particularly vital for addressing the common hurdles faced by children on the spectrum.
As parents, you may often feel overwhelmed by the challenges of mealtime. Establishing a consistent routine can bring a sense of security for your child, making them more receptive to trying new foods. Gradual exposure helps ease their anxiety, allowing them to explore different tastes and textures at their own pace. Positive reinforcement can transform mealtime into a rewarding experience, encouraging your child to embrace healthier options.
Moreover, modifying food textures can make a significant difference. Some children may have sensory sensitivities that make certain textures unpalatable. By experimenting with various preparations, you can discover what works best for your child.
These strategies not only aim to improve nutrition but also foster a more enjoyable mealtime atmosphere. We encourage you to share your experiences and insights, as your journey can inspire others facing similar challenges. Together, we can create a supportive community that empowers families to navigate these important aspects of their children's health.
Introduction
Children with autism often navigate a complex landscape of eating habits, shaped by sensory sensitivities and strict food preferences. With nearly 90% of these children exhibiting selective eating behaviors, caregivers are faced with the significant challenge of fostering a healthier relationship with food while addressing unique dietary needs. This article unveils effective strategies designed to enhance eating habits in children with autism, offering practical insights that promise to transform mealtime from a source of anxiety into an opportunity for growth and enjoyment.
How can parents turn the tide on these eating challenges and help their children embrace a more varied and nutritious diet? Together, let’s explore these possibilities.
Explore the Connection Between Autism and Eating Behaviors
Children with developmental differences often display unique eating habits shaped by sensory sensitivities, strict meal preferences, and anxiety surrounding unfamiliar foods. Research reveals that approximately 97.67% of children with autism exhibit autism eating habits, often gravitating towards specific textures and colors, which can lead to a limited diet. For example, many autistic individuals tend to prefer meals with consistent textures, such as crunchy or smooth purees, while steering clear of those that may overwhelm their sensory processing abilities. In fact, 77.4% of children with ASD demonstrate autism eating habits that cause them to turn away from foods based on their texture or consistency.
