Overview
This article highlights four effective strategies for achieving success in social skills autism therapy, focusing on the critical role of:
- Early intervention
- Effective teaching techniques
- Collaboration among caregivers
- Ongoing progress monitoring
Early intervention is vital, as research shows that timely training can significantly enhance social skills in children with autism. Moreover, the collaborative efforts of parents, educators, and therapists are essential in maximizing the effectiveness of these interventions. Together, they create a nurturing environment that fosters better interpersonal outcomes for children. As you navigate this journey, remember that support is available, and these strategies can make a meaningful difference in your child's development.
Introduction
Nurturing social skills in children with autism is a journey that is both crucial and complex. This journey often determines their ability to connect with peers and navigate social environments. Early intervention through targeted social skills autism therapy offers a transformative opportunity, laying a solid foundation for effective communication and relationship-building.
But what strategies can truly ensure success in this endeavor? How can parents, educators, and therapists come together to overcome the unique challenges faced by each child? These are questions that many caregivers grapple with, seeking not just answers but also support and understanding.
As we explore these strategies, we invite you to reflect on your own experiences. What challenges have you encountered? Together, we can uncover insights that will not only benefit your child but also enrich your journey as a caregiver.
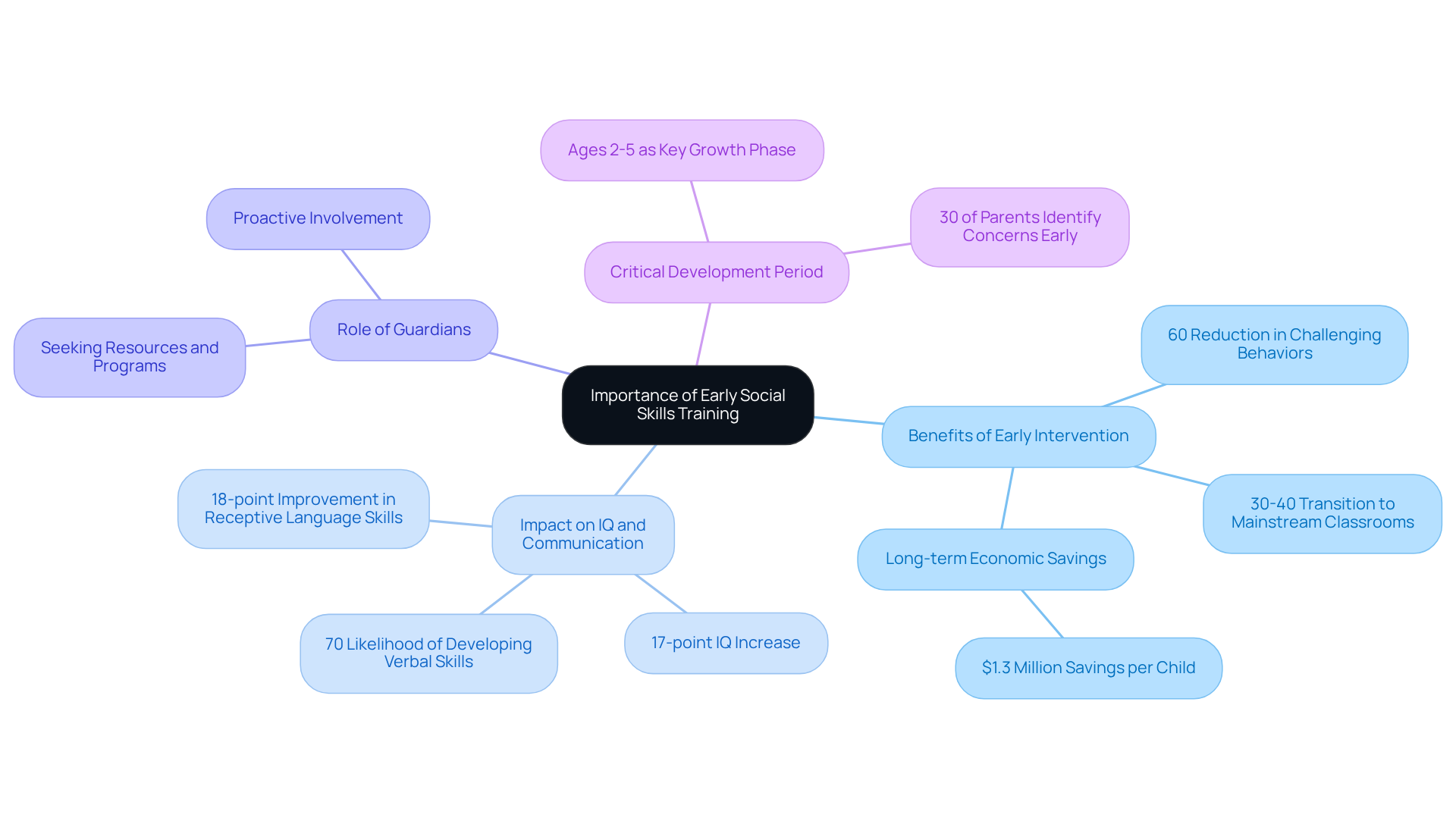
Recognize the Importance of Early Social Skills Training
