Overview
This article sheds light on the essential elements of autism diagnostic criteria for adults, focusing on ongoing social communication deficits and restricted, repetitive behaviors. Understanding these criteria is crucial, as they help unravel the complexities of autism. Accurate diagnoses can significantly improve the support and resources available for individuals on the spectrum. With rising diagnosis rates, it is clear that tailored interventions are more important than ever. By fostering awareness, we can create a more inclusive environment for those affected by autism.
Introduction
Understanding autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is crucial, especially as the prevalence of diagnoses among adults continues to rise. With nearly 1 in 45 individuals estimated to be autistic in the U.S. by 2025, the importance of clear diagnostic criteria cannot be overstated. This article delves into ten key elements of autism diagnostic criteria for adults, providing insights that empower individuals and families to navigate the complexities of the diagnostic process.
How can one effectively identify and understand these criteria to ensure accurate assessments and access to vital resources? Together, we can explore this journey, offering support and understanding every step of the way.
About ASD Media: Enhancing Understanding of Autism Diagnostic Criteria
At ASD Media, we deeply understand the challenges families face regarding the autism diagnostic criteria for adults in the realm of ABA therapy and the diagnostics of developmental disorders. Our commitment lies in providing valuable insights and strategies to help overcome these hurdles. By fostering a supportive community, we empower parents and professionals to effectively navigate the complexities of diagnostic criteria.
Our resources are designed to enhance understanding and improve outcomes for individuals with autism and ADHD. We believe that every family deserves access to the necessary tools and information. Recent insights from 2025 underscore the vital role of community participation in the diagnostic process. Collaborative initiatives have shown that they can lead to more accurate evaluations and improved support for those on the spectrum.
Successful community programs highlight that when families are engaged and informed, the diagnostic journey becomes more streamlined. This ultimately enhances the quality of care and support available. Experts emphasize the need for continuous education and resource sharing within communities to refine the autism diagnostic criteria for adults. By working together, we can positively influence diagnosis results and ensure that every child receives the care they need.
DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria: Key Elements for Adult Autism Diagnosis
The DSM-5 outlines specific autism diagnostic criteria for adults with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), focusing on two primary areas: ongoing deficits in social communication and interaction, and restricted, repetitive behavior patterns. These criteria must manifest across various contexts and lead to significant impairment in daily functioning. As of 2025, nearly 1 in 45 individuals in the U.S. is estimated to be autistic, with the CDC estimating that nearly 5.5 million U.S. individuals are autistic. This highlights the growing acknowledgment of diagnoses in this age group, which is essential for individuals seeking a formal diagnosis. Understanding these factors forms the basis of clinical assessments and guides the assistance services available.
Recent changes in the autism diagnostic criteria for adults have broadened the understanding of autism, allowing for more inclusive assessments that reflect the spectrum's diversity. This evolution recognizes the emotional and psychological challenges faced by individuals diagnosed later in life, validating their experiences and stressing the necessity for continuous assistance. Real-world examples, such as case studies illustrating the application of these criteria in clinical settings, underscore the necessity for tailored approaches that consider individual experiences and challenges.
Moreover, community support plays a vital role in enhancing the quality of life for autistic adults. It reinforces the importance of accessible resources and networks, reminding us that we are not alone on this journey. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences, as together we can foster a supportive environment for all those affected by autism.
Social Communication Deficits: Recognizing Essential Symptoms
Social communication deficits are a hallmark of autism, presenting significant challenges in understanding and using both verbal and nonverbal communication. For adults on the spectrum, initiating conversations, maintaining eye contact, and interpreting social cues can be particularly difficult. These struggles can profoundly impact their social interactions and relationships. Imagine a scenario where an individual finds it hard to gauge the right moment to respond in a conversation, leading to misunderstandings or awkward pauses. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial—not only for self-identification but also for clinicians during the diagnostic process of autism diagnostic criteria adults, as they directly affect social interactions and relationships.
