Overview
This article presents four essential steps for effectively communicating with non-verbal toddlers. It emphasizes the importance of:
- Understanding their non-verbal cues
- Implementing nurturing communication techniques
- Creating a supportive environment
- Utilizing helpful tools and resources
By recognizing and responding to a toddler's silent signals, parents can significantly enhance their child's emotional expression and overall development. This not only fosters a more engaging atmosphere but also nurtures the child's growth in a compassionate setting. Together, these strategies create a foundation for meaningful interactions that can transform the parent-child relationship.
Introduction
In a world where words often take center stage, the silent language of non-verbal communication holds immense power, especially for young children navigating their early developmental stages. Have you ever noticed how a smile or a frown can convey so much more than words? From the subtle nuances of facial expressions to the energetic gestures of tiny hands, these signals form the foundation of how toddlers express their needs and emotions. As research increasingly underscores the significance of these non-verbal cues, parents and caregivers are presented with a unique opportunity to enhance their interactions and foster meaningful connections.
This article delves into the essentials of understanding and implementing effective communication techniques. We will explore how to create supportive environments and utilize innovative tools that empower non-verbal toddlers to thrive in their social worlds. Together, let's embark on this journey of discovery, ensuring our little ones feel heard and understood every step of the way.
Understand Non-Verbal Communication Basics
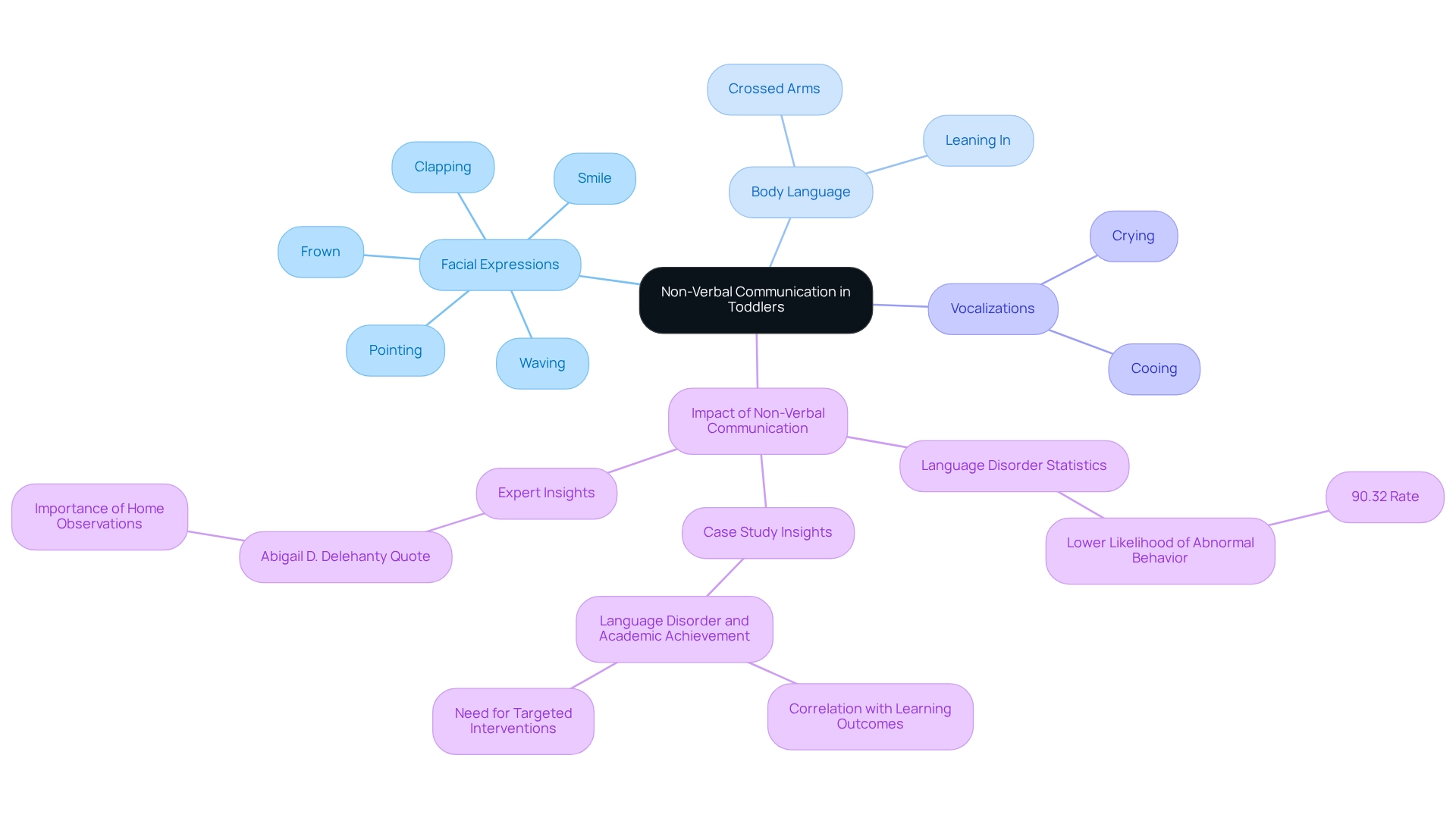
Non-verbal interaction in non verbal toddler behavior encompasses a range of signals that children use to express their needs and feelings. Understanding these signals is vital for nurturing effective interactions with a non verbal toddler and supporting their overall development. Let’s explore some key forms of non-verbal communication that can help you connect with your child:
- Facial Expressions: A smile often indicates happiness, while a frown may suggest discomfort or displeasure. Recognizing these expressions can empower you to gauge your non verbal toddler's emotional state, as gestures such as pointing, waving, or clapping convey messages. For instance, a child might point to a toy they desire, clearly indicating their interest or need.