Understanding these connections is essential for caregivers who wish to create a supportive mealtime environment that respects these preferences while encouraging healthier choices. Recognizing that a child may shy away from crunchy items due to sensory overload can help parents gradually introduce softer alternatives. Strategies such as sensory interventions and graduated exposure therapy have shown promise in enhancing food acceptance. This approach not only reduces stress during mealtimes but also enriches the overall dining experience, making it more enjoyable for both the child and the family.
As Geneviève Petitpierre noted, 'Unusual autism eating habits are prevalent among individuals on the spectrum,' highlighting the need for tailored approaches. By embracing methods that consider sensory sensitivities, caregivers can effectively navigate the challenges of feeding difficulties associated with the condition.
Identify Common Eating Challenges in Children with Autism
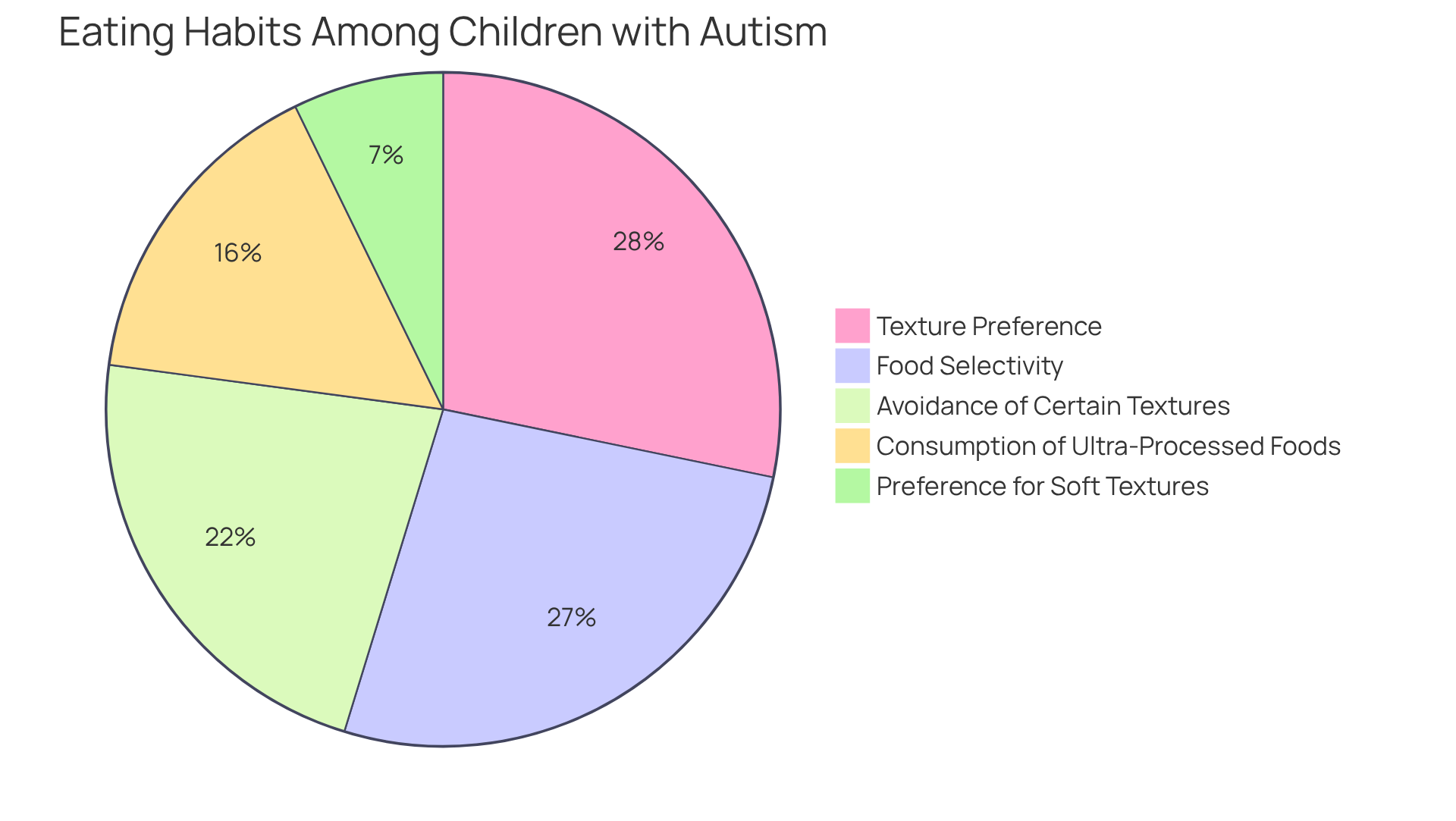
Children with autism often face significant eating challenges, which are commonly referred to as autism eating habits, including selective eating, aversions to certain foods, and sensitivities to textures. It's concerning to note that research shows about 89% of children on the spectrum have autism eating habits that include limited diets, frequently rejecting entire food categories, particularly fruits and vegetables. This can lead to serious nutritional deficiencies, as many children might prefer processed, calorie-dense foods over healthier options. Such deficiencies can result in health issues, underscoring the importance of addressing these dietary challenges for their overall health and development. Additionally, mealtime can become a source of anxiety, with children displaying distress when confronted with unfamiliar foods, often due to sensory sensitivities that affect their eating experiences.
To effectively address these challenges, parents can play a vital role by closely monitoring their child's autism eating habits, paying attention to patterns of refusal or preference. Keeping a dietary journal can be particularly beneficial, as it helps track which foods are accepted or rejected, providing valuable insights for future meal planning. This practice can uncover specific likes and dislikes, allowing for more personalized meal strategies.
- Gradual exposure to new foods, combined with positive reinforcement, can encourage a more varied diet and alleviate anxiety surrounding mealtimes.
- Understanding these common dietary obstacles is crucial for fostering healthier nutritional practices that consider autism eating habits in children with developmental disorders.
- By sharing experiences and seeking support, parents can navigate these challenges together, creating a more positive mealtime environment.