According to the CDC, an estimated 2.2% of individuals in the U.S. are autistic, with diagnoses among the 26-34 age group rising by an astonishing 450% since 2011. This growing awareness underscores the importance of understanding the autism diagnostic criteria adults and how it manifests in adulthood. Real-life examples reveal that social communication challenges can lead to feelings of isolation and frustration. For instance, a grown individual might struggle to interpret a friend’s tone of voice, resulting in miscommunication and feelings of rejection. Such experiences highlight the need for tailored support and resources to navigate these difficulties effectively.
To truly support individuals on the autism spectrum, advocates can foster open discussions about these challenges. Encouraging access to resources that aid in social skills development is vital. How can we create an environment where these conversations flourish? By sharing experiences and insights, we can collectively work towards understanding and supporting each other in this journey.
Restricted and Repetitive Behaviors: Identifying Core Characteristics
Understanding restricted and repetitive behaviors (RRBs) is crucial for anyone seeking to support individuals on the spectrum. These behaviors, which include repetitive movements, insistence on sameness, and a deep focus on specific interests, are not just quirks; they play a significant role in daily life and social interactions. For many individuals, RRBs serve as coping strategies that help manage anxiety in unfamiliar or stressful situations. It's important to note that research indicates around 40% of individuals with autism face anxiety disorders, which can heighten the frequency and intensity of RRBs.
Consider the real-world implications of RRBs in the lives of adults. For example, someone may flap their hands when feeling anxious or adhere to a strict routine to find comfort. Unfortunately, these behaviors can create barriers to social relationships and job opportunities, as only 15% of autistic adults with a college degree are fully employed. This highlights the need for greater understanding and support.
Identifying RRBs is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective intervention based on the autism diagnostic criteria for adults. Experts emphasize that a nuanced approach is necessary, as these behaviors can vary widely among individuals. Recognizing specific patterns of RRBs can lead to more tailored support strategies. For instance, the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS-2) is a respected tool for assessing behaviors that align with the autism diagnostic criteria for adults, ensuring individuals receive the appropriate diagnoses and interventions suited to their unique needs.