- Body Language: The positioning of your child's body can reveal their emotions. Leaning in may show interest, whereas crossed arms might suggest withdrawal or discomfort.
- Vocalizations: Sounds such as cooing or crying serve as methods of expression. Context is crucial; recognizing when and why these sounds occur can provide insight into your child's needs.
Recent studies highlight the significance of these silent signals in early development. For example, children with language difficulties were found to have a notably reduced chance of exhibiting atypical behavior, with a rate of 90.32% (ranging from 83.34% to 94.57%). This suggests a connection between effective silent interaction and positive behavioral outcomes. Furthermore, a case study on language disorders and academic success revealed that children with such impairments were considerably less likely to achieve a 'good level of development' in academic evaluations. This underscores the necessity for targeted interventions that incorporate alternative means of expression.
The authors express gratitude to Surrey County Council, along with the schools, educators, families, and participants who contributed to the study, enhancing the reliability of these findings. Experts emphasize that observing a non verbal toddler's communication and gestures in their home environment can facilitate earlier identification of autism and support family-centered intervention planning. By acknowledging and responding to these silent cues, you can create a more engaging and nurturing atmosphere, ultimately enriching your child's developmental journey. How have you noticed your child communicating non-verbally? Share your experiences and let’s support each other in this important journey.
Implement Effective Communication Techniques
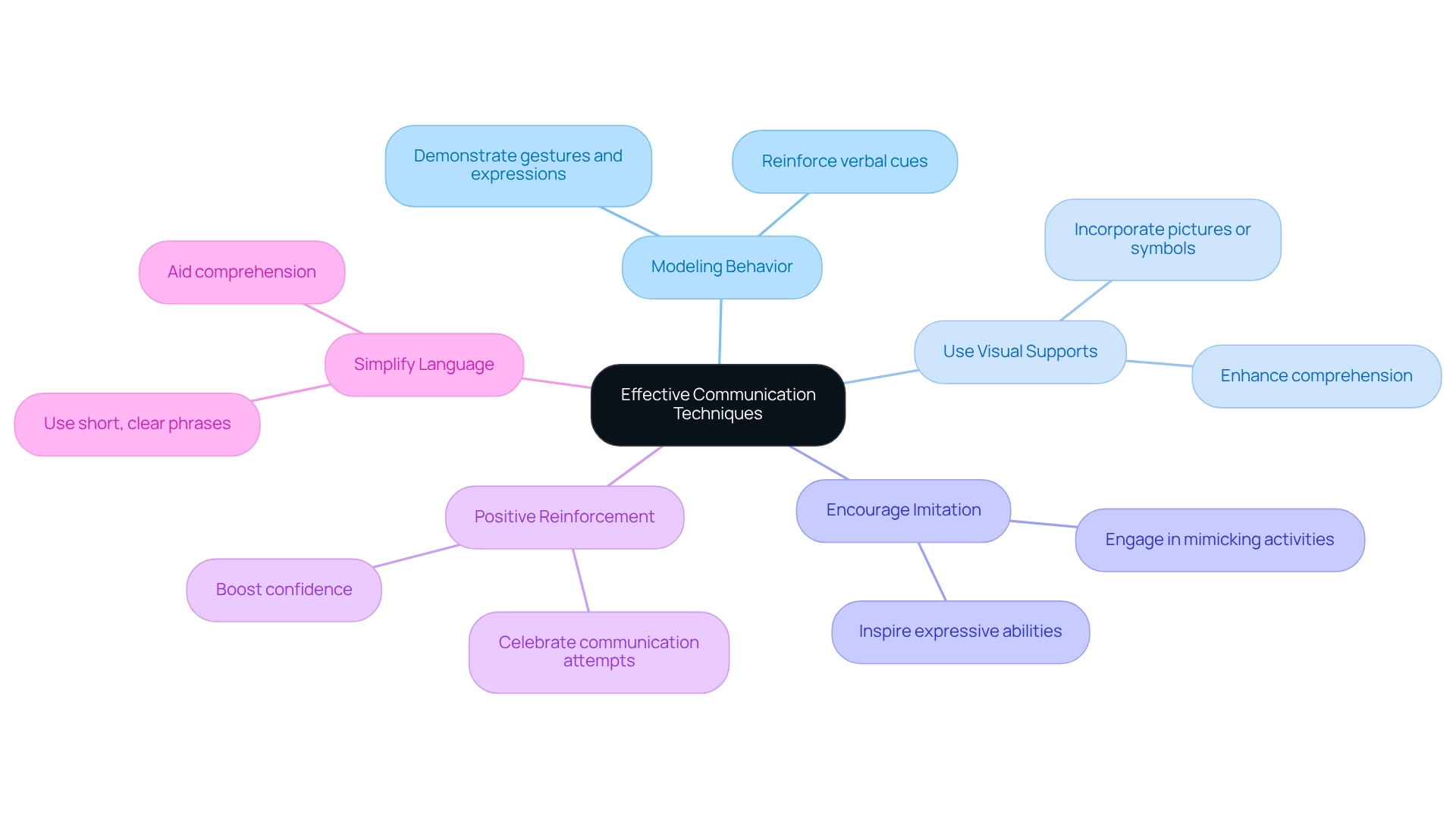
To effectively communicate with your non verbal toddler, consider the following nurturing techniques:
- Modeling Behavior: Demonstrate the gestures and expressions you wish your non verbal toddler to adopt. For instance, if you want them to wave goodbye, do so while verbally saying goodbye. This approach not only teaches the action but also reinforces the verbal cue, creating a comforting routine for your little one.
- Use Visual Supports: Incorporate pictures or symbols that represent common needs or activities. Visual aids can significantly enhance comprehension, helping your child connect images to their wishes and encouraging interaction in a meaningful way.
- Encourage Imitation: Engage in activities that prompt your young one to mimic your actions or sounds. Simple actions, such as clapping your hands or making animal sounds, can inspire imitation, which is vital for developing their expressive abilities and fostering a joyful learning environment.