Research consistently shows that early training through social skills autism therapy for children with autism can lead to remarkable improvements in their ability to connect with peers. Engaging in early intervention not only helps reduce the risk of maladaptive behaviors and social withdrawal but also lays the groundwork for effective communication and relationship-building, which can be supported through social skills autism therapy. Programs that incorporate play-based education and structured social interactions have proven to be particularly effective in enhancing social skills autism therapy.
For example, children who begin therapy before the age of three experience an average increase of 17 points in their IQ scores, which correlates with better interpersonal functioning. Additionally, children receiving ABA therapy are 70% more likely to develop verbal communication skills within two years, underscoring the importance of early intervention in fostering communication abilities that are closely tied to the development of interpersonal skills.
As caring guardians, it’s vital to actively seek out resources and programs that emphasize social skills autism therapy for early interpersonal skills training. This proactive approach significantly boosts the chances of successful integration as children grow. The most critical period for brain development and interpersonal growth occurs between the ages of 2 and 5, making early interventions during this time essential for long-term success.
Moreover, it’s noteworthy that 30% of parents of children with ASD identify concerns before their child reaches one year of age. This highlights the importance of early identification and proactive involvement in pursuing intervention resources. Together, we can create a nurturing environment that supports our children’s growth and development.
Implement Effective Strategies for Social Skills Development
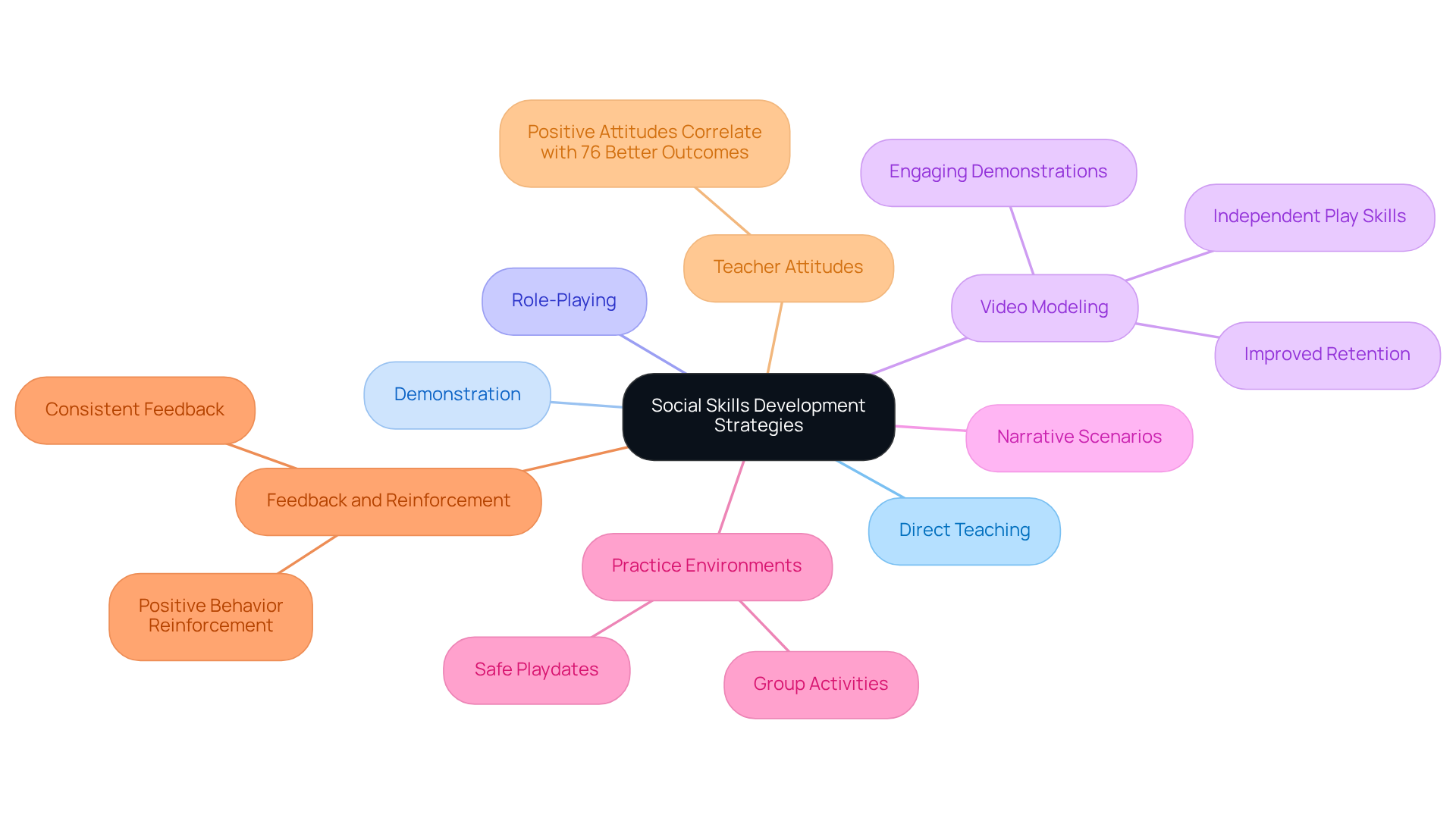
To effectively nurture social skills autism therapy in children with autism, techniques such as direct teaching, demonstration, and role-playing are essential. One particularly effective tool is video modeling, which allows children to visualize appropriate interactions through engaging video demonstrations. Research indicates that video modeling significantly enhances learning opportunities, with studies showing it to be more effective