In 2025, ongoing discussions within the neurodiversity community continue to stress the importance of recognizing RRBs. These behaviors are vital for understanding the broader spectrum of neurodevelopmental conditions. By fostering awareness and providing resources, we can enhance the quality of life for individuals on the spectrum and support their journey toward fulfilling lives. Let’s work together to create a more inclusive environment, where everyone feels understood and valued.
Sensory Processing Issues: Understanding Their Impact on Diagnosis
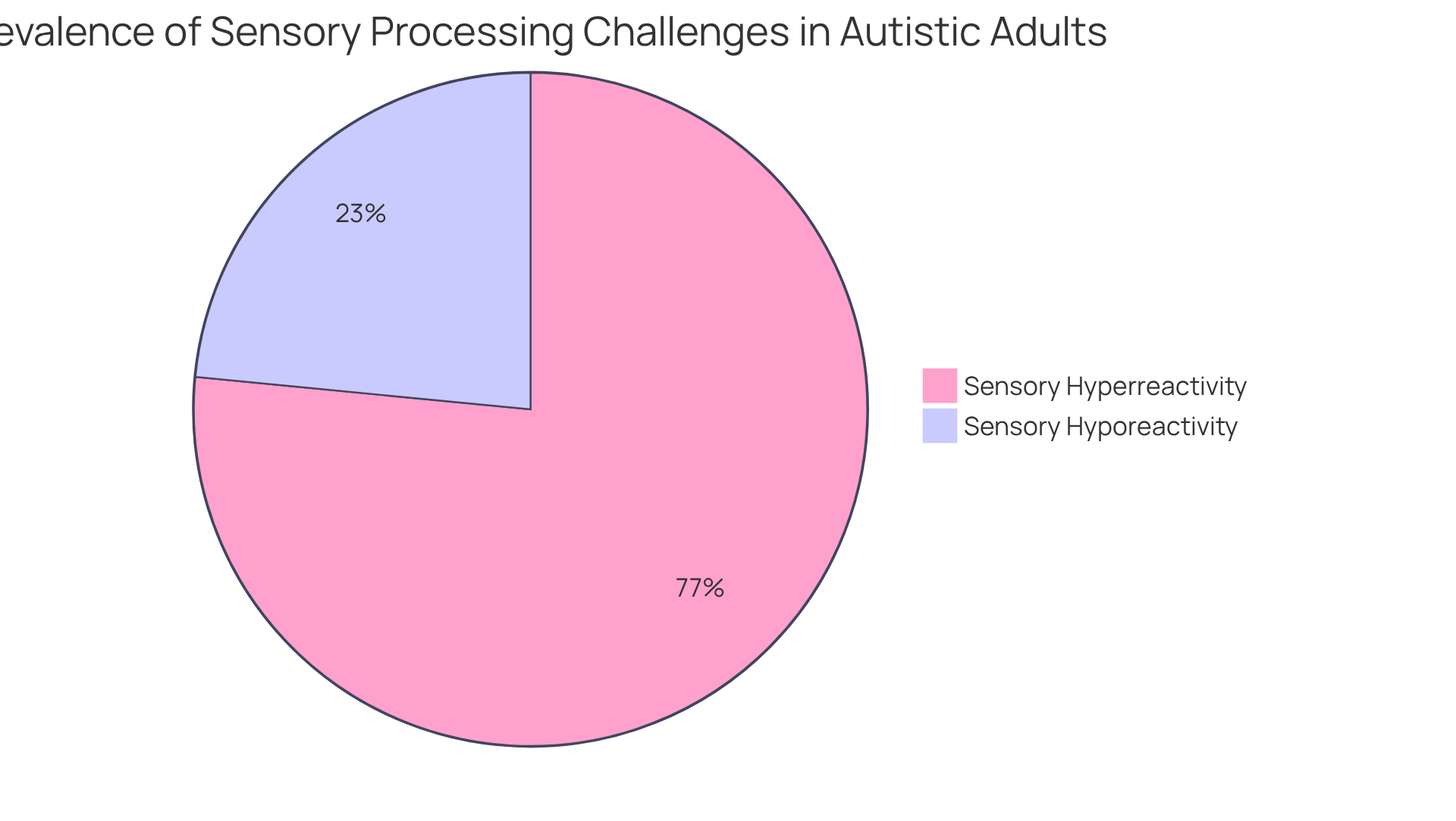
Sensory processing challenges are prevalent among adults on the autism spectrum, often appearing as hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity to various stimuli. For instance, an individual may find everyday sounds, like a ringing phone or the hum of fluorescent lights, overwhelmingly distressing, which can lead to anxiety or meltdowns. On the other hand, some may not respond to sensory inputs that typically provoke strong reactions, such as pain or extreme temperatures, complicating their ability to navigate daily life. Research indicates that approximately 93.3% of individuals with developmental disorders report sensory hyperreactivity, while 28.6% identify as sensory hyporeactive, underscoring the significance of these challenges.
These sensory difficulties profoundly impact social interactions and overall quality of life, making it crucial for clinicians to integrate sensory processing considerations into diagnoses related to the condition. Occupational therapists stress that understanding these sensory sensitivities can empower individuals to advocate for necessary accommodations, such as:
- Quiet spaces
- Sensory-friendly environments
Such adjustments can greatly enhance daily functioning and social engagement. As one occupational therapist insightfully noted, "Recognizing sensory triggers is the first step in emotional regulation."
In 2025, acknowledging sensory processing difficulties is more essential than ever, as ongoing studies continue to highlight their importance in the diagnostic standards for the condition. By addressing these concerns, healthcare providers can offer more precise diagnoses and tailored support, ultimately improving the lives of individuals on the spectrum. Coping strategies, such as utilizing noise-canceling headphones and creating sensory-friendly environments, can also be effective in managing sensory overload and enriching daily experiences.
