Overview
The article focuses on the importance of understanding common ABA (Applied Behavior Analysis) medical abbreviations, which are crucial for effective communication and collaboration in therapeutic settings, particularly for individuals with autism and ADHD. It underscores that familiarizing oneself with these abbreviations, such as BCBA (Board Certified Behavior Analyst) and RBT (Registered Behavior Technician), enhances caregivers' ability to engage meaningfully in their child's treatment and advocate for their needs, as supported by case studies and research highlighting the positive impact of ABA interventions.
Introduction
Navigating the world of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) can feel overwhelming, especially for parents advocating for their children’s needs in medical contexts. This powerful framework is essential in understanding and modifying behaviors, particularly for children diagnosed with autism and ADHD. As ABA continues to gain recognition for its effectiveness in therapeutic settings, it becomes increasingly important for parents and caregivers to familiarize themselves with its principles and terminology. By doing so, they not only enhance their ability to communicate with professionals but also empower themselves to actively participate in their child's developmental journey.
This article delves into the significance of ABA, the importance of understanding its abbreviations, and highlights key terms that every parent advocate should know to ensure their child's success.
Understanding Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) in Medical Context
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) represents a robust scientific framework designed to understand and enhance specific behaviors. This methodology holds particular importance in medical settings, especially for individuals diagnosed with autism and ADHD, highlighting the relevance of the aba medical abbreviation. Through structured interventions, ABA practitioners can drive meaningful behavioral changes that significantly enhance an individual's quality of life.
By employing principles from learning theory, they meticulously assess behaviors and implement tailored strategies aimed at fostering positive outcomes. Recent studies, including those by Shokoohirad M. and Rahim Zadeh, have underscored the effectiveness of ABA programs, associated with the aba medical abbreviation, in enhancing emotional and social skills among individuals with autism, reflecting the critical role of ABA in therapeutic environments. As noted by Kristen R Choi, PhD, MS, RN, 'The purpose of this study was to examine patterns of service receipt and patient outcomes for individuals receiving the ABA medical abbreviation for Applied Behavior Analysis in an integrated healthcare system where commercially insured youths were covered by a state autism mandate.'
