Overview
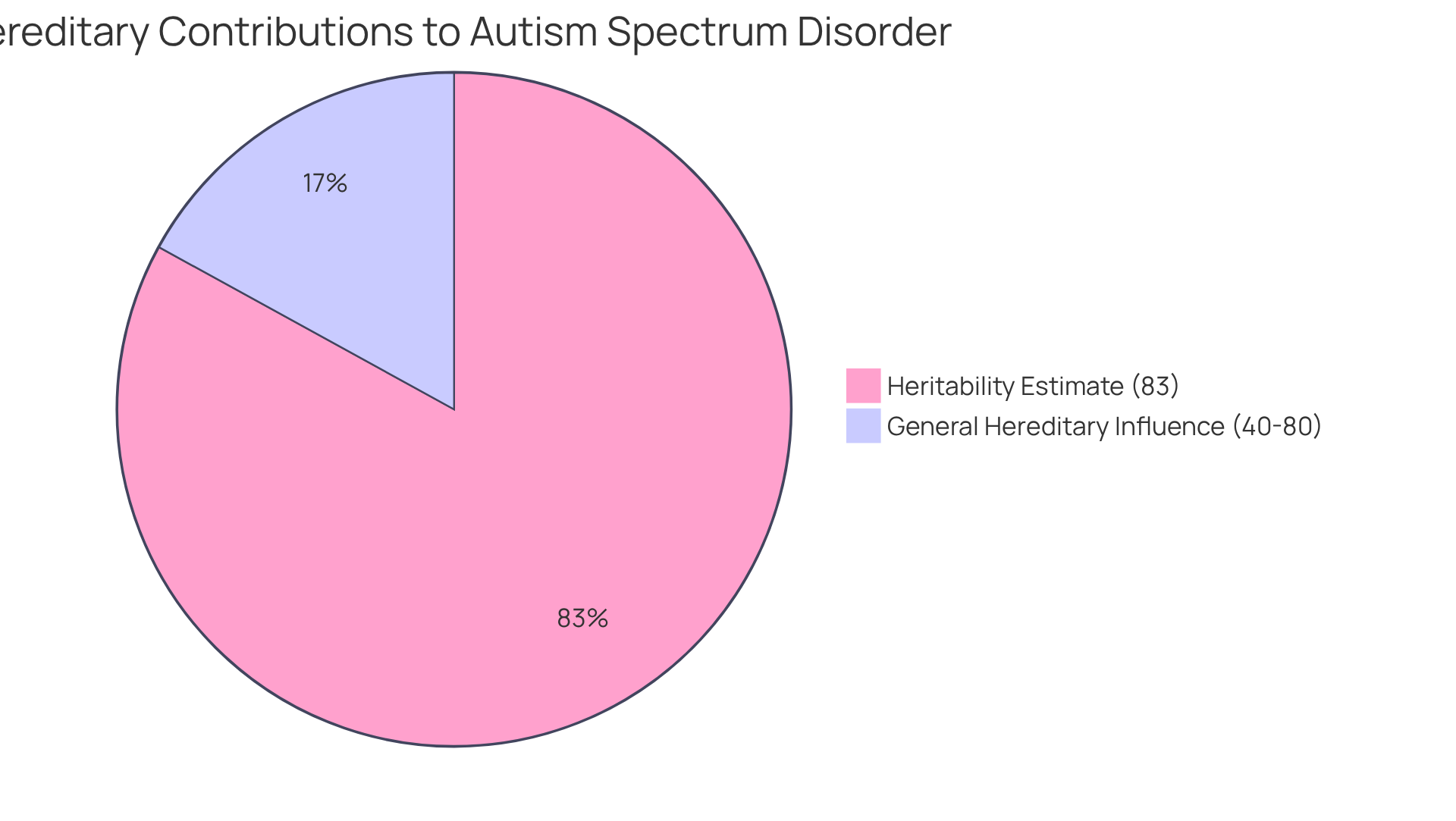
Have you ever wondered if autism could run in families? This article delves into the question of whether autism can be hereditary, revealing that genetic factors play a significant role in the risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). In fact, heritability estimates suggest that the likelihood can range from 40% to as high as 83%. This finding is particularly enlightening for parents seeking answers.