than traditional narratives in fostering independent play skills. For instance, a study involving a 6-year-old child with autism found that video modeling led to improved retention of interpersonal skills over time, with maintenance probes conducted 3, 5, and 7 weeks after the intervention revealing that the skills learned were sustained.
Incorporating narrative scenarios can also provide valuable context and clarity regarding various interpersonal situations, helping children understand expectations and appropriate responses. Creating safe environments for practice, such as playdates or group activities, allows children to apply these skills in real-life contexts. Consistent feedback and reinforcement of positive behaviors are crucial, as they help children internalize these skills and build confidence in their interactions. Importantly, positive teacher attitudes are linked to 76% better outcomes for autistic students, highlighting the significance of supportive environments. By embracing these strategies, parents and educators can greatly enhance the development of social skills autism therapy in individuals with autism, paving the way for more successful interactions and relationships. As Ignacio Estrada wisely stated, "If a young learner cannot grasp the way we instruct, perhaps we should educate in the manner they understand.
Foster Collaboration Among Parents, Educators, and Therapists
Encouraging cooperation among parents, teachers, and therapists is vital for enhancing the impact of training in interpersonal abilities for children with autism. Frequent meetings and transparent communication not only foster valuable insights into a young person's progress and challenges but also create a nurturing environment. For example, parents can share observations from home that guide therapists' approaches during sessions. Meanwhile, educators can provide feedback on how children are using their social skills in school settings. This collaborative approach ensures consistency across various environments, strengthens learning, and supports the application of skills.
