Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can be a challenging journey for families, especially when it comes to fostering social skills in children. Understanding the nuances of ASD is crucial, as it profoundly influences communication and social interactions. Research highlights the importance of early diagnosis and intervention, which can significantly enhance a child's ability to engage with peers and develop essential social capabilities.
This article explores effective strategies that empower parents to support their children in developing social skills:
- Modeling behaviors
- Structured playdates
- Utilizing social stories
- Visual aids
By equipping themselves with knowledge and resources, parents can create an environment that nurtures their child's social growth, ensuring they thrive both socially and emotionally.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder and Social Skills
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that significantly affects communication, behavior, and interpersonal interactions. Children with ASD may present a diverse array of challenges in autism and social skills, ranging from difficulties in initiating conversations to struggles in interpreting social cues. For instance, a case study titled 'Developmental Evaluation of Youth with ASD in Wisconsin' revealed that 808 individuals with ASD were reported, with 581 receiving a developmental evaluation by age 36 months.
Notably, the evaluation rate for individuals with an IQ ≤70 was only 57.5%, compared to 82.2% for those with an IQ >70, highlighting significant disparities in access to early intervention. Moreover, individuals who underwent two years of intensive Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy beginning before age three demonstrated greater improvements in cognitive and language abilities compared to a control group, emphasizing the significance of early and effective intervention strategies. Furthermore, the average age of diagnosis for young individuals from lower-income households is 4.7 years, compared to 5.2 years for those from higher-income families, underscoring the critical need for equitable access to early evaluation and support.
Understanding how ASD influences autism and social skills is a crucial step toward creating an environment where youngsters can thrive both relationally and emotionally.
The Role of Early Diagnosis and Intervention in Social Skills Development
Extensive research underscores the significance of early diagnosis and intervention in fostering social skills in individuals with autism and social skills. The diagnosis process for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is crucial for identifying individuals who may need early intervention, involving recommended screening methods and specialist evaluations. When parents promptly seek assessment and support, young individuals gain access to personalized programs that effectively target their unique challenges.
Notably, early intervention services, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), have been demonstrated to significantly improve communication and interaction skills, which are crucial for developing autism and social skills, establishing a robust foundation for future engagement. As mentioned by Fuller EA et al., significant enhancements in youngsters' communication can be attained when clinicians commence early intervention, suggesting that the outlook for individuals on the autism spectrum can be greatly improved during the essential early phases of communication development. Furthermore, recent studies, such as those referenced by PMID: 37692637, highlight the effectiveness of early intervention strategies.