Furthermore, the statistical significance level for hypothesis testing in these studies is set at 0.05, providing empirical backing for the effectiveness of ABA interventions. For parents and professionals alike, understanding the fundamentals of the ABA medical abbreviation is essential; it not only facilitates effective communication but also strengthens collaborative efforts in supporting the developmental needs of youth. Additionally, case studies such as 'How the ABA medical abbreviation Therapy Transforms Emotional and Behavioral Health in Children' illustrate the overall impact of ABA therapy on emotional regulation and behavioral outcomes, further emphasizing its importance in improving the lives of children with autism and ADHD.
Why Familiarity with ABA Abbreviations Matters
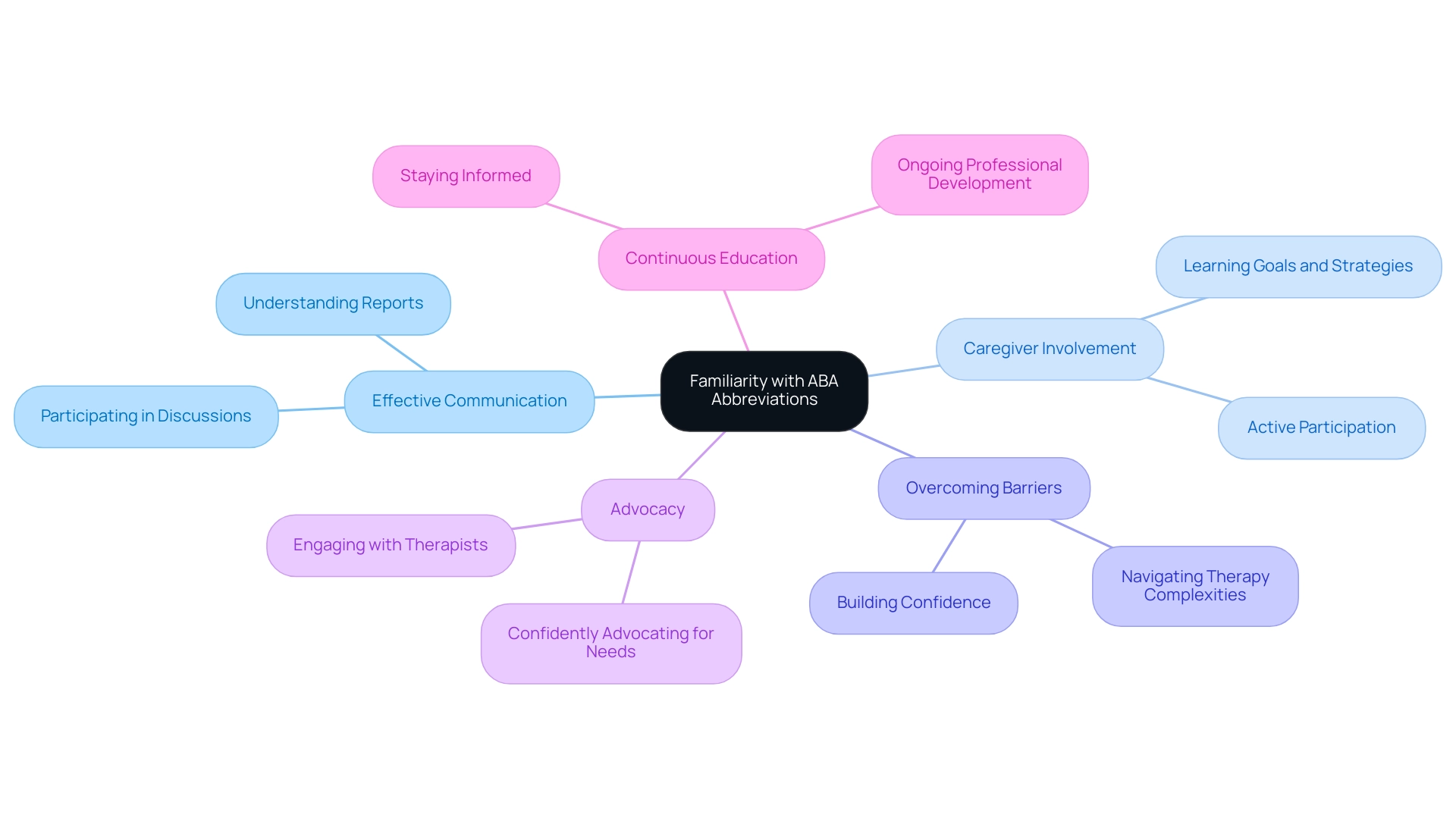
A strong grasp of the aba medical abbreviation is essential for effective communication in the field of Applied Behavior Analysis. These abbreviations frequently appear in clinical documents, treatment plans, and discussions among professionals, making them essential for guardians and caregivers. Acquaintance with these terms enables guardians to understand reports thoroughly, participate in significant discussions with therapists, and advocate confidently for their dependents' needs.
As Erin Vollmer, a speech-language pathologist and co-founder of TherapyWorks, aptly puts it,
When caregivers are actively involved in the process, they’re able to learn the goals, strategies, and therapeutic techniques that can be used to help the young one continue to practice and make gains at home.
Understanding ABA terminology not only fosters confidence but also transforms caregivers into active participants in their child's care. This knowledge is crucial in overcoming communication barriers that often arise in ABA treatment, ensuring that families can navigate the complexities of therapy with clarity and assurance.
Notably, only 3 of the 11 interventions identified by the NAC as meeting quality standards might be considered practices in the sense that they are manualized, which underscores the importance of being well-versed in the ABA medical abbreviation and its related practices and terminology. Additionally, as Shira confirms, the list of terms is not exhaustive, indicating that guardians should continuously seek to expand their knowledge. Continuous education is essential in this field, as emphasized in case studies on ongoing professional development, ensuring that practitioners and guardians alike stay informed about the latest research and evolving practices in ABA.