- Positive Reinforcement: Celebrate your little one's attempts to communicate, whether through gestures or sounds. Positive reinforcement motivates them to continue expressing themselves, boosting their confidence in conveying ideas and emotions.
- Simplify Language: Use short, clear phrases when communicating with your child. This approach aids comprehension and makes it easier for non-verbal toddlers to respond appropriately, ensuring they feel understood and valued.
These strategies not only enhance interactions but also support the overall growth of non-verbal toddlers, paving the way for more effective exchanges. It's important to recognize that recent statistics indicate the occurrence of autism among Pacific Islander youth is 3.33%, underscoring the necessity for effective communication strategies designed for diverse populations. Furthermore, the CDC reports that individuals of two or more races have a prevalence rate of 1 in 44, highlighting the significance of acknowledging the unique needs of various groups. Continuous global initiatives aimed at promoting understanding and support for autism are essential in cultivating an inclusive atmosphere for every young person, fostering a sense of belonging and acceptance.
Create a Supportive Communication Environment
To cultivate a supportive interaction environment for your non verbal toddler, consider these nurturing strategies:
- Minimize Distractions: Create a calm space by reducing background noise and clutter. This enables your child to focus on interactions without feeling overwhelmed. It's crucial, as settings with fewer distractions can significantly improve language skills in toddlers. In Wisconsin, where the autism occurrence is 1 in 77 youths (1.3%), establishing such environments is essential for successful interaction.
- Engage in Play: Use playtime as a wonderful opportunity for interaction. Select toys that encourage engagement, like blocks or dolls, and narrate your actions as you play together. Participating in play fosters bonding and enhances your child's ability to express themselves.
- Establish Routines: Consistent daily routines help children anticipate activities and understand expectations. Visual schedules can be particularly effective in illustrating the day's events, providing a structured setting that enhances communication without words. Communities can play a vital role by advocating for local programs that support single-parent households with children on the autism spectrum, thereby strengthening the overall support system.
- Be Present: Show your child that you are engaged by maintaining eye contact and adopting an open posture. This silent cue conveys your interest and encourages them to engage, underscoring the significance of presence in communication.
- Use Positive Body Language: Smile, nod, and employ encouraging gestures to reinforce your child's attempts to communicate. Positive body language boosts their confidence and willingness to share their thoughts, fostering a supportive communication environment.