Parents are strongly encouraged to collaborate with healthcare providers and educators to explore the plethora of resources and interventions available as soon as they observe developmental delays, ensuring their offspring receive the necessary support for optimal growth.
Effective Strategies for Enhancing Social Skills in Children with Autism
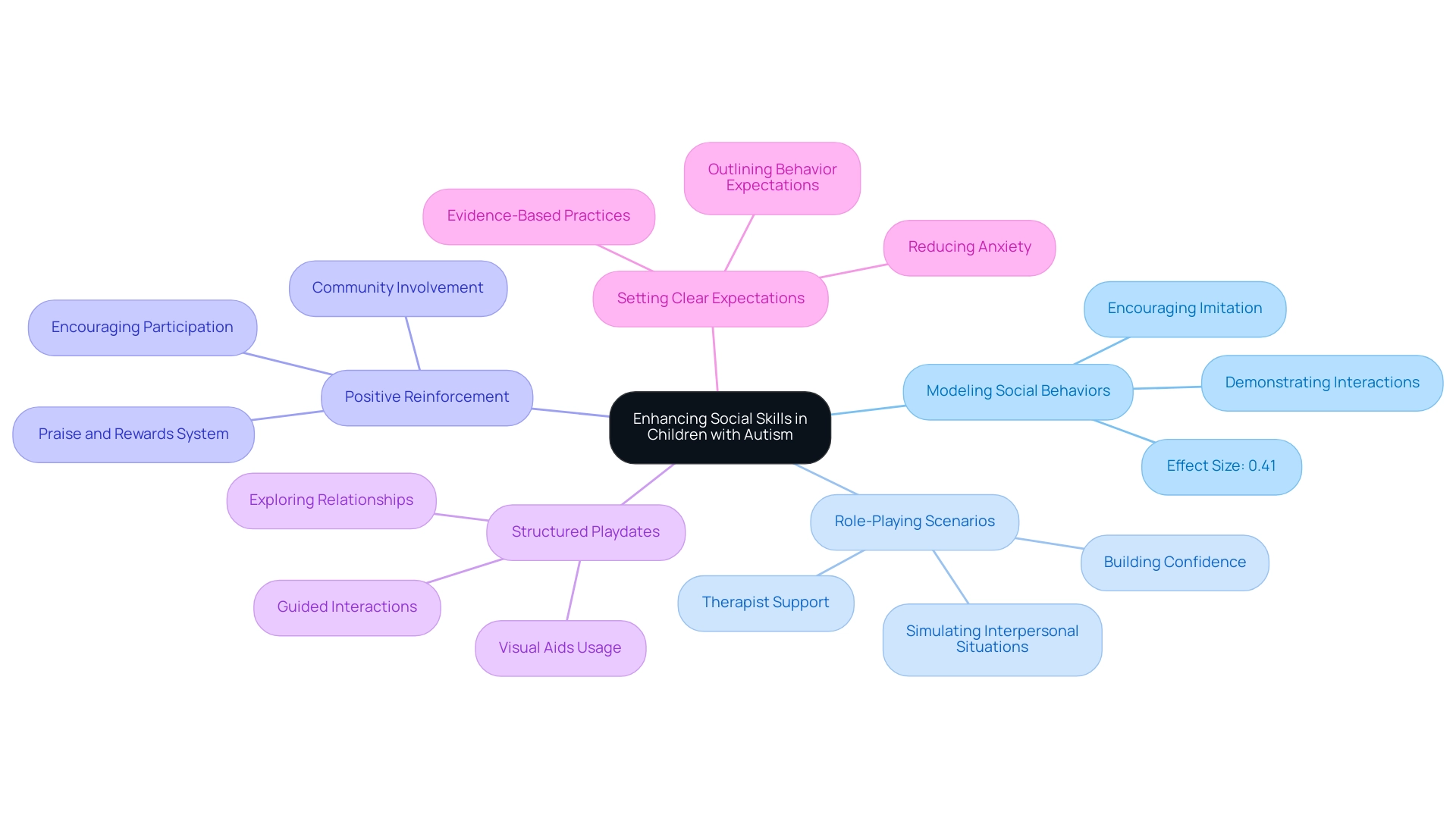
- Modeling Social Behaviors: One of the most impactful ways parents can aid their offspring's social development is by modeling appropriate interactions. Demonstrating simple actions like greetings, sharing, and turn-taking allows young individuals to observe and absorb these behaviors in a natural context. This foundational approach not only fosters understanding but also encourages imitation, which is crucial for developing autism and social skills in individuals. Teacher-report measures have shown an effect size of 0.41, highlighting the effectiveness of such strategies.
- Engaging in role-playing scenarios provides a dynamic method for youngsters to practice interpersonal skills in a safe environment. By simulating various interpersonal situations, parents can help their children navigate interactions with greater ease and confidence. This technique has shown promise in enhancing interpersonal capabilities, making real-world engagements less daunting. Recent articles highlight the effectiveness of role-playing in the development of autism and social skills, supported by opinions from therapists in the field.
- Positive Reinforcement: Establishing a system of praise and rewards can significantly enhance a young person's willingness to participate in interactions with others. When young individuals receive positive feedback for exhibiting desired behaviors, they are more likely to repeat those actions. This strategy not only builds confidence but also strengthens the importance of community involvement.
- Structured Playdates: Arranging playdates with peers can offer a structured opportunity for youngsters to practice their interpersonal skills. These controlled environments enable guided interactions, facilitating exploration of relationships and learning from experiences in a supportive setting. Employing visual aids, such as visual schedules and narratives, can further assist children with autism and social skills in comprehending and maneuvering through these interpersonal situations.
- Setting Clear Expectations: Before entering any communal situation, it’s beneficial to outline clear expectations for behavior. This preparation helps young individuals understand what is anticipated of them, reducing anxiety and boosting their readiness to engage with others. By clarifying roles and responsibilities, parents prepare their offspring for success in interpersonal interactions. It is essential to depend on thoroughly examined strategies, as demonstrated by the case study on publication bias in GSIs research, emphasizing the need for evidence-based practices in skills development.