Co-Occurring Conditions: Navigating Complex Diagnoses
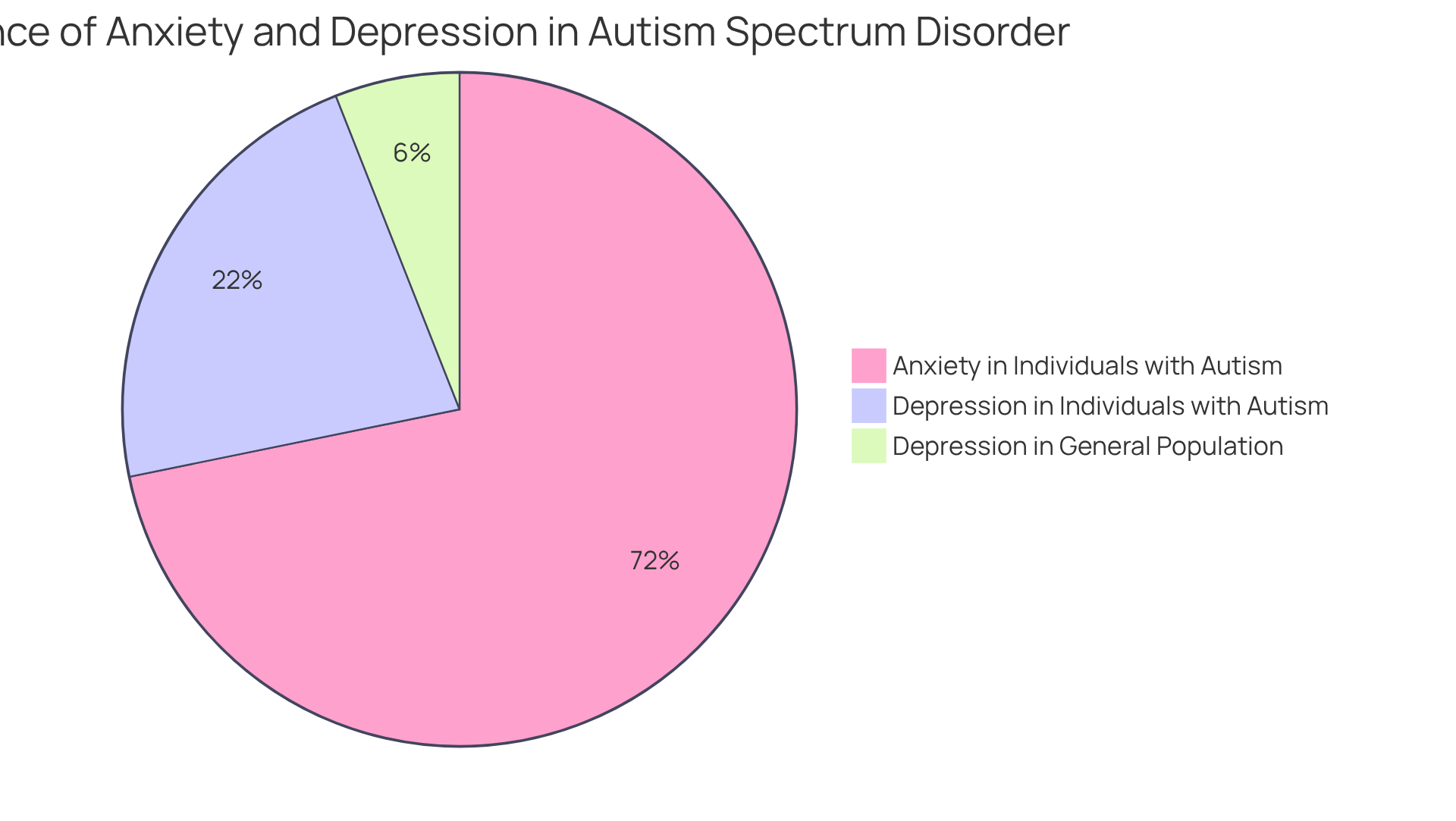
Co-occurring conditions such as anxiety, depression, and ADHD are prevalent among adults with this condition, significantly complicating the diagnostic process. It's concerning to note that studies indicate up to 84% of individuals on the spectrum may experience various types of anxiety, while around 26% endure depression—a rate that is notably higher than the general population's 7%. These overlapping symptoms can obscure the underlying diagnosis of autism, making it crucial for clinicians to embrace integrated treatment approaches that address both the autism diagnostic criteria for adults and its co-occurring issues.