As the CDC emphasizes, the economic impact of autism affects not only families but society as a whole, highlighting the need for greater awareness and assistance. By applying these strategies, you can create a nurturing atmosphere that promotes effective interaction for your non verbal toddler, ultimately enhancing their social abilities and engagements. Innovative therapies are also essential to support individuals with autism and their families, further underscoring the importance of these strategies.
Utilize Tools and Resources for Enhanced Communication
To enhance interaction with your silent toddler, consider these helpful tools and resources:
- Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) Devices: These range from simple picture boards to advanced speech-generating devices, enabling young children to express their thoughts and desires effectively. However, it’s important to recognize that around one-third of AAC systems are abandoned. This statistic underscores the need for user-friendly designs that align with the child’s strengths and interaction context, ensuring these devices are not only accessible but also culturally responsive to their background. Teaching basic sign language can greatly improve communication for a non-verbal toddler. Starting with simple signs like 'more' or 'all done' allows your little one to express their wants and feelings. Experts emphasize that sign language enhances interaction and fosters independence and confidence in a non-verbal toddler. As noted by Brighter Strides ABA, these tools play a vital role in empowering individuals with autism, equipping them with the means to express themselves effectively.
- Visual Schedules: Using visual aids to outline daily routines can help your child grasp what to expect throughout the day. This clarity encourages them to communicate their needs at appropriate times, reducing frustration and enhancing their ability to engage with their surroundings.
- Apps and Technology: Explore various applications specifically designed to develop interaction skills. Many of these utilize pictures or symbols to facilitate communication, offering a modern approach to improving expressive abilities in toddlers. Staying updated on the latest tools for augmentative and alternative methods can provide parents with new strategies.
- Books and Resources: Seek literature that focuses on non-verbal communication strategies. These resources can offer valuable insights and techniques to support your child’s development, ensuring you adopt a comprehensive approach. Additionally, expert opinions on augmentative and alternative communication tools for toddlers can further validate the strategies you implement.
Incorporating these tools not only enhances communication but also nurtures a supportive environment where your child can thrive.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of non-verbal communication is vital for fostering meaningful connections with non-verbal toddlers. This article has highlighted key aspects of non-verbal cues, including:
- Facial expressions
- Gestures
- Body language
- Vocalizations
These are essential for parents and caregivers to recognize. By acknowledging these signals, caregivers can better support their child's emotional and developmental needs, enhancing their overall communication experience.
Implementing effective communication techniques such as:
- Modeling behavior
- Using visual supports
- Encouraging imitation
Lays a strong foundation for interaction. These strategies not only promote understanding but also help build a child's confidence in their ability to communicate. Creating a supportive environment by minimizing distractions, engaging in play, and establishing routines further enriches the child's social skills and interactions.
Utilizing tools and resources like:
- AAC devices
- Sign language
- Visual schedules
Can significantly enhance communication for non-verbal children. These innovative approaches empower toddlers to express their needs and feelings, fostering independence and confidence in their interactions.
In conclusion, by embracing the silent language of non-verbal communication, caregivers can profoundly impact their child's developmental journey. Recognizing and responding to these cues, employing effective techniques, and utilizing supportive tools will ensure that non-verbal toddlers feel heard and understood. This holistic approach not only nurtures their communication skills but also strengthens the bonds of connection that are essential during their formative years.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is non-verbal interaction in toddler behavior?
Non-verbal interaction in toddler behavior encompasses a range of signals that children use to express their needs and feelings, which is vital for nurturing effective interactions and supporting their overall development.
What are some key forms of non-verbal communication in toddlers?
Key forms of non-verbal communication in toddlers include facial expressions, body language, and vocalizations. These signals help convey their emotional states and needs.
How can facial expressions indicate a toddler's feelings?
Facial expressions such as a smile often indicate happiness, while a frown may suggest discomfort or displeasure. Recognizing these expressions allows caregivers to gauge the child's emotional state.
What does body language reveal about a toddler's emotions?
The positioning of a toddler's body can reveal their emotions; for example, leaning in may show interest, whereas crossed arms might indicate withdrawal or discomfort.
How do vocalizations serve as a form of communication for toddlers?
Vocalizations such as cooing or crying serve as methods of expression. Understanding the context of these sounds can provide insight into the toddler's needs.
What do recent studies say about non-verbal communication and child development?
Recent studies highlight the significance of silent signals in early development, indicating that effective silent interaction is linked to positive behavioral outcomes, particularly in children with language difficulties.
Why is it important to observe a non-verbal toddler's communication at home?
Observing a non-verbal toddler's communication and gestures in their home environment can facilitate earlier identification of autism and support family-centered intervention planning.
How can acknowledging non-verbal cues benefit a child's development?
By acknowledging and responding to non-verbal cues, caregivers can create a more engaging and nurturing atmosphere, ultimately enriching the child's developmental journey.