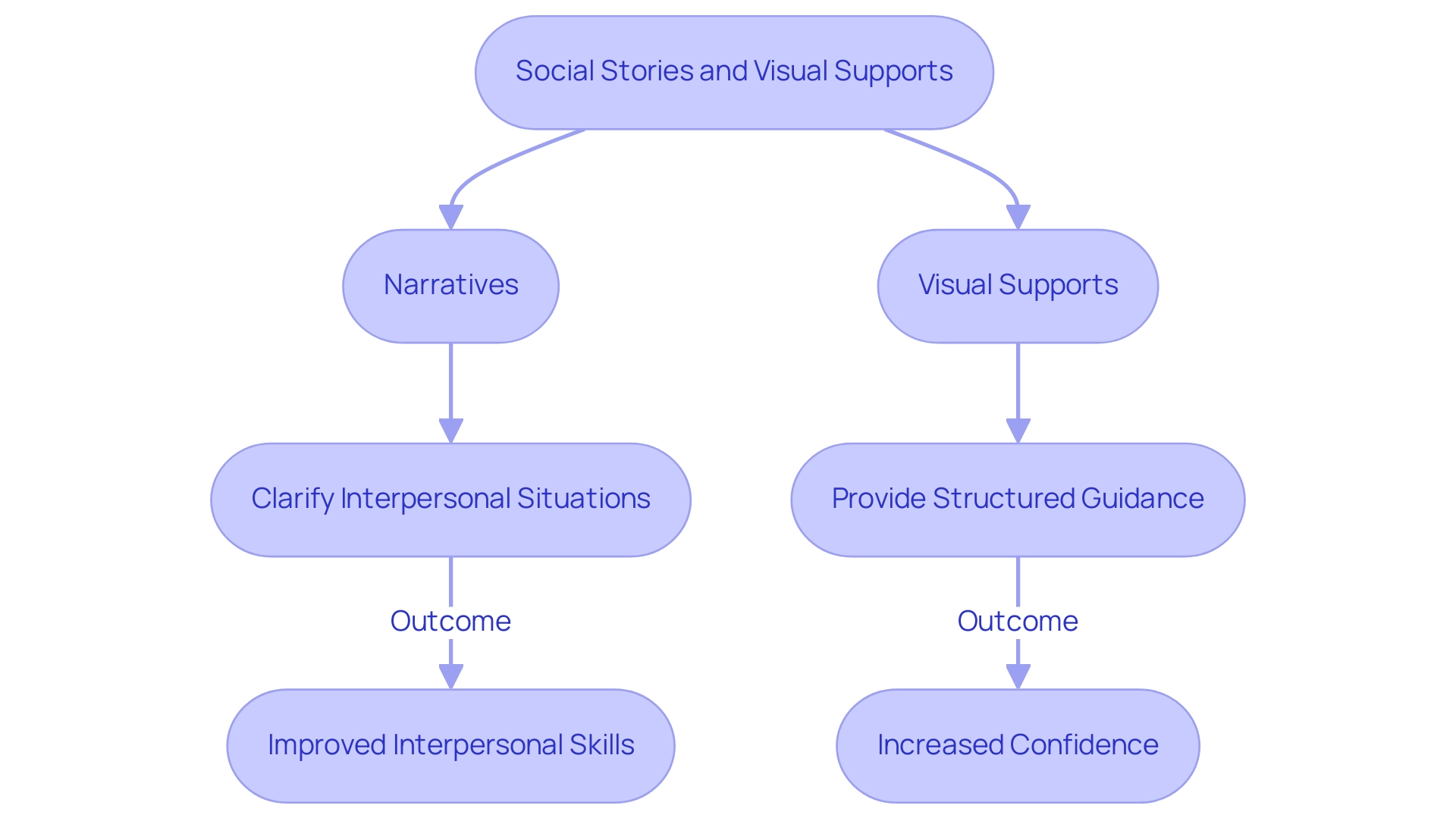
Utilizing Social Stories and Visual Supports for Skill Development
Narratives and visual aids have arisen as effective resources to support individuals with autism in managing interpersonal situations and expectations. Narratives, designed following Carol Gray's principles—which highlight clear objectives, relevance to the young person's experience, and organized content—comprise brief stories that clarify interpersonal situations, making them relatable and simpler to grasp. These tales not only assist children in visualizing suitable reactions but also foster a sense of familiarity in diverse situations.