Twin studies further support this conclusion, showing that identical twins often share higher concordance rates for autism. Additionally, researchers have identified specific genes linked to increased susceptibility, highlighting a strong hereditary component in the development of autism. Understanding these genetic influences can be both reassuring and empowering for families navigating this journey.
If you’re a parent looking for support or resources, know that you are not alone. Many families face similar challenges, and there are communities and professionals ready to help. Consider reaching out to local support groups or online forums where you can share your experiences and connect with others who understand your concerns.
Introduction
Understanding the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often leads families to ponder a critical question: can autism be hereditary? Recent research suggests that genetic factors play a significant role in the risk of developing autism, with estimates ranging from 40% to an astonishing 83%. This highlights the importance of considering hereditary influences. In this article, we will explore the intricate interplay of genetic and environmental factors that shape autism, offering families essential insights into their health journeys. As we delve deeper, consider this: how do these hereditary elements interact with environmental influences, and what implications might this have for future generations?
Assess Genetic Factors in Autism Inheritance
Understanding the hereditary elements that influence whether autism can be hereditary is essential for families navigating this complex condition. Recent studies reveal that the question of whether autism can be hereditary is significant, as hereditary factors contribute to approximately 40-80% of the risk associated with ASD. Notably, twin studies consistently demonstrate a higher concordance rate for identical twins compared to fraternal twins, which suggests that the question of whether autism can be hereditary is significant. For example, an analysis of data from over 2 million children in Sweden estimated the heritability of ASD at an impressive 83%. This suggests that the question of whether autism can be hereditary indicates that inherited factors play a crucial role in the disorder's development.