Top 10 Common ABA Medical Abbreviations You Should Know
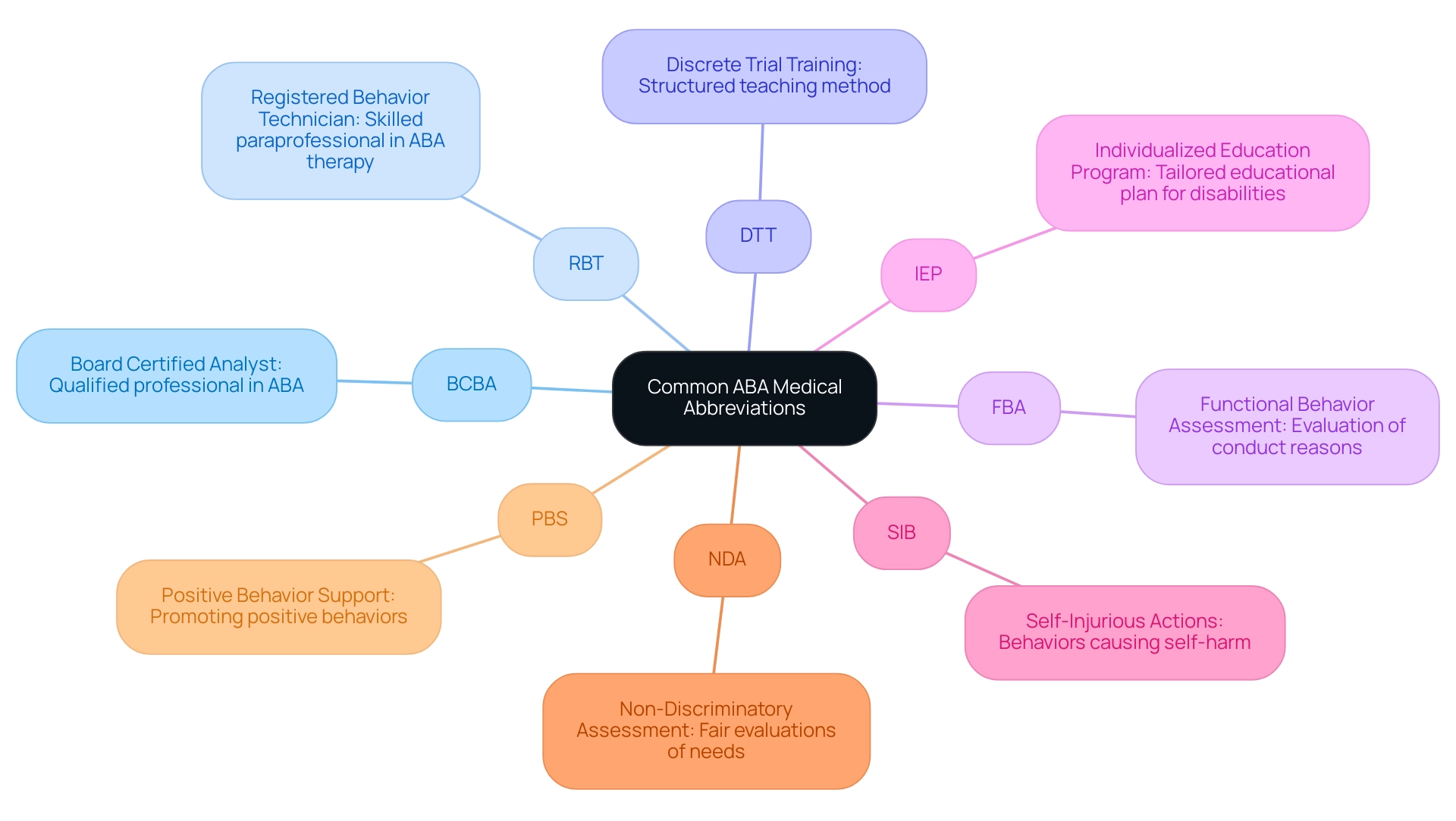
Here are the top 10 common ABA medical abbreviation examples that every parent advocate should be familiar with: The aba medical abbreviation stands for Applied Behavior Analysis, a scientific discipline dedicated to understanding and modifying conduct, which is particularly important in programs like the Maryland Children's Health Program (MCHP) that provides medical coverage for uninsured children under 19.