Complementing interpersonal narratives, visual supports—such as charts, diagrams, and other illustrative aids—provide clear, structured guidance on interactions. In a recent study involving thirty-nine voluntary adults who presented lures to participants, all participants met mastery of the eighteen interpersonal abilities introduced, with three achieving this milestone solely through the use of narrative scenarios. By seamlessly integrating these tools into everyday practices, parents can significantly enhance their offspring's ability to navigate interpersonal situations, ultimately fostering confidence and improving overall interaction skills.
As noted by educators, integrating these supports into special education training can amplify their effectiveness, ensuring students receive the guidance they need to thrive socially.
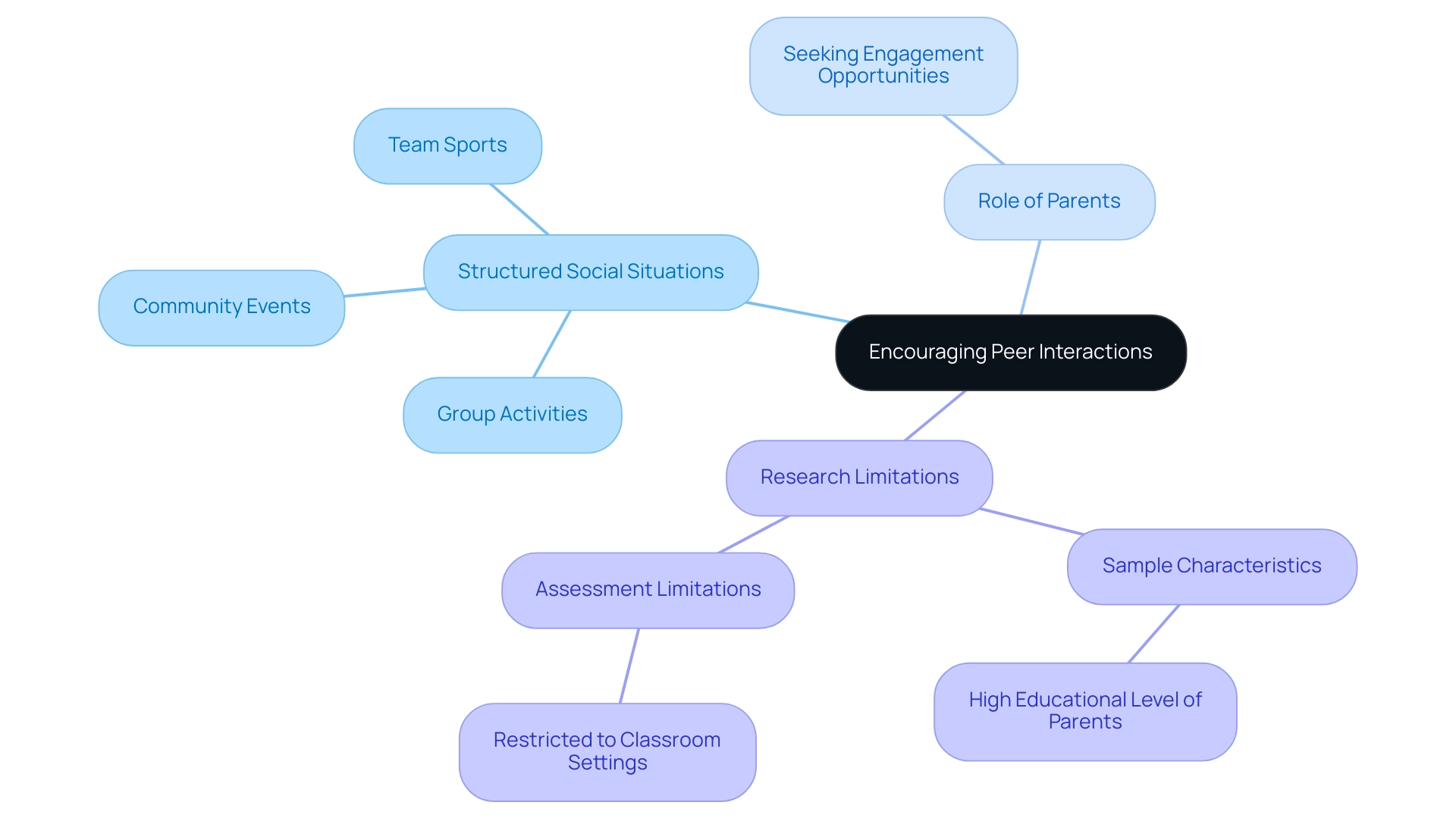
Encouraging Peer Interactions and Structured Social Situations
Encouraging peer interactions is crucial for individuals with autism as they navigate their interpersonal development. Parents can establish organized interactions—such as group activities, team sports, or community events—where youngsters can connect with peers in a supportive setting. Research has indicated that youngsters with access to typical peers are more likely to form connections compared to those in isolated special education environments.