Implement Effective Strategies to Enhance Eating Habits
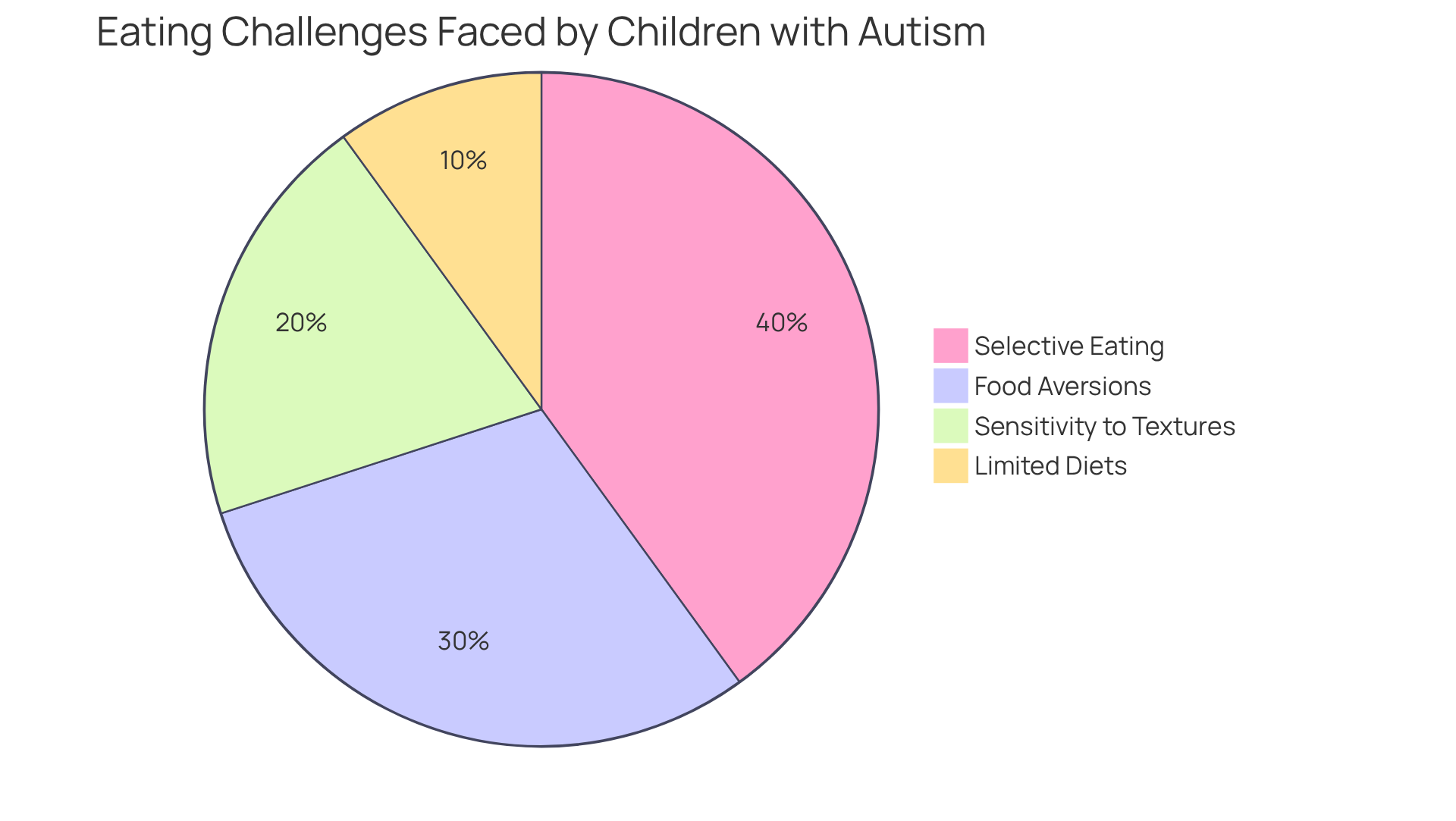
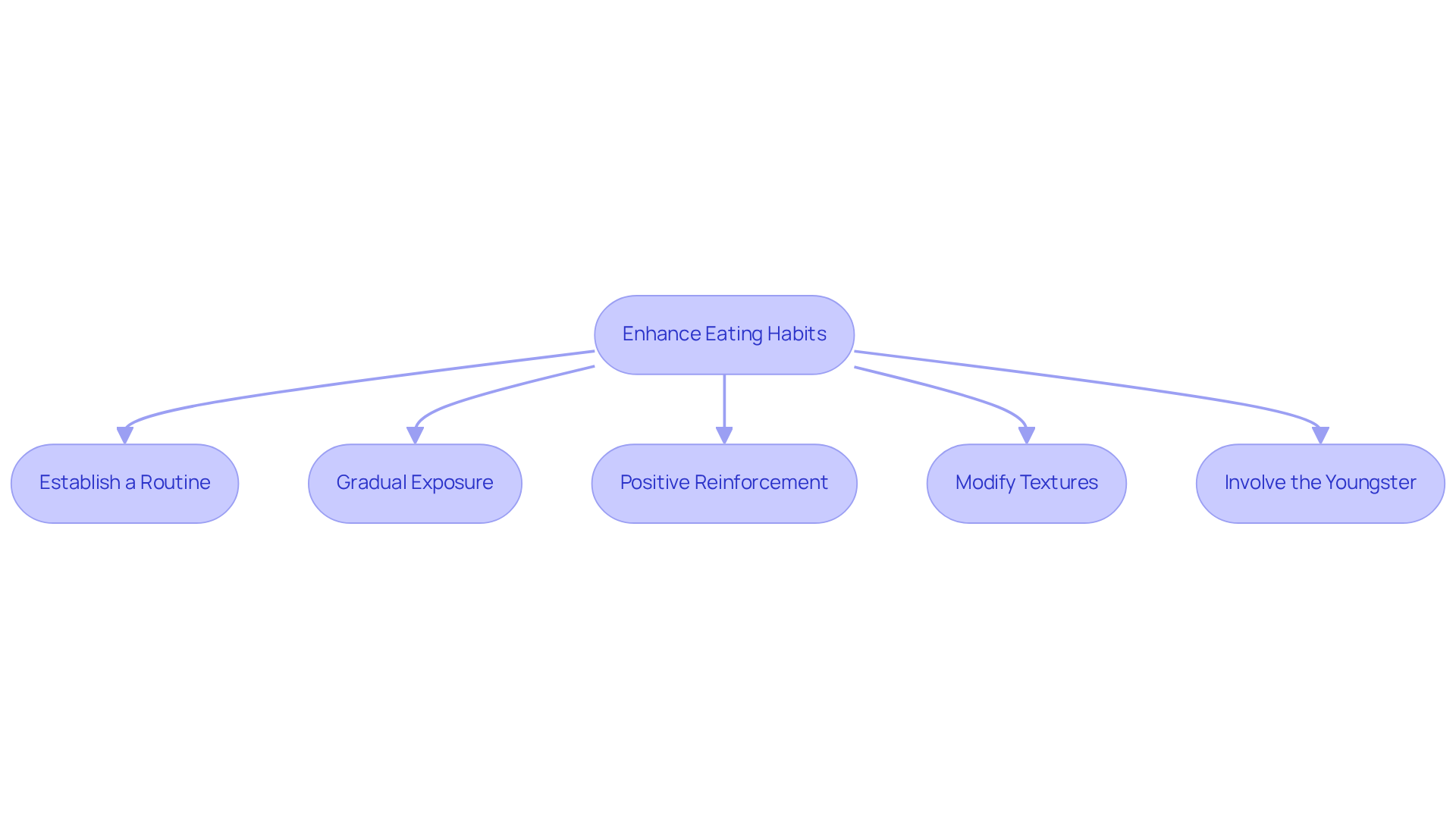
To enhance the eating habits of children with autism, consider the following nurturing strategies:
- Establish a Routine: Create a consistent mealtime schedule to provide predictability, significantly reducing anxiety around eating. It's important to note that studies show individuals with autism eating habits are five times more likely to encounter considerable feeding difficulties. Establishing a routine can be vital for comfort during meals.
- Gradual Exposure: Introduce new items slowly, starting with small, manageable portions. For example, begin with a pea-sized portion and gradually increase it as your child becomes more comfortable. Research indicates that gradual exposure can effectively decrease anxiety and reluctance toward new foods, allowing children to broaden their diets over time. Cheri Fraker highlights meal chaining as a beneficial method, relying on a child's innate preferences and successful dining experiences.
- Positive Reinforcement: Use praise or small rewards when your child tries new dishes. This approach encourages a positive association with eating. Experts note that positive reinforcement can inspire children to interact with meals more eagerly, cultivating a nurturing mealtime environment. One parent observed that their child's weight gain had a significant impact on their mental condition and meal acceptance, underscoring the importance of positive experiences during dining.