Research shows that effective information exchange significantly boosts the success of ABA therapy. In fact, a one-point increase in parental self-efficacy correlates with improved interaction outcomes (B = 1.0, p = .024). Furthermore, children whose parents are actively involved in therapy demonstrate enhanced interaction and social abilities, underscoring the importance of a cohesive support network. By integrating diverse perspectives and maintaining organized communication protocols, all participants can work together to create a supportive atmosphere that nurtures the child's growth.
However, it is essential to recognize common challenges, such as the difficulties parents may encounter when communicating with schools, which can impede collaboration. As David S. Mandell wisely notes, "Effective communication between parents and teachers is essential for enhancing special education service delivery and the transfer of abilities." Let us strive to overcome these obstacles together, ensuring that every child receives the comprehensive support they deserve.

Monitor Progress and Adapt Strategies for Individual Needs
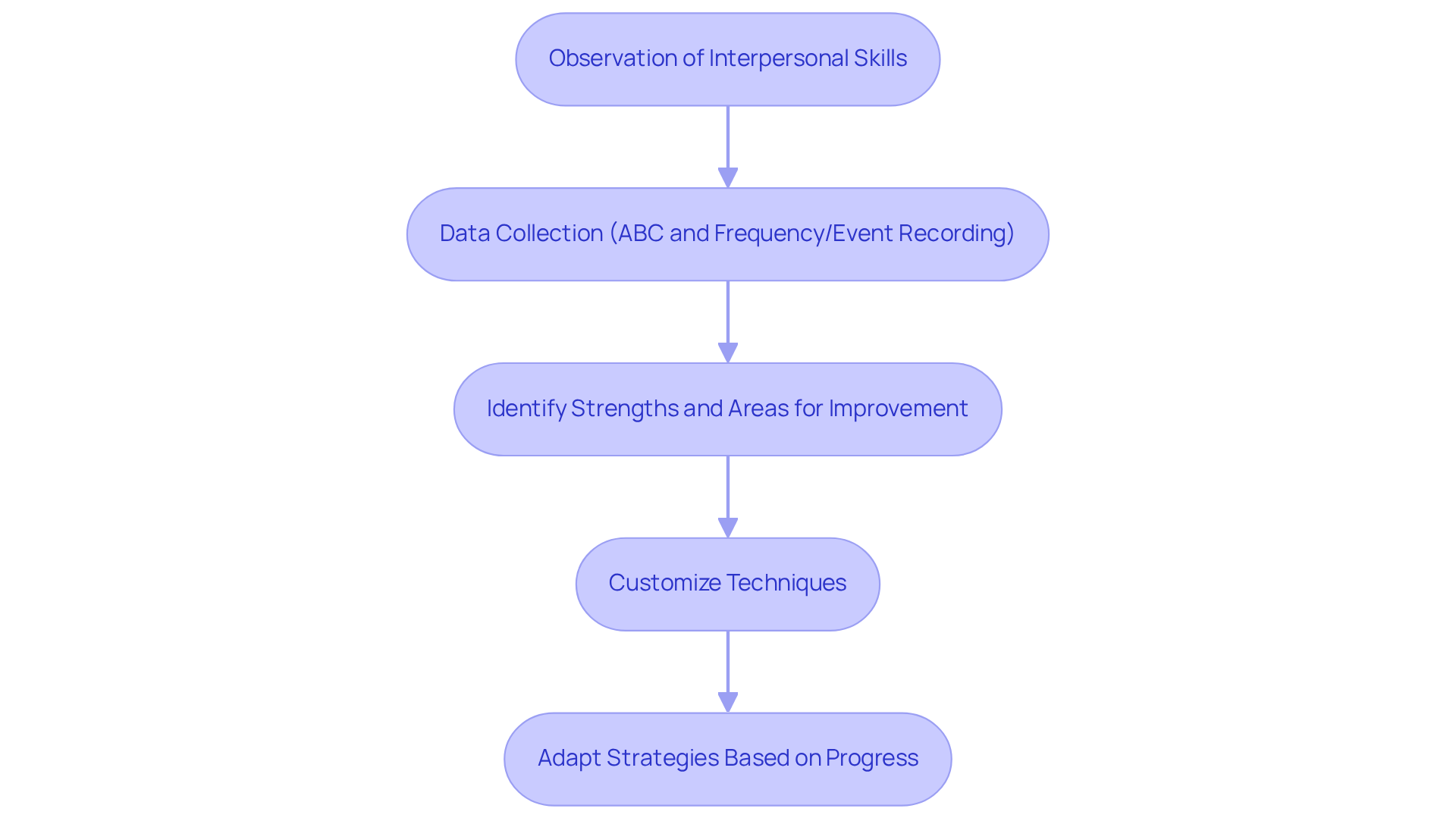
Consistently evaluating youngsters' interpersonal abilities through observations, checklists, and input from parents and educators is essential for tracking progress. This data not only helps identify strengths but also highlights areas needing improvement. For instance, if a young person excels at starting conversations but struggles to keep them going, we can customize techniques to enhance skills like turn-taking and active listening—skills that are crucial for successful interactions.