For instance, the case study 'Building Effective Autism Treatment Plans: A Collaborative and Compassionate Approach' highlights how personalized care can lead to improved outcomes for individuals facing multiple diagnoses. Mental health experts, including Patricia Wright, PhD, MPH, emphasize that understanding the interplay between this developmental disorder and these conditions is vital for providing comprehensive support.
As the landscape of developmental disorder care evolves, the focus on holistic approaches that consider the complete range of a person's health is becoming increasingly significant. It is essential for us to advocate for these integrated strategies, ensuring that every individual receives the compassionate care they deserve.
Diagnostic Assessment Process: Steps for Adults Seeking Evaluation
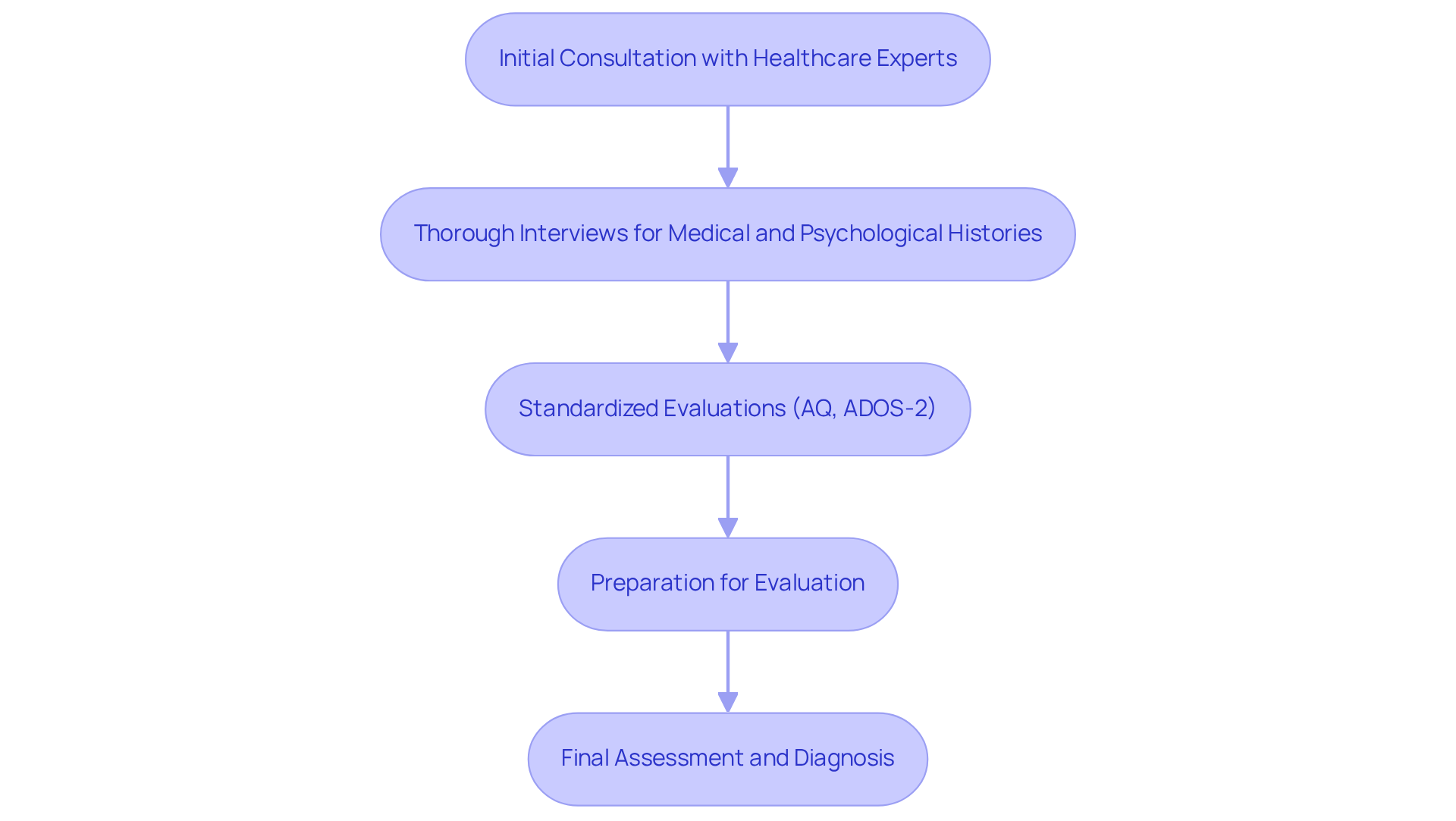
The diagnostic evaluation procedure for adults with developmental disorders often includes the autism diagnostic criteria adults and is multifaceted, typically encompassing several key steps. Initially, individuals engage in discussions with healthcare experts who specialize in evaluations related to developmental disorders. These consultations often involve thorough interviews where clinicians gather extensive medical and psychological histories, along with insights into a person's social interactions and communication styles. Standardized evaluations, such as the Autism Spectrum Quotient (AQ) and the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS-2), are frequently employed to assess characteristics related to the autism diagnostic criteria adults. As noted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, "An effective evaluation synthesizes information from many sources," ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the person's unique profile.