- Modify Textures: Experiment with various food textures to discover what your child prefers. For instance, pureeing vegetables may make them more appealing for children sensitive to texture. Understanding sensory preferences is essential, as many autistic individuals may have specific aversions related to autism eating habits that can be addressed through texture modification. Research has shown that accommodating sensory needs can improve treatment outcomes.
- Involve the Youngster: Allow your child to engage in meal planning and preparation, which can boost their interest in trying new foods. Involving children in the cooking process not only empowers them but also helps them feel a sense of control over their food choices. This sense of agency is crucial for developing healthy dietary habits. Collaborating with experts can further enhance this process, ensuring that the strategies are tailored to the individual's unique needs.
Seek Professional Guidance and Resources for Support
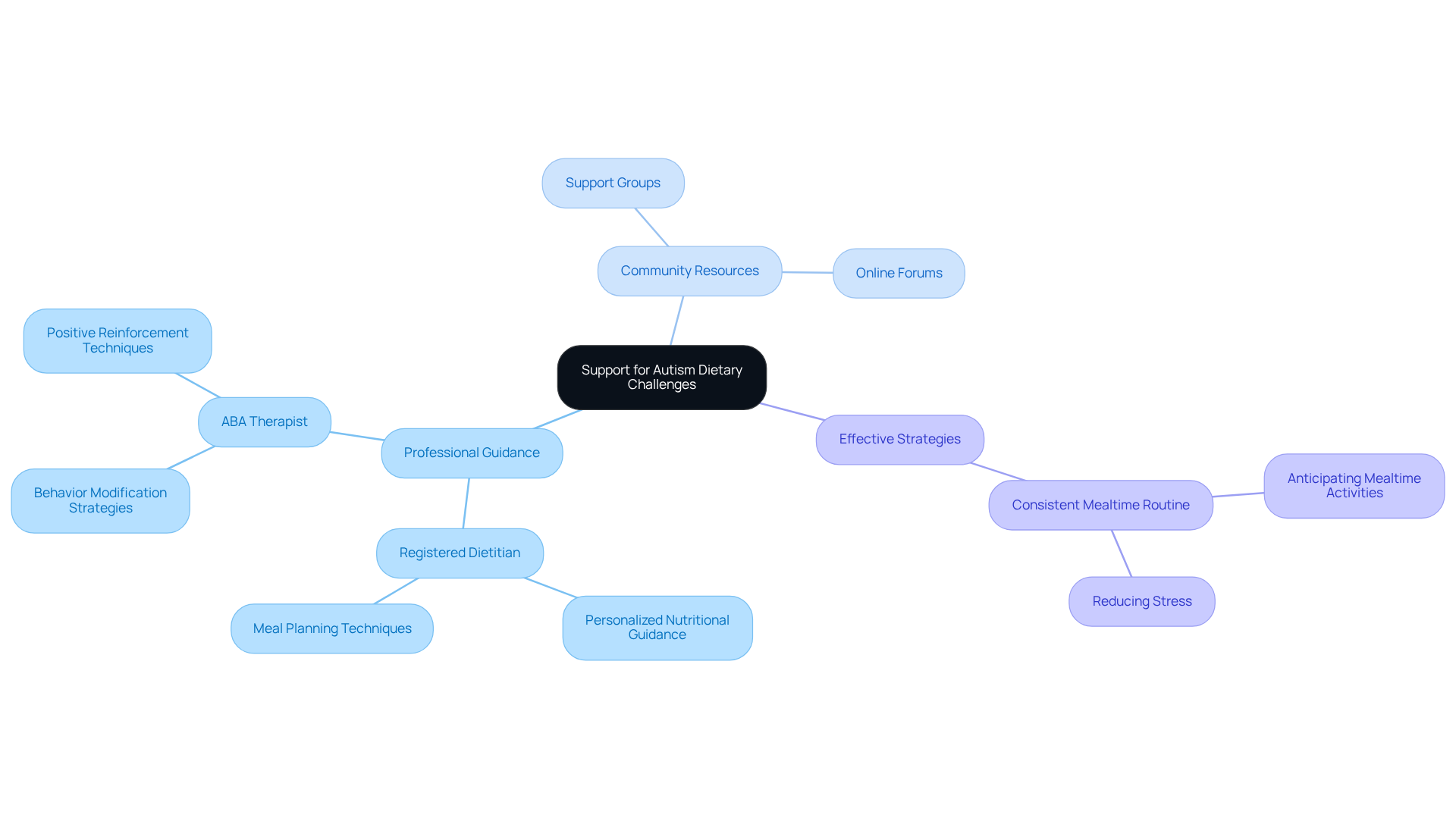
As parents, it’s essential to actively seek professional advice when navigating your child's dietary difficulties. Consulting with a registered dietitian is particularly important, as they can offer personalized nutritional guidance and meal planning techniques tailored to the unique needs and autism eating habits of autistic individuals. Did you know that around 70% of individuals with autism face some form of feeding challenge related to their autism eating habits? This statistic highlights the vital role registered dietitians play in addressing these issues. Many young individuals thrive with their expertise, benefiting from balanced diets that tackle specific nutritional deficiencies.