As Jody W. Zylke, MD, noted, "In a reexamination of an earlier study on the familial likelihood of ASD, the heritability was assessed to be 83%, leading to the question of whether autism can be hereditary, indicating that hereditary factors may account for the majority of the threat for ASD." This highlights the importance of understanding the genetic landscape of autism, which is highly heterogeneous and intricate. Recent research has identified specific genes, such as PLEKHA8 and PRR25, linked to increased susceptibility to the condition, further emphasizing the complexity of hereditary influences.
Moreover, studies indicate a significant connection between language delay and hereditary risk, suggesting that language delay could be a fundamental aspect of developmental disorders. For families seeking deeper insights into autism-related genes and their inheritance patterns, resources like the SFARI Gene database can provide invaluable information. By fostering a foundational understanding of genetic influences, families can better comprehend the implications for their loved ones and seek the support they need as they explore if and how autism can be hereditary.
Evaluate Environmental Influences on Autism Development
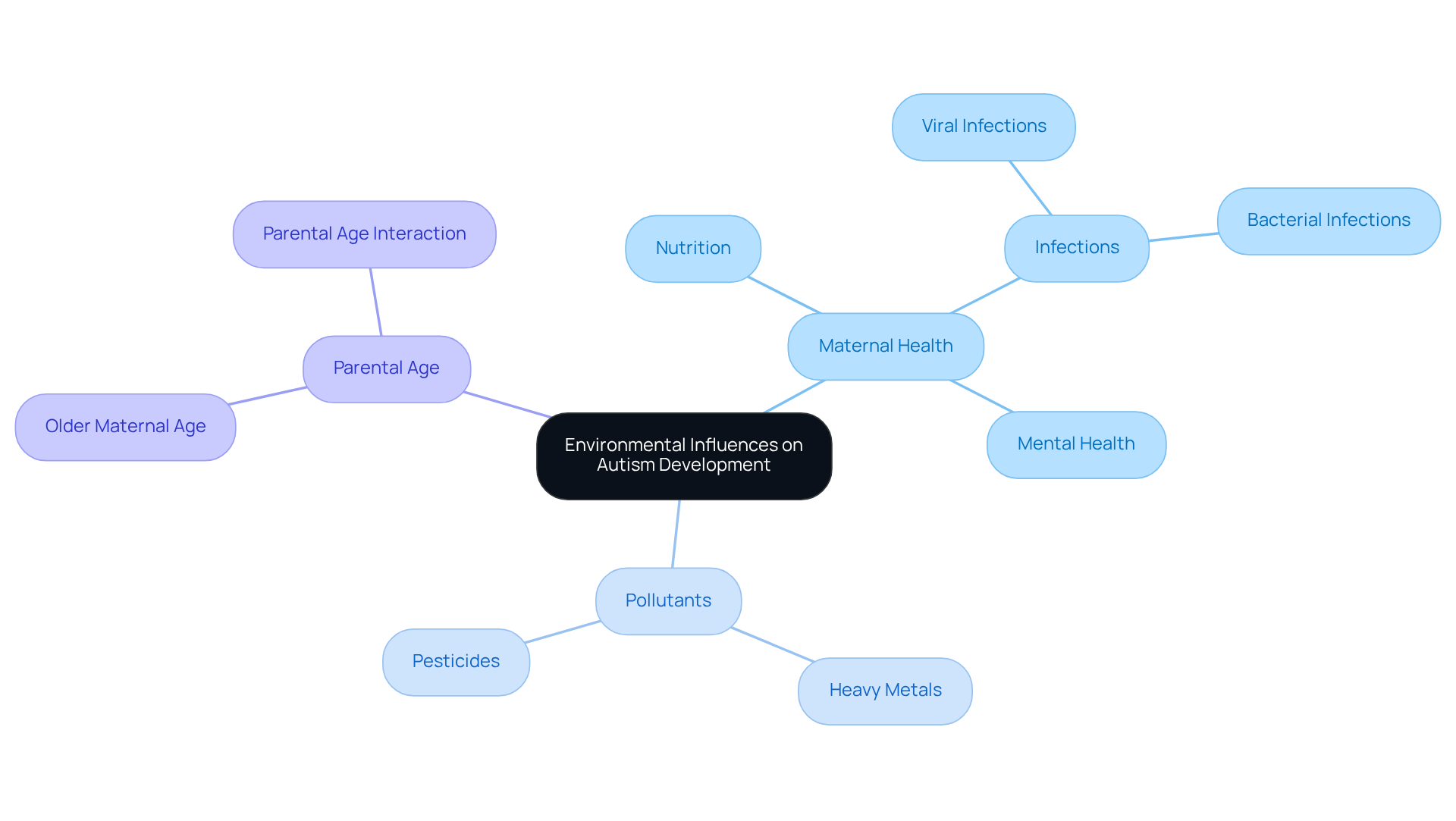
When considering the environmental impacts on the development of neurodevelopmental disorders, it’s important to think about factors that directly affect families. Maternal health during pregnancy, exposure to pollutants, and parental age are significant elements to reflect upon. Research shows that prenatal exposure to specific environmental toxins, like heavy metals and pesticides, can increase the risk of developmental disorders. Additionally, maternal factors such as nutrition, infections during pregnancy, and mental health play a crucial role in the likelihood of developing conditions like Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
As you explore this topic, consider how these environmental factors may interact with hereditary inclinations and whether autism can be hereditary. Understanding these connections can be a comforting step towards recognizing the complexities of developmental disorders. By examining the research that addresses these environmental influences, you can gain a more comprehensive perspective on the various elements that may contribute to these challenges faced by individuals and their families. Together, we can work towards supporting each other through this journey.