Preparing for an autism evaluation can significantly enhance both the experience and outcomes. Individuals are encouraged to document their developmental history, including any challenges they have faced in social settings, sensory sensitivities, and behavioral patterns. This preparation not only aids clinicians in making informed assessments but also empowers individuals to articulate their experiences more effectively.
Real-life examples underscore the importance of this process. For instance, a case study highlighted an individual who, after years of masking their autistic traits, sought evaluation and received a diagnosis that validated their lifelong challenges. This diagnosis opened doors to assistance services and workplace adjustments, ultimately improving their quality of life. Moreover, the impact of late diagnosis is profound, as many individuals may not have received the essential support earlier in life.
The average duration of autism diagnostic assessments for adults can vary, typically ranging from several hours to multiple sessions over weeks. This timeframe allows for a thorough assessment, ensuring that all facets of the person's experiences are considered. The costs for assessments can range from $2,000 to $6,000, which is a significant factor for many individuals seeking a diagnosis. As specialists emphasize, understanding the intricacies of autism diagnostic criteria adults is essential for providing suitable resources and support, ultimately fostering a more inclusive environment for individuals who are neurodivergent. Furthermore, it is crucial to recognize that 40-50% of autistic individuals have faced anxiety, highlighting the mental health challenges that may accompany the condition and underscoring the importance of timely diagnosis and support.
Self-Assessment Tools: Empowering Adults to Identify Autism Traits
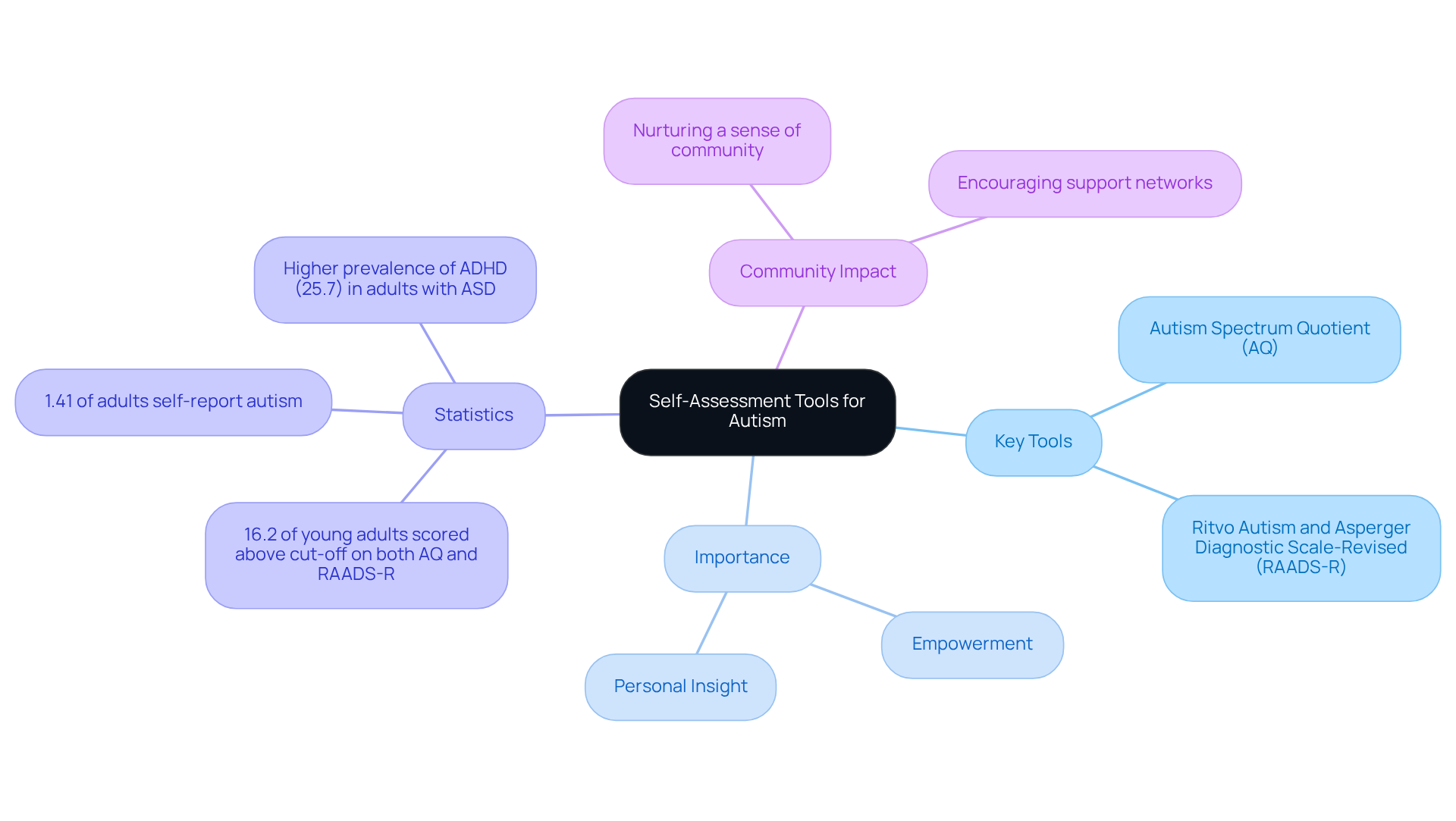
Self-evaluation tools, such as the Autism Spectrum Quotient (AQ) and various questionnaires, are invaluable for individuals seeking to recognize traits associated with autism. These instruments offer an initial glimpse into personal experiences, helping users determine whether to pursue a formal diagnosis. For example, studies reveal that 16.2% of young adults in psychiatric settings scored above the cut-off on both the AQ and the Ritvo Autism and Asperger Diagnostic Scale-Revised (RAADS-R), highlighting the prevalence of autistic traits in this demographic.