Dr. Jill Locke, a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, emphasizes, "Positive peer interactions are crucial for the development of young individuals with autism, significantly impacting their ability to connect and thrive in various settings." By actively seeking out social engagement opportunities, parents play a pivotal role in their offspring's growth, ensuring that they are not just participants but thriving members of their communities.
However, it is important to acknowledge that the study's findings may have limitations, including a sample with a relatively high educational level among parents and the assessment of peer relationships being restricted to classroom settings.
These factors may affect the generalizability of the results, particularly for children with clinical ASD.
Conclusion
By implementing effective strategies, parents can play a transformative role in enhancing their children's social skills, especially for those on the autism spectrum. The combination of:
- modeling appropriate behaviors
- engaging in role-playing scenarios
- utilizing positive reinforcement
creates a supportive framework that encourages children to interact confidently with their peers. Structured playdates and clear expectations further bolster these efforts, providing children with practical opportunities to practice and refine their social interactions in a safe environment.
Additionally, the integration of social stories and visual supports serves as a powerful tool in demystifying social situations for children with autism. These resources not only clarify expectations but also empower children to navigate their social worlds with greater ease. The importance of fostering peer interactions cannot be overstated, as these connections are vital for developing meaningful relationships and social competence.
In conclusion, by equipping themselves with knowledge and employing these strategies, parents can significantly impact their children's social development. Early diagnosis and intervention remain crucial, but the ongoing support and encouragement from parents can make all the difference, ensuring that children with ASD not only thrive socially but also develop the essential skills they need to navigate life successfully. Through commitment and proactive engagement, families can cultivate an environment that nurtures their children's growth, paving the way for a brighter and more connected future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that significantly affects communication, behavior, and interpersonal interactions.
What challenges do children with ASD typically face?
Children with ASD may experience a variety of challenges, including difficulties in initiating conversations and interpreting social cues.
What was revealed in the case study titled "Developmental Evaluation of Youth with ASD in Wisconsin"?
The study reported 808 individuals with ASD, with 581 receiving a developmental evaluation by age 36 months, highlighting disparities in access to early intervention.
How does IQ affect the evaluation rate for individuals with ASD?
The evaluation rate for individuals with an IQ ≤70 was only 57.5%, compared to 82.2% for those with an IQ >70, indicating significant disparities in access to early intervention.
What impact does early intervention have on individuals with ASD?
Individuals who received two years of intensive Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy starting before age three showed greater improvements in cognitive and language abilities compared to a control group.
What is the average age of diagnosis for children with ASD from different income backgrounds?
The average age of diagnosis for children from lower-income households is 4.7 years, while it is 5.2 years for those from higher-income families.
Why is early diagnosis and intervention important for children with ASD?
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for fostering social skills and providing personalized programs that target the unique challenges faced by individuals with ASD.
What role do parents play in the diagnosis and intervention process for ASD?
Parents are encouraged to seek assessment and support promptly when they observe developmental delays, allowing their children to access necessary resources and interventions for optimal growth.
What are some effective early intervention services for children with ASD?
Early intervention services, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), have been shown to significantly improve communication and interaction skills essential for developing social skills.
How can parents ensure their children receive the necessary support for ASD?
Parents should collaborate with healthcare providers and educators to explore available resources and interventions as soon as developmental delays are observed.