Gather Family Medical History and Genetic Information
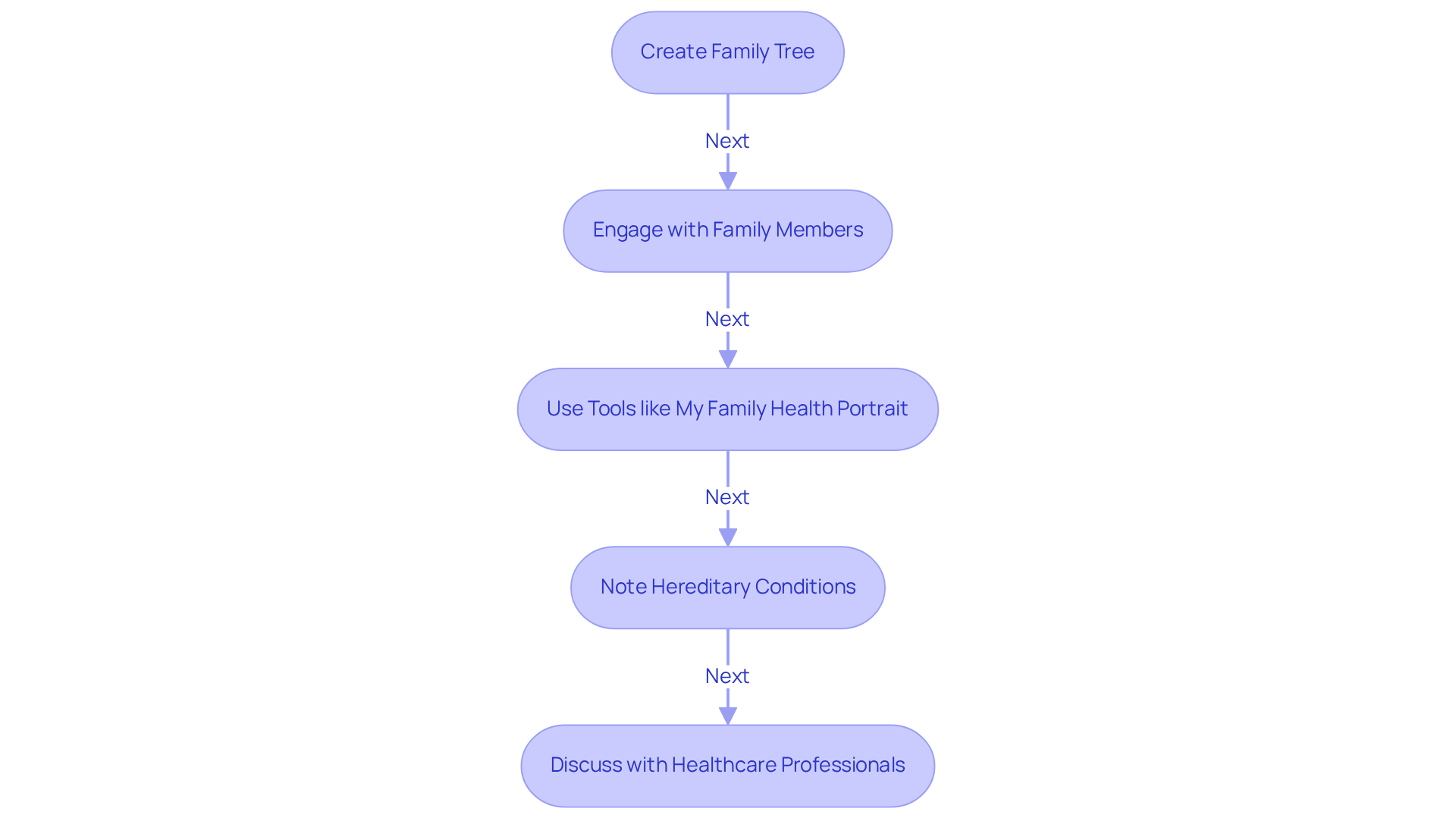
Gathering your family's medical history and hereditary information can feel overwhelming, but it’s a crucial step in understanding your loved ones' health. Start by creating a detailed family tree that highlights any health issues related to developmental disorders. This process not only helps you see the bigger picture but also opens up conversations with family members about any known instances of developmental disorders, ADHD, or similar conditions.