While self-assessment cannot replace professional evaluation, it serves as a meaningful first step in understanding one's neurodiversity. Advocates emphasize that self-identification can empower individuals, nurturing a sense of community and support. As Dr. Catherine Saunders observed, "Adults self-reporting as autistic were less likely to report being involved in decisions about care and treatment," which underscores the significance of recognizing one's traits.
The AQ, specifically designed for self-identification, plays a crucial role in this journey. It encourages individuals to reflect on their social interactions, communication styles, and sensory sensitivities—often key indicators of the condition. With current estimates suggesting that approximately 1.41% of adults self-report autism—higher than the APMS estimate of 0.8%—the value of these tools is clear. They not only enhance personal insight but also spark important conversations about neurodevelopmental conditions in broader societal contexts, ultimately fostering a more inclusive understanding of neurodiversity.
Moreover, self-assessment instruments like the AQ and RAADS-R should inspire comprehensive diagnostic evaluations according to autism diagnostic criteria for adults to ensure individuals receive the support they need. It’s essential to recognize that each person’s journey is unique, and these tools can be a gentle guide toward understanding and embracing one’s neurodiversity.
Benefits of Formal Diagnosis: Accessing Support and Resources
Receiving an official diagnosis can be a significant turning point, offering many advantages that can truly enhance your journey. It opens the door to tailored assistance services, educational resources, and community programs designed to support you. Imagine how a diagnosis can pave the way for necessary accommodations in both the workplace and educational settings, ultimately improving your overall quality of life. Understanding these benefits can inspire you to seek assessment and advocate for your needs, empowering you to take the next steps with confidence.