- BCBA - Board Certified Analyst: A qualified professional who has completed the necessary certification to practice ABA effectively.
- RBT - Registered Behavior Technician: A skilled paraprofessional who provides ABA therapy under the guidance of a BCBA.
- DTT - Discrete Trial Training: A structured method of teaching that breaks skills down into small, manageable components for systematic learning.
- FBA - Functional Behavior Assessment: A crucial evaluation process aimed at uncovering the underlying reasons for specific conduct.
- IEP - Individualized Education Program: A tailored educational plan designed for students with disabilities, potentially incorporating ABA strategies to support their learning, especially relevant for Transitioning Youth services.
- SIB - Self-Injurious Actions: Activities where individuals harm themselves, often addressed through targeted ABA interventions to promote safer alternatives.
- NDA - Non-Discriminatory Assessment: Assessments conducted with fairness to ensure unbiased evaluation of a child's needs and abilities.
- PBS - Positive Behavior Support: An approach grounded in ABA principles that focuses on promoting positive behaviors and reducing challenging ones.
Understanding the aba medical abbreviation, which stands for Applied Behavior Analysis, and its relevance as a therapeutic method that integrates cognitive and behavioral strategies, not only enhances communication but also empowers parents and professionals alike to work collaboratively in the therapeutic journey. For instance, the case study on Functional Communication Training (FCT) demonstrates how effective communication strategies can reduce challenging behaviors, fostering a supportive environment for children.
Conclusion
Navigating the landscape of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is crucial for parents advocating for their children's needs, particularly those diagnosed with autism and ADHD. The insights shared in this article highlight the significance of understanding ABA as a robust framework for fostering positive behavioral changes through structured interventions. By familiarizing themselves with the core principles and essential terminology of ABA, parents can enhance their communication with professionals and actively engage in their child's developmental journey.
Moreover, grasping common ABA abbreviations is not merely an academic exercise; it empowers parents to advocate effectively for their children’s needs. As demonstrated, a strong command of these terms facilitates meaningful dialogue with therapists and helps in comprehending treatment plans and reports. This knowledge is pivotal in overcoming communication barriers and ensuring that families can navigate the complexities of ABA therapy confidently.
Ultimately, the journey towards understanding and utilizing ABA is a powerful tool for parents. By embracing this knowledge, they not only support their children's emotional and behavioral health but also foster a collaborative environment with professionals. As ABA continues to evolve and gain recognition, informed parent advocates will play a vital role in shaping the therapeutic landscape for their children, ensuring brighter futures and improved outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)?
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a scientific framework designed to understand and enhance specific behaviors, particularly important in medical settings for individuals diagnosed with autism and ADHD.
How does ABA benefit individuals with autism and ADHD?
ABA employs structured interventions to drive meaningful behavioral changes that significantly enhance an individual's quality of life, improving emotional and social skills.
What principles does ABA use to assess and implement strategies?
ABA utilizes principles from learning theory to meticulously assess behaviors and implement tailored strategies aimed at fostering positive outcomes.
What evidence supports the effectiveness of ABA programs?
Recent studies, including those by Shokoohirad M. and Rahim Zadeh, have highlighted the effectiveness of ABA programs in enhancing emotional and social skills among individuals with autism.
What was the focus of Kristen R Choi's study on ABA?
Kristen R Choi's study examined patterns of service receipt and patient outcomes for individuals receiving ABA in an integrated healthcare system, particularly focusing on commercially insured youths under a state autism mandate.
What is the statistical significance level for hypothesis testing in ABA studies?
The statistical significance level for hypothesis testing in ABA studies is set at 0.05, providing empirical backing for the effectiveness of ABA interventions.
Why is understanding the ABA medical abbreviation important for parents and professionals?
Understanding the ABA medical abbreviation is essential for effective communication and strengthens collaborative efforts in supporting the developmental needs of youth.
Can you provide an example of the impact of ABA therapy?
Case studies, such as 'How the ABA Therapy Transforms Emotional and Behavioral Health in Children,' illustrate the overall impact of ABA therapy on emotional regulation and behavioral outcomes, emphasizing its importance for children with autism and ADHD.