As you talk with your relatives, consider using tools like the US Surgeon General's 'My Family Health Portrait' to keep everything organized. This can make a significant difference in how you view the information. Additionally, don't forget to note any hereditary conditions within your family, as these insights can provide information on whether autism can be hereditary and shed light on potential challenges ahead.
Ultimately, this thorough family medical history will be invaluable when discussing risk factors with healthcare professionals. By taking these steps, you’re not just collecting data; you’re building a foundation of understanding that can guide your family's health journey. Remember, you’re not alone in this process—many parents are navigating similar paths, and sharing experiences can be incredibly supportive.
Consult Healthcare Professionals for Genetic Testing Options
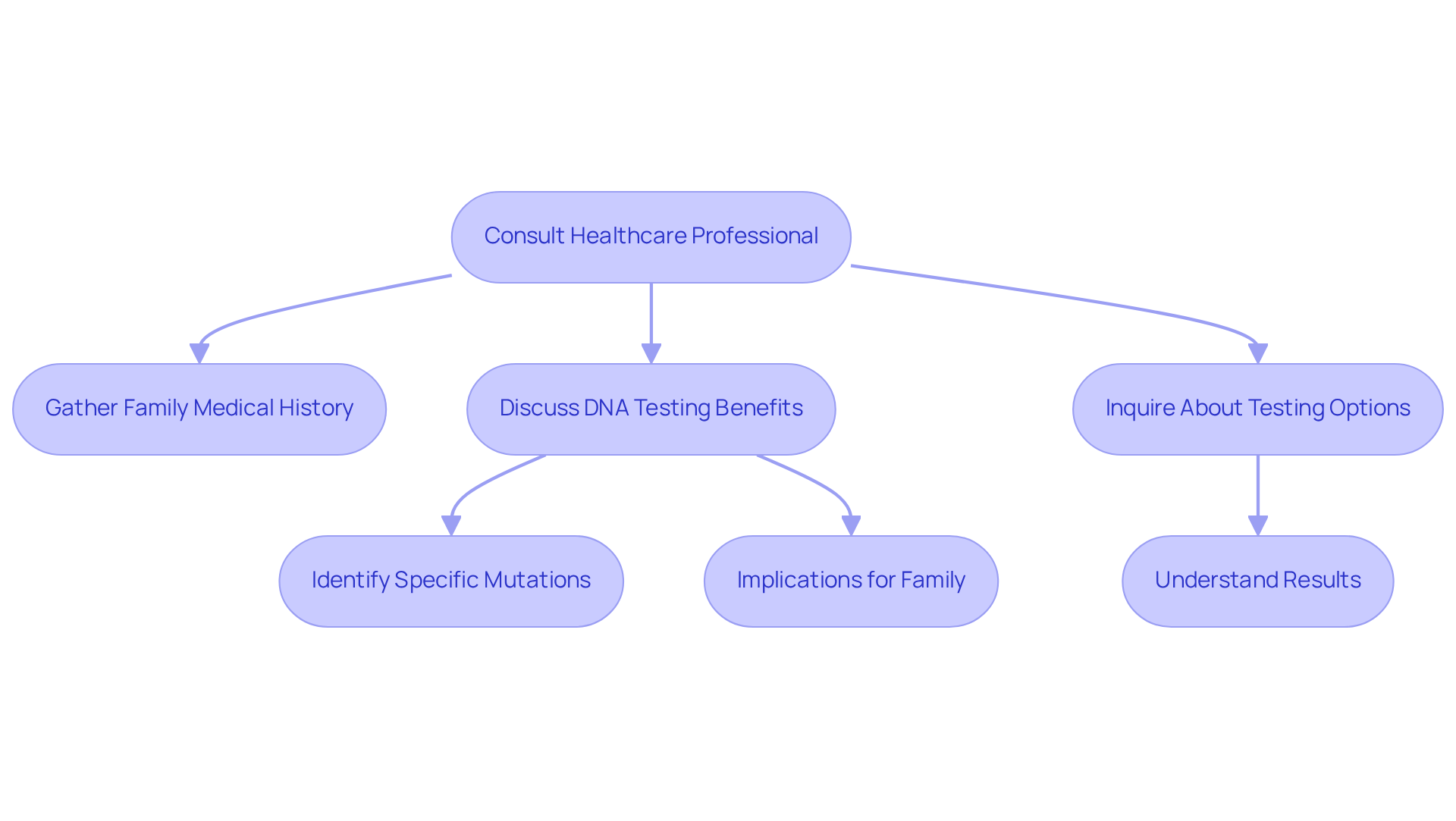
If you're looking to explore testing options for developmental disorders, consider starting with a meeting with a counselor or a specialist. To make the most of this consultation, gather your family medical history and any relevant information about your child's developmental milestones. During your appointment, discuss the potential benefits of DNA testing. For instance, it can help identify specific mutations linked to autism, which can guide tailored intervention strategies that meet your child's unique needs.