Ongoing Support and Resources: Building a Community for Adults with Autism
Continual assistance and resources are vital for individuals on the spectrum as they navigate their unique challenges. Community organizations and support groups play an essential role in creating spaces where individuals can share their experiences, seek advice, and forge connections. For instance, programs designed for adults with developmental differences offer ongoing support, skill enhancement, and opportunities for social interaction, significantly enriching their quality of life. Engaging with these resources fosters a sense of belonging and empowerment, enabling individuals diagnosed under autism diagnostic criteria adults to thrive both personally and professionally.
Community leaders emphasize the importance of establishing support networks, highlighting that collaboration among various organizations can lead to more effective services and greater awareness of the strengths of autistic individuals. Real-world examples, such as the Adult Autism Center, demonstrate how structured environments can promote personal growth and independence, ultimately contributing to a more inclusive society. By tapping into community resources, support services that cater to the autism diagnostic criteria adults can help enhance the overall well-being and success of autistic adults. Together, let’s build a community that uplifts and empowers every individual on the spectrum.
Conclusion
Understanding the autism diagnostic criteria for adults is not just important; it is a vital step toward creating a society that embraces and supports the unique challenges faced by individuals on the spectrum. This article highlights essential elements of these criteria, focusing on:
- Social communication deficits
- Restricted and repetitive behaviors
- Sensory processing issues
It also emphasizes the importance of co-occurring conditions and the diagnostic assessment process, which together provide a comprehensive understanding of adult autism.
The insights shared throughout this article reveal how community engagement and tailored support can profoundly enhance the diagnostic journey and overall quality of life for autistic individuals. From self-assessment tools that empower personal recognition of traits to the benefits of a formal diagnosis that opens doors to vital resources, each aspect plays a crucial role in navigating the complexities of autism. Moreover, ongoing support and the establishment of community networks are pivotal in creating an environment where individuals can truly thrive.
Ultimately, it is imperative to advocate for continued awareness and understanding of autism diagnostic criteria. By fostering discussions, sharing experiences, and utilizing available resources, we can build a more supportive framework for adults with autism. Together, we have the opportunity to not only improve individual lives but also to celebrate the rich diversity that neurodiversity brings to our communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ASD Media's mission?
ASD Media aims to enhance understanding of autism diagnostic criteria for adults and provide insights and strategies to help families navigate the complexities of autism and ADHD diagnostics.
Why is community participation important in the autism diagnostic process?
Community participation is vital as it leads to more accurate evaluations and improved support for individuals on the spectrum, making the diagnostic journey more streamlined.
What are the primary areas of focus in the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for adult autism?
The DSM-5 diagnostic criteria focus on ongoing deficits in social communication and interaction, as well as restricted, repetitive behavior patterns, which must manifest across various contexts and significantly impair daily functioning.
How prevalent is autism among adults in the U.S.?
As of 2025, nearly 1 in 45 individuals in the U.S. is estimated to be autistic, with approximately 5.5 million individuals affected.
What recent changes have been made to autism diagnostic criteria for adults?
Recent changes have broadened the understanding of autism, allowing for more inclusive assessments that reflect the diversity of the spectrum and recognizing the emotional and psychological challenges faced by individuals diagnosed later in life.
What are social communication deficits in the context of autism?
Social communication deficits refer to challenges in understanding and using verbal and nonverbal communication, such as initiating conversations, maintaining eye contact, and interpreting social cues.
How have diagnoses among the 26-34 age group changed since 2011?
Diagnoses among the 26-34 age group have risen by 450% since 2011, highlighting a growing awareness of autism in adults.
What impact do social communication challenges have on individuals with autism?
Social communication challenges can lead to feelings of isolation and frustration, as individuals may struggle to interpret social cues, resulting in misunderstandings and difficulties in relationships.
How can advocates support individuals on the autism spectrum with social communication challenges?
Advocates can foster open discussions about these challenges and promote access to resources that aid in social skills development, creating an environment for supportive conversations.