In addition to working with dietitians, collaborating with an ABA therapist can introduce effective behavior modification strategies. Techniques like positive reinforcement and gradual exposure to new foods can help foster healthier dietary habits. These professionals are skilled at identifying triggers and developing strategies that encourage positive mealtime experiences, making a significant difference for your child.
Beyond direct professional support, engaging with resources such as support groups and online forums can be incredibly beneficial. These platforms offer valuable insights and shared experiences from other families facing similar challenges, creating a nurturing community where understanding flourishes. By tapping into these resources, you can cultivate a supportive atmosphere that promotes healthy eating habits related to autism eating habits, ultimately enhancing your child’s relationship with food and encouraging overall well-being.
Establishing a consistent mealtime routine is another effective strategy for improving autism eating habits. It can help children with autism anticipate mealtime activities, which reduces stress and paves the way for a more positive eating experience. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; there are numerous avenues of support available to help you and your child thrive.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing the unique eating habits of children with autism is essential for their overall health and well-being. By recognizing sensory sensitivities and implementing tailored approaches, caregivers can significantly enhance mealtime experiences. This not only promotes healthier dietary choices but also nurtures a more positive relationship with food.
Key insights include:
- The importance of establishing routines.
- Gradually introducing new foods.
- Using positive reinforcement to ease anxiety around meals.
Seeking professional guidance is also crucial, as registered dietitians and therapists can offer invaluable support tailored to each child's needs. Engaging with community resources and sharing experiences with other parents can further enrich the journey toward better eating habits.
Ultimately, creating a supportive and understanding environment is vital for children with autism. By embracing these strategies, parents can empower their children to explore new foods and cultivate healthier eating patterns, paving the way for improved nutrition and overall quality of life. Taking proactive steps today can lead to lasting changes that benefit both children and their families in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions
What unique eating habits are commonly observed in children with autism?
Children with autism often display unique eating habits influenced by sensory sensitivities, strict meal preferences, and anxiety regarding unfamiliar foods. Many gravitate towards specific textures and colors, leading to a limited diet.
How prevalent are autism eating habits among children with autism?
Research indicates that approximately 97.67% of children with autism exhibit autism eating habits, with many preferring meals with consistent textures, such as crunchy or smooth purees.
What factors influence the food preferences of children with autism?
Factors influencing food preferences include sensory processing abilities, with 77.4% of children with ASD turning away from foods based on their texture or consistency.
Why is it important for caregivers to understand the eating habits of children with autism?
Understanding these eating habits is essential for caregivers to create a supportive mealtime environment that respects the child's preferences while encouraging healthier food choices.
What strategies can caregivers use to help children with autism accept a wider variety of foods?
Caregivers can use strategies such as sensory interventions and graduated exposure therapy to enhance food acceptance, reduce stress during mealtimes, and improve the overall dining experience.
How can caregivers approach the introduction of new foods to children who are sensitive to textures?
Caregivers can gradually introduce softer alternatives to crunchy items, recognizing that sensory overload may cause the child to shy away from certain foods.
What does Geneviève Petitpierre highlight about autism eating habits?
Geneviève Petitpierre notes that unusual eating habits are prevalent among individuals on the autism spectrum, emphasizing the need for tailored approaches to address these challenges.