It's important to understand that Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) raises the question of can autism be hereditary, with estimates suggesting about 90% of cases may be influenced by genetics. Additionally, studies indicate that the question of whether can autism be hereditary is supported by evidence showing the heritability of ASD is around 50%, particularly noted in twin and familial studies. Don’t hesitate to inquire about the various tests available, such as chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) and whole exome sequencing (WES). Both tests have demonstrated significant diagnostic yields in recent research, providing valuable insights.
Moreover, DNA analysis can help identify family members who may be at risk of developing ASD, broadening the implications for your entire family. Understanding the results of these tests is crucial, as they can significantly influence your child's treatment and support options. However, it's also essential to be aware that DNA testing can sometimes yield inconclusive or unclear results, which can understandably be frustrating for families.
By taking this proactive approach, you empower yourself to make informed decisions about genetic testing and its role in understanding autism. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and seeking support is a vital step in advocating for your child's needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the hereditary nature of autism is not just a complex endeavor; it is a crucial journey for families navigating this condition. The evidence highlights that genetic factors significantly contribute to autism risk, with heritability estimates ranging from 40% to an impressive 83%. This underscores the importance of acknowledging both genetic predispositions and environmental influences when exploring whether autism can be hereditary.
Key insights reveal the intricate interplay between genetics and environmental factors, such as maternal health and exposure to toxins, which can further complicate the understanding of autism's origins. Gathering family medical history and consulting healthcare professionals for genetic testing can provide valuable information, empowering families to make informed decisions regarding their loved ones’ health.
Ultimately, recognizing the multifaceted nature of autism inheritance fosters a deeper understanding of the disorder and encourages proactive measures for families. By embracing both genetic and environmental insights, individuals can better navigate the complexities of autism, ensuring they are equipped to support their loved ones effectively. Engaging with healthcare providers and utilizing available resources paves the way for informed choices, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for those affected by autism.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of assessing genetic factors in autism inheritance?
Understanding hereditary elements is essential for families as hereditary factors contribute to approximately 40-80% of the risk associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
How much does heritability contribute to autism?
Recent studies estimate the heritability of ASD at around 83%, indicating that inherited factors play a crucial role in the disorder's development.
What do twin studies reveal about the inheritance of autism?
Twin studies show a higher concordance rate for identical twins compared to fraternal twins, suggesting that genetic factors significantly influence the likelihood of developing autism.
What specific genes have been linked to autism susceptibility?
Recent research has identified specific genes, such as PLEKHA8 and PRR25, that are associated with an increased risk of developing autism.
Is there a connection between language delay and hereditary risk?
Yes, studies indicate a significant connection between language delay and hereditary risk, suggesting that language delay may be a fundamental aspect of developmental disorders.
Where can families find more information about autism-related genes?
Families can access resources like the SFARI Gene database for deeper insights into autism-related genes and their inheritance patterns.
Why is understanding the genetic landscape of autism important for families?
It helps families comprehend the implications of genetic influences on autism, allowing them to seek appropriate support and resources for their loved ones.