Individualized strategies not only tackle specific challenges but also foster a more effective learning environment, ensuring that each child's unique needs are met. Observational evaluations have shown considerable effectiveness in autism treatment, highlighting the role of social skills autism therapy, with research indicating that targeted interventions can lead to measurable improvements in interpersonal interactions.
For example, data collection methods such as ABC Data Collection and Frequency/Event Recording play a vital role in tracking progress and adapting strategies accordingly. By continuously adjusting approaches based on individual progress, practitioners can create a supportive framework that promotes growth and development in social skills autism therapy.
Have you noticed similar challenges with your child? Sharing experiences can help us learn from one another, creating a community of support. Let's continue to adapt our strategies to ensure every child thrives socially.
Conclusion
Nurturing social skills in children with autism is not only essential; it is a multifaceted journey that requires the dedication of parents, educators, and therapists alike. Early intervention plays a critical role, showcasing how targeted social skills autism therapy can significantly enhance a child's ability to connect with others and thrive in social environments. By implementing effective strategies, fostering collaboration, and continuously monitoring progress, caregivers can create a supportive atmosphere that promotes meaningful interactions.
Key insights reveal the importance of early training, which can lead to remarkable improvements in communication and relationship-building. Techniques such as video modeling and role-playing are effective tools for developing social skills. Collaboration among parents, educators, and therapists ensures a cohesive approach tailored to each child's unique needs. Furthermore, ongoing assessments of progress allow for strategies that directly address specific challenges, ultimately enhancing the child's social competence.
The journey of developing social skills in children with autism is a shared responsibility, yielding profound benefits. It is crucial for caregivers to actively engage in this process, seeking resources and fostering open communication among all parties involved. By embracing these strategies and committing to collaborative efforts, every child can be empowered to navigate social situations with confidence and success, paving the way for fulfilling relationships and a brighter future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is early social skills training important for children with autism?
Early social skills training is crucial as it leads to significant improvements in children's ability to connect with peers, reduces the risk of maladaptive behaviors and social withdrawal, and lays the groundwork for effective communication and relationship-building.
What are the benefits of engaging in early intervention for children with autism?
Engaging in early intervention can result in an average increase of 17 points in IQ scores for children who begin therapy before the age of three and increases the likelihood of developing verbal communication skills by 70% within two years.
What types of programs are effective for social skills autism therapy?
Programs that incorporate play-based education and structured social interactions have proven to be particularly effective in enhancing social skills autism therapy.
What age range is considered critical for brain development and interpersonal growth in children?
The critical period for brain development and interpersonal growth occurs between the ages of 2 and 5, making early interventions during this time essential for long-term success.
How common is it for parents to identify concerns about autism in their children?
Approximately 30% of parents of children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) identify concerns before their child reaches one year of age, highlighting the importance of early identification and proactive involvement.
What can guardians do to support their children’s social skills development?
Guardians should actively seek out resources and programs that emphasize social skills autism therapy for early interpersonal skills training, significantly boosting the chances of successful integration as children grow.




